 )
) 1 西南财经大学工商管理学院, 成都 611130
2 中国科学技术大学管理学院, 合肥 230026
收稿日期:2016-11-16出版日期:2018-06-10发布日期:2018-04-28通讯作者:翁清雄E-mail:wqx886@ustc.edu.cnThe analysis of characteristics and internal mechanisms of multisource feedback
ZHANG Yun1, WENG Qingxiong2( )
) 1 School of Business and Administration, Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu 611130, China
2 School of Management, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
Received:2016-11-16Online:2018-06-10Published:2018-04-28Contact:WENG Qingxiong E-mail:wqx886@ustc.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 多源评价在国外企业中的运用已日益成熟, 但在我国还停留在探索与发展阶段。基于已有的研究发现, 围绕评价过程、评价源及被评价者三方面对多源评价的特点及内在机制进行了探讨与分析。从评价过程看, 其评价目的具有多重性, 评价形式注重匿名性, 且评价结果的合理应用非常重要; 从评价源看, 不同评价源间的评价一致性较低, 且易造成晕轮效应和宽大效应; 从被评价者来看, 个体对多源评价结果的反应, 受到个性特征、反馈信号及自我-他人评价间差距等因素影响。研究也发现, 多源评价所带来的绩效改进结果具有不稳定性。基于此, 如何提高多源评价过程的有效性与准确性, 改善评价者对评价结果的反应, 以及如何对多源评价结果进行有效汇总等是未来值得研究的重要内容。
图/表 3

图1多源评价的结构图
 图1多源评价的结构图
图1多源评价的结构图
图2个体对多源评价评价结果的反应
 图2个体对多源评价评价结果的反应
图2个体对多源评价评价结果的反应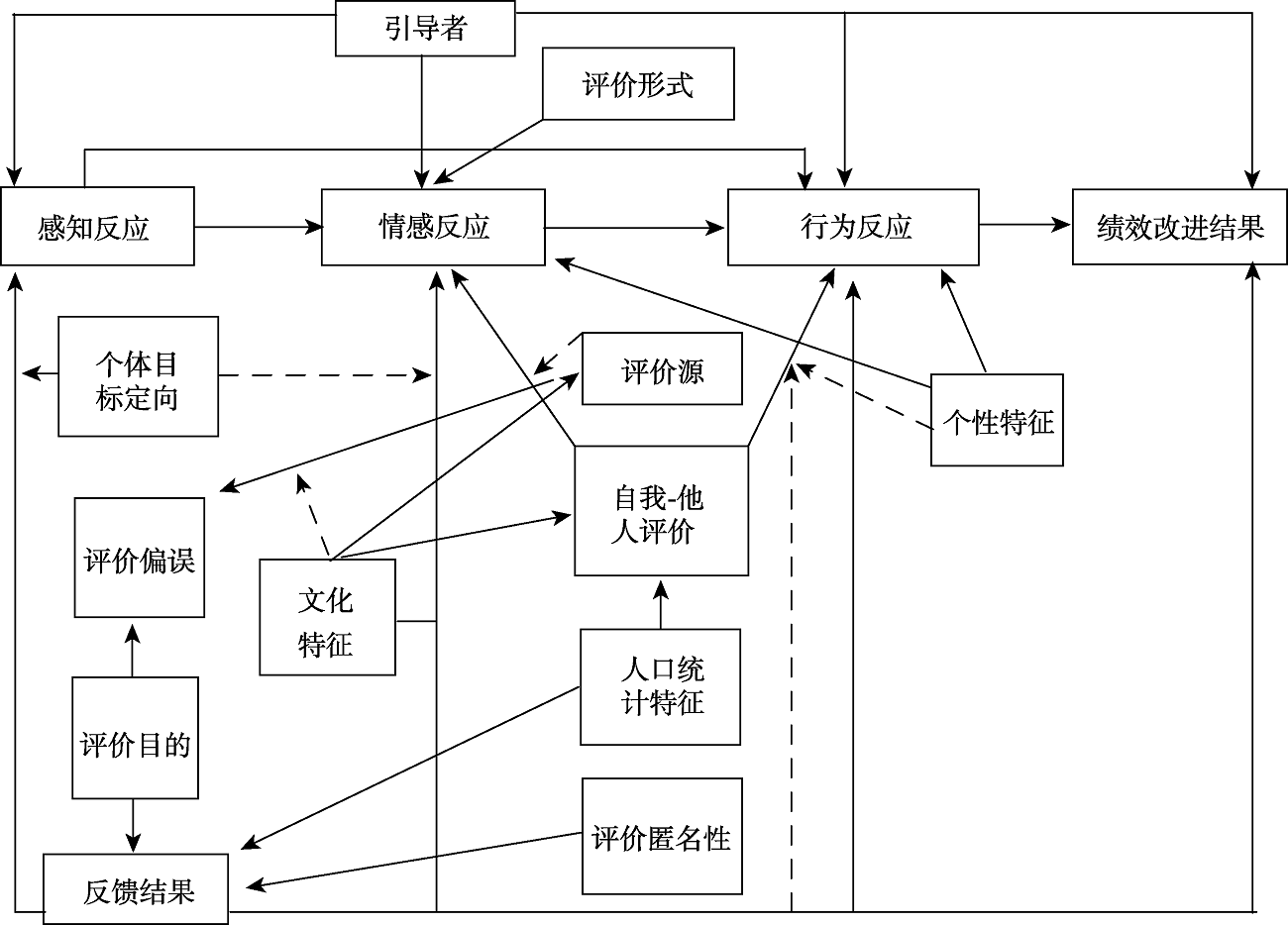
图3多源评价中所涉及的主要因素
 图3多源评价中所涉及的主要因素
图3多源评价中所涉及的主要因素参考文献 76
| [1] | 刘凤瑜 . ( 2000). 一种有效的效绩评价模式: 360度反馈的基本原理与过程. 南开管理评论, ( 1), 71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3448.2000.01.017URL |
| [2] | 陆昌勤, 方俐洛, 凌文辁 . ( 2001). 360度反馈及其在人力资源管理中的效用. 中国管理科学, 9( 3), 74-80. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-207X.2001.03.012URL |
| [3] | 许庆瑞, 王勇, 陈劲 . ( 2002). 绩效评价源与多源评价. 科研管理, 23( 3), 84-89. |
| [4] | Amundsen, S.,& Martinsen, ?. L . ( 2014). Self-other agreement in empowering leadership: Relationships with leader effectiveness and subordinates' job satisfaction and turnover intention. The Leadership Quarterly, 25( 4), 784-800. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2014.04.007URL |
| [5] | Antonioni, D.,& Park, H.(2001). The relationship between rater affect and three sources of 360-degree feedback ratings. Journal of Management, 27( 4), 479-495. doi: 10.1177/014920630102700405URL |
| [6] | Atwater,L. E., & Brett, J. F . ( 2005). Antecedents and consequences of reactions to developmental 360° feedback. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 66( 3), 532-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2004.05.003URL |
| [7] | Atwater,L. E., & Brett, J. F . ( 2006). 360-degree feedback to leaders: Does it relate to changes in employee attitudes? Group & Organization Management, 31( 5), 578-600. doi: 10.1177/1059601106286887URL |
| [8] | Atwater,L. E, Brett, J. F., & Charles, A. C . ( 2007). Multisource feedback: Lessons learned and implications for practice. Human Resource Management, 46( 2), 285-307. doi: 10.1002/hrm.20161URL |
| [9] | Atwater L. E., Wang M., Smither J. W., & Fleenor J. W . ( 2009). Are cultural characteristics associated with the relationship between self and others’ ratings of leadership? Journal of Applied Psychology, 94( 4), 876-886. doi: 10.1037/a0014561URLpmid: 19594231 |
| [10] | Beenen G., Pichler S., & Levy P. E . ( 2017). Self-determined feedback seeking: The role of perceived supervisor autonomy support. Human Resource Management, 56( 4), 555-569. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21787URL |
| [11] | Bernardin H. J., Tyler C. L., & Villanova P . ( 2009). Rating level and accuracy as a function of rater personality. International Journal of Selection & Assessment, 17( 3), 300-310. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2389.2009.00472.xURL |
| [12] | Bernardin H. J., Konopaske R., & Hagan C. M . ( 2012). A comparison of adverse impact levels based on top-down, multisource, and assessment center data: Promoting diversity and reducing legal challenges. Human Resource Management, 51( 3), 313-341. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21472URL |
| [13] | Bernardin H. J., Thomason S., Buckley M. R., & Kane J. S . ( 2016). Rater rating-level bias and accuracy in performance appraisals: The impact of rater personality, performance management competence, and rater accountability. Human Resource Management, 55( 2), 321-340. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21678URL |
| [14] | Beus J. M., Jarrett S. M., Bergman M. E., & Payne S. C . ( 2012). Perceptual equivalence of psychological climates within groups: When agreement indices do not agree. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 85( 3), 454-471. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8325.2011.02049.xURL |
| [15] | Bono,J. E, & Colbert, A. E . ( 2005). Understanding responses to multi-source feedback: The role of core self-evaluations. Personnel Psychology, 58( 1), 171-203. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2005.00633.xURL |
| [16] | Bono J. E., Hooper A. C., & Yoon D. J . ( 2012). Impact of rater personality on transformational and transactional leadership ratings. The Leadership Quarterly, 23( 1), 132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.11.011URL |
| [17] | Braddy P. W., Gooty J., Fleenor J. W., & Yammarino F. J . ( 2014). Leader behaviors and career derailment potential: A multi-analytic method examination of rating source and self-other agreement. The Leadership Quarterly, 25( 2), 373-390. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2013.10.001URL |
| [18] | Brett,J. F., & Atwater, L. E . ( 2001). 360° feedback: Accuracy, reactions, and perceptions of usefulness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86( 5), 930-942. doi: 10.1037//0021-9010.86.5.930URL |
| [19] | Brown, M.,& Benson, J.(2003). Rated to exhaustion? Reactions to performance appraisal processes. Industrial Relations Journal, 34( 1), 67-81. doi: 10.1111/1468-2338.00259URL |
| [20] | Brown A., Inceoglu I., & Lin Y . ( 2017). Preventing rater biases in 360-degree feedback by forcing choice. Organizational Research Methods, 20( 1), 121-148. doi: 10.1177/1094428116668036URL |
| [21] | Brutus, S.,& Derayeh, M.(2002). Multisource assessment programs in organizations: An insider's perspective. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 13( 2), 187-202. doi: 10.1002/hrdq.1023URL |
| [22] | Carson, M.(2006). Saying it like it isn't: The pros and cons of 360-degree feedback. Business Horizons, 49( 5), 395-402. doi: 10.1016/j.bushor.2006.01.004URL |
| [23] | Chappelow,C. T . ( 2004). 360-degree feedback. In C. D. McCauley & E. van Velsor (Eds.), The center for creative leadership handbook of leadership development (pp. 58-84). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. |
| [24] | Conway J. M., Lombardo K., & Sanders K. C . ( 2001). A meta-analysis of incremental validity and nomological networks for subordinate and peer rating. Human Performance, 14( 4), 267-303. doi: 10.1207/S15327043HUP1404_1URL |
| [25] | Culbertson S. S., Henning J. B., & Payne S. C . ( 2013). Performance appraisal satisfaction. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 12( 4), 189-195. doi: 10.1027/1866-5888/a000096URL |
| [26] | Eckert R., Ekelund B. Z., Gentry W. A., & Dawson J. F . ( 2010). I don't see me like you see me, but is that a problem? Cultural influences on rating discrepancy in 360-degree feedback instruments. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 19( 3), 259-278. doi: 10.1080/13594320802678414URL |
| [27] | Facteau,J. D., & Craig, S. B . ( 2001). Are performance appraisal ratings from different rating sources comparable? Journal of Applied Psychology, 86( 2), 215-227. doi: 10.1037//0021-9010.86.2.215URLpmid: 11393435 |
| [28] | Farndale, E.,& Kelliher, C.(2013). Implementing performance appraisal: Exploring the employee experience. Human Resource Management, 52( 6), 879-897. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21575URL |
| [29] | Fleenor J. W., Smither J. W., Atwater L. E., Braddy P. W., & Sturm R. E . ( 2010). Self-other rating agreement in leadership: A review. The Leadership Quarterly, 21( 6), 1005-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2010.10.006URL |
| [30] | Harbi S. A., Thursfield D., & Bright D . ( 2017). Culture, Wasta and perceptions of performance appraisal in Saudi Arabia. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28( 19), 2792-2810. doi: 10.1080/09585192.2016.1138987URL |
| [31] | Hassan, S.,& Rohrbaugh, J.(2009). Incongruity in 360-degree feedback ratings and competing managerial values: Evidence from a public agency setting. International Public Management Journal, 12( 4), 421-449. doi: 10.1080/10967490903103375URL |
| [32] | Heslin,P. A., & Latham, G. P . ( 2004). The effect of upward feedback on managerial behavior. Applied Psychology, 53( 1), 23-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-0597.2004.00159.xURL |
| [33] | Hoffman B., Lance C. E., Bynum B., & Gentry W. A . ( 2010). Rater source effects are alive and well after all. Personnel Psychology, 63( 1), 119-151. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2009.01164.xURL |
| [34] | Ikramullah M., Van Prooijen J. W., Lqbal M. Z., & Ul-Hassan F. S . ( 2016). Effectiveness of performance appraisal: Developing a conceptual framework using competing values approach. Personnel Review, 45( 2), 334-352. doi: 10.1108/PR-07-2014-0164URL |
| [35] | Iqbal M. Z., Akbar S., & Budhwar P . ( 2015). Effectiveness of performance appraisal: An integrated framework. International Journal of Management Reviews, 17( 4), 510-533. doi: 10.1111/ijmr.12050URL |
| [36] | Judge,T. A., & Bono, J. E . ( 2001). Relationship of core self-evaluations traits—self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability—with job satisfaction and job performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86( 1), 80-92. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.1.80URL |
| [37] | Kampk?tter, P.(2017). Performance appraisals and job satisfaction. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28( 5), 750-774. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2469875URL |
| [38] | Karkoulian S., Assaker G., & Hallak R . ( 2016). An empirical study of 360-degree feedback, organizational justice, and firm sustainability . Journal of Business Research, 69( 5), 1862-1867. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.10.070URL |
| [39] | Kim K. Y., Atwater L., Patel P. C., & Smither J. W . ( 2016). Multisource feedback, human capital, and the financial performance of organizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 101( 11), 1569-1584. doi: 10.1037/apl0000125URLpmid: 27504657 |
| [40] | Kopperud K. H., Martinsen ?., & Humborstad, S. I. W.(2014). Engaging leaders in the eyes of the beholder: On the relationship between transformational leadership, work engagement, service climate, and self-other agreement. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 21( 1), 29-42. doi: 10.1177/1548051813475666URL |
| [41] | Kossek E. E., Huang J. L., Piszczek M. M., Fleenor J. W., & Ruderman M . ( 2017). Rating expatriate leader effectiveness in multisource feedback systems: Cultural distance and hierarchical effects. Human Resource Management, 56( 1), 151-172. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21763URL |
| [42] | Krasman, J.(2010). The feedback-seeking personality: Big five and feedback-seeking behavior. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 17( 1), 18-32. doi: 10.1177/1548051809350895URL |
| [43] | London, M.,& Smither, J. W . ( 1995). Can multi-source feedback change perceptions of goal accomplishment, self-evaluations, and performance-related outcomes? Theory-based applications and directions for research. Personnel Psychology, 48( 4), 803-839. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.1995.tb01782.xURL |
| [44] | London, M.(2001). The great debate: Should multisource feedback be used for administration or development only? In D. W. Bracken, C. W. Timmreck, & A. H. Church (Eds.), The handbook of multisource feedback: The comprehensive resource for designing and implementing MSF processes(pp. 368-385). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. |
| [45] | London, M.,& Smither, J. W . ( 2002). Feedback orientation, feedback culture, and the longitudinal performance management process. Human Resource Management Review, 12( 1), 81-100. doi: 10.1016/S1053-4822(01)00043-2URL |
| [46] | Luffarelli J., Gon?alves D., & Stamatogiannakis A . ( 2016). When feedback interventions backfire: Why higher performance feedback may result in lower self-perceived competence and satisfaction with performance. Human Resource Management, 55( 4), 591-614. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21739URL |
| [47] | Luthans, F.,& Peterson, S. J . ( 2003). 360-degree feedback with systematic coaching: Empirical analysis suggests a winning combination. Human Resource Management, 42( 3), 243-256. doi: 10.1002/hrm.10083URL |
| [48] | Markham S. E., Smith J. W., Markham I. S., & Braekkan K. F . ( 2014). A new approach to analyzing the Achilles' heel of multisource feedback programs: Can we really trust ratings of leaders at the group level of analysis? The Leadership Quarterly, 25( 6), 1120-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2014.10.003URL |
| [49] | Markham S. E., Markham I. S., & Smith J. W . ( 2015). At the crux of dyadic leadership: Self-other agreement of leaders and direct reports—Analyzing 360-degree feedback. The Leadership Quarterly, 26( 6), 958-977. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2015.10.001URL |
| [50] | Markham S. E., Markham I. S., & Smith J. W . ( 2017). A review, analysis, and extension of peer-leader feedback agreement: Contrasting group aggregate agreement vs. self-other agreement using entity analytics and visualization. The Leadership Quarterly, 28( 1), 153-177. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2016.10.001URL |
| [51] | Maylett, T.(2009). 360-degree feedback revisited: The transition from development to appraisal. Compensation & Benefits Review, 41( 5), 52-59. doi: 10.1177/0886368709337922URL |
| [52] | McCarthy,A. M., & Garavan, T. N . ( 2007). Understanding acceptance of multisource feedback for management development. Personnel Review, 36( 6), 903-917. doi: 10.1108/00483480710822427URL |
| [53] | Mero N. P., Guidice R. M., & Brownlee A. L . ( 2007). Accountability in a performance appraisal context: The effect of audience and form of accounting on rater response and behavior. Journal of Management, 33( 2), 223-252. doi: 10.1177/0149206306297633URL |
| [54] | Mishra, V.,& Roch, S. G . ( 2013). Cultural values and performance appraisal: Assessing the effects of rater self- construal on performance ratings. The Journal of Psychology, 147( 4), 325-344. doi: 10.1080/00223980.2012.694377URLpmid: 23885636 |
| [55] | Ng K. Y., Koh C., Ang S., Kennedy J. C., & Chan K.-Y . ( 2011). Rating leniency and halo in multisource feedback ratings: Testing cultural assumptions of power distance and individualism-collectivism. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96( 5), 1033-1044. doi: 10.1037/a0023368URLpmid: 21480684 |
| [56] | O’Neill T. A., Goffin R. D., & Gellatly I. R . ( 2012). The use of random coefficient modeling for understanding and predicting job performance ratings: An application with field data. Organizational Research Methods, 15( 3), 436-462. doi: 10.1177/1094428112438699URL |
| [57] | Pichler, S.(2012). The social context of performance appraisal and appraisal reactions: A meta-analysis. Human Resource Management, 51( 5), 709-732. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21499URL |
| [58] | Pulakos,E. D., & O’Leary, R. S . ( 2011). Why is performance management broken? Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 4( 2), 146-164. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-9434.2011.01315.xURL |
| [59] | Randall, R.,& Sharples, D.(2012). The impact of rater agreeableness and rating context on the evaluation of poor performance. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 85( 1), 42-59. doi: 10.1348/2044-8325.002002URL |
| [60] | Rogers E., Rogers C. W., & Metlay W . ( 2002). Improving the payoff from 360-degree feedback. Human Resource Planning, 25( 3), 44-54. |
| [61] | Rosen C. C., Kacmar K. M., Harris K. J., Gavin M. B., & Hochwarter W. A . ( 2017). Workplace politics and performance appraisal: A two-study, multilevel field investigation. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 24( 1), 20-38. doi: 10.1177/1548051816661480URL |
| [62] | Russo S. D., Miraglia M., & Borgogni L . ( 2017). Reducing organizational politics in performance appraisal: The role of coaching leaders for age-diverse employees. Human Resource Management, 56( 5), 769-783. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21799URL |
| [63] | Semeijn J. H., Van Der Heijden, B. I. J. M.,& Van Der Lee, A.(2014). Multisource ratings of managerial competencies and their predictive value for managerial and organizational effectiveness. Human Resource Management, 53( 5), 773-794. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21592URL |
| [64] | Shipper F., Hoffman R. C., & Rotondo D. M . ( 2007). Does the 360 feedback process create actionable knowledge equally across cultures? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 6( 1), 33-50. doi: 10.5465/AMLE.2007.24401701URL |
| [65] | Smither,J. W., & Walker, A. G . ( 2004). Are the characteristics of narrative comments related to improvement in multirater feedback ratings over time? Journal of Applied Psychology, 89( 3), 575-581. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.89.3.575URLpmid: 15161414 |
| [66] | Smither,J. W, London, M., & Reilly, R. R . ( 2005). Does performance improve following multisource feedback? A theoretical model, meta-analysis, and review of empirical findings. Personnel Psychology, 58( 1), 33-66. doi: 10.1111/peps.2005.58.issue-1URL |
| [67] | Smither J. W., Brett J. F., & Atwater L. E . ( 2008). What do leaders recall about their multisource feedback? Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 14( 3), 202-218. doi: 10.1177/1071791907308463URL |
| [68] | Spence,J. R., & Keeping, L. M . ( 2010). The impact of non-performance information on ratings of job performance: A policy-capturing approach. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 31( 4), 587-608. doi: 10.1002/job.648URL |
| [69] | Sumelius J., Bj?rkman I., Ehrnrooth M., M?kel? K., & Smale A . ( 2014). What determines employee perceptions of HRM process features? The case of performance appraisal in MNC subsidiaries. Human Resource Management, 53( 4), 569-592. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21604URL |
| [70] | Vecchio,P. R., &Anderson, R. J . ( 2009). Agreement in self-other ratings of leader effectiveness: The role of demographics and personality. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 17( 2), 165-179. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2389.2009.00460.xURL |
| [71] | Verbos,A. K., Miller, J. S, & Goswami, A.(2014). Employee social cognition and performance evaluation process reactions. Personnel Review, 43( 4), 515-535. doi: 10.1108/PR-01-2011-0011URL |
| [72] | Woehr D. J., Sheehan M. K., & Bennett J. W . ( 2005). Assessing measurement equivalence across rating sources: A Multitrait-Multirater approach. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90( 3), 592-600. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.90.3.592URLpmid: 15910153 |
| [73] | Wong,K. F. E., & Kwong, J. Y. Y . ( 2007). Effects of rater goals on rating patterns: Evidence from an experimental field study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92( 2), 577-585. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.2.577URLpmid: 17371102 |
| [74] | Wood D., Harms P., & Vazire S . ( 2010). Perceiver effects as projective tests: What your perceptions of others say about you. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 99( 1), 174-190. doi: 10.1037/a0019390URLpmid: 20565194 |
| [75] | Xie J. L., Chen Z. G., & Roy J. P . ( 2006). Cultural and personality determinants of leniency in self-rating among Chinese people. Management & Organization Review, 2( 2), 181-207. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8784.2006.00043.xURL |
| [76] | Yamazaki, Y.,& Yoon, J.(2016). A cross-national study of fairness in Asia: How perceptions of a lack-of-group bias and transparency in the performance evaluation system relate to job satisfaction. Human Resource Management, 55( 6), 1059-1077. doi: 10.1002/hrm.21707URL |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 李朋波, 陈黎梅, 褚福磊, 孙雨晴, 周莹. 我是高材生:资质过剩感及其对员工的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1313-1330. |
| [2] | 郝喜玲 刘依冉 杜晶晶 郑方. 失败恐惧的形成及对创业行为的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [3] | 刘豆豆 胥彦 李超平. 中国情境下家长式领导与绩效关系的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [4] | 汤一鹏, 任芷宇, 蒲小萍, 韩韦. 人际真诚在同事互动及团队工作中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 597-609. |
| [5] | 吴伟炯, 冯镜铭, 林怿洵, 赵霞. 通勤恢复活动对工作激情的动态影响及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 610-624. |
| [6] | 董小炜, 秦昕, 陈晨, 黄鸣鹏, 邓惠如, 周汉森, 宋博迪. 组织行为学中的时间相关研究与未来方向[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 747-760. |
| [7] | 严秋斯, 隋杨, 郝雪晶. 亲组织不道德行为的解释机制与理论模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 338-352. |
| [8] | 尹奎, 张凯丽, 赵景, 巩振兴. 员工授权期望的效应及其理论机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 353-364. |
| [9] | 张建平 刘善仕 林澍倩 张亚 李焕荣. 领导授权赋能与领导有效性的关系:基于元分析的检验[J]. 心理科学进展, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [10] | 赵锴, 向姝婷. 如何解决团队创新悖论?基于成员认知风格“组型”与“构型”视角的探究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 1-18. |
| [11] | 李朋波, 周莹, 王震, 孙雨晴. 借花献佛: 顾客导向偏离行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2150-2159. |
| [12] | 陈丝璐, 张光磊, 刘文兴. 伦理导向人力资源管理实践的跨层次作用机制:基于社会情境与社会认知理论[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(11): 1800-1813. |
| [13] | 向姝婷, 赵锴, 宁南. “赋能”还是“负担”?领导者授权行为对员工工作行为影响的双刃剑效应探究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(11): 1814-1835. |
| [14] | 李方君, 钟旭朋. 促进型和抑制型建言的差异[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(11): 1939-1952. |
| [15] | 李馨, 刘培, 肖晨洁, 王笑天, 李爱梅. 组织中权力如何促进亲社会行为?责任感知的中介作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(9): 1586-1598. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4350
