 ), 耿银凤2, 姚东伟1, 曹华1, 张建勋1(
), 耿银凤2, 姚东伟1, 曹华1, 张建勋1( ), 许琼英1
), 许琼英1 1 西北师范大学心理学院, 物质成瘾与康复研究所, 兰州 730070
2 菏泽信息工程学校学前教育科, 山东 菏泽 274000
收稿日期:2018-01-29出版日期:2019-04-25发布日期:2019-02-22通讯作者:王斌强,张建勋E-mail:wbq0824@sina.com;zjxwyky@126.com基金资助:* 国家自然基金项目资助The influence of hypothetical and real money rewards on the risky decision-making of the abstinent heroin user
YANG Ling1, WANG Binqiang1( ), GEN Yinfeng2, YAO Dongwei1, CAO Hua1, ZHANG Jianxun1(
), GEN Yinfeng2, YAO Dongwei1, CAO Hua1, ZHANG Jianxun1( ), XU Qiongying1
), XU Qiongying1 1 Institute of Substance Addiction and Rehabilitation, School of Psychology, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou 730070, China
2 Department of Preschool Education, Heze Information Engineering School of Shandong Province, Heze 247000, China
Received:2018-01-29Online:2019-04-25Published:2019-02-22Contact:WANG Binqiang,ZHANG Jianxun E-mail:wbq0824@sina.com;zjxwyky@126.comSupported by:31660276摘要/Abstract
摘要: 已有研究表明海洛因成瘾者风险决策能力受损, 但少有研究关注不同幅度金钱奖赏对戒断期海洛因成瘾者风险决策的影响以及这种影响是否会受到金钱奖赏类型的调节。因此, 本研究使用气球模拟风险任务(BART), 通过两个实验探究不同幅度虚拟和真实金钱奖赏对海洛因戒断者风险决策的影响。结果显示, 在虚拟奖赏情景下, 海洛因戒断者未爆破气球按键次数和爆破气球个数均显著大于正常组被试, 以及两组被试在25分奖赏条件下的未爆破气球按键次数和爆破气球个数均显著大于1分奖赏; 而在真实奖赏情景下, 海洛因戒断者未爆破气球按键次数和爆破气球个数均显著小于正常组被试, 以及两组被试在25分奖赏条件下的未爆破气球按键次数和爆破气球个数均显著小于1分奖赏。研究结果表明, 金钱奖赏类型和金钱奖赏幅度会影响被试的风险决策行为。在虚拟奖赏情景下, 两组被试的风险偏好水平随着奖赏幅度的增加显著升高, 但是戒断期海洛因成瘾者的风险偏好水平高于正常组被试; 而在真实奖赏情景下, 两组被试的风险偏好水平随着奖赏幅度的增加显著降低, 同时戒断期海洛因成瘾者的风险偏好水平低于正常组被试。
图/表 5

图1BART流程图
 图1BART流程图
图1BART流程图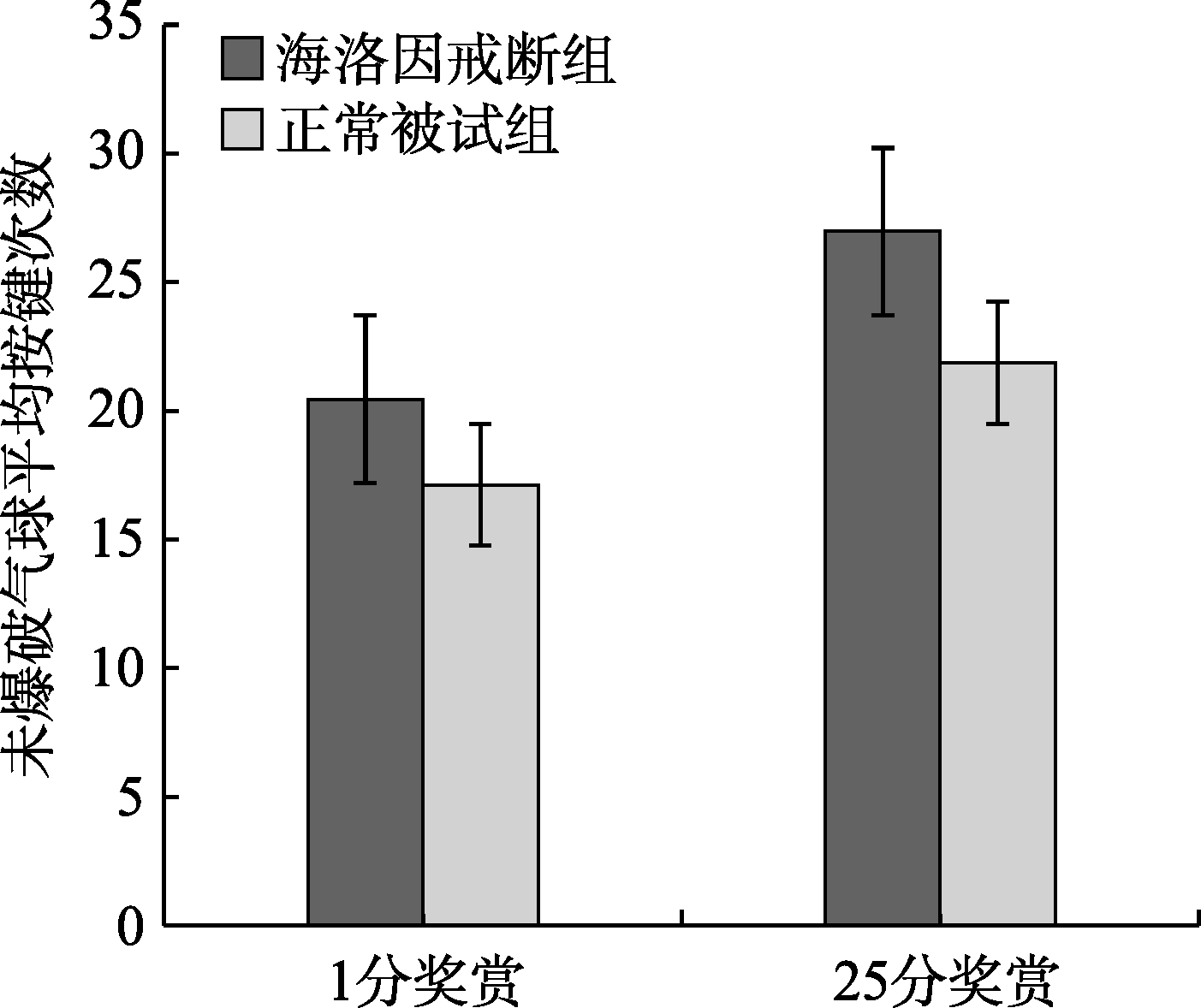
图2两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数
 图2两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数
图2两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数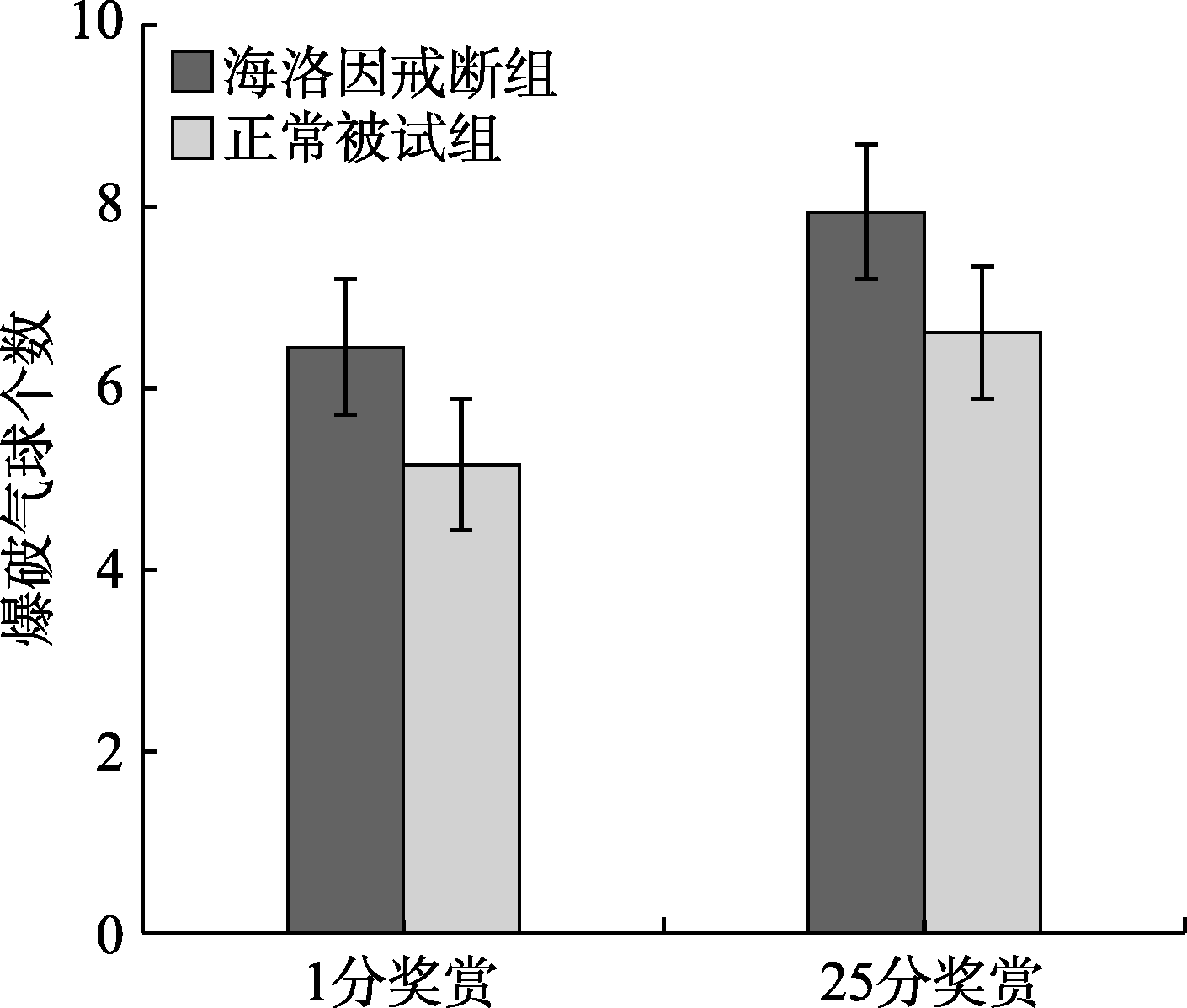
图3两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数
 图3两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数
图3两组被试在虚拟奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数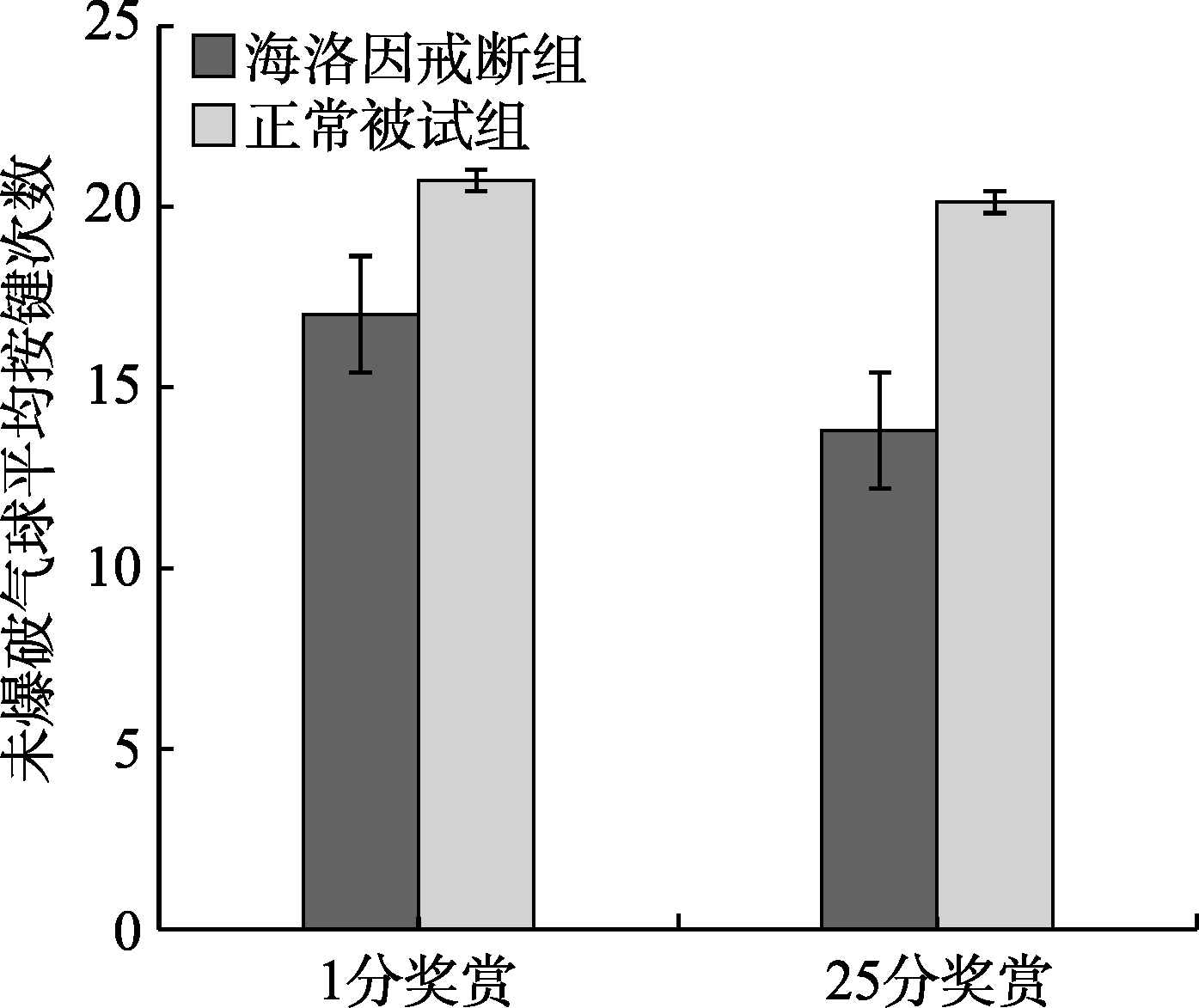
图4两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数
 图4两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数
图4两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下未爆气球平均按键次数
图5两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数
 图5两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数
图5两组被试在真实奖赏1分/25分收益下爆破气球个数参考文献 56
| [1] | Alfonso J. P., Caracuel A., Delgado-Pastor L. C., & Verdejo-García A . ( 2011). Combined goal management training and mindfulness meditation improve executive functions and decision-making performance in abstinent polysubstance abusers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 117( 1), 78-81. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.12.025URLpmid: 21277705 |
| [2] | Bechara A., Damasio A. R., Damasio H., & Anderson S. W . ( 1994). Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition, 50( 1-3), 7-15. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(94)90018-3URL |
| [3] | Bickel W. K., Odum A. L., & Madden G. J . ( 1999). Impulsivity and cigarette smoking: Delay discounting in current, never, and ex-smokers. Psychopharmacology, 146( 4), 447-454. doi: 10.1007/PL00005490URLpmid: 10550495 |
| [4] | Bickel W. K., Pitcock J. A., Yi R., & Angtuaco E. J . ( 2009). Congruence of BOLD response across intertemporal choice conditions: Fictive and real money gains and losses. Journal of Neuroscience, 29( 27), 8839-8846. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5319-08.2009URL |
| [5] | Black A. C., & Rosen M.I . ( 2011). A money management-based substance use treatment increases valuation of future rewards. Addictive Behaviors, 36( 1-2), 125-128 doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2010.08.014URLpmid: 2981645 |
| [6] | Bolla K. I., Eldreth D. A., London E. D., Kiehl K. A., Mouratidis M., & Contoreggi C., .. Ernst M . ( 2003). Orbitofrontal cortex dysfunction in abstinent cocaine abusers performing a decision-making task. Neuroimage, 19( 3), 1085-1094. doi: 10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00113-7URL |
| [7] | Bolla K. I., Eldreth D. A., Matochik J. A., & Cadet J. L . ( 2005). Neural substrates of faulty decision-making in abstinent marijuana users. Neuroimage, 26( 2), 480-492. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.02.012URLpmid: 15907305 |
| [8] | Bolla K., Ernst M., Kiehl K., Mouratidis M., Eldreth D., Contoreggi C., .. London E . ( 2004). Prefrontal cortical dysfunction in abstinent cocaine abusers. Journal of Neuropsychiatry & Clinical Neurosciences, 16( 4), 456-464. doi: 10.1176/jnp.16.4.456URLpmid: 2771441 |
| [9] | Bornovalova M. A., Cashman-Rolls A., O'Donnell J. M., Ettinger K., Richards J. B., Dewit H., & Lejuez C W . ( 2009). Risk taking differences on a behavioral task as a function of potential reward/loss magnitude and individual differences in impulsivity and sensation seeking. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior, 93( 3), 258-262. |
| [10] | Bornovalova M. A., Daughters S. B., Hernandez G. D., Richards J. B., & Lejuez C. W . ( 2005). Differences in impulsivity and risk-taking propensity between primary users of crack cocaine and primary users of heroin in a residential substance-use program. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 13( 4), 311-318. doi: 10.1037/1064-1297.13.4.311URLpmid: 16366761 |
| [11] | Crowley T. J., Dalwani M. S., Mikulichgilbertson S. K., Du Y. P., Lejuez C. W., Raymond K. M., & Banich M. T . ( 2010). Risky decisions and their consequences: Neural processing by boys with antisocial substance disorder. Plos One, 5( 9), e12835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012835URL |
| [12] | Ersche K. D., Fletcher P. C., Lewis S. J. G., Clark L., Stocks-Gee G., London M., .. Sahakian B. J . ( 2005). Abnormal frontal activations related to decision-making in current and former amphetamine and opiate dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology, 180( 4), 612-623. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2205-7URLpmid: 16163533 |
| [13] | Ersche K. D., Fletcher P. C., Roiser J. P., Fryer T. D., London M., & Robbins T. W., & Sahakian B. J . ( 2006). Differences in orbitofrontal activation during decision- making between methadone-maintained opiate users, heroin users and healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology, 188( 3), 364-373. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0515-zURLpmid: 16953385 |
| [14] | Estle S. J., Green L., Myerson J., & Holt D. D . ( 2006). Differential effects of amount on temporal and probability discounting of gains and losses. Memory & Cognition, 34( 4), 914-928. doi: 10.3758/BF03193437URLpmid: 17063921 |
| [15] | Fein, G., &Chang, M. ( 2008). Smaller feedback ern amplitudes during the bart are associated with a greater family history density of alcohol problems in treatment- naive alcoholics. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 92( 1-3), 141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.07.017URLpmid: 2430520 |
| [16] | García-Rodríguez O., Secades-Villa R., Weidberg S., & Yoon J. H . ( 2013). A systematic assessment of delay discounting in relation to cocaine and nicotine dependence. Behavioural Processes, 99, 100-105. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2013.07.007URLpmid: 23872502 |
| [17] | Goldstein R. Z., Parvaz M. A., Maloney T., Alia-Klein N., Woicik P. A., Telang F., .. Volkow N. D ( 2008). Compromised sensitivity to monetary reward in current cocaine users: An ERP study. Psychophysiology, 45( 5), 705-713. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2008.00670.xURLpmid: 2574641 |
| [18] | Goldstein R. Z., Tomasi D., Alia-Klein N., Cottone L. A., Zhang L., Telang F., & Volkow N. D ( 2007). Subjective sensitivity to monetary gradients is associated with frontolimbic activation to reward in cocaine abusers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 87( 2-3), 233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.08.022URLpmid: 16997508 |
| [19] | Gonzalez R., Schuster R. M., Mermelstein R. M., & Diviak K. R . ( 2015). The role of decision-making in cannabis- related problems among young adults. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 154, 214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.06.046URL |
| [20] | Gorini A., Lucchiari C., Russell-Edu W., &Pravettoni G . ( 2014). Modulation of risky choices in recently abstinent dependent cocaine users: A transcranial direct-current stimulation study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 661. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00661URLpmid: 4145470 |
| [21] | Hanlon C. A., Wesley M. J., Stapleton J. R., Laurienti P. J., & Porrino L. J . ( 2011). The association between frontal- striatal connectivity and sensorimotor control in cocaine users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 115( 3), 240-243. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.11.008URLpmid: 21193273 |
| [22] | Hanson K. L., Thayer R. E., & Tapert S. F . ( 2014). Adolescent marijuana users have elevated risk-taking on the balloon analog risk task. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 28( 11), 1080-1087. doi: 10.1177/0269881114550352URL |
| [23] | Hevey D., Thomas K., Laureanoschelten S., Looney K., & Booth R . ( 2017). Clinical depression and punishment sensitivity on the bart. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 670. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00670URLpmid: 5411816 |
| [24] | Hinvest N. S., & Anderson I. M ., ( 2010). The effects of real versus hypothetical reward on delay and probability discounting. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 63( 6), 1072-1084. doi: 10.1080/17470210903276350URLpmid: 19890767 |
| [25] | Hopko D. R., Lejuez C. W., Daughters S. B., Aklin W. M., Osborne A., Simmons B. L., & Strong D. R ( 2006). Construct validity of the balloon analogue risk task (BART): Relationship with MDMA use by inner-city drug users in residential treatment. Journal of Psychopathology & Behavioral Assessment, 28( 2), 95-101. doi: 10.1007/s10862-006-7487-5URL |
| [26] | Ji L. Y., Chen N. X., Ding J. H., & Wei P ., ( 2015). Monetary incentive modulates the localized attentional interference effect. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47( 6), 721-733. |
| [ 纪丽燕, 陈宁轩, 丁锦红, 魏萍 . ( 2015). 奖赏预期调节局部注意干扰效应. 心理学报, 47( 6), 721-733.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00721URL | |
| [27] | Johnson, M. W., & Bickel, W. K . ( 2002). Within-subject comparison of real and hypothetical money rewards in delay discounting. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 77( 2), 129-146. doi: 10.1901/jeab.2002.77-129URLpmid: 11936247 |
| [28] | Kahneman, D., &Tversky, A. ( 1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47( 2) 263-291. doi: 10.2307/1914185URL |
| [29] | Kohno M., Morales A. M., Ghahremani D. G., Hellemann G., & London E. D . ( 2014). Risky decision-making: Prefrontal function and mesocorticolimbic resting-state connectivity in methamphetamine users. JAMA Psychiatry, 71( 7), 812-820. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.399URLpmid: 24850532 |
| [30] | Lawrence A. J., Luty J., Bogdan N. A., Sahakian B. J., & Clark L . ( 2009). Problem gamblers share deficits in impulsive decision-making with alcohol-dependent individuals. Addiction, 104( 6), 1006-1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02533.xURLpmid: 19466924 |
| [31] | Lejuez C. W., Aklin W. M., Jones H. A., Richards J. B., Strong D. R., Kahler C. W., & Read J. P . ( 2003). The balloon analogue risk task (BART) differentiates smokers and nonsmokers. Experimental & Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11( 1), 26-33. doi: 10.1037/1064-1297.11.1.26URLpmid: 12622341 |
| [32] | Lejuez C. W., Read J. P., Kahler C. W., Richards J. B., Ramsey S. E., Stuart G. L., .. Brown. R. J . ( 2002). Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: The balloon analogue risk task (BART). Journal of Experimental Psychology Applied, 8( 2), 75-84. doi: 10.1037/1076-898X.8.2.75URLpmid: 12075692 |
| [33] | Li X. Y., Zhang F., Zhou Y., Zhang M., Wang X., & Shen M. W . ( 2013). Decision-making deficits are still present in heroin abusers after short- to long-term abstinence. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 130( 1-3), 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.10.012URLpmid: 23131777 |
| [34] | Madden G. J., Begotka A. M., Raiff B. R., & Kastern L. L . ( 2003). Delay discounting of real and hypothetical rewards. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11( 2), 139-145. doi: 10.1037/1064-1297.11.2.139URLpmid: 12755458 |
| [35] | No?l X., Bechara A., Dan B., Hanak C., & Verbanck P . ( 2007). Response inhibition deficit is involved in poor decision making under risk in nonamnesic individuals with alcoholism. Neuropsychology, 21( 6), 778-786 doi: 10.1037/0894-4105.21.6.778URL |
| [36] | Passetti F., Clark L., Mehta M. A., Joyce E., & King M . ( 2008). Neuropsychological predictors of clinical outcome in opiate addiction. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 94( 1-3), 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.10.008URLpmid: 18063322 |
| [37] | Petry, N. M . ( 2001). Delay discounting of money and alcohol in actively using alcoholics, currently abstinent alcoholics, and controls. Psychopharmacology, 154( 3), 243-250. doi: 10.1007/s002130000638URLpmid: 11351931 |
| [38] | Petry, N. M.,& Casarella, T. , ( 1999). Excessive discounting of delayed rewards in substance abusers with gambling problems. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 56( 1), 25-32. doi: 10.1016/S0376-8716(99)00010-1URLpmid: 10462089 |
| [39] | Redish A. D., Jensen S., & Johnson A . ( 2008). A unified framework for addiction: Vulnerabilities in the decision process. Behavioral & Brain Sciences, 31( 4), 415-437. |
| [40] | Reynolds B., Karraker K., Horn K., Richards J.B . ( 2003). Delay and probability discounting as related to different stages of adolescent smoking and non-smoking. Behavioural Processes, 64( 3), 333-344. doi: 10.1016/S0376-6357(03)00168-2URLpmid: 14580702 |
| [41] | Rogers R. D., Everitt B. J., Baldacchino A., Blackshaw A. J., Swainson R., Wynne K., .. Robbins T.W . ( 1999). Dissociable deficits in the decision-making cognition of chronic amphetamine abusers, opiate abusers, patients with focal damage to prefrontal cortex, and tryptophan-depleted normal volunteers: Evidence for monoaminergic mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology, 20( 4), 322-339. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00091-8URLpmid: 10088133 |
| [42] | Tian L M., Yuan J. C., & Li Y. M . ( 2017). Effects of peer presence and self-esteem on adolescent risk-taking behavior: Evidence from an ERP study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50( 1), 47-57. |
| [ 田录梅, 袁竞驰, 李永梅 . ( 2018). 同伴在场和自尊水平对青少年冒险行为的影响: 来自ERPs的证据. 心理学报, 50( 1), 47-57.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2018.00047URL | |
| [43] | Vadhan N. P., Hart C. L., Haney M., van Gorp W. G., & Foltin R. W . ( 2009). Decision-making in long-term cocaine users: Effects of a cash monetary contingency on gambling task performance. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 102( 1-3), 95-101. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.02.003URLpmid: 2694492 |
| [44] | Vaidya J. G., Block R. I., O'Leary D. S., Ponto L. B., Ghoneim M. M., & Bechara A . ( 2012). Effects of chronic marijuana use on brain activity during monetary decision- making. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37( 3), 618-629. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.227URLpmid: 21956445 |
| [45] | van den. Bos. R., Houx B. B., & Spruijt B. M . ( 2006). The effect of reward magnitude differences on choosing disadvantageous decks in the Iowa gambling task. Biological Psychology, 71( 2), 155-161. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2005.05.003URLpmid: 16095798 |
| [46] | Verdejo-Garcia A., Albein-Urios N., Martinez-Gonzalez J. M., Civit E., De la Torre R., & Lozano O . ( 2014). Decision-making impairment predicts 3-month hair-indexed cocaine relapse. Psychopharmacology, 231( 21), 4179-4187. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3563-9URL |
| [47] | Verdejo-Garcia A., Benbrook A., Funderburk F., David P., Cadet J. L., & Bolla K. I . ( 2007). The differential relationship between cocaine use and marijuana use on decision-making performance over repeat testing with the iowa gambling task. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 90( 1), 2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.02.004URLpmid: 17367959 |
| [48] | Xu S. H., Fang Z., & Rao H. Y . ( 2013). Real or hypothetical monetary rewards modulates risk taking behavior. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45( 8), 874-886. |
| [ 徐四华, 方卓, 饶恒毅 . ( 2013). 真实和虚拟金钱奖赏影响风险决策行为. 心理学报, 45( 8), 874-886.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2013.00874URL | |
| [49] | Xu S. H., Pan Y., Qu Z., Fang, Z, Yang, Z. j., Yang F., .. Rao H. Y . ( 2018). Differential effects of real versus hypothetical monetary reward magnitude on risk-taking behavior and brain activity. Scientific Reports, 8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21820-0URL |
| [50] | Xu S. H., Pan. Y., Wang Y., Spaeth A. M., Qu Z., & Rao H. Y . ( 2016). Real and hypothetical monetary rewards modulate risk taking in the brain. Scientific Reports, 6( 1). doi: 10.1038/srep29520URLpmid: 27383241 |
| [51] | Yan W. S., Li S., & Sui N . ( 2011). Research paradigms and neural mechanisms for decision-making deficits in addicts. Advances in Psychological Science, 19( 5), 652-663. |
| [ 严万森, 李纾, 隋南 . ( 2011). 成瘾人群的决策障碍: 研究范式与神经机制. 心理科学进展, 19( 5), 652-663.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2011.00652URL | |
| [52] | Yao Y. W., Chen P. R., Li C. S. R., Hare T. A., Li S., Zhang J. T., .. Fangg X. Y . ( 2017). Combined reality therapy and mindfulness meditation decrease intertemporal decisional impulsivity in young adults with internet gaming disorder. Computers in Human Behavior, 68( 5), 210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.11.038URL |
| [53] | Zhao H. C., Huang X. L., & He Q. H ., ( 2016). Cognitive dysfunction and underlying neural basis in substance addiction. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61( 34), 3672-3683. |
| [ 赵海潮, 黄小璐, 何清华 . ( 2016). 物质成瘾所伴随的认知功能缺陷及其神经基础. 科学通报, 61( 34), 3672-3683.] | |
| [54] | Zhao Q. L., Li H. Q., Hu B., Wu H. Y., & Liu Q. Y . ( 2017). Abstinent heroin addicts tend to take risks: ERP and source localization. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 11( 6), 1-12. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00681URL |
| [55] | Zhou P. Y., Liu D. W., Zhou R. L., Sun B. L., Xiao J., & Li S . ( 2014 a). Impairment of drug addiction on decision making and recovery after abstinence. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 22( 6), 951-956. |
| [ 周平艳, 刘丹玮, 周仁来, 孙本良, 肖洁, 李松 . ( 2014 a). 药物成瘾对决策行为的损伤及戒断后的恢复. 中国临床心理学杂志, 22( 6), 951-956.] | |
| [56] | Zhou P. Y., Liu D. W., Zhou R. L., Sun B. L., Xiao J., & Li S . ( 2014 b). Sensitivity to monetary reward in drug abstainers at different post-drug withdrawal phases: An ERP study. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 22( 4), 571-576. |
| [ 周平艳, 刘丹玮, 周仁来, 孙本良, 肖洁, 李松 . ( 2014 b). 不同戒断期毒品戒断者对金钱奖赏敏感性的ERP研究 . 中国临床心理学杂志, 22( 4), 571-576.] |
相关文章 11
| [1] | 张银玲, 虞祯, 买晓琴. 社会价值取向对自我-他人风险决策的影响及其机制[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(7): 895-908. |
| [2] | 周蕾, 李爱梅, 张磊, 李纾, 梁竹苑. 风险决策和跨期决策的过程比较:以确定效应和即刻效应为例[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(3): 337-352. |
| [3] | 陈嘉欣;何贵兵. “金钱−环境”复合收益的风险决策:价值取向的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(4): 500-512. |
| [4] | 陆青云;陶芳标;侯方丽;孙莹. 青少年应激下皮质醇应答与风险决策相关性的性别差异[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(5): 647-655. |
| [5] | 徐四华;方卓;饶恒毅. 真实和虚拟金钱奖赏影响风险决策行为[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(8): 874-886. |
| [6] | 徐四华. 网络成瘾者的行为冲动性—— 来自爱荷华赌博任务的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(11): 1523-1534. |
| [7] | 贺伟,龙立荣. 薪酬体系框架与考核方式对个人绩效薪酬选择的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(10): 1198-1210. |
| [8] | 张锋,周艳艳,李鹏,沈模卫. 海洛因戒除者的行为冲动性: 基于DDT和IGT任务反应模式的探讨 [J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(06): 642-653. |
| [9] | 张文慧,王晓田. 自我框架、风险认知和风险选择[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(06): 633-641. |
| [10] | 王晓田. 投资决策进化心理学的研究:预期的私人资金分配和父母对子女的差异性精力投入[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(03): 406-414. |
| [11] | 何贵兵,白凤祥. 风险决策中的参照点效应研究[J]. 心理学报, 1997, 29(2): 178-186. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4428
