全文HTML
--> --> --> 我国城镇污水处理厂出水执行《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准,出水中有机物、氮磷含量不仅高于地表水环境标准Ⅴ类水,也远高于水体富营养化氮磷标准。污水厂排放入河水质呈现微污染状态,长此以往造成河流水体向富营养化发展[1-2]。原位生态净化技术是在微污染水源地(如水库、湖泊、河流等地)就地采取措施处理水体污染物,不需要将微污染水进行转移,达到净化水质的目的,具有省时、高效、对环境影响小的优点[3-4]。常见原位生态净化技术有水生植物修复、人工浮岛、微生物修复和近自然河岸带等,其中人工浮岛利用挺水植物去除水体中污染物且适用范围广,但由于植物自身和季节变化的影响,其对污染物去除能力有限;生态河床由基质生物膜与水生植物构成,可有效去除水体中氮、磷等物质,提升河流自净能力,但温度变化对其净化能力影响较大;生态滤坝具有良好的过滤性能,能够有效去除SS,对COD等污染物去除效果不明显,易受渗流量变化影响[5-8]。单一原位生态净化技术去污能力有限,并不能满足河流水质的净化要求,而通过不同类型技术组合应用,能够有效改善水质,提高净化能力[9-10]。FANG等[11]通过底泥疏浚措施,并组合水生植物修复带、人工浮岛等技术,构建集成生态工程净化富营养化河水,监测结果表明,COD、TP和TN去除量从40.32、2.49和33.69 t·a?1提升至74.36、3.75和58.28 t·a?1,明显改善河流水质,并增强河流去除污染物能力。SZKLAREK等[12]选择物理沉淀、石灰石吸附和水生植物,设计沉淀区、生化反应区和生物过滤区,构建沉淀-生物过滤系统,应用于小城市河流雨水净化,运行2个水文年后,该系统对TSS、TP、
1.1. 实验装置、进水水质和设计
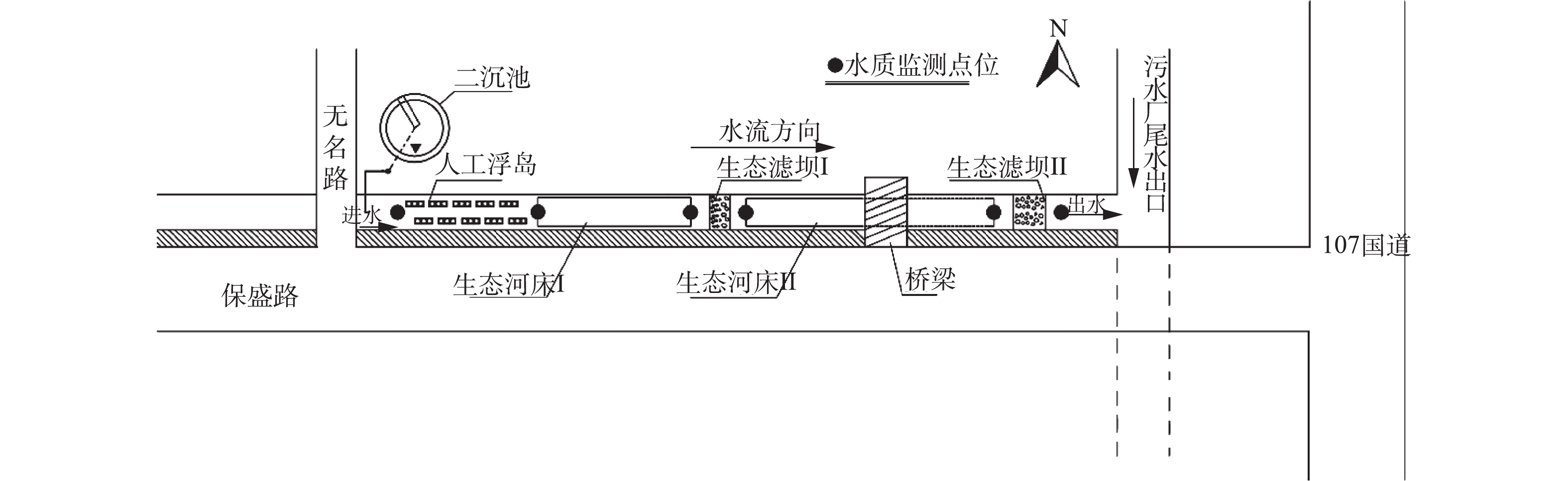
现场实验河道由城市内河道改造而成,实验河道平面如图1所示,河道全长180 m,河段坡降接近于0,河道底宽2~3 m,边坡为混凝土硬质护坡,其边坡系数约为0.7。实验河道内沿程技术处理单元分别是人工浮岛、生态河床Ⅰ、生态滤坝Ⅰ、生态河床Ⅱ和生态滤坝Ⅱ。各处理单元主要参数见表1。现场实验河道进水为河南省长葛市污水净化公司二级出水,秋季(10—11月)和冬季(12—翌年2月)河道进水水质参数如表2所示,水力参数如表3所示。
本实验周期为2017年10月—2018年2月,组合技术改善措施包括3个方面优化配置。1)控制实验河段进水流量,在10月、11月和12月,保持河道进水为2 400 m3·d?1,然后在1月和2月,利用潜水泵和变频器调整进水流量为800 m3·d?1和400 m3·d?1,研究减小流量对组合技术净化效果的影响,不同流量调整设置1周作为适应期。实验期间在监测点位(见图1)处取水样监测,每周2次水质监测。2)铁炭填料投加,在11月,监测河道内微生物活性和硝化/反硝化强度,之后在生态河床(Ⅰ、Ⅱ)均匀添加铁炭填料,完成后,每隔1个月对微生物监测1次,其中在11月和1月各进行1次高通量测序。3)耐寒植物栽种,在11月,监测河道内植物株高和生长面积,随后在人工浮岛补栽耐寒植物羊蹄和水芹菜,生态河床Ⅰ补栽粉绿狐尾藻,生态河床Ⅱ补栽菹草和伊乐藻;完成后,每隔1个月对植物株高和生长面积监测1次。最后筛选、处理数据,分析研究改善措施完成后,组合技术净化效果的变化情况。
1.2. 分析方法
COD、TP、NH4+-N、TN的测定参见文献中的方法[13],使用0.45 μm滤膜过滤原水样,然后同时测定原水样和过滤后水样TP,差值为粒径大于0.45 μm的颗粒态TP量。温度和DO采用HANA便携式DO测定仪测定,pH采用HANA便携式pH计测定。利用卷尺测定挺水植物生长高度,固定网格测定沉水植物生长区域面积;利用荧光显色法测定生态河床段内微生物活性[14],硝化/反硝化强度的测定参考文献中的方法[15]。在河道内添加铁炭填料前后,取生态河床段内足量的基质样品,干冰低温密闭保存,委托上海生工生物有限公司完成样品的高通量测序工作。采用Excel2013和Origin2018软件完成数据处理和绘图,并借助SPSS19.0软件完成显著性差异分析。
2.1. 有机物去除效果
由表2和表3可知,秋季和冬季进水COD为24~50 mg·L?1,10—12月进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1,1月进水流量为800 m3·d?1,2月进水流量为400 m3·d?1,组合技术对COD去除情况如图2所示。COD作为水质监测中一项化学指标,能够反映水体被有机物污染程度。秋、冬季,组合技术进水COD较为接近,由图2(a)可看出,在10—12月,组合技术对COD的去除率为23.6%、16.4%和14.3%,在进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1时,随着温度降低,组合技术对COD的去除效果逐渐减小。由图2(b)可知,在12—2月,组合技术对COD去除率为14.3%、15.7%和19%,即在低温条件下,减小进水流量,COD去除效果逐渐增大。经统计学(ANOVA)分析,冬季不同流量之间组合技术对COD的去除率没有显著性差异(P>0.05)。可知改善措施对COD去除效果影响不明显。2.2. NH4+-N和TN去除效果
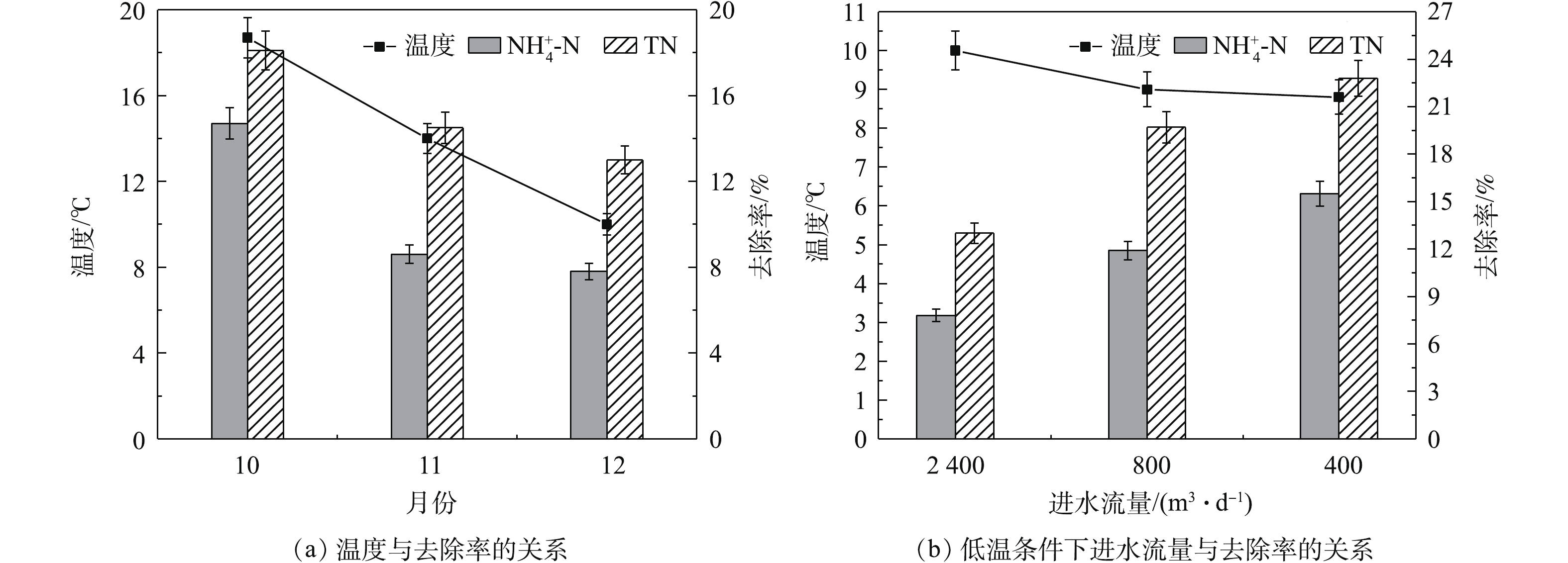
由表2可知,秋、冬季节组合技术进水NH4+-N浓度多集中在0.3~6 mg·L?1,TN浓度集中在20~40 mg·L?1,组合技术对NH4+-N和TN去除情况如图3所示。氮是生物生长代谢的必需营养物质,但也是造成水体富营养化的重要原因。由图3(a)可看出,当进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1时,在10—12月,组合技术对NH4+-N去除率为14.7%、8.6%和7.8%,TN去除率为18.1%、14.5%和13%,随着秋冬季节交替,导致温度降低,组合技术对NH4+-N和TN去除率明显下降。由图3(b)可知,在12—翌年2月,组合技术对NH4+-N去除率为7.8%、11.9%和15.5%,TN去除率为13%、19.7%和22.8%。进入冬季之后,随着进水流量的减小,NH4+-N和TN去除率逐渐升高,流量减小至400 m3·d?1时,NH4+-N和TN去除率达到最大。微生物硝化/反硝化作用对NH4+-N和TN的去除起到主要作用,且受温度变化影响显著,当温度降低时,微生物硝化/反硝化过程均受到影响,使得在冬季低温条件下组合技术对NH4+-N和TN去除率变化趋势一致。经统计学(ANOVA)分析,进水流量在2 400、800和400 m3·d?1之间变化时,组合技术对NH4+-N和TN的去除率都具有显著性差异(P<0.05),由此可见,低温条件下,河道内改善措施能够对氮类的去除效果造成明显影响。
2.3. TP去除效果
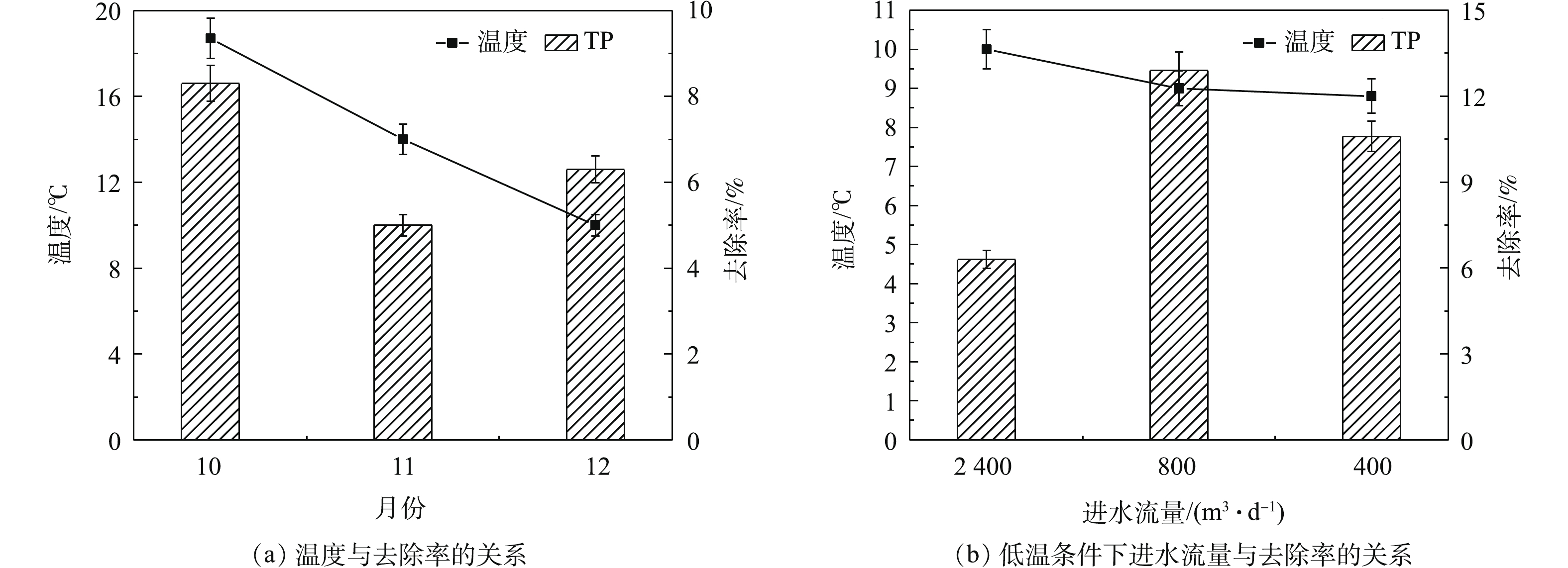
由表2可知,秋、冬季节进水TP浓度集中在0.5~0.95 mg·L?1,组合技术对TP去除情况如图4所示。由图4(a)可看出,在10—12月,组合技术对TP的去除率为8.3%、5%和6.3%。整体来看,当进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1时,组合技术对TP去除率随温度降低而减小。在11—12月,TP去除率出现小幅度升高,这与植物体死亡造成内源污染具有一定关系,11月枯萎死亡植物体沉积在水底产生内源污染,影响组合技术对TP的去除效果;12月耐寒植物已栽种生长,水生植物发挥对磷的去除作用,同时铁炭填料的吸附絮凝作用也有助于磷的去除,使得组合技术对TP去除率出现升高。由图4(b)可知,在12—2月,组合技术对TP去除率为6.3%、12.9%和10.6%,即低温条件下,减小河道进水流量能够增强组合技术对TP的去除效果,但并不是流量越小越好,在进水流量为800 m3·d?1时,TP达到最大去除率。经统计学(ANOVA)分析,进水流量变化时,组合技术对TP去除效果具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。通过对进水TP成分分析,发现二级出水中颗粒态磷(粒径大于0.45 μm)占比为60%~90%,可见磷的去除以基质吸附和沉降等物理作用为主,这也说明了在进水流量为800 m3·d?1时,产生的水力条件更适宜去除颗粒态磷。2.4. 植物与微生物净化情况
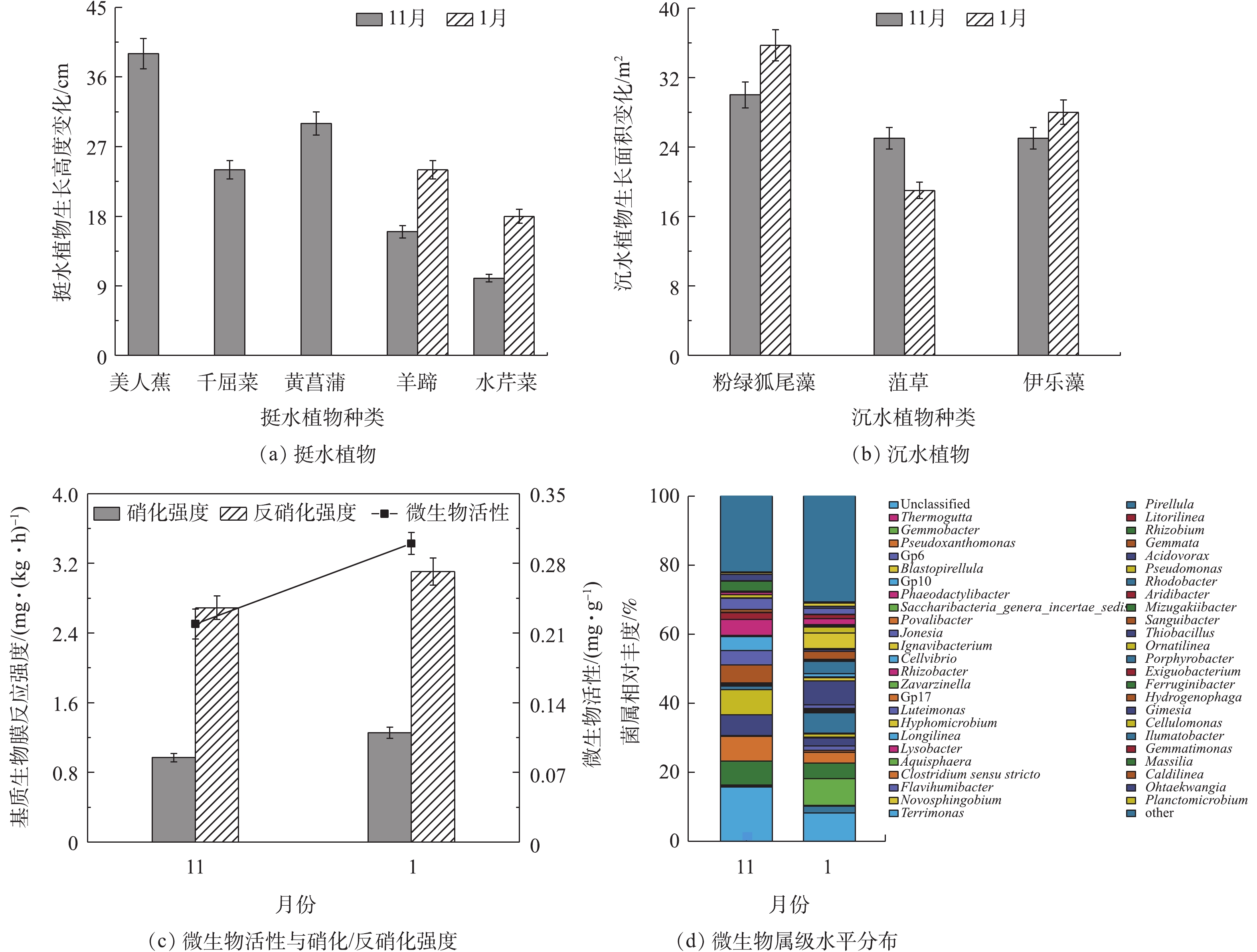
微生物是去除污染物的主要贡献者,水生植物次之,同时也存在着一定程度物理化学作用。11月和1月河道内挺水植物和沉水植物的生长情况以及微生物活性、硝化/反硝化强度和种属变化情况如图5所示。由图5(a)和图5(b)可看出,11月和1月实验河道内水生植物变化明显,美人蕉、千屈菜和黄菖蒲在进入冬季后枯萎死亡,而羊蹄和水芹菜在低温条件仍保持生长,可见冬季羊蹄和水芹菜对水质仍能保持净化作用;1月与11月粉绿狐尾藻生长面积相比,增大约5.7 m2,菹草生长面积减小近6 m2,伊乐藻生长面积增大约3 m2,即冬季粉绿狐尾藻和伊乐藻的净化潜力要强于菹草。由图5(c)可知,11月和1月实验河道内微生物活性为0.22 mg·g?1和0.3 mg·g?1,硝化强度为0.97 mg·(kg·h)?1和1.26 mg·(kg·h)?1,反硝化强度为2.69 mg·(kg·h)?1和3.11 mg·(kg·h)?1;同时由图5(d)可看出,11月与1月河道内丰度较高的菌属中均存在Gemmobacter (芽杆菌属,8%~10%)、Pseudoxanthomonas(假黄单胞菌属,3%~7%)等菌属;脱氮类微生物丰度存在一定差异,11月河道中检测出Rhizobium、Rhodobacter、Thiobacillus (根瘤菌6%、红杆菌3%、产硫酸杆菌1%)等菌属;1月存在Rhizobium、Rhodobacter、Thiobacillus、Hyphomicrobium (根瘤菌4%、红杆菌6%、产硫酸杆菌7%、生丝微菌4%)等菌属。11月底,在实验河道内,大面积投加铁炭填料,由于铁炭填料内电解过程,产生的Fe2+与[H]能够加速微生物代谢过程中电子传递和酶基因的表达,从而增强微生物活性和硝化/反硝化能力,加快对污染物的氧化分解[16]。此外,耐寒植物的正常生长提供了微生物适宜的生存环境,也为微生物种属的丰富创造了条件。可见冬季河道内铁炭填料的内电解作用配合种植耐寒植物,能够有效提高微生物活性和硝化/反硝化强度,以及微生物种属丰度,使组合技术对污染物去除效果得到改善。3.1. 有机物去除效果改善分析
虽然原位生态组合技术能够有效净化河流水质,但受冬季低温条件影响,整体净化效果并不理想;通过改进净化设施,可提高组合技术净化能力。由图2看出,10—12月河道进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1时,组合技术对COD去除率随温度变化逐渐降低;进入冬季后,调整进水流量为800 m3·d?1和400 m3·d?1,低温条件下COD去除率由14.3%升高到19%,可见减小进水流量能够增大组合技术对COD去除效果。汪楚乔等[17]在冬季低温条件下利用人工湿地组合工艺对灌溉尾水进行处理,得出片面降低水力负荷并不能持续提高COD等污染物去除效果的结论。河道进水为二级出水,其自身可生化性较差,不利于微生物的去除;研究表明,铁炭填料在微环境中发生内电解,能够增强微生物活性和改善水体可生化性,从而提高污染物的去除率[18]。有****采用铁炭内电解结合上流式曝气生物滤池工艺去除微污染水体中有机物,并开展中试规模实验研究,结果表明,铁炭内电解预处理去除15.6%有机物,并显著提高了后续处理设施去除效果[19]。在冬季河道约70%的面积内添加铁炭填料,由图5(c)可知,1月微生物活性要高于11月的微生物活性,表明铁炭填料内电解作用增强了河道内微生物活性,强化了微生物对COD的去除;同时河道内栽种耐寒植物,不仅对COD具有去除作用,而且也为微生物创造生长代谢环境,有利于微生物净化作用的发挥[20]。组合技术通过减小流量,降低进水污染负荷,并结合铁炭填料和耐寒植物,强化微生物和植物去除能力,从而使得12—2月COD去除效果持续稳定提高。3.2. NH4+-N和TN去除效果改善分析
氮类污染物一直是污水处理过程中重点去除对象。由图3看出,10—12月河道进水流量为2 400 m3·d?1时,组合技术对NH4+-N和TN的去除率都逐渐降低;在1—2月,调整进水流量为800 m3·d?1和400 m3·d?1后,NH4+-N和TN的去除率达到15.5%和22.8%,高于秋季脱氮水平。经统计学分析,在冬季3种进水流量下,组合技术对NH4+-N和TN的去除效果变化显著。进水流量2 400、800和400 m3·d?1对应HRT为2.8、6.9和11.2 h,在污水处理过程中,延长HRT有利于氮去除[21];结合图3实验结果可知,进水流量为400 m3·d?1时,氮类污染物去除效果最好,其进水HRT最长,因此,冬季河道进水流量的改变导致HRT延长,增强组合技术对氮类污染物去除能力。由图5(c)和图5(d)可知,11月河道内微生物硝化/反硝化强度都低于1月,同时1月河道内脱氮微生物(如Rhizobium、Rhodobacter、Thiobacillus、Hyphomicrobium等)在种属和丰度方面都要高于11月,表明进入冬季后,河道内微生物脱氮能力得到提高。微生物硝化/反硝化强度和种属丰度的变化与河道内大面积添加铁炭填料有很大关系,郑晓英等[22]通过研究发现,冬季内电解湿地微生物群落多样性优于普通湿地,同时脱氮微生物总量上有明显优势,为普通湿地的8.7倍,其硝化/反硝化强度更高,脱氮效果更好。在利用生物膜电极与人工湿地结合处理污水厂尾水的研究中发现,这种耦合系统中电极区域产生内电解作用,能够增加自养细菌(如Thiobacillus)的丰度,并增强反硝化程度约20.8%[23]。SHEN等[24]利用铁炭内电解强化潜流人工湿地去除效果,结果表明,经强化后的潜流人工湿地TN去除率可达(81.45±1.27)%,显著高于普通人工湿地;此外,内电解可以为反硝化过程提供电子,加速反应过程的进行,并能够增加脱氮类微生物丰度。由此可知,组合技术铁炭内电解使得微生物活性和硝化/反硝化强度增强,并增大脱氮微生物种属丰度,进而增强脱氮能力。冬季河道内挺水植物和沉水植物生长状况不同,其对NH4+-N和TN的去除有限;研究表明,微生物反硝化作用可去除54%~94%的TN,植物仅去除7.5%~14.3%[25]。水生植物的存在能够调节水体pH和DO环境,促进微生物硝化、反硝化作用的进行[26]。通过控制进水流量削减污染物量,同时结合耐寒植物与铁碳填料内电解,增强微生物脱氮能力,从而改善组合技术对NH4+-N和TN去除效果。3.3. TP去除效果改善分析
受污染河流水体中TP去除较为复杂,其存在多种磷形态,去除途经包括微生物固定、水生植物吸收、化学反应和吸附沉淀等物理过程[27]。由图4看出,在10—11月,TP的去除率由8.3%降低至5%;在12—翌年2月,河道进水流量为2 400、800和400 m3·d?1,TP去除率为6.3%、12.9%和10.6%,可知当进水流量减小至800 m3·d?1时,组合技术对TP的去除效果最好。已知二级出水中颗粒态磷占比60%以上,使得TP去除以吸附和沉降等物理作用为主,进水流量为800 m3·d?1时,在河道内产生的水力条件有助于颗粒态磷的沉降,且水力扰动不会造成磷的二次污染[28]。铁炭填料除具有较强的氧化还原能力外,还具有较好的吸附和絮凝功能,内电解过程产生Fe2+或Fe3+,能够促进磷的絮凝沉淀[24, 29];同时河道内搭配种植不同类型水生植物,沿水流方向布置耐寒挺水植物-浮水植物-沉水植物,有助于颗粒态磷的沉降吸附,可将进水TP中颗粒态磷去除55%~86.9%。在对表流人工湿地研究中,通过构建不同类型挺水植物、浮水植物和沉水植物,能够实现78%的TP去除率和80%的SS去除率[30]。因此,在处理类似污染水体时,可调整合适进水流量,搭配铁炭填料和不同类型水生植物,有利于达到最佳TP去除效果。2)冬季河道内添加铁炭填料,内电解作用将微生物活性和硝化/反硝化强度提高至0.3 mg·g?1和1.26 mg·(kg·h)?1/3.11 mg·(kg·h)?1,并增加脱氮微生物种属丰度,从而增强组合技术对污染水体的脱氮能力。
3)组合技术沿水流方向布置挺水植物-浮水植物-沉水植物,并结合铁炭填料吸附絮凝作用,能够较好地去除二级出水中TP,可净化水体中55%~86.9%的颗粒态磷。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 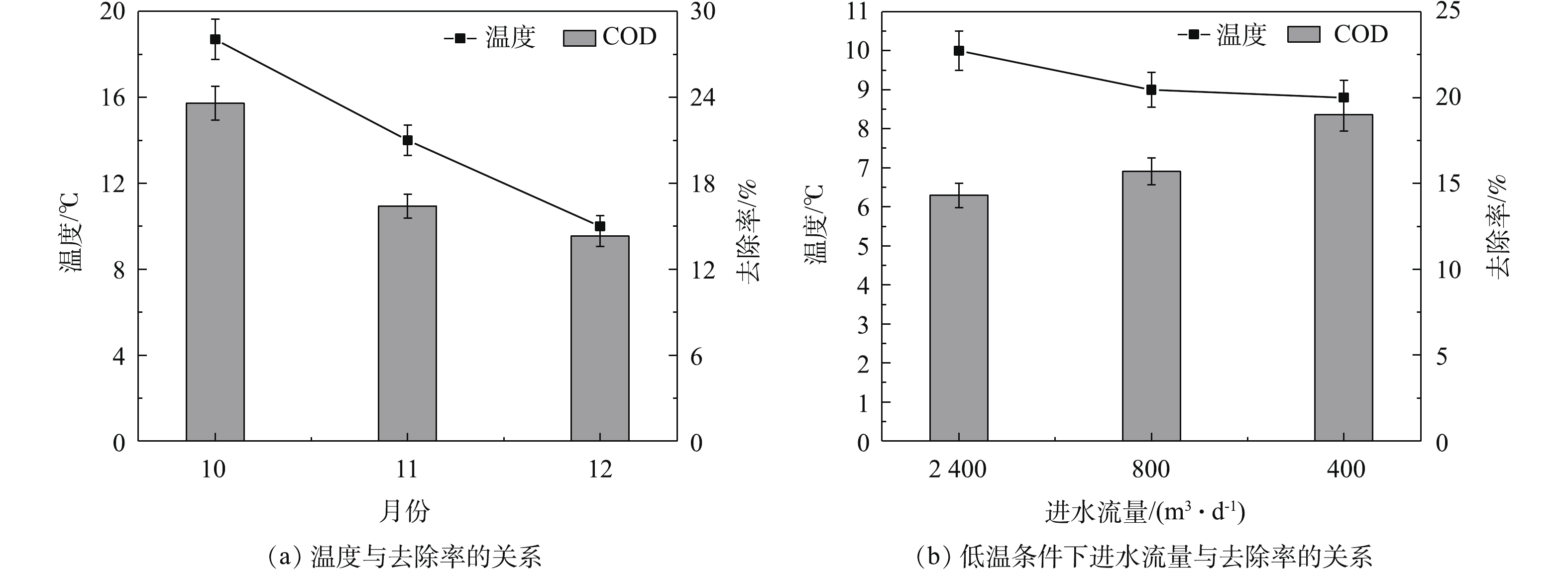



 点击查看大图
点击查看大图