 )
) 东北师范大学心理学院, 长春 130024
收稿日期:2018-05-08出版日期:2019-04-15发布日期:2019-02-22通讯作者:张向葵E-mail:zhangxiangkui@126.comEating disorders among adolescents: The form and mechanism of peer influence
ZHANG Tianyu, ZHANG Xiangkui( )
) School of Psychology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China
Received:2018-05-08Online:2019-04-15Published:2019-02-22Contact:ZHANG Xiangkui E-mail:zhangxiangkui@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 饮食失调在青少年群体中非常普遍, 同伴被认为是一种重要的影响因素。梳理其作用机制, 对青少年饮食失调的预防和干预有重要意义。研究表明, 同伴对青少年饮食失调具有消极影响, 主要表现为感知到的同伴行为、实际的同伴行为、身体不满意的中介作用、以及同伴质量的影响。研究者从直接、间接的角度就同伴对青少年饮食失调的作用机制及影响进行了阐释。未来的研究应深化研究内容, 如增加关于同伴影响的长期效应、同伴属性划分、影响路径作用大小以及同伴与饮食失调的其它社会影响因素间的交互作用等方面的研究。
图/表 2

图1同伴对青少年饮食失调的直接影响
 图1同伴对青少年饮食失调的直接影响
图1同伴对青少年饮食失调的直接影响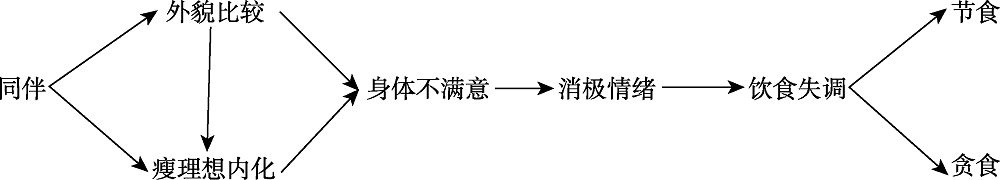
图2同伴对青少年饮食失调的间接影响
 图2同伴对青少年饮食失调的间接影响
图2同伴对青少年饮食失调的间接影响参考文献 76
| [1] | 陈红 . ( 2006). 青少年的身体自我: 理论与实证. 北京: 新华出版社. |
| [2] | 陈红, 羊晓莹, 翟理红, 何玉兰, 陈瑞, 高笑 . ( 2007). 不同年龄段女性负面身体自我状况及相关因素. 中国心理卫生杂志, 21 (8), 531-534. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2007.08.007URL |
| [3] | 施启琰, 寇慧, 陈红 . ( 2017). 男性理想体型变化及其影响因素. 心理科学进展, 25, (4), 627-638. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2017.00627URL |
| [4] | 唐锐, 陈红, 鲁小芳 . ( 2006). 女性瘦身理想的心理学阐释. 中国临床康复, 10, (42), 146-148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-8225.2006.42.063URL |
| [5] | 王玉慧, 吕振勇, 陈红, 吴双双, 肖子伦 . ( 2016). 男性身体意象失调: 大众媒体的影响及作用机制. 心理科学进展, 24, (2), 282-292. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00282URL |
| [6] | 王玉慧, 谢笑春, 陈红, 雷雳 . ( 2017). 女性身体意象失调: 社交网站的影响及作用机制. 中国临床心理学杂志, 25, (6), 1079-1082. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2017.06.018URL |
| [7] | 吴双双, 吕振勇, 陈红, 王玉慧, 肖子伦 . ( 2016). 肥胖谈论: 心理学视角下的沟通方式. 心理科学进展, 24, (1), 111-119. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00111URL |
| [8] | 羊晓莹, 陈红 . ( 2006). 饮食失调的相关影响因素分析. 中国临床康复, 10, (10), 152-154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-8225.2006.10.057 |
| [9] | 张镇, 郭博达 . ( 2016). 社会网络视角下的同伴关系与心理健康. 心理科学进展, 24, (4), 591-602. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00591URL |
| [10] | Adams G., Turner H., & Bucks R . ( 2005). The experience of body dissatisfaction in men. Body Image, 2, (3), 271-283. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2005.05.004URLpmid: 18089194 |
| [11] | Ata R. N., Ludden A. B., & Lally M. M . ( 2007). The effects of gender and family, friend, and media influences on eating behaviors and body image during adolescence. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 36, (8), 1024-1037. |
| [12] | Bearman S. K., Presnell K., Martinez E., & Stice E . ( 2006). The skinny on body dissatisfaction: A longitudinal study of adolescent girls and boys. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 35, (2), 217-229. doi: 10.1007/s10964-005-9010-9URLpmid: 16912810 |
| [13] | Berkman N. D., Lohr K. N., & Bulik C. M . ( 2010). Outcomes of eating disorders: A systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 40, (4), 293-309. doi: 10.1002/eat.20369URLpmid: 17370291 |
| [14] | Blodgett Salafia, E. H., &Gondoli D.M . ( 2011). A 4-year longitudinal investigation of the processes by which parents and peers influence the development of early adolescent girls' bulimic symptoms. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 31, (3), 390-414. doi: 10.1177/0272431610366248URL |
| [15] | Boyce W. F., Davies D., Gallupe O., & Shelley D . ( 2008). Adolescent risk taking, neighborhood social capital, and health. Journal of Adolescent Health, 43, (3), 246-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2008.01.014URLpmid: 18710679 |
| [16] | Byrne D., &Nelson D. ( 1965). Attraction as a linear function of proportion of positive reinforcements. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1, (6), 659-663. doi: 10.1037/h0022073URLpmid: 14300244 |
| [17] | Carey R. N., Donaghue N., & Broderick P . ( 2011). ‘what you look like is such a big factor’: Girls’ own reflections about the appearance culture in an all-girls’ school. Feminism & Psychology, 21, (3), 299-316. |
| [18] | Carlson J.D . ( 2004). Body image among adolescent girls and boys: A longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 40, (5), 823-835. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.40.5.823URLpmid: 15355169 |
| [19] | Chang F. C., Lee C. M., Chen P. H., Chiu C. H., Pan Y. C., Huang T. F . ( 2013). Association of thin-ideal media exposure, body dissatisfaction and disordered eating behaviors among adolescents in Taiwan. Eating Behaviors, 14, (3), 382-385. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.05.002URLpmid: 23910785 |
| [20] | Compeau A., &Ambwani S. ( 2013). The effects of fat talk on body dissatisfaction and eating behavior: The moderating role of dietary restraint. Body Image, 10, (4), 451-461. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2013.04.006URLpmid: 23726516 |
| [21] | Crandall C.S . ( 1988). Social contagion of binge eating. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55, (4), 588-598. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.55.4.588URLpmid: 3193348 |
| [22] | Dejong H., Van Den Eynde F., Broadbent H., Kenyon M. D., Lavender A., Startup H., & Schmidt U . ( 2013). Social cognition in bulimia nervosa: A systematic review. European Psychiatry, 28, (1), 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.07.002URLpmid: 21920709 |
| [23] | Eisenberg M.E., &Neumarksztainer D. ( 2010). Friends' dieting and disordered eating behaviors among adolescents five years later: Findings from project eat. Journal of Adolescence Health, 47, (1), 67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.12.030URLpmid: 20547294 |
| [24] | Ferguson C. J., Muñoz M. E., Garza A., & Galindo M . ( 2014). Concurrent and prospective analyses of peer, television and social media influences on body dissatisfaction, eating disorder symptoms and life satisfaction in adolescent girls. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 43, (1), 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s10964-012-9898-9URLpmid: 23344652 |
| [25] | Field A. E., Camargo C. A., Taylor C. B., Berkey C. S., Roberts S. B., & Colditz G. A . ( 2001). Peer, parent, and media influences on the development of weight concerns and frequent dieting among preadolescent and adolescent girls and boys. Pediatrics, 107, (1), 54-63. |
| [26] | Field A. E., Javaras K. M., Ms Aneja P., Ms Kitos N., Dr Camargo C. A., Dr Taylor C. B., Dr Laird. N. M . ( 2008). Family, peer, and media predictors of becoming eating disordered. Jama Pediatrics, 162, (6), 574-579. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.162.6.574URLpmid: 3652375 |
| [27] | Gerbasi M. E., Richards L. K., Thomas J. J., Agnewblais J. C., Thompsonbrenner H., Gilman S. E., Becker A. E . ( 2014). Globalization and eating disorder risk: Peer influence, perceived social norms, and adolescent disordered eating in Fiji. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 47, (7), 727-737. doi: 10.1002/eat.22349URLpmid: 4211968 |
| [28] | Gerner B., &Wilson P.H . ( 2005). The relationship between friendship factors and adolescent girls' body image concern, body dissatisfaction, and restrained eating. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 37, (4), 313-320. doi: 10.1002/eat.20094URLpmid: 15856495 |
| [29] | Hallinan M.T., &Williams R.A . ( 1989). Interracial friendship choice in secondary schools. American Sociological Review, 54, (1), 67-78. doi: 10.2307/2095662URL |
| [30] | Hamm J.V . ( 2000). Do birds of a feather flock together? the variable bases for African American, Asian American, and European American adolescents' selection of similar friends. Developmental Psychology, 36, (2), 209-219. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.36.2.209URLpmid: 10749078 |
| [31] | Helfert S., &Warschburger P. ( 2011). A prospective study on the impact of peer and parental pressure on body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls and boys. Body Image, 8, (2), 101-109. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2011.01.004URLpmid: 21354379 |
| [32] | Hutchinson D.M., &Rapee R.M . ( 2007). Do friends share similar body image and eating problems? The role of social networks and peer influences in early adolescence. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, (7), 1557-1577. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.11.007URLpmid: 17258173 |
| [33] | Hutchinson D. M., Rapee R. M., & Taylor A . ( 2010). Body dissatisfaction and eating disturbances in early adolescence: A structural modeling investigation examining negative affect and peer factors. Journal of Early Adolescence, 30, (4), 489-517. doi: 10.1177/0272431609340522URL |
| [34] | Jackson T., &Chen H. ( 2008 a). Predicting changes in eating disorder symptoms among adolescents in China: An 18-month prospective study. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 37, (4), 874-885. doi: 10.1080/15374410802359841URLpmid: 18991136 |
| [35] | Jackson T., &Chen H. ( 2008 b). Predicting changes in eating disorder symptoms among Chinese adolescents: A 9-month prospective study. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 64, (1), 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.08.015URLpmid: 18158004 |
| [36] | Jackson T., &Chen H. ( 2010). Sociocultural experiences of bulimic and non-bulimic adolescents in a school-based Chinese sample. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38, (1), 69-76. doi: 10.1007/s10802-009-9350-0URLpmid: 19707866 |
| [37] | Jackson T., &Chen H. ( 2011). Risk factors for disordered eating during early and middle adolescence: Prospective evidence from mainland Chinese boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 120, (2), 454-464. doi: 10.1037/a0022122URLpmid: 21319924 |
| [38] | Jackson T., &Chen H. ( 2014). Risk factors for disordered eating during early and middle adolescence: A two year longitudinal study of mainland Chinese boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42, (5), 791-802. doi: 10.1007/s10802-013-9823-zURLpmid: 24221725 |
| [39] | Jacobi C., Hayward C., De Zwaan. M., Kraemer H. C., & Agras W. S . ( 2004). Coming to terms with risk factors for eating disorders: Application of risk terminology and suggestions for a general taxonomy. Psychological Bulletin, 130, (1), 19-65. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.130.1.19URLpmid: 14717649 |
| [40] | Jeon K.C., &Goodson P. ( 2015). Us adolescents’ friendship networks and health risk behaviors: A systematic review of studies using social network analysis and add health data. Peerj, 3, (1), e1052. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1052URLpmid: 4493707 |
| [41] | Jones D. C., Vigfusdottir T. H., & Lee Y . ( 2004). Body image and the appearance culture among adolescent girls and boys: An examination of friend conversations, peer criticism, appearance magazines, and the internalization of appearance ideals. Journal of Adolescent Research, 19, (3), 323-339. doi: 10.1177/0743558403258847URL |
| [42] | Jung J., Forbes G. B., & Lee Y. J . ( 2009). Body dissatisfaction and disordered eating among early adolescents from Korea and the us. Sex Roles, 61, (1-2), 42-54. doi: 10.1007/s11199-009-9609-5URL |
| [43] | Karazsia B.T., &Crowther J.H . ( 2009). Social body comparison and internalization: Mediators of social influences on men's muscularity-oriented body dissatisfaction. Body Image, 6, (2), 105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2008.12.003URLpmid: 19244001 |
| [44] | Keery H., Van Den. Berg. P., & Thompson J. K . ( 2004). An evaluation of the tripartite influence model of body dissatisfaction and eating disturbance with adolescent girls. Body Image, 1, (3), 237-251. |
| [45] | Kirsch A. C., Shapiro J. B., Conley C. S., & Heinrichs G . ( 2016). Explaining the pathway from familial and peer social support to disordered eating: Is body dissatisfaction the link for male and female adolescents?. Eating Behaviors, 22, 175-181. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2016.06.018URL |
| [46] | McCabe M.P., &Ricciardelli L.A . ( 2005). A prospective study of pressures from parents, peers, and the media on extreme weight change behaviors among adolescent boys and girls. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 43, (5), 653-668. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2004.05.004URLpmid: 15865919 |
| [47] | Mccarthy M. ( 1990). The thin ideal, depression and eating disorders in women. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 28, (3), 205-214. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(90)90003-2URLpmid: 2196049 |
| [48] | McPherson M., Smithlovin L., & Cook J. M . ( 2001). Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annual Review of Sociology, 27, (1), 415-444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.27.1.415URL |
| [49] | Menzel J. E., Schaefer L. M., Burke N. L., Mayhew L. L., Brannick M. T., & Thompson J. K . ( 2010). Appearance- related teasing, body dissatisfaction, and disordered eating: A meta-analysis. Body Image, 7, (4), 261-270. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2010.05.004URLpmid: 20655287 |
| [50] | Meyer C., &Waller G. ( 2001). Social convergence of disturbed eating attitudes in young adult women. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 189, (2), 114-119. doi: 10.1097/00005053-200102000-00007URLpmid: 11225684 |
| [51] | Montoya R.M., &Horton R.S . ( 2012). A meta-analytic investigation of the processes underlying the similarity- attraction effect. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 30, (1), 64-94. |
| [52] | Mooney E., Farley H., & Strugnell C . ( 2009). A qualitative investigation into the opinions of adolescent females regarding their body image concerns and dieting practices in the republic of Ireland (ROI). Appetite, 52, (2), 485-491. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2008.12.012URLpmid: 19154765 |
| [53] | Myers T.A., &Crowther J.H . ( 2009). Social comparison as a predictor of body dissatisfaction: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118, (4), 683-698. doi: 10.1037/a0016763URLpmid: 19899839 |
| [54] | Neumark-Sztainer D., Wall M., Larson N. I., Eisenberg M. E., & Loth K . ( 2011). Dieting and disordered eating behaviors from adolescence to young adulthood: Findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 111, (7), 1004-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2011.04.012URLpmid: 3140795 |
| [55] | Nichter M., &Vuckovic N. ( 1994). Fat talk: Body image among adolescent girls. In N. Sault (Ed.), Many Mirrors: Body Image and Social Relations (pp. 109-131). New Brunswick,NJ: Rutgers University Press |
| [56] | Paxton S. J., Eisenberg M. E., & Neumark-Sztainer D . ( 2006). Prospective predictors of body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls and boys: A five-year, longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 42, (5), 888-899. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.42.5.888URLpmid: 16953694 |
| [57] | Paxton S. J., Schutz H. K., Wertheim E. H., & Muir S. L . ( 1999). Friendship clique and peer influences on body image concerns, dietary restraint, extreme weight-loss behaviors, and binge eating in adolescent girls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 108, (2), 255-266. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.108.2.255URLpmid: 10369035 |
| [58] | Paxton S. J., Wertheim E. H., Gibbons K., Szmukler G. I., Hillier L., & Petrovich J. L . ( 1991). Body image satisfaction, dieting beliefs, and weight loss behaviors in adolescent girls and boys. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 20, (3), 361-379. |
| [59] | Rayner K. E., Schniering C. A., Rapee R. M., & Hutchinson D. M . ( 2013). A longitudinal investigation of perceived friend influence on adolescent girls' body dissatisfaction and disordered eating. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 42, (5), 643-656. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2012.743103URLpmid: 23215623 |
| [60] | Rayner K. E., Schniering C. A., Rapee R. M., Taylor A., & Hutchinson D. M . ( 2013). Adolescent girls' friendship networks, body dissatisfaction, and disordered eating: Examining selection and socialization processes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 122, (1), 93-104. doi: 10.1037/a0029304URLpmid: 22867115 |
| [61] | Rodgers R. F., Ganchou C., Franko D. L., & Chabrol H . ( 2012). Drive for muscularity and disordered eating among French adolescent boys: A sociocultural model. Body Image, 9, (3), 318-323. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2012.03.002URLpmid: 22494958 |
| [62] | Schulte S.J., &Thomas J. ( 2013). Relationship between eating pathology, body dissatisfaction and depressive symptoms among male and female adolescents in the united Arab emirates. Eating Behaviors, 14, (2), 157-160. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.01.015URLpmid: 23557812 |
| [63] | Schutz H.K., &Paxton S.J . ( 2007). Friendship quality, body dissatisfaction, dieting and disordered eating in adolescent girls. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 46, (1), 67-83. doi: 10.1348/014466506X115993URLpmid: 17472202 |
| [64] | Sharpe H., Schober I., Treasure J., & Schmidt U . ( 2014). The role of high-quality friendships in female adolescents' eating pathology and body dissatisfaction. Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity, 19, (2), 159-168. doi: 10.1007/s40519-014-0113-8URLpmid: 24668325 |
| [65] | Shroff H., &Thompson J.K . ( 2006). The tripartite influence model of body image and eating disturbance: A replication with adolescent girls. Body Image, 3, (1), 17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2005.10.004URLpmid: 18089205 |
| [66] | Spear L.P . ( 2000). The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 24, (4), 417-463. |
| [67] | Steinberg L., &Monahan K.C . ( 2007). Age differences in resistance to peer influence. Developmental Psychology, 43, (6), 1531-1543. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.43.6.1531URLpmid: 18020830 |
| [68] | Stice E. ( 2002). Risk and maintenance factors for eating pathology: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 128, (5), 825-848. |
| [69] | Taylor C. B., Bryson S., Luce K. H., Cunning D., Celio A., Abascal L. B., … Wilfley D. E . ( 2006). Prevention of eating disorders in at-risk college-age women. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63, (8), 881-888. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.881URLpmid: 3837629 |
| [70] | Taylor C. B., Sharpe T., Shisslak C., Bryson S., Estes L. S., Gray N., … Killen J. D . ( 1998). Factors associated with weight concerns in adolescent girls. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 24, (1), 31-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-108X(199807)24:13.0.CO;2-1URLpmid: 9589309 |
| [71] | Thompson J. K., Heinberg L. J., Altabe M. N., & Tantleff-Dunn S . ( 1999). Exacting beauty: Theory, assessment, and treatment of body image disturbance. Washington, DC:American Psychological Association. |
| [72] | Vander Wal, J. S., & Thelen, M. H . ( 2000). Predictors of body image dissatisfaction in elementary-age school girls. Eating Behaviors, 1, (2), 105-122. doi: 10.1016/S1471-0153(00)00011-8URLpmid: 15001054 |
| [73] | Veenstra R., Dijkstra J. K., Steglich C., & Van Zalk, M. H. W. ( 2013). Network-behavior dynamics. The Authors. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 23, (3), 399-412. |
| [74] | Webb H.J., &Zimmer-Gembeck M.J . ( 2014). The role of friends and peers in adolescent body dissatisfaction: A review and critique of 15years of research. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 24, (4), 564-590. |
| [75] | Woelders L. C. S., Larsen J. K., Scholte R. H. J., Cillessen A. H. N., & Engels R. C. M. E . ( 2010). Friendship group influences on body dissatisfaction and dieting among adolescent girls: A prospective study. Journal of Adolescent Health, 47, (5), 456-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.03.006URLpmid: 20970080 |
| [76] | Zalta A.K., &Keel P.K . ( 2006). Peer influence on bulimic symptoms in college students. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 115, (1), 185-189. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.115.1.185URLpmid: 16492110 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张玮玮, 朱莉琪. 同伴对青少年冒险行为的影响及其作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1462-1471. |
| [2] | 柴晓运, 林丹华. 化危为机:青少年学校转折期的过渡[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 864-874. |
| [3] | 何清华, 李丹丹. 中国儿童青少年跨期决策的发展与脑发育机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(3): 381-389. |
| [4] | 史攀, 黄于飞, 张翰之, 冷雪晨, 陈红. 消极身体意象对青少年的负面影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(2): 294-304. |
| [5] | 庞焯月, 席居哲, 左志宏. 儿童青少年创伤后应激障碍(PTSD)治疗的研究热点 ——基于美国文献的知识图谱分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(7): 1182-1196. |
| [6] | 兰公瑞, 李厚仪, 盖笑松. 人生目的:一个能预示积极发展的心理结构[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(12): 2192-2202. |
| [7] | 邓小平, 徐晨, 程懋伟, 张向葵. 青少年偏差行为的同伴选择和影响效应:基于纵向社会网络的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(11): 1898-1909. |
| [8] | 杨玲; 曹华;耿银凤; 徐景; 张燕;苏波波. 基于门户理论视角下的青少年物质成瘾[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1237-1245. |
| [9] | 蒋奖;曾陶然;杨淇越;于方静. 青少年物质主义的成因、测量与干预[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1266-1278. |
| [10] | 张镇;郭博达. 社会网络视角下的同伴关系与心理健康[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(4): 591-602. |
| [11] | 高鑫;邢淑芬;赵军燕. 父母的心理控制与儿童心理社会功能的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(11): 1792-1801. |
| [12] | 吴双双;吕振勇;陈红;王玉慧;肖子伦. 肥胖谈论:心理学视角下的沟通方式[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 111-119. |
| [13] | 肖玉琴;张卓;宋平;杨波. 冷酷无情特质:一种易于暴力犯罪的人格倾向[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(9): 1456-1466. |
| [14] | 张颖;冯廷勇. 青少年风险决策的发展认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(7): 1139-1148. |
| [15] | 钟歆;刘聚红;陈旭. 青少年同伴依恋:基于发展的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(7): 1149-1158. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4656
