摘要/Abstract
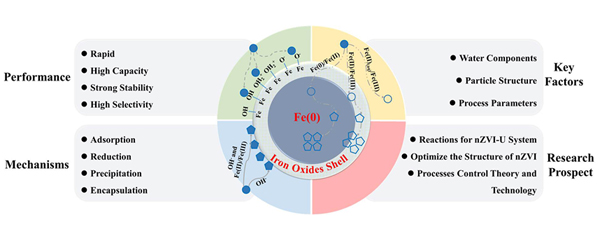
由于铀矿采冶、核能利用等类活动的影响, 铀引起的水体污染问题日益严重. 纳米零价铁(nanoscale zero-valent iron, nZVI)及其复合材料可高效富集水溶液中低浓度的铀, 在放射性废水的处理与铀的资源回收方面具有巨大的应用潜力. 但是, 不同研究对nZVI分离铀的机理和性能尚未形成一致的解释. 因此, 本综述归纳了nZVI分离铀的研究进展, 概括了溶液及固相反应机理(如吸附作用、还原作用、沉淀作用), 重点分析了水质因素(如pH、U(VI)浓度、阳离子、阴离子、溶解氧)的影响机制. 后续研究可注重分析铀废水中nZVI的结构转化规律及水质因素的协同作用对nZVI固定铀的机理、性能的影响; 并基于放射性废水的水质或水处理工艺的特征, 优化nZVI材料结构且评估其处理放射性废水的长期稳定性和生态毒性; 确定nZVI固定铀的性能与水质组分及水处理工艺运行参数的数学相关性, 建立监测和调控工艺的方法.
关键词: 纳米零价铁, 铀, 放射性废水, 反应机理, 水质因素
In the processes of uranium mining and nuclear power utilization, water pollution caused by radioactive contaminants (e.g., uranium) is becoming increasingly serious. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) and its composites can be used to enrich low-concentrated uranium ions from radioactive wastewater effectively. Published works have demonstrated that nZVI has great application potential to treat uranium-contanined radioactive wastewater. However, published researches on the performance and mechanisms for U(VI) immobilization by nZVI between different papers are not unanimous. Based on the research progress, this review summarizes the aqueous and solid reaction mechanisms (e.g., adsorption, reduction and precipitation) between nZVI and U(VI) ions, and specifically discusses the effects of solution factors (e.g., pH, U(VI) concentration, cations, anions and dissolved oxygen) on U(VI) immobilization. Before the field-scale application of nZVI to remedy uranium wastewater, deep researches should be conducted to investigate: (i) the phase transformation of nZVI in uranium wastewater and the synergistic effect of solution factors on the ability of nZVI to separate uranium; (ii) based on the characteristics of radioactive solution and wastewater treatment processes, the structure of nZVI particles needs to be optimized and their long-term stability and ecotoxicity needs to be evaluated; (iii) confirm the mathematical correlation between the performation of nZVI to immobilize uranium and wastewater components and operation parameters, and then extabilish the monitoring and regulating method for wastewater treatment technology.
Key words: nanoscale zero-valent iron, uranium, radioactive wastewater, reaction mechanism, solution factor
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
