 )
) 1 中国科学院心理健康重点实验室(中国科学院心理研究所), 北京 100101
2 中国科学院大学心理学系, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院行为科学重点实验室(中国科学院心理研究所), 北京 100101
4 香港理工大学电子计算学系, 香港
收稿日期:2018-08-14出版日期:2019-04-25发布日期:2019-02-22通讯作者:刘萍萍E-mail:liupp@psych.ac.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(31600887)Accept or reject?The nudge effect of response options on making a balanced choice between enhancement and enrichment classes
LIU Jun1,2, ZHANG Zhen1,2, SUN Yan2,3, HAN Bu-Xin1,2, LU Qin4, LIU Ping-Ping1,2( )
) 1 CAS Key Laboratory of Mental Health, Institute of Psychology, Beijing 100101, China
2 Department of Psychology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 CAS Key Laboratory of Behavioral Science, Institute of Psychology, Beijing 100101, China
4 Department of Computing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
Received:2018-08-14Online:2019-04-25Published:2019-02-22Contact:LIU Ping-Ping E-mail:liupp@psych.ac.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 近年课外辅导成为学生学习生活的重要部分, 人们普遍选择拓展课数较多, 选择基础课数较少。为了实现基础课及拓展课学习的均衡发展, 本研究在“接受或拒绝反应模式” (
图/表 11
表1实验1和实验2课程类型控制的分析结果
| 课程类型 | 课程名字 | M | SD | t(19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拓展课 | 儿童情商课 | 4.95 | 0.22 | 39.00*** |
| 素质体能 | 4.80 | 0.70 | 11.57*** | |
| 语言艺术 | 4.60 | 0.75 | 9.49*** | |
| 思维逻辑 | 4.85 | 0.37 | 22.58*** | |
| 创意美术 | 5.0 | 0 | — | |
| 基础课 | 语文作文 | 1.4 | 0.60 | -11.96*** |
| 数学冲刺 | 1.45 | 0.51 | -13.58*** | |
| 语文阅读 | 1.20 | 0.52 | -15.39*** | |
| 数学基础 | 1.15 | 0.49 | -16.91*** | |
| 英语基础 | 1.3 | 0.57 | -13.31*** |
表1实验1和实验2课程类型控制的分析结果
| 课程类型 | 课程名字 | M | SD | t(19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拓展课 | 儿童情商课 | 4.95 | 0.22 | 39.00*** |
| 素质体能 | 4.80 | 0.70 | 11.57*** | |
| 语言艺术 | 4.60 | 0.75 | 9.49*** | |
| 思维逻辑 | 4.85 | 0.37 | 22.58*** | |
| 创意美术 | 5.0 | 0 | — | |
| 基础课 | 语文作文 | 1.4 | 0.60 | -11.96*** |
| 数学冲刺 | 1.45 | 0.51 | -13.58*** | |
| 语文阅读 | 1.20 | 0.52 | -15.39*** | |
| 数学基础 | 1.15 | 0.49 | -16.91*** | |
| 英语基础 | 1.3 | 0.57 | -13.31*** |

图1基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验1)
 图1基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验1)
图1基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验1)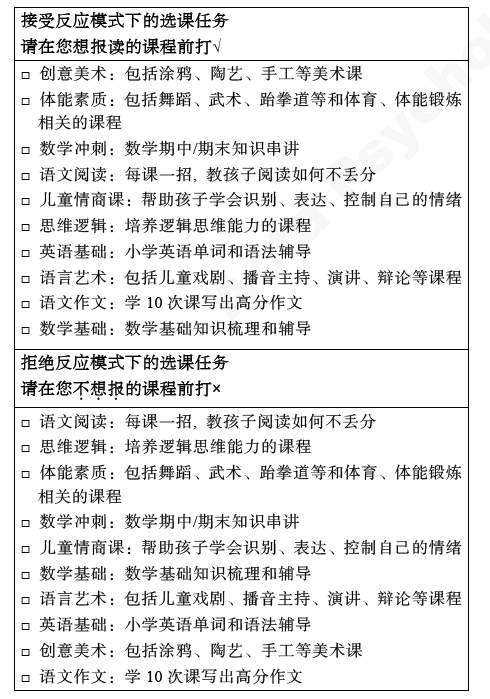
图2不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验1和实验2)
 图2不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验1和实验2)
图2不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验1和实验2)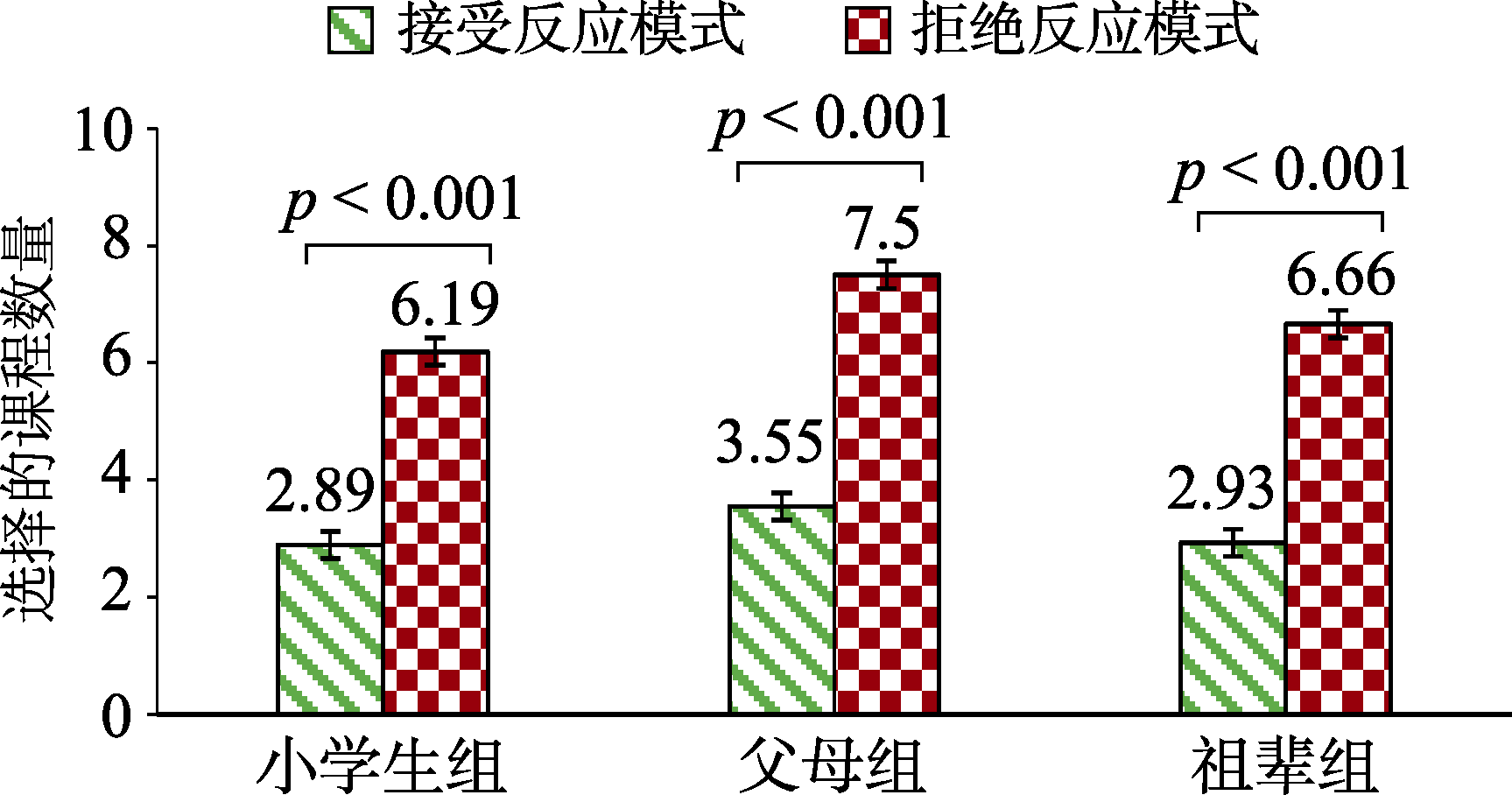
图3被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
 图3被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
图3被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
图4被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程类型数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
 图4被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程类型数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
图4被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程类型数量(实验1) 注: 误差线为标准误
图5同一家庭被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误
 图5同一家庭被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误
图5同一家庭被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误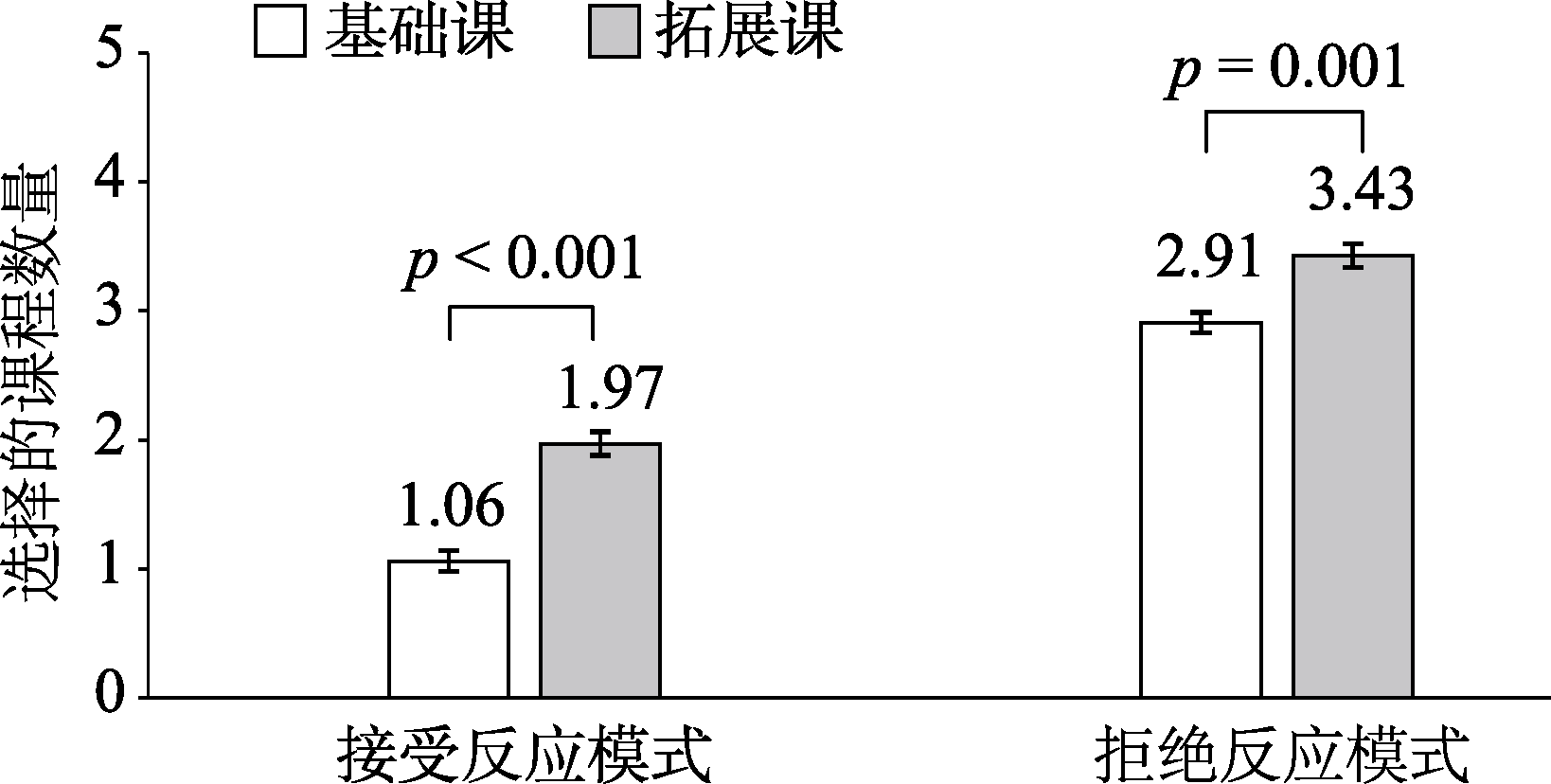
图6被试在不同反应模式下对不同类型课程的选择(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误
 图6被试在不同反应模式下对不同类型课程的选择(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误
图6被试在不同反应模式下对不同类型课程的选择(实验2) 注: 误差线为标准误表2实验3课程类型控制的分析结果
| 课程类型 | 课程名字 | M | SD | t(19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拓展课 | 书法课 | 4.75 | 0.44 | 17.62*** |
| 美术课 | 4.80 | 0.41 | 19.62*** | |
| 合唱团 | 4.65 | 0.49 | 15.08*** | |
| 基础课 | 语文作文辅导 | 1.30 | 0.57 | -13.31*** |
| 数学辅导 | 1.20 | 0.52 | -15.39*** | |
| 英语辅导 | 1.35 | 0.59 | -12.57*** |
表2实验3课程类型控制的分析结果
| 课程类型 | 课程名字 | M | SD | t(19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拓展课 | 书法课 | 4.75 | 0.44 | 17.62*** |
| 美术课 | 4.80 | 0.41 | 19.62*** | |
| 合唱团 | 4.65 | 0.49 | 15.08*** | |
| 基础课 | 语文作文辅导 | 1.30 | 0.57 | -13.31*** |
| 数学辅导 | 1.20 | 0.52 | -15.39*** | |
| 英语辅导 | 1.35 | 0.59 | -12.57*** |
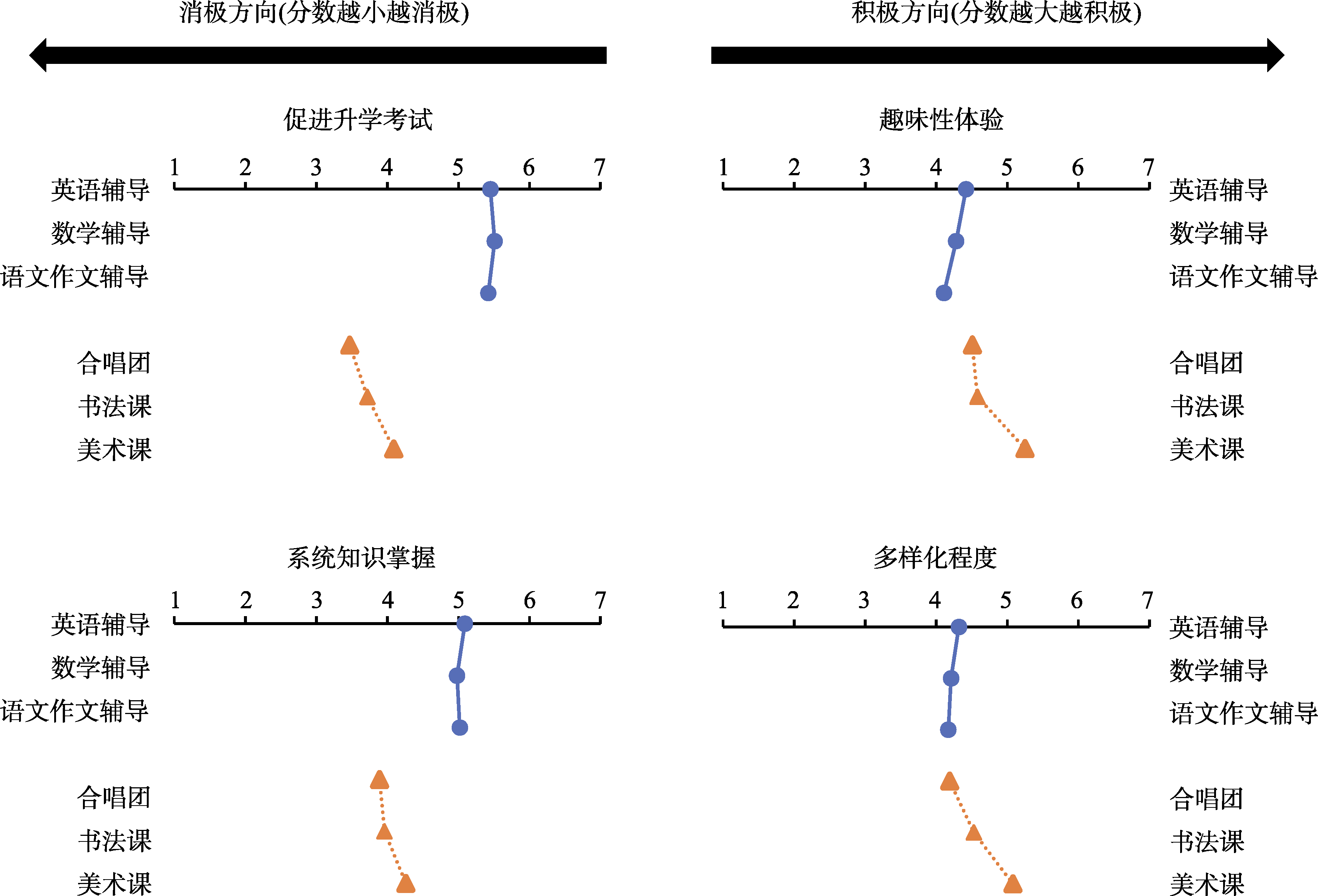
图7基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验3)
 图7基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验3)
图7基础课和拓展课在不同维度上的积极与消极特征评分(实验3)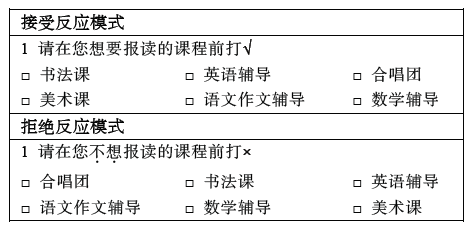
图8不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验3)
 图8不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验3)
图8不同反应模式下的选课任务(实验3)
图9被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验3) 注: 误差线为标准误
 图9被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验3) 注: 误差线为标准误
图9被试在不同反应模式下选择的课程数量(实验3) 注: 误差线为标准误参考文献 49
| [1] | Benartzi S., Beshears J., Milkman K. L., Sunstein C. R., Thaler R. H., Shankar M., … Galing S . ( 2017). Should governments invest more in nudging? Psychological Science, 28( 8), 1041-1055. doi: 10.1177/0956797617702501URLpmid: 28581899 |
| [2] | Bertini M., Ofek E., & Dan A . ( 2009). The impact of add-on features on consumer product evaluations. Journal of Consumer Research, 36(1), 17?28. doi: 10.1086/596717URL |
| [3] | Chapman G. B., Li M., Colby H., & Yoon H . ( 2010). Opting in vs opting out of influenza vaccination. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 304( 1), 43-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.892URLpmid: 20606147 |
| [4] | Chen, J., & Proctor, R. W . ( 2017). Role of accentuation in the selection/rejection task framing effect. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146(4), 543?568. doi: 10.1037/xge0000277URLpmid: 28383992 |
| [5] | Chen,X. L ( 2014). Conflict and cooperation: A study of the relationship between educational institutions and schools (Unpublished master’s thesis). Nanjing Normal University. |
| [ 陈晓陆 . ( 2014). 冲突与合作: 辅导机构与学校的关系研究(硕士学位论文). 南京师范大学.] | |
| [6] | Dhar, R., &Wertenbroch, K. ( 2000). Consumer choice between hedonic and utilitarian goods. Journal of Marketing Research, 37(1), 60?71. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.37.1.60.18718URL |
| [7] | Fu,H. X . ( 2014). Problems and reflections on the market of after-school tutoring market in primary and secondary schools (Unpublished master’s thesis). Capital Normal University, Beijing. |
| [ 付洪秀 . ( 2014). 中小学课外辅导市场存在的问题及其反思(硕士学位论文). 首都师范大学, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Goldstein D. G., Johnson E. J., Herrmann A., & Heitmann M . ( 2008). Nudge your customers toward better choices. Harvard Business Review, 86(12), 99?106. |
| [9] | Huang, D . ( 2015). School extracurricular training market regulation research (Unpublished master’s thesis). Guangxi Normal University. |
| [ 黄笛 . ( 2015). 公共管理视域下的中小学课外培训市场规制研究(硕士学位论文). 广西师范大学.] | |
| [10] | Huang Y. N., Song X. Y., Shao Y., Li S., & Liang Z. Y . ( 2018). Nudging: Default option effect and response mode promote organ donor registry participation in China. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(8), 868?879. |
| [ 黄元娜, 宋星云, 邵洋, 李纾, 梁竹苑 . ( 2018). 以小拨大: 默认选项和反应模式效应助推中国器官捐献登记. 心理学报, 50(8), 868?879.] | |
| [11] | Ji,L. F . ( 2015). Comparison and consideration of the after-school tutoring in primary and secondary schools in China, South Korea, Japan and European Union. Journal of Beijing Institute of Education, 29(3), 67?72. |
| [ 季林飞 . ( 2015). 中、韩、日、欧盟中小学课外教育的比较与思考. 北京教育学院学报(社会科学版), 29(3), 67?72.] doi: 10.16398/j.cnki.jbjieissn1008-228x.2015.03.014URL | |
| [12] | Jin L. Y., Zou D. Q., & Qiu L. J . ( 2009). The effect of option framing on consumer choice in service customization context. Nankai Business Review, 12(6), 90?100. |
| [ 金立印, 邹德强, 裘理瑾 . ( 2009). 服务定制情境下选项的战略呈现: 呈现框架对消费者选择的影响. 南开管理评论, 12(6), 90?100.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3448.2009.06.012URL | |
| [13] | Kahneman D., Knetsch J. L., & Thaler R. H . ( 1991). Anomalies: The endowment effect, loss aversion, and status quo bias. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 5(1), 193?206. doi: 10.1257/jep.5.1.193URL |
| [14] | Levin I. P., Schreiber J., Lauriola M., & Gaeth G. J . ( 2002). A tale of two pizzas: Building up from a basic product versus scaling down from a fully-loaded product. Marketing Letters, 13( 4), 335-344. doi: 10.1023/A:1020370516638URL |
| [15] | Li M., Sun Y., & Chen,H. ., (in press). The decoy effect as a nudge: Boosting hand hygiene with a worse option. Psychological Science, . |
| [16] | Li P. N., Wang Y. S., Yang J. H., & Sun Y . ( 2017). Application of behavioral decision theory in energy conservation management. Journal of Psychological Science, 40(3), 760?765. |
| [ 李鹏娜, 王延伸, 杨金花, 孙彦 . ( 2017). 行为决策理论在能源节约管理中的应用. 心理科学, 40(3), 760?765.] | |
| [17] | Li, S. ( 2016). Neither "carrot" nor "stick": A new shortcut to nudge social development. Management Insights, 6, 92?96. |
| [ 李纾 . ( 2016). 既非“胡萝卜”也非“大棒”: 助推社会发展的一条新捷径. 管理视野, 6, 92?6.] | |
| [18] | Liu, J. Y.,& Bray, M. , ( 2017). Determinants of demand for private supplementary tutoring in China: Findings from a national survey. Education Economics, 25(2), 205?218. doi: 10.1080/09645292.2016.1182623URL |
| [19] | Liu, W. C . ( 2002). Laying a foundation for the lifelong development of students - Building a new curriculum system with elegant characteristics. Hunan Education,(15), 33?34. |
| [ 刘维朝 . ( 2002). 为学生的终身发展奠基——全面构建有雅礼特色的课程新体系. 湖南教育, ( 15), 33-34.] | |
| [20] | Liu Y., Polman E., Liu Y. F., & Jiao J. L . ( 2018). Choosing for others and its relation to information search. Organizational Behavior & Human Decision Processes, 147, 65?75. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2018.05.005URL |
| [21] | Liu Y. F., Wang P., Zhuang J. Y., Zhong J., Sun Q. Z., & Liu Y . ( 2014). Self-other differences in decision-making: Questions, studies and reflection. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(4), 580?587. |
| [ 刘永芳, 王鹏, 庄锦英, 钟俊, 孙庆洲, 刘毅 . ( 2014). 自我-他人决策差异: 问题、研究与思考. 心理科学进展, 22(4), 580?587.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00580URL | |
| [22] | Liu, Y., & Sun, Y. , ( 2014). New avenues for framing effect research in decision-making: From risky to intertemporal and from verbal to graph framing. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(8), 1205?1217. |
| [ 刘扬, 孙彦 . ( 2014). 行为决策中框架效应研究新思路——从风险决策到跨期决策, 从言语框架到图形框架. 心理科学进展, 22(8), 1205?1217.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.01205URL | |
| [23] | Lu, J. Y., & Shang, X. S . ( 2018). Making decisions for others: Multi-dimensional psychological mechanisms and decision feelings. Advances in Psychological Science, 26(9), 1545?1552. |
| [ 陆静怡, 尚雪松 . ( 2018). 为他人做决策: 多维度心理机制与决策体验. 心理科学进展, 26(9), 1545?1552.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2018.01545URL | |
| [24] | Ma J. J., Ma X. X., & Zhang L . ( 2008). Preference asymmetry between utilitarian and hedonic products in acquisition and forfeiture - Compact disc versus music CD. Journal of Marketing Science, 4(1), 107?119. |
| [ 马京晶, 马欣昕, 张黎 . ( 2008). 选择与放弃中对产品实用性和享乐性的不同偏好——以电脑光盘和音乐cd为例. 营销科学学报, 4(1), 107?119.] | |
| [25] | Mark, B., &Ora, K. ( 2013). Behind the fa?ade of fee-free education: Shadow education and its implications for social justice. Oxford Review of Education, 39(4), 480?497. doi: 10.1080/03054985.2013.821852URL |
| [26] | Mourali, M., &Nagpal, A. ( 2013). The powerful select, the powerless reject: Power's influence in decision strategies. Journal of Business Research, 66(7), 874?880. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.12.005URL |
| [27] | Park C. W., Jun S. Y., & MacInnis D. J . ( 2000). Choosing what I want versus rejecting what I do not want: An application of decision framing to product option choice decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 37(( 2), 187-202. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.37.2.187.18731URL |
| [28] | Peng H. M., Xia S. Y., Ruan F., & Pu B. Y . ( 2016). Age differences in consumer decision making under option framing: From the motivation perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 7: 1736. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01736URLpmid: 5098115 |
| [29] | Peng, P . ( 2008). Shadow education: Foreign research on private tutoring and its inspiration. Comparative Education Review, 1, 61?65. |
| [ 彭湃 . ( 2008). "影子教育": 国外关于课外补习的研究与启示. 比较教育研究, 1, 61?65.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8495.2007.09.004URL | |
| [30] | Polman,E. ( 2010). Information distortion in self-other decision making. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(2), 432?435. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2009.11.003URL |
| [31] | Polman,E. ( 2012). Effects of self-other decision making on regulatory focus and choice overload. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 102( 5), 980-993. doi: 10.1037/a0026966URLpmid: 22429272 |
| [32] | Pornpitakpan,C. ( 2009). Cross-cultural generalization of the effect of option choice framing on product option choices. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 21(3), 342?354. doi: 10.1108/13555850910973838URL |
| [33] | Shafir,E. ( 1993). Choosing versus rejecting: Why some options are both better and worse than others. Memory & Cognition, 21(4), 546?556. doi: 10.3758/BF03197186URLpmid: 8350746 |
| [34] | Shen, J. M., & Xie, L. M . ( 2001). On the rejuvenation of the vitality of research-based curriculum - Also on the relationship between research-based curriculum and foundation and enrichment curriculum. Curriculum, Teaching Material and Method,(10), 1?5. |
| [ 沈建民, 谢利民 . ( 2001). 试论研究型课程生命活力的焕发——兼论研究型课程与基础型课程、拓展型课程的关系. 课程. 教材. 教法, (10), 1?5.] | |
| [35] | Sokolova, T., &Krishna, A. ( 2016). Take it or leave it: How choosing versus rejecting alternatives affects information processing. Journal of Consumer Research, 43(4), 614?635. doi: 10.1093/jcr/ucw049URL |
| [36] | Sunstein, C. R., & Reisch, L. A . ( 2014). Automatically green: Behavioral economics and environmental protection. Harvard Environmental Law Review, 38( 1), 127-158. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2245657URL |
| [37] | Thaler, R. H.,& Benartzi, S. , ( 2004). Save more tomorrow using behavioral economics to increase employee saving. Journal of Political Economy, 112( 1), S164-S187. doi: 10.1086/380085URL |
| [38] | Thaler R. H., & Sunstein, C. R. , ( 2008) . Nudge: Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness New Haven, CT: Yale University Press Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness.New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. |
| [39] | Trope, Y., &Liberman, N. ( 2003). Temporal construal. Psychological Review, 110( 3), 403-421. |
| [40] | Tversky, A., &Kahneman, D. ( 1974). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science, 185(4157), 1124?1131. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4157.1124URL |
| [41] | Tversky, A., &Kahneman, D. ( 1981). The framing of decisions and the psychology of choice. Science, 211( 4481), 453-458. |
| [42] | Tversky A., Sattath S., & Slovic P . ( 1988). Contingent weighting in judgment and choice. Psychological Review, 95(3), 371?384. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.95.3.371URL |
| [43] | Wang, W. C . ( 2002). The nature and offerings of enrichment curriculum. Research of Modern Basic Education,(4), 61?65. |
| [ 王维臣 . ( 2002). 拓展课程的定位与设置——国外经验的启示. 现代基础教育研究, (4), 61?65.] | |
| [44] | Wu, Q. S., & Yu , Y. ( 2011). Extra-curricular selection for primary school students from urban families - A consumption perspective. Journal of Xuzhou Normal University (Educational Science Edition),(4), 49?52. |
| [ 伍青生, 俞晔 . ( 2011). 城市小学生家庭课外教育选择行为特征——基于消费视角的研究. 徐州师范大学学报(教育科学版), (4), 49?52.] | |
| [45] | Xue, H. ( 2015). From school education to shadow education: Education competition and social reproduction. Peking University Education Review, 13(3), 47?69. |
| [ 薛海平 . ( 2015). 从学校教育到影子教育: 教育竞争与社会再生产. 北京大学教育评论, 13(3), 47?69.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9468.2015.03.004URL | |
| [46] | Yao J., Liu J. J., & Gao C . ( 2016). Research on the impact of product attributes’ evaluability on purchase decision: Moderating effects of involvement. Nanjing University of Finance & Economics, (6), 84?91. |
| [ 姚杰, 刘俊杰, 高成 . ( 2016). 产品属性评估性对选购决策的影响研究: 卷入度调节作用. 南京财经大学学报, (6), 84?91.] | |
| [47] | Yuan S., Zhang X., & Duan Y . ( 2017). Analysis of the influencing factors on the decision making process of family children training based on the ISM model and AHP-entropy method. Chinese Journal of Systems Science, 25(4), 94?100. |
| [ 袁胜军, 张新阳, 段亚丽 . ( 2017). 基于ISM和AHP-Entropy的家庭儿童培训消费决策影响因素研究. 系统科学学报, 25(4), 94?100.] | |
| [48] | Zhang,B . ( 2017). Shadow education and the cultural reproduction of China new middle classes - Speaking from Bourdieu's theory of cultural capital. Theory & Practice of Education, 37(22), 17?20. |
| [ 张冰 . ( 2017). “影子教育”与中国“新中间阶层”的文化再生产——从布迪厄的文化资本理论说开去. 教育理论与实践, 37(22), 17?20.] | |
| [49] | Zhang,G. Y., & Zhang, M. , ( 2016). Goal framing effects on the purchasing decision of tourism services in customization scenarios. Tourism Tribune, 31(1), 57?67. |
| [ 张广宇, 张梦 . ( 2016). 定制化情境下旅游服务购买决策的目标框架效应. 旅游学刊, 31(1), 57?67.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2016.01.011URL |
相关文章 13
| [1] | 吕薇. 回避与趋近性负性人格特质对应激心血管反应模式的不同影响[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(6): 758-776. |
| [2] | Gerd Gigerenzer, 栾胜华, 刘永芳. 人非理性且难教化?论支持自由家长主义的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(4): 395-406. |
| [3] | 何贵兵, 李纾, 梁竹苑. 以小拨大:行为决策助推社会发展[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 803-813. |
| [4] | Nicolao Bonini, Constantinos Hadjichristidis, Michele Graffeo. 绿色助推[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 814-826. |
| [5] | 路西, HSEE. 联合评估和单独评估:富有潜力的助推手段[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 827-839. |
| [6] | 王晓庄, 安晓镜, 骆皓爽, 徐晟, 于馨, 胡施雅, 王玉涵. 锚定效应助推国民身心健康:两个现场实验 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 848-857. |
| [7] | 李爱梅, 王海侠, 孙海龙, 熊冠星, 杨韶丽. “长计远虑”的助推效应:怀孕与环境跨期决策 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 858-867. |
| [8] | 黄元娜, 宋星云, 邵洋, 李纾, 梁竹苑. 以小拨大:默认选项和反应模式效应助推中国器官捐献登记 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 868-879. |
| [9] | 段婧,刘永芳,何琪. 决策者角色及相关变量对风险偏好的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(3): 369-376. |
| [10] | 田伟,辛涛. 基于等级反应模型的规则空间方法[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(2): 249-262. |
| [11] | 刘永芳,毕玉芳,王怀勇. 情绪和任务框架对自我和预期他人决策时风险偏好的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(03): 317-324. |
| [12] | 丁树良,祝玉芳,林海菁,蔡艳. Tatsuoka 矩阵理论的修正[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(02): 175-181. |
| [13] | 罗跃嘉,魏景汉. 跨感觉通路ERP注意成分的研究[J]. 心理学报, 1997, 29(2): 195-201. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4420
