摘要/Abstract
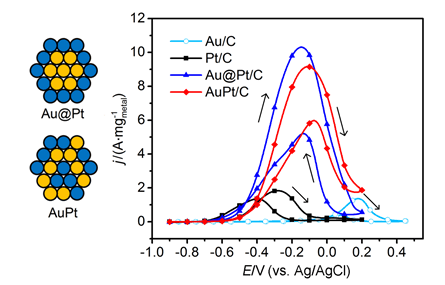
乙醇电氧化(EOR)是直接乙醇燃料电池和电解乙醇制氢共有的阳极反应.Au@Pt核壳和AuPt合金是广泛使用的两种电催化材料,迄今尚无两者对EOR性能的对比研究.以CO作为还原剂和淬灭剂合成了近似Pt单层的Au@Pt/C催化剂,作为对照,以NaBH4还原法合成了相同Au∶Pt物质的量比和金属载量的AuPt/C催化剂;运用透射电子显微镜(TEM)、扫描透射电子显微镜-能谱仪(STEM-EDS)、X射线粉末衍射(XRD)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等手段综合表征了两者结构之差异,同时以电化学循环伏安法和计时电流法测试了在碱性体系中其对EOR的电催化性能.结果表明,相比于商业化的Pt/C和Au/C,Au@Pt/C和AuPt/C对EOR的活性和稳定性均有着显著提升;Au@Pt/C对EOR的电催化活性和对C—C键断裂能力略优于AuPt/C.双金属催化剂中Au与Pt之间的晶格应力和部分电荷转移等效应可能是其性能提升的主要原因.
关键词: 乙醇电氧化, 电催化, 金-铂催化剂, 核壳结构, 合金结构
Ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR) is a common anode process for direct ethanol fuel cell (DEFC) and ethanol reforming electrolyzer. Au@Pt and AuPt alloy are widely used bimetallic catalysts, yet no comparative study has been reported of electrocatalysis of EOR on these two differently structured catalysts. The present work aims to synthesize and characterize carbon supported Au@Pt and AuPt with controlled composition and size, and compare their electrocatalytic activities and stabilities toward EOR in alkaline media. For the synthesis of Au@Pt/C, a 5-nm Au colloid was first obtained by adding excessive amount of sodium borohydride to a chloroauric acid precursor containing sodium citrate with a mixed ice-water bath. CO gas was bubbled into the Au colloidal solution at 60℃ under strong stirring to reduce a desired amount of potassium tetrachloroplatinate(Ⅱ) to terminate Pt quasi-monolayer shell on Au nanoparticle core. A sonicated carbon black (Vulcan XC-72) aqueous slurry was then dropwise added to the above Au@Pt colloid, and the mixture was kept stirring for 48 h to ensure the exhaustive loading of Au@Pt nanoparticles onto the carbon support. For the synthesis of AuPt/C with the same Au:Pt molar ratio and metal loading as that for Au@Pt/C, coreduction of the Au(Ⅲ) and Pt(Ⅱ) species was attained by using sodium borohydride as the reducing agent with the rest procedures being same as the above mentioned. X-ray diffractometry (XRD) revealed that the diffraction peaks for Au@Pt/C were virtually same as those for Au/C, consistent with a Pt quasi-monolayer, while the diffraction peaks for AuPt/C located in between those for Au/C and Pt/C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results were consitent with the different structures of the two catalysts, and the Pt core level shift suggested an upshift of Pt d-band center for both bimetallic catalysts. Cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry revealed markedly increased EOR current on Au@Pt/C and AuPt/C, as compared to that of Pt/C and Au/C. CO-stripping voltammetry on Au@Pt/C and AuPt/C indicated that surface reconstruction occurred by potential cycling, resulting in a decrease of exposed Pt sites but not the electrocatalytic activities. 1H NMR analysis confirmed the C2 pathway is predominant. Nevertheless, Au@Pt/C outperformed AuPt/C and Pt/C with a lower onset oxidation potential and a higher peak current for EOR, as well as a slightly higher selectivity toward C1 pathway. Although the synergetic effect of Au-Pt bimetallic interface for EOR is not well understood, the enhanced adsorption of ethanol, OH, acetyl and CO on Pt sites may be accountable for the observed results.
Key words: ethanol oxidation reaction, electrocatalysis, AuPt bimetallic catalysts, core-shell structure, alloy structure
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
