摘要/Abstract
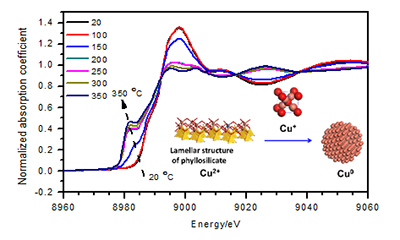
铜基催化剂的价态组成与制备方法、还原温度有关,也是决定其催化性能的关键因素.本文对比研究Cu-Zn/SiO2和Cu/SiO2催化剂前驱体在不同还原温度下的价态组成及其醋酸甲酯加氢性能.采用同步辐射X射线吸收谱原位表征催化剂前驱体的Cu K边的X射线近边吸收谱(XANES),通过线性组合分析方法(LCF)拟合XANES吸收谱得到了催化剂前驱体在不同还原温度下氧化态(Cu2+、Cu+)和金属态(Cu0)的组分含量.结果表明:(1)采用蒸氨法添加Zn制备的Cu-Zn/SiO2催化剂前驱体铜组分还原度高;(2)催化剂前驱体在还原过程中Cu+主要存在于低温还原阶段(<250℃),且Cu0+Cu+含量较低(≤ 40%);(3)金属态铜是醋酸酯加氢反应的活性中心.
关键词: Cu/SiO2, Cu-Zn/SiO2, 醋酸甲酯, 乙醇, XANES
The valence states of copper-based catalyst are still controversial for whether Cu+ exists or even dominates the corresponding catalysis performance, especially for the catalyst prepared by unconventional method. For example, Cu/SiO2 catalyst prepared by deposition-precipitation exhibits different ratio of Cu0 and Cu+ in the literatures. Zinc-doping Cu/SiO2 catalyst is primarily chosen for carbonyl hydrogenation. Additionally, the copper catalysts employed in the industrial reactor require a doping of zinc for catalyst stability and relatively low temperature reduction, which makes the valence states of copper catalyst under working conditions even more complicated. In this paper, copper phyllosilicate, 15 wt% Cu-5.0 wt% Zn/SiO2, was prepared by ammonia evaporation method with the following procedures:(1) complexation of Cu/Zn to silicasol by mixing of an amount of copper ammonia solution (0.5 mol/L) and zinc ammonia solution (0.5 mol/L) with silicasol (5%, SiO2) for 5 h at room temperature, and then decomposition of metal ammonia under 95℃; (2) dried, crushed and calcined at 450℃ for 4 h. The Cu/SiO2 catalyst precursor without the addition of zinc was prepared with the same procedures as Cu-Zn catalyst precursor. The valence states of copper catalyst of Cu-Zn/SiO2 and Cu/SiO2 catalyst during hydrogen reduction in the temperature range of 20℃ to 350℃ has been studied by in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy characterization under the atmosphere of 10% H2 in He, 50 mL/min. Valence state composition was analyzed by using Linear Combination Fitting (LCF) method based on X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES) spectra, which indicated:(1) the reduction degree of Cu2+ to Cu0 is increased with the addition of zinc; (2) Cu+ occurred and mainly existed at low reduction temperature (<250℃) with a low concentration, but it diminished completely at high reduction temperature; (3) Cu0 could be the active center for hydrogenation of methyl acetate to ethanol.
Key words: Cu/SiO2, Cu-Zn/SiO2, methyl acetate, ethanol, XANES
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
