

1. 暨南大学 生物医药研究院, 广东 广州 510632;
2. 暨南大学 基因工程药物国家工程研究中心, 广东 广州 510632;
3. 暨南大学 生物工程系, 广东 广州 510632
收稿日期:2021-01-08;接收日期:2021-03-26;网络出版时间:2021-04-12
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(No. 2013AA102801),广东省科技计划(No. 2013B090600141),广东省级财技术研究开发补助项目资助
摘要:血管内皮生长因子(Vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF165) 是一种高度特异性的促血管内皮细胞生长因子,高纯度的VEGF165对于抗肿瘤药物和生物标志物研发检测试剂必不可少。目前关于VEGF165的异源表达方法,纯化步骤多且产物纯度不高。以毕赤酵母表达系统为基础,构建人血管内皮生长因子(VEGF165) 多拷贝的表达载体。按照酵母密码子偏好性优化人血管内皮生长因子基因(vegf165) 的密码子,在毕赤酵母BBPB表达载体基础上,用Biobrick生物积块的方法,构建以Pgap为启动子的五拷贝rhVEGF165表达载体,同时添加组氨酸标签。利用His标签和VEGF165自身的肝素结合结构域,仅用两步亲和层析纯化得到纯度高于98%的rhVEGF165蛋白。rhVEGF165纯化后浓度为0.45 mg/mL,且具有生物学活性。该异源表达策略简化了rhVEGF165的纯化步骤,rhVEGF165具有天然VEGF165的生物学活性,且纯度达到目前文献报道的最高水平。
关键词:人血管内皮生长因子vegf165高效表达多拷贝毕赤酵母
Production of high-purity recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor (rhVEGF165) by Pichia pastoris
Weijie Zhou1,2, Fengmei Wu1,2, Dongsheng Yao1,2, Chunfang Xie2,3


1. Institute of Biomedicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong, China;
2. National Engineering Research Center of Genetic Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong, China;
3. Department of Bioengineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong, China
Received: January 8, 2021; Accepted: March 26, 2021; Published: April 12, 2021
Supported by: National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013AA102801), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2013B090600141), Guangdong Provincial Research and Development Financial Subsidy Project
Corresponding author: Chunfang Xie. E-mail: xiechunfang28@aliyun.com.
Abstract: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165) is a highly specific vascular endothelial growth factor that can be used to treat many cardiovascular diseases. The development of anti-tumor drugs and disease detection reagents requires highly pure VEGF165 (at least 95% purity). To date, the methods for heterologous expression and purification of VEGF165 require multiple purification steps, but the product purity remains to be low. In this study, we optimized the codons of the human VEGF165 gene (vegf165) according to the yeast codon preference. Based on the Pichia pastoris BBPB vector, we used the Biobrick method to construct a five-copy rhVEGF165 recombinant expression vector using Pgap as the promoter. In addition, a histidine tag was added to the vector. Facilitated by the His tag and the heparin-binding domain of VEGF165, we were able to obtain highly pure rhVEGF165 (purity > 98%) protein using two-step affinity chromatography. The purified rhVEGF165 was biologically active, and reached a concentration of 0.45 mg/mL. The new design of the expression vector enables production of active and highly pure rhVEGF165) in a simplified purification process, the purity of the biologically active natural VEGF165 reached the highest reported to date.
Keywords: human vascular endothelial growth factorvegf165efficient expressionmultiple copiesPichia pastoris
血管内皮生长因子(Vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF),又称血管通透因子(Vascular permeability factor,VPF),是一种高度特异性的促血管内皮细胞生长因子,具有促进血管通透性增加、细胞外基质变性、肿瘤生长、类风湿性关节炎和新生血管性眼疾的能力[1-3]。在促血管生成作用方面,VEGF的6种异构体中,以VEGF165的活性最高和含量最多,并且VEGF165对肿瘤生长的影响最为重要[4];VEGF165作为血管生成的直接效应分子,在血管系统的发育和分化中起至关重要的作用,VEGF165已被用于冠心病防治的实验研究,它可促进小冠状血管侧支循环的建立,恢复心肌血流供应,延缓梗塞面积扩大,促进缺血心肌的功能恢复[5]。高纯度的VEGF165是研发抗肿瘤药物和生物标志物检测试剂等研究的基础[6-7]。因此,一个简便、成本低廉、能获得高纯度以及有活性的VEGF165的表达系统则尤为重要。
天然VEGF165蛋白分子含有16对二硫键[8],在异源表达系统中容易发生二硫键错配,并且二硫键错配的杂质蛋白很难去除,进而影响蛋白活性和降低正确结构蛋白的纯度,不利于制备工艺的放大[9],所以利用体外异源表达系统获得活性高、纯度高且结构正确的蛋白具有一定的挑战性。因其糖基化不影响其生物学功能,只影响其表达分泌的功能,所以其重组基因可以通过真核表达系统以及原核表达系统进行异源表达。根据过往报道,VEGF165可以在酿酒酵母Saccharomyces cerevisiae[10]、毕赤酵母Pichia pastoris[11]、大肠杆菌Escherichia coli[12]、昆虫细胞[13]和哺乳动物细胞[14]等多种异源蛋白表达系统中进行表达。但是以上表达系统均有各自的缺点:酿酒酵母表达系统表达水平低、分泌效率低、不易进行高密度发酵;甲醇诱导毕赤酵母表达系统筛选高拷贝重组菌株的工作量大、诱导培养周期长、单交换整合转化子在高密度发酵时不稳定;大肠杆菌表达系统易形成包涵体,在复性过程中极易发生二硫键错配,大大降低了蛋白活性和正确结构蛋白的纯度、回收率低;昆虫细胞表达系统获取表达产物的操作步骤繁杂、成本较高;哺乳动物细胞表达系统表达量很低、培养成本高、操作技术要求高。
与传统的筛选高拷贝重组菌株的方法不同,本研究利用实验室已经构建的毕赤酵母BBPB Biobrick生物积块组装以Pgap为启动子的多拷贝rhVEGF165重组毕赤酵母;且在每一个表达盒构建策略上将VEGF165自身的信号肽替换成酵母α-因子信号肽,让rhVEGF165成熟肽分泌到培养上清中,同时在远离VEGF165功能区的C末端添加了6个组氨酸标签,利用His标签和VEGF165的肝素结合域(VEGF165第111–165位氨基酸) [15-16],只需通过两步特异性的亲和层析纯化即可获得高纯度的rhVEGF165蛋白。
1 材料与方法1.1 质粒和菌株毕赤酵母GS115由本实验室保存;大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,购自广州鼎国生物技术公司;Paox-Pgap-BBPB质粒、Taox-PgHT-BBPB质粒和Taox-Pgap-BBPB质粒由本实验室构建;ss1-VEGF165-pGH质粒由上海捷瑞生物工程有限公司合成;HUVEC细胞株由暨南大学细胞系邝志和研究员提供。
1.2 主要试剂和培养基限制性核酸内切酶(EcoRⅠ-HF、XbaⅠ、SpeⅠ-HF、PstⅠ-HF)、核酸连接酶(T4 DNA ligase)、糖苷内切酶(Endo H)、琼脂糖凝胶回收试剂盒等均购自NEB公司;质粒小提试剂盒购自TIANGEN公司;Western blotting检测试剂盒购自江苏凯基生物技术有限公司;CCK-8检测试剂盒购自Beyotime/碧云天;ELISA Kit for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165 (VEGF165)购自Uscn公司;Quick Start Bradford蛋白测定试剂盒购自Bio-Rad公司;SDS-PAGE凝胶配置试剂盒购自生工生物工程(上海) 股份有限公司。
LB液体培养基(g/L):酵母提取物5.0,蛋白胨10.0,氯化钠10.0。LB固体培养基中加琼脂粉15.0 g。
MD固体培养基(g/L):丙三醇10.0,无氨基酵母氮源13.4,生物素0.4 mg/L,琼脂粉15.0。YPG液体培养基(g/L):酵母提取物10.0,大豆蛋白胨20.0,丙三醇10.0。
1.3 仪器与器材ECM399电转仪,BTX公司;Sigma 4K-15高速冷冻离心机,BECKMAN公司;Mini蛋白质电泳仪、Western blotting电泳仪,Bio-Rad公司;AKTA pure纯化仪,GE Healthcare公司。
1.4 目的基因的获取从NCBI核酸数据库中查找VEGF165的核酸序列(GenBank登录号:AF486837.1) 和氨基酸序列(GenBank登录号:AAM03108.1),去除其本身信号肽基因序列(前78 bp),在目的基因前加上信号肽序列ss1基因序列;在目的基因末尾添加组氨酸标签。使用本实验室的克隆载体来构建多拷贝目的基因表达盒,故在信号肽基因前和目的基因后的5′端和3′端分别添加EcoRⅠ、Xba Ⅰ和Spe Ⅰ、PstⅠ限制性核酸内切酶酶切位点。序列由上海捷瑞生物工程有限公司进行全基因合成。
1.5 单拷贝目的基因表达盒的构建克隆载体Taox-PgHT-BBPB (简写为TH-BBPB)、Paox-Pgap-BBPB (简写为PP-BBPB) 和Taox-Pgap-BBPB (简写为TP-BBPB) (TH-BBPB、PP-BBPB、TP-BBPB为本实验室前期构建) 上均含有EcoRⅠ、XbaⅠ、SpeⅠ、PstⅠ这4个限制性核酸内切酶位点。XbaⅠ和SpeⅠ是一对同尾酶,同尾酶产生相同的粘性末端,两个粘性末端连接后,原来的酶切位点将消失[17]。
用EcoRⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切全基因合成的质粒ss1-vegf165-Pgh (简写为sV-pGH),同时用EcoRⅠ和XbaⅠ双酶切TH-BBPB载体,T4 DNA连接酶连接回收后的目的片段,连接产物sV-TH-BBPB转化DH5α感受态细胞,通过氨苄(1 mg/mL) 抗性筛选阳性克隆;用EcoRⅠ和XbaⅠ酶切鉴定阳性克隆并切胶回收目的载体。EcoRⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切PP-BBPB质粒,切胶回收PP片段,与胶回收后的目的载体进行连接,转化DH5α感受态细胞。筛选阳性克隆,双酶切鉴定,获得重组单拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒质粒PP-sV-TH-BBPB。
1.5.1 二至五拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒的构建用PstⅠ和XbaⅠ双酶切sV-Pgh,切胶回收sV片段,与经PstⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切胶回收后的PP-BBPB载体片段通过T4 DNA连接酶进行连接,获得PP-sV-BBPB。
用EcoRⅠ和XbaⅠ双酶切sV-TH-BBPB质粒,与经EcoRⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切切胶回收后的TP-BBPB片段通过T4 DNA连接酶连接获得TP-sV-TH-BBPB。
用PstⅠ和XbaⅠ双酶切sV-pGH质粒,与经PstⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切切胶回收后的TP-BBPB片段通过T4 DNA连接酶连接获得TP-sV-TH-BBPB。
用EcoRⅠ和SpeⅠ双酶切PP-sV-BBPB,与经EcoRⅠ和XbaⅠ双酶切胶回收后的TP-sV-TH-BBPB载体片段通过T4 DNA连接酶进行连接,获得PP-sV-TP-sV-TH-BBPB两拷贝目的基因质粒。
通过不同的双酶切组合对TH-BBPB、PP-BBPB、TP-BBPB、sV-pGH进行酶切、连接成PP-sV、TP-sV、TP-sV-TH的载体片段,从而构建出PP-sV-TP-sV-TP-sV-TH-BBPB、PP-sV-TP-sV- TP-sV-TP-sV-TH-BBPB、PP-sV-TP-sV-TP-sV-TP- sV-TP-sV-TH-BBPB (三、四、五拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒)。
1.5.2 重组质粒电击转化毕赤酵母GS115以及重组子的筛选重组质粒经XbaⅠ和SpeⅠ线性化后,1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后切胶回收目的片段,并将目的片段电击转入毕赤酵母GS115感受态细胞中,涂布于MD固体培养基平板,置于28 ℃恒温培养箱中培养,待长出单菌落,挑取单克隆于5 mL YPG液体培养基中,于28 ℃、200 r/min振荡培养72 h,12 000 r/min离心1min收集上清,SDS-PAGE法检测培养上清,再进行银染分析筛选阳性单克隆。
1.5.3 蛋白质印迹法进一步鉴定重组子取20 μL银染结果符合预期的重组子单克隆菌液进行离心,取上清液进行SDS-PAGE。并基于蛋白质C端的组氨酸标签,利用一抗(小鼠抗His标签抗体)和二抗(HRP标记的羊抗小鼠抗体)进行Western blotting实验加以验证。
1.6 重组菌的扩大培养重组菌接入2 L的YPD培养基(使用磷酸钾溶液调节改良pH至6.0),在30 ℃条件下置于220 r/min摇床中培养3 d。
1.7 亲和层析重组菌的发酵上清液经硫酸铵沉淀处理后依次进行Ni Sepharose 6 Fast Flow镍柱亲和层析、HiTrap Heparin肝素亲和层析,得到重组人VEGF165蛋白(rhVEGF165) 进行SDS-PAGE检验,用Image-Pro Plus软件对SDS-PAGE图进行灰度扫描分析,计算目的蛋白的纯度。
1.7.1 目的蛋白液浓缩和缓冲液置换用截留分子量为3 kDa或10 kDa的Amicon Ultra-15超滤管浓缩肝素亲和层析洗脱收集的目的蛋白液,将蛋白液置于超滤管上层内槽,离心去除多余的纯化缓冲液。然后用后续实验所需的缓冲液置换原洗脱缓冲液,反复置换3次并浓缩至2.5 mL。用0.22 μm滤头过滤后,将浓缩蛋白液置于4 ℃保存。
1.7.2 考马斯亮蓝染色法测蛋白浓度采用Quick Start Bradford蛋白测定试剂盒制备蛋白标准曲线和测定样品蛋白浓度。以不同浓度的标准蛋白(BSA) 和染液,在595 nm处的吸光值制作蛋白浓度标准曲线,用于计算目的蛋白的浓度。
1.8 VEGF165蛋白的生物学活性检测1.8.1 糖蛋白分子鉴定糖苷内切酶H (Endo H) 是一种重组糖苷酶,能够对N-糖蛋白中的高甘露糖和某些杂合型寡聚糖的壳二糖核心结构进行切割[18],可用其验证重组表达的VEGF165蛋白是否发生糖基化。rhVEGF165经过Endo H酶切后进行SDS-PAGE分析,再用Western blotting实验进一步验证Endo H酶切前后的蛋白条带是否为目的蛋白。
1.8.2 VEGF165对人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC) 的促增殖活性检测CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8) 试剂盒是应用于细胞增殖和细胞毒性的快速、高灵敏度检测的试剂盒。VEGF165在体外可促进血管内皮细胞的生长和增殖,故可通过CCK-8试剂盒测定rhVEGF165对人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC) 的促增殖作用[19]。
选择处于对数生长期的HUVEC细胞,以10 000个细胞/mL接种至96孔板,每个孔加入100 μL的细胞悬液;细胞悬液继续培养2 h;向加有细胞的孔内分别加入梯度浓度的纯化浓缩后的rhVEGF165,每个浓度各重复9组,对照组为纯细胞培养液;每个孔加入新鲜完全培养基补足总体积至190 μL,再每孔加入10 μL的CCK-8溶液,轻轻晃动96孔板,酶标仪检测450 nm波长的吸光度值,作为原始的A450吸光值;将96孔板置于细胞培养箱内继续培养8 h后再用酶标仪检测450 nm波长处的吸光度值。
2 结果与分析2.1 目的基因的获取将携带目的基因的甘油菌用平板划线法分离单克隆:将甘油菌液用接种环划线于LB平板上分离获取单克隆,单克隆于5 mL LB试管培养基培养过夜,提取质粒。双酶切sV-pGH质粒,1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定结果如图 1所示,sV-pGH质粒经EcoRⅠ和SpeⅠ酶切后得到两条带,分别是载体pGH和目的片段sV,sV大小为800 bp,pGH大小为2 907 bp,核酸电泳结果显示酶切产物片段大小符合预期。
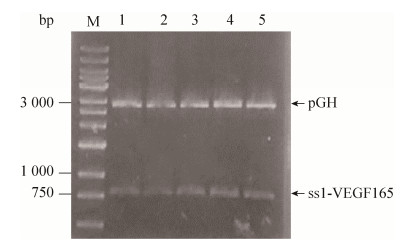 |
| 图 1 sV-pGH质粒双酶切鉴定 Fig. 1 Double enzyme digest products of the sV-pGH plasmid (Lanes 1–5). Lane M: 12K standard nucleic acid. |
| 图选项 |
2.2 多拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒的构建2.2.1 PP-sV-TH-BBPB重组表达盒的构建连接产物sV-TH-BBPB克隆载体经EcoRⅠ和PstⅠ酶切后验证得到条带是BBPB载体和sV-TH片段;如图 2所示,连接产物PP-sV-TH-BBPB双酶切鉴定成功,获得重组单拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒质粒PP-sV-TH-BBPB。
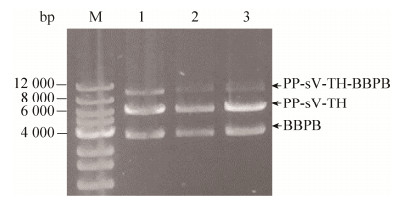 |
| 图 2 PP-sV-TH-BBPB双酶切鉴定 Fig. 2 Double enzyme digest products of the PP-sV-TH-BBPB (Lanes 1–3). Lane M: 12K standard nucleic acid. |
| 图选项 |
2.2.2 二至五拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒的构建Biobrick构建表达盒,转化后挑取单克隆,其质粒经EcoRⅠ和PstⅠ酶切后电泳显示有两条带,核酸电泳结果(图 3) 显示酶切产物片段大小符合预期,说明二至五拷贝克隆载体构建成功。
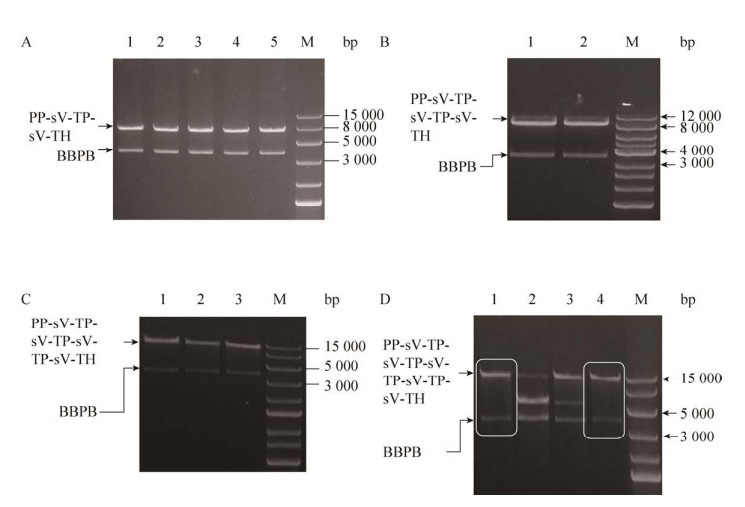 |
| 图 3 重组质粒双酶切产物核酸电泳鉴定图 Fig. 3 Double enzyme digest products of the recombinant products (in lanes labeled with different numbers). Lane M: 12K standard nucleic acid. Yeast expression cassette with different copies of the target gene: (A) two copies, (B) three copies, (C) four copies, and (D) five copies. |
| 图选项 |
2.3 多拷贝目的基因片段电转毕赤酵母GS115菌株以及重组菌的筛选线性化的多拷贝目的基因片段电转染毕赤酵母GS115(his4)感受态细胞,涂布于MD平板,挑取单克隆进行试管培养。重组菌培养上清经SDS-PAGE检测,对凝胶进行银染处理后的部分银染结果如图 4所示。
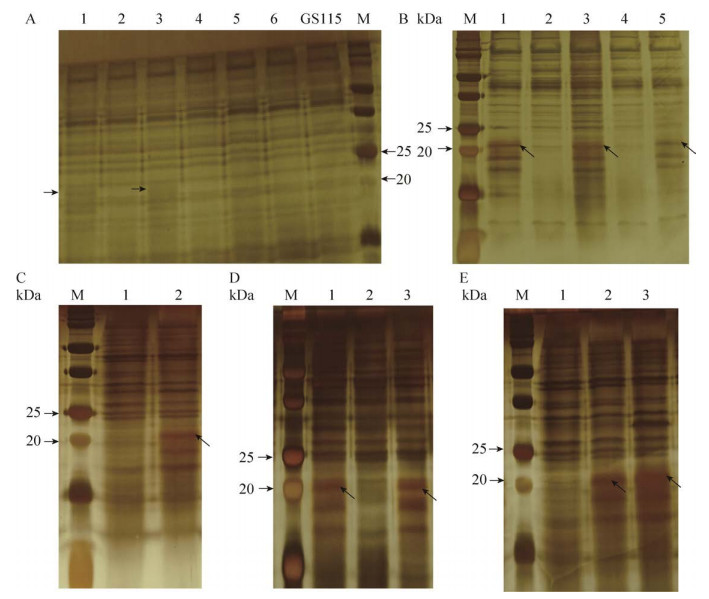 |
| 图 4 SDS-PAGE凝胶银染结果图 Fig. 4 The silver staining results of SDS-PAGE. Lane: the culture supernatant of the selected monoclonal recombinant; lane GS115: the blank control; lane M: the standard protein; the arrow indicates the target protein band. Yeast expression cassette with different copies of the target gene: (A) single copy, (B) two copies, (C) three copies, (D) four copies, and (E) five copies. |
| 图选项 |
图 4中带有红色数字的泳道均为阳性单克隆,其中箭头所指的条带为rhVEGF165。单拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒1和3的培养上清液在20 kDa和25 kDa之间较空白对照多表达出目的蛋白条带,但是表达量很低,为纳克级。其中五拷贝目的基因酵母表达盒的单克隆2和3的培养上清液在20 kDa和25 kDa之间较空白对照多表达出目的蛋白条带。经筛选获得多拷贝目的重组菌株,且目的蛋白表达量随基因拷贝数的增加而升高。
2.4 目的蛋白的纯化2.4.1 镍柱亲和层析镍柱亲和层析收集的各洗脱液经SDS-PAGE鉴定结果如图 5所示,洗脱峰2和3均含有目的蛋白条带,洗脱峰2收集液含有少量杂带,洗脱峰3收集液除了目的条带基本无杂带。说明镍柱亲和层析能高效分离纯化目的蛋白和去除杂蛋白。经Image-Pro Plus软件对SDS-PAGE图进行灰度扫描分析,计算出目的蛋白纯度为96.02%。
 |
| 图 5 镍柱纯化洗脱峰收集液SDS-PAGE检测结果 Fig. 5 The SDS-PAGE of the eluent of nickel column purification. Lane M: the standard protein; the collection solution of eluate peak 1 (lane 1), eluate peak 3 (lane 2); eluate peak 2 (lane 3); lane 4: sample solution before purification; the protein band in the blue frame is the target protein band. |
| 图选项 |
2.4.2 肝素亲和层析肝素亲和层析收集的洗脱液使用浓缩离心管浓缩脱盐后,经SDS-PAGE鉴定结果如图 6所示,洗脱峰1收集液(泳道3) (线性梯度洗脱时NaCl浓度约为0.5 mol/L) 和洗脱峰2收集液(泳道4) (线性梯度洗脱时NaCl浓度为0.6–0.8 mol/L) 均含大量目的蛋白,说明肝素亲和层析能高效纯化和高选择性富集目的蛋白,经Image-Pro Plus软件对SDS-PAGE图进行灰度扫描分析,计算出目的蛋白纯度为98.63%。
 |
| 图 6 肝素亲和层析洗脱峰收集液SDS-PAGE检测结果 Fig. 6 The SDS-PAGE of the eluent of heparin affinity chromatography. Lane M: the standard protein; lane 1 and 2: the collection solution of nickel column purification elution peak 2 and 3; lane 3 and 4: the collection solution of heparin affinity chromatography elution peak 1 and 2, the protein band in the blue frame is the target protein band. |
| 图选项 |
2.4.3 浓缩目的蛋白液浓度测定采用Quick Start Bradford蛋白测定试剂盒制得的蛋白质浓度标准曲线为y=0.847 8x+0.026 9 (R2=0.999 3)。将测得的A595值代入标准曲线方程中计算出浓缩蛋白液rhVEGF165的浓度为0.45 mg/mL。表 1总结了rhVEGF165的纯化。
表 1 rhVEGF165的纯化Table 1 Purification of rhVEGF165
| Purification steps | Protein volume (mL) | Protein purity (%) | Total protein (mg) | Recovery rate (%) | Purified fold |
| Medium supernatant | 2 000 | – | 119.42 | 100 | 1 |
| Ammonium sulfate precipitation | 130 | – | 94.06 | 78.76 | 15.38 |
| Nickel column purification | 55 | 96.02 | 2.13 | 1.78 | 36.36 |
| Heparin affinity chromatography | 45 | 98.63 | 2.05 | 1.71 | 44.44 |
| Ultrafiltration | 4 | 98.63 | 1.81 | 1.52 | 500 |
表选项
2.5 VEGF165蛋白的生物学活性检测2.5.1 糖蛋白分子鉴定结果将目的蛋白氨基酸序列于在线N-糖基化位点预测网站(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc/)上预测,发现目的蛋白氨基酸序列在第101-103位处有一个N-糖基化位点(Asn-Ile-Thr)。
纯化浓缩蛋白液经Endo H酶切后的SDS-PAGE检测结果如图 7A所示,目的蛋白经Endo H酶切后目的蛋白分子量较大的条带的分子量减小了2–3 kDa,说明目的蛋白在毕赤酵母GS115中分泌表达时大部分发生了N-糖基化修饰,且糖基化位点只有一个,与文献报道和在线N-糖基化位点预测结果一致。而分子量较小的条带分子量保持不变,说明未发生糖基化。
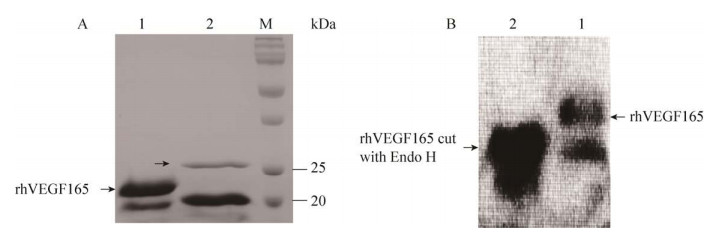 |
| 图 7 Endo H酶切前后目的蛋白的SDS-PAGE鉴定图与Western blotting鉴定图 Fig. 7 The SDS-PAGE and Western blotting of target protein before and after cut with Endo H. (A) The SDS-PAGE identification. Lane 1: the purified and concentrated rhVEGF165 protein solution; lane 2: rhVEGF165 protein solution cut with Endo H; lane M: the standard protein; the protein band indicated by the arrow is Endo H. (B) The Western blotting identification Lane 1: the purified and concentrated rhVEGF165 protein solution; lane 2: rhVEGF165 protein solution cut with Endo H. |
| 图选项 |
Western blotting验证Endo H酶切前后的产物的结果如图 7B所示,发现目的蛋白液经Endo H酶切后两条带的分子量均减小了2–3 kDa,说明目的蛋白的两条带在毕赤酵母GS115分泌表达过程中均发生了糖基化。
2.5.2 重组VEGF165蛋白对HUVEC细胞的促增殖活性将梯度浓度的rhVEGF165蛋白(0、1、5、10、15、20、25 μg/mL) 作用于HUVEC细胞8 h,随后通过CCK-8试剂盒检测细胞增殖情况。HUVEC细胞的A450吸光值在相同的培养条件下会随着VEGF165蛋白浓度的增加而增加(图 8),即rhVEGF165促进细胞增殖作用以剂量依赖性方式显著增加,这与其他文献所测得rhVEGF165的活性结果一致(表 2)。说明由毕赤酵母GS115重组表达的VEGF165蛋白具有天然生物学活性,且经纯化浓缩等一系列处理后对HUVEC细胞仍然具有很强的促增殖作用。
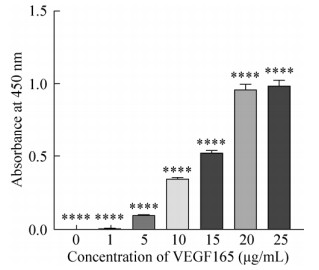 |
| 图 8 不同浓度VEGF165对HUVEC细胞的促增殖作用 Fig. 8 The effect of different concentration of VEGF165 on HUVEC cells proliferation. * indicates the significant difference between the experimental groups (*P? < 0.05;** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.000 1). The error bars indicated standard deviation. |
| 图选项 |
表 2 检测rhVEGF165活性的方法以及结果汇总Table 2 Summary of methods for detecting the effect rhVEGF165 on promoting cell proliferation
| Expression system | Cell proliferation assay | Whether the proliferation effect of rhVEGF165 is significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner | References |
| E. coli | MTT assay | Yes | [12] |
| E. coli | 10% alamarBlue | Yes | [20] |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | WST-1 cell proliferation assay system (TaKaRa) | Yes | [10] |
| Insect cell | CellTiter 96 Non-radioactive cell proliferation assay (Promega) procedure | Yes | [13] |
| Pichia pastoris | MTT assay | Yes | [11] |
| Pichia pastoris | Cell Counting Kit-8 | Yes | This paper |
表选项
3 讨论VEGF是一种血管内皮细胞特异性有丝分裂原,能够促进内皮细胞分裂增殖,加强血管的通透性、促进新血管以及骨组织的生成[21-23];以VEGF165为治疗靶标研制开发抗肿瘤药物和生物标志物研发检测试剂成为研究热点,高纯度的VEGF165则成为各种研究的基础。为提供一个能够快速简便得到高纯度有活性VEGF165的方法,本文通过上游设计构建目的基因表达盒,利用毕赤酵母表达系统进行异源表达。
本研究在选择表达系统时克服了大肠杆菌原核表达系统以及昆虫细胞、酿酒酵母和哺乳动物细胞等真核表达系统的缺点与不足(表 3);同时利用BBPB载体通过“Biobirck”法构建多拷贝VEGF165基因,实现了提高rhVEGF165表达量的目的,表达盒构建策略能明确知道基因的拷贝数和目的蛋白表达量与其基因拷贝数的相关性,避免了G418压力筛选的不确定性,减少了G418压力筛选高拷贝菌株的工作量,克服了毕赤酵母筛选高拷贝菌株的难点。筛选获得的重组菌株GV5-18表达的目的蛋白量相对较高。
表 3 VEGF165在不同的异源表达系统下表达纯化的优缺点Table 3 Summary of the advantages and disadvantages of VEGF165 expression and purification using different heterologous expression systems
| Expression system | Advantages and disadvantages | References |
| E. coli | Advantages: large-scale expression of rhVEGF165, low cost and short cycle Disadvantages: cumbersome purification, easy to produce inclusion bodies, the refolding process of inclusion bodies is extremely prone to mismatches of disulfide bonds, too much protein affects the activity and purity | [12] |
| Mammalian cell | Advantages: rhVEGF165 expressed in mammalian cells has a natural conformation, and the glycosylation sequence is the same as the natural one Disadvantages: low expression level, high training cost, and high technical requirements for operation | [24] [25] [14] |
| Insect cell | Advantages: high expression level, correct protein folding and glycosylation modification Disadvantages: sometimes the glycosylation sequence is different from the natural one, and the purification steps are complicated and costly | [13] |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Disadvantages: low expression level, low purity, difficulty in high-density fermentation, easy loss of plasmids, unstable subculture cells, low secretion efficiency, and prone to hyperglycosylation | [10] |
| Pichia pastoris | Advantages: high expression level of multi-copy recombinant strains, low culture cost, correct protein folding and glycosylation modification Disadvantages: the workload of screening multi-copy recombinant strains is large, and the single exchange integrated transformants are unstable during high-density fermentation | [11] |
表选项
本研究通过上游设计目的基因表达元件以改良目的蛋白下游纯化工艺:1) 将VEGF165自身的信号肽替换成毕赤酵母α-因子信号肽实现了目的蛋白的高效分泌表达,并在VEGF165序列的C端添加His标签,通过His标签和VEGF165肝素结合结构域,采用镍柱与肝素亲和层析进行蛋白纯化,线性梯度洗脱的分离纯化策略实现了目的蛋白高效分离和浓缩的效应,表达产物仅经两步亲和层析后获得了纯度达到98.63%的rhVEGF165蛋白(表 4)。2) 选择Pgap启动子进行表达,免去了菌液培养时需添加甲醇的步骤,与文献报道的甲醇毕赤酵母诱导表达相比,简化了培养过程,缩短了培养时间,表达的蛋白符合医用要求,稳定性更佳,分泌表达过程中目的蛋白降解率低。但是缺点为重组菌株目的蛋白表达量会较低,后期可以通过改造Pgap调控因子、构建和筛选更高拷贝数的重组菌株、使用发酵罐大规模培养等方法继续提高其表达量。考马斯亮蓝法测得rhVEGF165蛋白浓度达到0.45 mg/mL,带His标签的rhVEGF165能够促进HUVEC细胞的增殖,证明具有天然VEGF165的生物学活性。
表 4 VEGF165在不同的纯化策略的纯化结果Table 4 Summary of the purification of VEGF165 from fermentation supernatant using different purification strategies
| Expression system | Purification steps | Purity of rhVEGF165 after purification | Purified fold | Summary of purification strategies | References |
| E. coli | 1.Nickel–nitrilotriacetic acid resin column | 97% | – | Using his tag, one-step purification obtains rhVEGF165 with 97% purity. | [12] |
| Mammalian cell (Sf21) | 1.Heparin affinity 2.30 kDa cut-off membrane for ultrafiltration 3.Ion exchange chromatography 4.FPLC | 95.85% | 119.75 | The purity of rhVEGF165 obtained by the three-step purification procedure is only 95.85%. Too many purification steps will reduce the yield of the target protein. | [23] |
| Pichia pastoris (GS115) | 1.Sephadex G-25 2.Heparin Sepharose FF 3.Sephacryl S-100 | 95% | – | Using methanol-induced protein expression, 95% purity rhVEGF165 was obtained through three chromatographic separation and purification. Too many purification steps would reduce the protein yield. | [11] |
| Pichia pastoris (GS115) | 1.Nickel column purification 2.Heparin affinity chromatography 3.Ultrafiltration | 98.63% | 500 | Using non-methanol to induce Pichia pastoris expression, through upstream design optimization purification strategy, two-step purification to obtain 98.63% purity rhVEGF165. | this paper |
| –: not reported in the article. | |||||
表选项
本研究的纯化策略结合了非甲醇诱导的毕赤酵母表达系统,不仅能够减少粗酶液杂蛋白的含量,还简化了rhVEGF165的纯化步骤来减少纯化过程所带来的蛋白损失,是目前文献报道的最高纯度(表 4),高纯度且有活性的VEGF165能进一步为探索研发关于VEGF165的药物研究奠定基础。
参考文献
| [1] | 张淑芝. 血管内皮生长因子研究进展. 潍坊学院学报, 2014, 12(2): 54-58. Zhang SZ. Advances in the research of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Weifang Univ, 2014, 12(2): 54-58 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | Klagsbrun M, D'Amore PA. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 1996, 7(3): 259-270. DOI:10.1016/S1359-6101(96)00027-5 |
| [3] | Levy AP, Levy NS, Goldberg MA. Post-transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia. J Biol Chem, 1996, 271(5): 2746-2753. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.5.2746 |
| [4] | Birk DM, Barbato J, Mureebe L, et al. Basic science review: current insights on the biology and clinical aspects of VEGF regulation. Vascul Endovascul Surgery, 2008, 42(6): 517-530. |
| [5] | Ng EWM, Shima DT, Calias P, et al. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(2): 123-132. DOI:10.1038/nrd1955 |
| [6] | Radema SA, Witteveen PO, Gebbink MB, et al. The clinical perspective of angiogenesis inhibitors. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd, 2003, 147(35): 1675-1680. |
| [7] | Kimoto M, Nakamura M, Hirao I. Post-ExSELEX stabilization of an unnatural-base DNA aptamer targeting VEGF165 toward pharmaceutical applications. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(15): 7487-7494. |
| [8] | Nagy JA, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF. Vegf-a and the induction of pathological angiogenesis. Ann Rev Pathol Mechan Dis, 2007, 2: 251-275. DOI:10.1146/annurev.pathol.2.010506.134925 |
| [9] | Lee IL, Li PS, Yu WL, et al. Prokaryotic expression, refolding, and purification of functional human vascular endothelial growth factor isoform 165: purification procedures and refolding conditions revisited. Protein Expr Purif, 2011, 76(1): 54-58. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2010.08.014 |
| [10] | Kang WK, Lee MH, Kim YH, et al. Enhanced secretion of biologically active, non-glycosylated VEGF from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol, 2013, 164(4): 441-448. DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.02.004 |
| [11] | 王晓, 黄晓平, 周宇, 等. 重组人VEGF165蛋白在毕赤酵母中高效表达与多克隆抗体的制备. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(6): 695-700. Wang X, Huang XP, Zhou Y, et al. High level expression of recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 protein in Pichia pastoris and preparation of VEGF165 polyclonal antibody. J Huaqiao Univ (Nat Sci), 2014, 35(6): 695-700 (in Chinese). |
| [12] | Kang W, Kim S, Lee S, et al. Characterization and optimization of vascular endothelial growth factor165 (rhVEGF165) expression in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif, 2013, 87(2): 55-60. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2012.10.004 |
| [13] | Zhang TY, Liu RP, Luo Q, et al. Expression and characterization of recombinant human VEGF165 in the middle silk gland of transgenic silkworms. Transgenic Res, 2019, 28(5/6): 601-609. DOI:10.1007/s11248-019-00173-y |
| [14] | 唐浩, 陈勇, 夏昆, 等. VEGF165在哺乳动物细胞中的稳定表达. 中国医师杂志, 2004, 6(7): 868-871. Tang H, Chen Y, Xia K, et al. The stable expression of VEGF165 in mammalian cells. J Chin Physician, 2004, 6(7): 868-871 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-1372.2004.07.002 |
| [15] | Siemeister G, Marme D, Martiny-Baron G. The α-helical domain near the amino terminus is essential for dimerization of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273(18): 11115-11120. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.18.11115 |
| [16] | Wiesmann C, Fuh G, Christinger HW, et al. Crystal structure at 1.7 ? resolution of VEGF in complex with domain 2 of the Flt-1 receptor. Cell, 1997, 91(5): 695-704. DOI:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80456-0 |
| [17] | 王令, 郭苗苗, 杜伟立, 等. 多靶点CRISPR表达载体系统的设计和构建. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2017, 36(4): 1518-1525. Wang L, Guo MM, Du WL, et al. Design and construction of CRISPR expression vector system harboring multi-target sites. Genomics and applied biology, 2017, 36(4): 1518-1525 (in Chinese). |
| [18] | 徐云巧, 李婷婷, 吴彩娥, 等. 糖蛋白的去糖基化方法研究进展. 中国生物工程杂志, 2017, 37(5): 97-106. Xu YQ, Li TT, Wu CE, et al. Research progress on the methods of deglycosylation of glycoproteins. China Biotechnol, 2017, 37(5): 97-106 (in Chinese). |
| [19] | Ashikari-Hada S, Habuchi H, Kariya Y, et al. Heparin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor165-dependent mitogenic activity, tube formation, and its receptor phosphorylation of human endothelial cells comparison of the effects of heparin and modified heparins. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(36): 31508-31515. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M414581200 |
| [20] | 周晓雷, 朱重悦, 张世光, 等. 重组人血管内皮生长因子165在大肠杆菌中的可溶性表达、纯化与体外活性评价. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(1): 42-46. Zhou XL, Zhu CY, Zhang SG, et al. Prokaryotic soluble expression and purification of functional human vascular endothelial growth factor 165. Sci Technol Eng, 2016, 16(1): 42-46 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.01.007 |
| [21] | Dai J, Rabie ABM. VEGF: an essential mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondral ossification. J Dent Res, 2007, 86(10): 937-950. DOI:10.1177/154405910708601006 |
| [22] | Geiger F, Bertram H, Berger I, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene-activated matrix (VEGF165-GAM) enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in large segmental bone defects. J Bone Miner Res, 2005, 20(11): 2028-2035. DOI:10.1359/JBMR.050701 |
| [23] | Bluteau G, Julien M, Magne D, et al. VEGF and VEGF receptors are differentially expressed in chondrocytes. Bone, 2007, 40(3): 568-576. DOI:10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.024 |
| [24] | Lee GY, Jung WW, Kang CS, et al. Expression and characterization of human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165) in insect cells. Protein Expr Purif, 2006, 46(2): 503-509. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2005.09.023 |
| [25] | 韦方, 邓云坤, 乔慧. 人VEGF165基因的克隆、表达和活性鉴定. 贵州医药, 2005, 29(1): 3-6. Wei F, Deng YK, Qiao H. The clone, expression and activity identify of human vascular endothelial growth factor. Guizhou Med J, 29(1): 3-6 (in Chinese). |
