摘要/Abstract
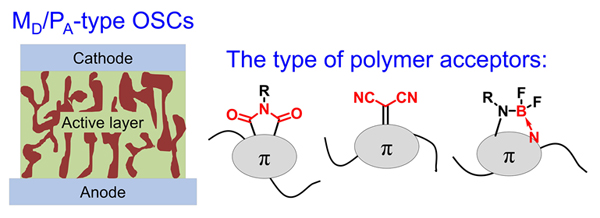
有机太阳能电池具有低成本、柔性和质量轻等优势, 是一种有应用前景的光伏技术, 受到人们的广泛关注. 有机太阳能电池的光敏活性层通常由p-型有机半导体(包括小分子和高分子)与n-型有机半导体(包括小分子和高分子)共混而成. 小分子给体/高分子受体型有机太阳能电池具有形貌热稳定性优异的特点, 值得深入研究. 本综述旨在总结小分子给体/高分子受体型有机太阳能电池的研究进展, 分别介绍了基于酰亚胺基、氰基和含硼氮配位键(B←N)的高分子受体的活性层材料体系的发展状况. 在器件性能方面, 通过分子设计、相分离形貌调控, 改善了小分子给体/高分子受体的匹配性, 将该类电池的能量转换效率从最初的0.29%提升至目前的9.51%, 为性能的进一步提升总结了经验; 在稳定性方面, 基于该体系形貌热稳定性优异的特点, 开发出高温耐受型有机太阳能电池器件. 最后, 展望了小分子给体/高分子受体型有机太阳能电池的未来发展方向和前景.
关键词: 有机太阳能电池, 小分子给体, 高分子受体, 相分离形貌, 热稳定性
Due to their advantages of low cost, flexibility and light weight, organic solar cells (OSCs) are considered to be a promising photovoltaic technology for practical applications and have received great attentions. The active layers of OSCs are the blends of conjugated small molecule/polymer electron donors and electron acceptors. Before 2013, the most-widely used electron acceptors are fullerene derivatives. Nevertheless, the weak absorption in the visible region, limited electronic tunability, and poor morphological stability hinder their further application in OSCs. Non-fullerene electron acceptors with good light harvesting ability and tunable energy levels have developed rapidly in past few years. Based on the types of electron donor and acceptor materials, non-fullerene OSCs may be classified into four types, including polymer donor/polymer acceptor blend (PD/PA), polymer donor/small molecule acceptor blend (PD/MA), small molecule donor/polymer acceptor blend (MD/PA), and small molecule donor/small molecule acceptor blend (MD/MA). Among various kinds of OSCs, MD/PA-type OSCs possess the excellent morphology stability under thermal stress, which is worthy of further study. Although the advantages of MD/PA-type OSCs, there are still large challenges in their development. The power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of MD/PA-type OSCs are still much lower than that of other type OSCs, due to the limited material combination of small molecule donors and polymer acceptors and undesirable phase separation morphology of the active layers. In this review, we summarize the research progress of OSCs based on small molecule donors and polymer acceptors, and introduce the active layer material systems from three type polymer acceptors, i.e.the imide group, cyano group and boron-nitrogen coordination bond (B←N) unit based polymer acceptors. Benefiting from the development of both donor and acceptor materials as well as the manipulation of phase-separation morphology in active layers, the good match between small molecule donors and polymer acceptors is achieved. This not only boosts the large improvement in PCE from 0.29% to 9.51%, but also contributes to a high-temperature tolerant photovoltaic device. Finally, we also present an outlook of the future development of high-performance MD/PA-type OSCs.
Key words: organic solar cell, small molecule donor, polymer acceptor, phase-separation morphology, thermal stability
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
