摘要/Abstract
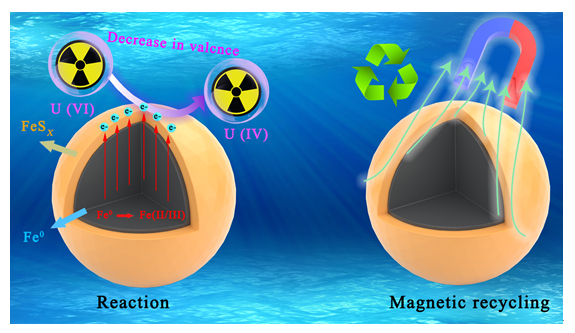
近年来, 放射性污染物铀(U(VI))在水环境中的排放对生态环境和生物健康造成严重的威胁. 本研究采用液相还原法制备了硫化纳米零价铁(S-NZVI)材料, 并将其用于水中U(VI)的去除. 首先, 我们采取了一系列的微观表征技术探究了S-NZVI的表面特征及材料特性. 结果表明, 相比于纳米零价铁(NZVI), S-NZVI颗粒不易团聚, 性质更加稳定. 随后, 通过宏观实验探究了反应时间、温度、pH、背景离子浓度等因素对S-NZVI去除U(VI)的影响. 结果表明, S-NZVI对U(VI)的最大去除量高达562.5 mg•g-1, 且在100 min内达到反应平衡. 宏观实验和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析表明S-NZVI对U(VI)的去除机理是吸附和氧化还原协同作用的结果. 此外, S-NZVI可以通过外加磁场从水中快速地进行分离, 便于材料再回收与利用. 综上, 本研究构筑了一种制备简单、便于回收且高效的U(VI)净化材料, 未来可能会在放射性核素的处理处置等相关工作中起到重要作用.
关键词: U(VI), 硫化纳米零价铁, 吸附, 氧化还原, 协同作用
In recent years, uranium (U(VI)), a radioactive contaminant, has been widely used in industrial production and military fields. Although the industry has developed, its discharge in water poses a serious threat to the natural environment and biological health. In order to solve this problem, in this study, we prepared sulfide nano zero-valent iron (S-NZVI) material by liquid-phase reduction using NaBH4, FeSO4•7H2O and Na2S2O4 as main materials in N2-filled glove box, and applied them to U(VI) removal from water. First of all, serial microscopic characterization techniques were adopted to explore the surface morphology and physicochemical properties of S-NZVI. The results showed that the S-NZVI particles are less agglomerated and more stable compared to nano zero-valent iron (NZVI). Subsequently, we investigated the effects of reaction time, temperature, pH, and background ion concentration on the removal of U(VI) by S-NZVI through macroscopic batch experiments. The consequence indicated that the maximum removal of U(VI) by S-NZVI at room temperature (20 ℃) could reach 562.5 mg•g-1, and the reaction equilibrium could be received within 100 min. And more importantly, the eliminated process of S-NZVI is consistent with Langmuir single-molecule layer adsorption model, and the conditions for optimal performance were at ambient temperature (20 ℃) and pH=7~8. Combined with the results of macroscopic experiments and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, the removal mechanism of U(VI) by S-NZVI may be attributed to the synergistic effect of adsorption and redox reaction. In addition, S-NZVI can be separated from water rapidly by external magnetic field due to its magnetic property, which is convenient for material recycle and reutilization. In conclusion, this study has prepared a facile, recyclable, and efficient material for U(VI) decontamination, which may play a significant role in the future of environmental protection, nuclear waste remediation, and other related fields.
Key words: U(VI), sulfide nanoscale zero-valent iron, adsorption, redox, synergistic effect
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
