全文HTML
--> --> --> 鸻鹬类是东亚-澳大利西亚迁飞路线上重要的水鸟类型。这类水鸟以滨海湿地中丰富的无脊椎动物为能量补给,对滨海湿地依赖度极高[1-3]。天津滨海湿地位于渤海湾底,是黄渤海湿地的重要组成部分,也是东亚-澳大利西亚迁飞路线上水鸟的重要停留站点[4-5]。近年来,天津滨海新区实施了较大规模围填海和基础设施建设工程,造成滨海滩涂湿地面积大幅锐减。其中,2006—2016年间湿地面积减幅高达408 km2[6]。作为对滨海湿地依赖度极高的水鸟类群[1-3],鸻鹬类的生存空间被大幅压缩,食物丰度和数量锐减,加剧了生态位重叠的鸻鹬类水鸟对食物的竞争,造成能量补给不足[4, 7-9],在此停歇、繁殖的鸻鹬类种群数量呈下降趋势[3, 5]。在滨海湿地退化的同时,天津滨海地区也在积极营建人工湿地,先后建成天津临港湿地一期[10]、南港工业区人工湿地[11]、开发区西区生态湿地[12]等项目。作为人工构建的仿自然生态处理系统,滨海人工湿地不仅承担着水质净化的原始目标责任,更是滨海区域景观与生态格局的重要组成部分,是邻近滨海湿地的潜在替代场所[13-15]。然而,传统滨海人工湿地以污水处理和园林景观为重,忽视生态修复,生境单一、干扰程度大、生态系统不完整,鸻鹬类栖息地价值不高[7]。
本研究以天津临港湿地二期工程为实例,围绕鸻鹬类栖息觅食空间、防护空间营造等方面,阐述滨海人工湿地鸻鹬类栖息地构建与生境恢复方法,以期为同类型人工湿地水鸟栖息地构建提供参考。
1.1. 项目建设背景
天津港保税区临港经济区始建于2003年,位于海河入海口南侧滩涂浅海区。这片区域每年能为上万只鸻鹬类提供觅食、栖息和繁殖场所。然而,被围海造地形成港口工业一体化海上工业新城后,这片区域成为天津滨海新区重要功能区之一。为修复围填海开发过程中被破坏的潮间滩涂湿地,临港经济区先后规划建设临港湿地一期和临港湿地二期(见图1(a))。临港湿地一期位于临港经济区西部,于2013年建成,占地面积60 hm2。这是一座以水处理为主要功能、兼具景观效果,国内唯一建于大型工业园区内的人工湿地,可通过对工业园区内污水处理厂尾水和雨水进行有效收集,以实现水的净化处理和循环利用。本项目为临港湿地二期,位于临港湿地一期南侧。二期工程在功能定位上是临港湿地一期的延续,承担对湿地一期出水的深度处理。同时,拟利用临港湿地一期工程的深度净化出水和区域雨水,恢复并重建滨海盐生湿地,为鸻鹬类创造觅食、栖息和繁殖的优良栖息场所。项目总占地面积约为107.7 hm2,于2019年启动建设,2020年6月完成主体施工。
1.2. 研究区生态环境现状
根据2017年该研究区域的土地利用类型分析(见图1(b)),区域中60.5%的土地为旱地、28%的土地为林地,而坑塘面积仅占4.3%,其余为公共设施、小径、其他土地、河道等。其中,河道北接湿地一期尾水,向下游穿过珠江道后,沿渤海十路西侧向南延伸,与临港湿地二期供排水系统分离。研究区域水源仅靠雨水和地下水自然补给,无法维持湿地水量平衡,已逐渐退化为干涸、硬化状态,土壤基质抗性较大。根据生物资源现状调查,研究区域现有种子植物6科13属14种,以盐生植被为主,芦苇、柽柳等高大植物呈零散或集群分布。区域内坑塘水体呈富营养化,浮游动植物较为丰富,共检出浮游植物110种、浮游动物28种,香农多样性指数分别为2.87和2.17。由于缺少大面积软湿浅滩,现场仅检出水生昆虫稻水蝇(Ephydra sp.)1种底栖动物,平均生物量也仅为0.6 g·m-2。此外,研究区域尚未监测到鱼类生长。
综上所述,研究区域内呈现缺少水源供给、滩涂湿地等重要生境丧失、生态系统组分不完整、动植物物种数量较少、底栖动物关键种丧失、生物群落结构单一、生物多样性指数较低等特征,已难以满足鸻鹬类的栖息地和食物需求。2018年全年在临港湿地二期建设场区范围仅观测到13种鸟,其中鸻鹬类4种,种群数量相对较少。
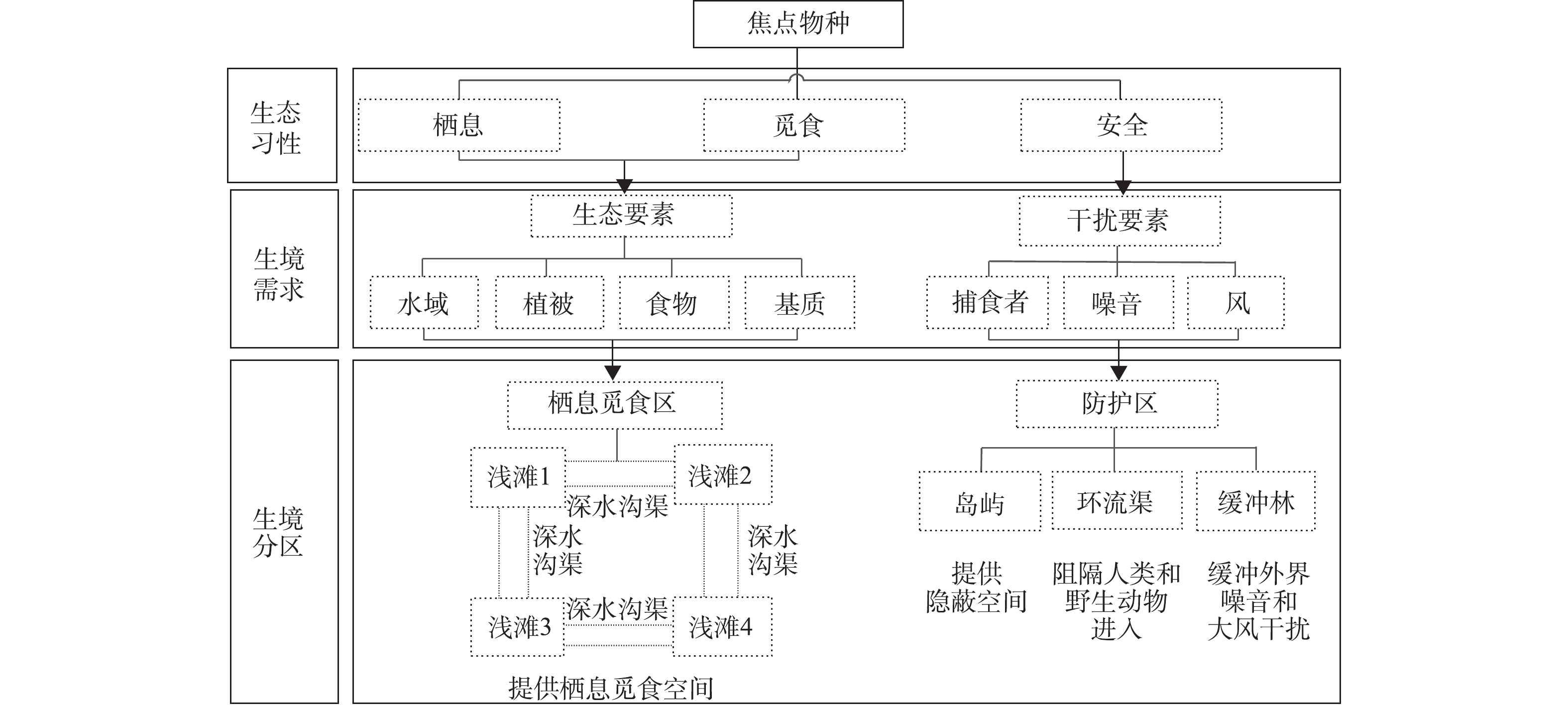
已有研究表明,白腰杓鹬、黑翅长脚鹬、红脚鹬、环颈鸻等4种焦点物种对生境要求高,倾向于选择植被覆盖率低[13]、裸露光滩[20-21]、面积充足[13, 22-23]、浅水位[24]等抗性低、持水量高的基质[25],主要以大型无脊椎动物为食[26]。焦点物种对捕食者警戒性高[27-28],觅食行为受到噪音干扰[29],对大风等恶劣天气耐受能力差[29]。因此,在栖息地营建时,应根据焦点物种的生境需求,营造适宜的栖息和觅食空间,为其提供充足的食物来源,同时创造相对独立、低干扰的隐蔽空间,以缓冲人类活动、天敌、大风等外界干扰影响。
考虑临港湿地二期呈南北向长条型,北部毗邻临港湿地一期,受人为干扰程度大。因此,在人工湿地景观分区规划时,将干扰性强的功能活动区集中在场地北侧,保留南部区域作为栖息地,中间区域作为缓冲区,形成条带型生态格局。人类活动空间由北向南逐渐减少,对水鸟的干扰也逐渐减弱,可使生境保育区在空间上与外界较好地隔离,从而有效保证临港二期湿地空间生态格局的稳定与安全。
根据生态学中的岛屿生物地理学理论,保护区内物种数随生境面积增大呈曲线增长[35]。因此,在人工湿地的有限范围内,应尽可能增大核心区的面积,以期获得湿地物种多样性的最大化[36]。本研究结合临港湿地二期实际,生境保育区规划面积为55 hm2,约占临港湿地二期总面积1/2。
4.1. 设计思路
临港湿地二期保育区以焦点物种生境需求作为规划设计的前提和基础,具体生境规划思路见图3。栖息地保育区生境布局俯视图和剖面图见图4。焦点物种倾向于选择在植被覆盖率低、裸露光滩、面积充足、浅水位的生境中栖息和觅食,因此,在鸻鹬类栖息地规划时,营建4个无植被或稀疏低矮植被覆盖浅滩作为觅食基质,为焦点物种营造足够的栖息和觅食空间。每个浅滩区域空间上相互独立、互不干扰,通过邻近深水沟渠的生态廊道作用实现彼此关联。考虑到焦点物种受不同因素(捕食者、噪音、风)的干扰,故设计岛屿、环流渠、缓冲林,为焦点物种创造低干扰空间。小型岛屿能为焦点物种提供隐蔽空间,作为繁殖、逃遁、栖息的优良场所;环流渠能阻隔行人和野生动物随意进入,还能增加水体循环量,起到改善水质作用;缓冲林能有效缓冲噪音、大风等因素干扰,可为焦点物种提供天然保护屏障。4.2. 生境恢复措施
1) 营建大面积浅滩,创造栖息和觅食空间。浅滩生境具有一定的水深和湿度条件,能为底栖生物提供较好的生存环境,有利于鸻鹬类的觅食,可较好地满足焦点物种的生境需求。因此,在保育区设计4个开阔的浅滩区域,面积共计约22 hm2,每个浅滩区域空间上相互独立、互不干扰,但又通过邻近深水沟渠的生态廊道作用实现彼此关联。将水引入深水沟渠,使用水位调节手段提高水位,漫灌入浅滩区,即可获得大片漫滩沼泽。受身体条件限制,焦点物种适宜栖息、觅食于在10 cm以下的浅水、湿润生境[23-24]。同时,根据《国家湿地公园湿地修复技术指南》,鸻鹬类(每年3—11月)浅滩水位控制在0~0.15 m。本研究中,焦点物种主要在春季(3—5月)和秋季(9—11月)迁徙季节在保育区停歇,黑翅长脚鹬属夏候鸟,夏季在此停留繁殖(5—8月)。因此,栖息地水位控制应分季节进行。迁徙季节(3—11月)设置足够的浅水区(水位小于15 cm),给迁徙水鸟提供更多觅食、栖息和繁殖场所。冬季(11月—翌年3月),为兼顾留鸟栖息空间,适当提高水位(30 cm以上),让水淹没浅滩,防止来年杂草入侵。
鸻鹬类水鸟倾向于选择无植被或稀疏低矮植被的区域栖息。因此,部分区域设计为无植被覆盖的光滩,部分区域配置低矮稀疏的植被,同时在湿地管理中加强植物管理与刈割,避免高大茂密植被过度生长。采用改善底质、增殖放流等方式,恢复摇蚊、沼虾、蠕虫等乡土底栖动物群落,为焦点物种提供足够数量和质量的食物。
2) 挖掘深水沟渠系统,构建生态廊道。在浅滩区外围深挖基底形成深水区,根据《国家湿地公园修复技术指南》[37],深度应保证天津滨海最冷月份底层水体不结冰,并预留0.5 m深的流动水体。深水区地形以凹形为主,形成由浅至深的过渡分布,为鱼类、贝类、水生昆虫等提供丰富的水下微地形[37]。深水沟渠系统可阻止人类和野生动物进入,既保证鸻鹬类水鸟的迁徙、觅食等活动不受干扰,又能提高保育区内部的连通性和整合度,为水鸟提供更广阔的活动空间。在深水沟渠边缘种植狭窄的芦苇带,可处理浅滩入水,起到改善水质作用。
3)构筑若干个小型岛屿,创建良好的隐蔽空间。岛屿具有相对独立的空间,能为焦点物种创造隐蔽空间,为其提供繁殖、逃遁、栖息的场所[38-39]。因此,在距离岸边一定距离的开阔水面处营造适宜焦点物种栖息的岛屿很有必要。保育区内部水域包括浅滩和深水区。深水区为沟渠形态,宽度较窄,且需维持一定的水动力,不适宜在其内部构建岛屿。浅滩面积大,且被深水区环绕,与外界隔离,只需微调地形就可形成若干个大小不等的岛屿,栖息地改造和干预程度小。因此,选择在浅滩区域内构筑若干个岛屿。
由于不同的焦点物种占据着不同的生态位,所以应尽量丰富岛屿的类型,构建不同大小、形态的岛屿,以提高景观的异质性。根据《湿地公园设计》[35],岛屿面积越大,单位面积内产生的湿地岸线越小。当岛屿面积超过3 000 m2时,单位面积内产生的湿地岸线变化幅度不大。为增大水陆交界岛屿岸线长度,规划设计了6个小型岛屿,面积1 100~3 083 m2不等。另外,通过在滨海自然湿地实地观测,面积较大的岛屿对鸻鹬类具有较大吸引力。同时,考虑兼顾焦点物种以外的水鸟栖息需求,结合保育区地形地貌,还规划设计了4个面积相对较大(4 152~14 221 m2)的岛屿,以营造水鸟多样的栖息环境,满足不同水鸟的最佳栖息面积需求。受保育区条件限制,岛屿设计较为集中,彼此靠近,一定程度上能够减缓核心斑块的破碎程度。根据生态学原理,岛屿边界应尽量曲折婉转,故设计了类型多样的凹岸、港湾,保留了有利于物种传播的边缘指状突出,不仅可增加鸟类觅食的区域,同时将湿地水域空间划分为多个相对独立的隐湾,减轻焦点物种在觅食和栖息上的竞争[35]。鸟岛上种植疏密相间的草本植被密丛,以保护繁殖季节的水鸟,使其免受外界干扰,为其提供隐蔽安全的繁衍栖息场所。
4)设计外周环流渠,提高水体循环动力。在湿地保育区外周规划2.4 km环流渠。环流渠宽10~20 m,水位保持在20~50 cm。在环流渠关键节点设置闸门,引入人工湿地处理后的净化水形成环流,并将水体停留时间控制在24 h左右,可有效减少湿地系统水体的长期停滞,增加水体循环量。在环流渠与深水渠之间设置2处调节闸门,以便于将环流渠水体引入保育区,实现灵活管理。环流渠的作用是,不仅能提高水动力,还能限制人类、流浪狗和其他大型野生动物随意进入,营造相对独立的低干扰空间,为鸻鹬类提供对潜在捕食者和威胁保持警觉的安全距离,保证其逃遁、繁殖、越冬、睡眠、栖息需求。
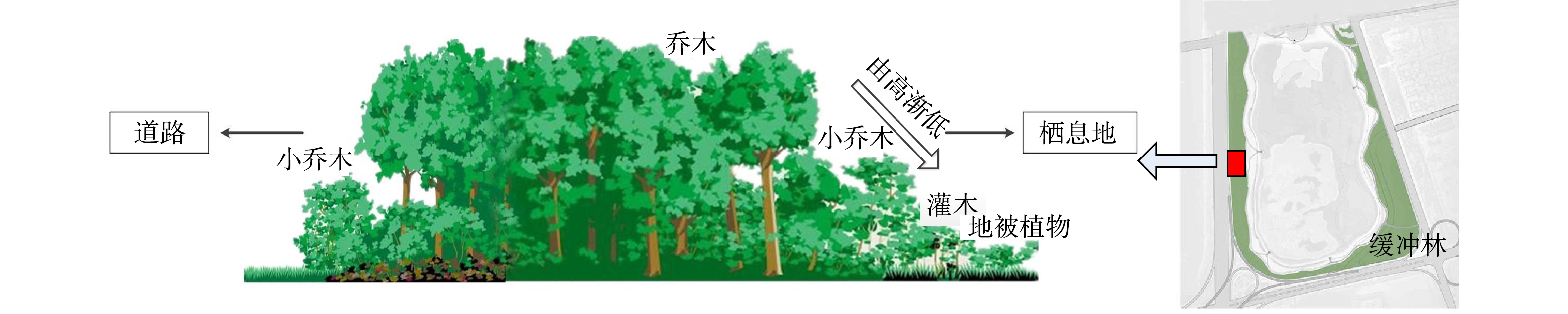
5)种植缓冲林,阻隔外界噪音干扰。保育区南侧紧邻津晋高速,西侧为秦滨高速,北部和东部分别为长江道、渤海十路,城市主干道、高速公路、支线公路纵横交错。保育区周边属声环境4a类区域,昼间分贝值达到70 dB,夜间可达55 dB。为保障焦点物种生境需求(50 dB以下[29]),需要降噪5~20 dB。缓冲林具有较好的降噪效果:林木具备引起乱反射的不平枝叶;多层次的柔性表面能起到减弱噪声的作用;树叶表面的气孔和粗糙的毛,还能吸收一部分声能,尤其能阻隔高频的车辆噪声。因此,规划在保育区与道路边界营造缓冲林。参考相关资料,紧邻公路的缓冲林带宽度宜在30 m以上[19, 40]。本项目考虑保育区实际土地利用现状,缓冲林带宽度设计为30~130 m。
缓冲林带沿道路先低后高分层设计,在车道近旁栽种灌木绿篱带、常绿阔叶小乔木[40],稍远处栽种乔木林带。由林带向栖息地,树木由高渐低,形成大乔木、小乔木、灌木、地被植物等不同层次植物配置(见图5)。为保证保育区降噪效果,小乔木以常绿阔叶植物为宜,选用树冠矮、分枝低、枝叶茂密品种,株距不宜过大;大乔木选用枝下高较低、郁闭度较高的树种,高度宜大于5 m;常绿灌木高度应达到所选乔木的枝下高,郁闭度应较高[40]。本项目在选择缓冲林植物物种时,依据“适地适树”的原则,大乔木选择洋白蜡、榆树、刺槐、毛白杨、火炬树等,小乔木选择金叶榆、紫叶李、木槿、紫叶碧桃、山楂等;常绿灌木选择大叶黄杨、小叶黄杨、铺地柏、金叶女贞等。
4.3. 生境恢复效果
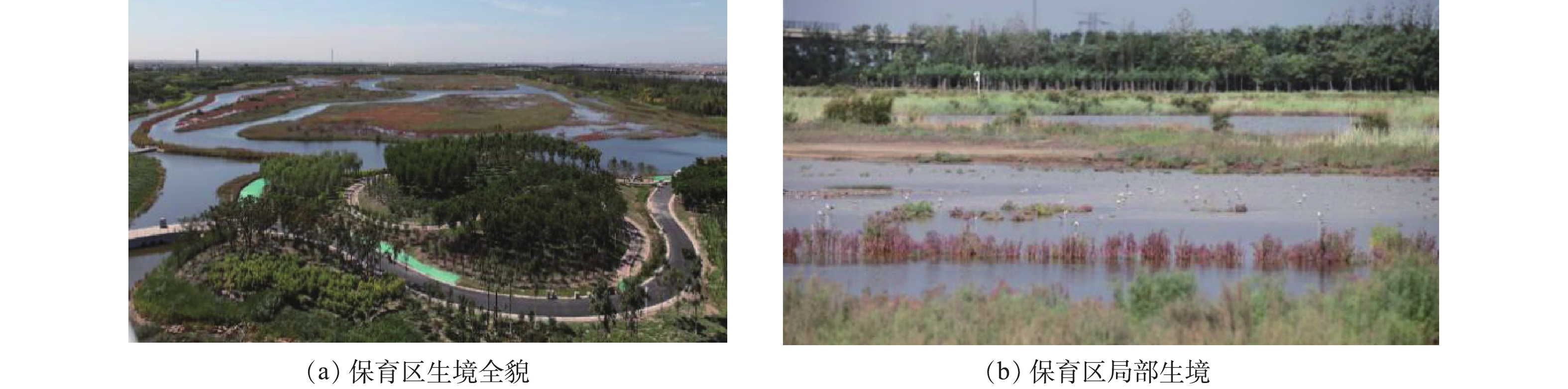
临港湿地二期从鸻鹬类的生态习性出发,仿照鸻鹬类自然栖息地设计而成。湿地建成之初(2020年6—11月)就已吸引了70余种鸟,夏季仅黑翅长脚鹬就观测到数百只,显著高于湿地营造前的鸟类种群数量,这在一定意义上说明了该湿地对鸟类的适宜性和有效性。后续,有必要对湿地进行长期跟踪监测和评估,及时了解湿地对水鸟特别是鸻鹬类的保育效果,并采取适宜性调整措施,提升临港湿地二期的生态服务功能,生境修复效果如图6所示。参考文献


 下载:
下载: 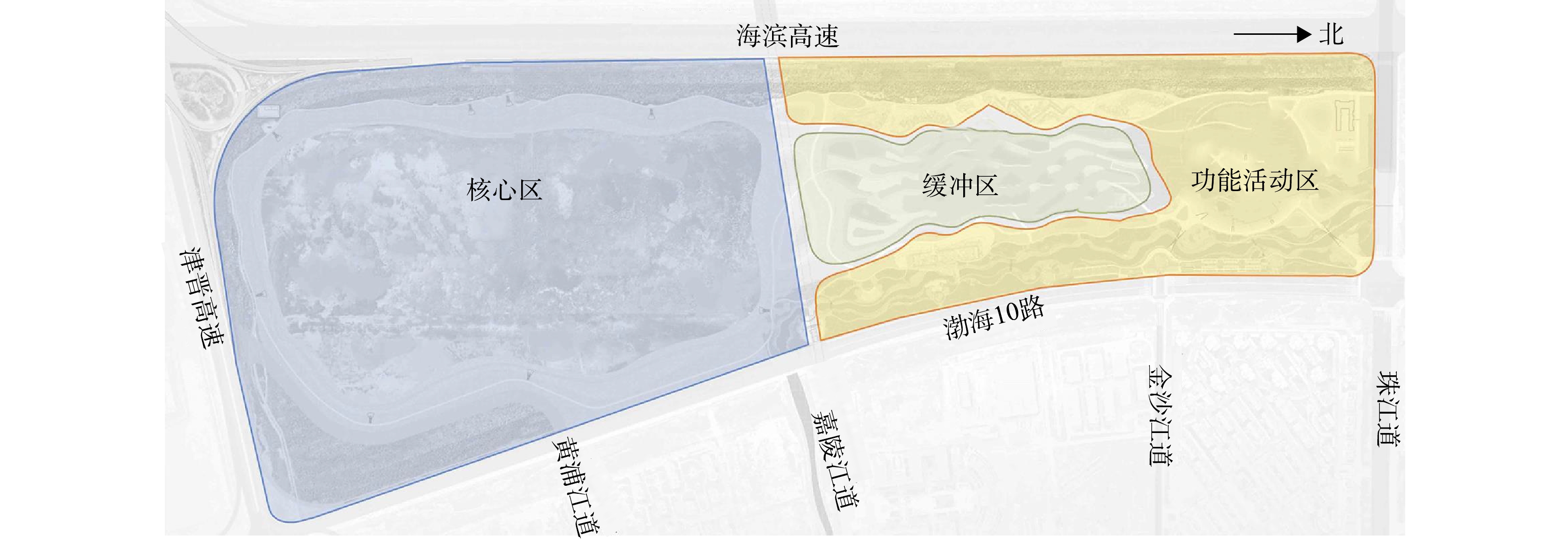


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图