 ,*,?,2), 邱涛*, 赵燕*
,*,?,2), 邱涛*, 赵燕*NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF MASS RATIO EFFECT ON FLOW-INDUCED VIBRATION OF TWO TANDEM SQUARE CYLINDERS AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBER1)
Du Xiaoqing ,*,?,2), Qiu Tao*, Zhao Yan*
,*,?,2), Qiu Tao*, Zhao Yan*通讯作者: 2)杜晓庆, 副教授, 主要研究方向: 结构风工程研究. E-mail:dxq@shu.edu.cn
收稿日期:2019-07-16接受日期:2019-10-3网络出版日期:2019-10-08
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-07-16Accepted:2019-10-3Online:2019-10-08
作者简介 About authors

摘要
为澄清串列双方柱流致振动的质量比效应, 采用数值模拟方法, 在雷诺数为150时, 研究了质量比($m^{\ast }=3$, 10, 20)对下游方柱振动响应特性的影响规律, 分析了下游方柱尾流模态的演变过程, 探讨了导致下游方柱振动的流固耦合机制. 结果表明: 质量比对下游方柱的流致振动有重要影响, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)时下游方柱的振动响应更为复杂, 随着折减速度的增大, 下游方柱并未出现传统“锁定”现象(即振动频率比$f_{y}$/$f_{\rm n} \approx1$的锁定), 而发生了“弱锁定”现象(即$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}<1$的锁定); 随着质量比的增加($m^{\ast }=10$和20), “弱锁定”现象消失, 而出现传统“锁定”现象, 且下游方柱横流向最大振幅减小. 质量比对串列双方柱的柱心间距有明显影响, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)时的柱间距在振动锁定区内会急剧减小, 而较高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)下的柱间距则变化不大. 此外, 质量比对串列双方柱的尾流模态和流固耦合机制也有显著影响, 其中低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下的情况更为多样.
关键词:
Abstract
To clarify the mass ratio effect on the flow-induced vibration of two tandem square cylinders, numerical simulation is employed to investigate the effect of mass ratio ($m^{\ast }=3$, 10, 20) on the vibration response characteristic of the downstream square cylinder at $Re=150$. The evolution of the wake modes are discussed, and the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) mechanism of the downstream square cylinder is analyzed as well. The results show that the mass ratio plays an important role in the flow-induced vibration of the downstream cylinder. When the mass ratio is small ($m^{\ast }=3$), the vibration response is very complicated for the downstream cylinder. With the increase of reduced flow speed, the downstream cylinder does not have the traditional lock-in phenomenon (with the lock-in frequency ratio around 1) but has the soft-lock-in phenomenon (with the lock-in frequency ratio less than 1). When the mass ratio is large ($m^{\ast }=10$ and 20), the soft-lock-in phenomenon disappears, while the traditional lock-in phenomenon occurs instead. The maximum transverse amplitude of the downstream cylinder decreases gradually with the increase of the mass ratio. Furthermore, the mass ratio has an obvious effect on the distance between two square cylinders. The distance between two cylinders severely decreases in the lock-in region for the small mass ratio but keeps almost constant for the larger mass ratio. In addition, the mass ratio also has a significant effect on the wake modes and FSI mechanisms of two tandem square cylinders. For the small mass ratio ($m^{\ast }=3$), the wake modes and the FSI mechanism are very diverse.
Keywords:
PDF (12767KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
杜晓庆, 邱涛, 赵燕. 低雷诺数串列双方柱流致振动质量比效应的数值研究1). 力学学报[J], 2019, 51(6): 1740-1751 DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-19-187
Du Xiaoqing, Qiu Tao, Zhao Yan.
引 言
流致振动在实际工程中时常发生, 易造成结构损坏, 因而引起工程界与学术界广泛关注[1-4]. 研究表明, 多柱体流致振动的影响因素众多, 干扰机理复杂[5-8], 而质量比对多柱体流致振标识码响规律尚未澄清.对于串列双柱体绕流, 其柱体周围流场较单柱体而言更加复杂, 已有不少****对其进行研究[9-15]. Sumner等[9]将串列双圆柱绕流的柱间流态分为3类, 即单一钝体流态、剪切层再附流态和双涡脱流态. Sohankar[10]对串列双方柱绕流的流态分类与Sumner等[9]相同. ****通常把从剪切层再附流态标识码脱流态转变的间距比($L$/$D$或$L/B$)称为临界间距比, 其中$L$为串列双柱体柱心间距、$D$为标识码径、$B$方柱边长. 对于圆柱, Tasaka等[11]通过实验得出双圆柱的临界间距比$L/D\approx3.5$; Papaioannou等[12]在雷诺数$Re=160$的串列圆柱绕流数值模拟中也得出相同的结论; 毕继红等[13]发现$Re=100$的双圆柱临界间距比$L/D=3.375\sim 3.5$. 对于方柱, Sohankar[10]得出低雷诺数串列双方柱绕流的临界间距比$L/B=3\sim 4$; Yen等[14]发现串列方柱在不同雷诺数下的临界间距比$L/B=3\sim 5$; Zhao等[15]则发现雷诺数$Re=100$的双方柱临界间距比$L/B=4$.
各国****对单圆柱流致振动的质量比效应开展了较为广泛的研究[16-19]. Mittal和Kumar[16]对单圆柱流致振动进行数值模拟得出, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=4.25$)单圆柱会出现“弱锁定”现象, 即柱体在振动锁定区内的振动频率与自振频率比$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}<1$; 较高质量比($m^{\ast}=25$)单圆柱未发现“弱锁定”现象. Tu等[17]发现低质量比单圆柱出现“标识码”现象时会伴有大幅横流向振动. 谷家扬等[18]对不同质量比($m^{\ast }=1$, 2和2.4)的运动单圆柱进行数值模拟, 发现单圆柱的横流向振幅和振动锁定区范围随质量比增大而减小. 陈正寿等[19]得到与谷家扬等[18]一致的结论.
以往对双圆柱流致振动质量比效应也进行一定的研究. Tofa等[20]研究了上游圆柱质量比的改变($m^{\ast}=2.36$, 5.19和8.76)对串列圆柱流致振动的影响, 发现下游圆柱横流向振幅随上游圆柱质量比的降低而减小. Jiang等[21]主要讨论了串列的上、下游圆柱在相同和不同质量比情况下的振动响应特性和涡脱模态, 并得出当上游圆柱的质量比较低时, 上、下游圆柱均出现大幅横流向振动; 高质量比圆柱会受到更大的气动升力, 但其横流向振幅小于低质量比圆柱. Prasanth和Mittal[22]以及Tu等[23]在低质量比串列双圆柱流致振动研究中均发现了“弱锁定”现象. 上述研究均表明, 质量比对双圆柱流致振动有显著影响.
与圆柱流致振动相比, ****对方柱流致振动质量比效应的研究主要是针对单方柱. Sen和Mittal[24-25]对雷诺数为50$\sim$250的运动单方柱进行数值模拟, 结果发现: 低质量比($m^{\ast}=1$)单方柱仅发生涡激振动并存在“弱锁定”现象, 且随着质量比增大, 其“弱锁定”现象减弱, 即振动频率与自振频率比$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}$接近于1. 许媛欣[26]对雷诺数$Re=200$的不同质量比($m^{\ast}=1$和10)的单方柱流致振标识码数值计算, 发现高质量比单方柱的气动力及流场特性变化规律与低质量比相似, 但其横流标识码幅值小于低质量比单方柱.
对于双方柱流致振动, 以往的研究甚少. Kumar等[27-28]研究了不同布置形式下固定的下游方柱对上游方柱横流向振动的干扰效应, 标识码游方柱横流向最大振幅出现在两方柱为串列布置的形式下. Pillalamarri等[29-30]则对雷诺数$Re=200$的上游方柱固定、下游方柱运动的串列双方柱标识码数值模拟研究, 结果表明: 与单方柱不同, 下游方柱在高折减速度下会发生驰振. Mithun和Tiwari[31]在雷诺数为100时, 对固定振幅且仅作同相位横流向振动的串列双方柱标识码值模拟, 研究了不同柱心间距的双方柱的横流向振动频率对其气动力特性和流场结构的影响, 标识码方柱的锁定区随振动频率改变而改变. Guan和Jaiman[32]则通过数值模拟, 在雷诺数$Re=200$时, 研究了刚性连接的并列双方柱流致标识码象, 并发现了4种流态即单一钝体流态、标识码流态、耦合涡脱流态以及双涡脱流态. 目前尚未见到研究双方柱流致振动质量比效应的文献.
为了进一步澄清质量比对双方柱流致振动的影响, 本文在雷诺数$Re=150$时, 以质量比$m^{\ast }=m/(\rho B^{2})=3$, 10和20($m$为单位长方柱质量, $\rho$为流体密度)、柱标识码$L=4B$的串列双方柱流致振动为对象, 重点研究了下游方柱的振动频率、振动幅值等振标识码特性随折减速度的变化规律, 探讨了下游方柱尾流模态的演变过程, 分析了导致下游方柱标识码流固耦合机制.
1 数值方法
方柱流致振动属于流固耦合问题, 其在计算过程中, 需将流体域和固体域的解进行耦合, 以此获得计算结果. 其中流体域考虑为二维不可压缩流体, 所需求解的控制方程为连续方程和动量方程(N-S方程).如图1所示, 双方柱流致振动可简化为质量$\!-\!$弹簧$\!-\!$阻尼系统. 其中, $V$为来流速度, 双方柱的柱心间距$L=4B$, $c$为结构阻尼, $k$为弹簧刚度. 为更清楚地辨别两方柱的各项参数, 本文将上游方柱的参数脚标设为1, 下游方柱的参数脚标设为2. 此外, 两方柱均考虑顺流向运动和横流向运动, 其控制方程为
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1双方柱计算模型
Fig.1Computational model of two tandem square cylinders
式中, $x$和$y$分别为方柱瞬时的顺流向位移与横流向位移; $F_{\rm D}(t)=0.5\rho U^{2} BC_{\rm D}$和$F_{\rm L}(t)=0.5\rho U^{2}BC_{\rm L}$分别为作用在单位长方柱上的顺流向气动力与横流向气动力, 其中, $C_{\rm D}$和$C_{\rm L}$分别为阻力和升力系数.
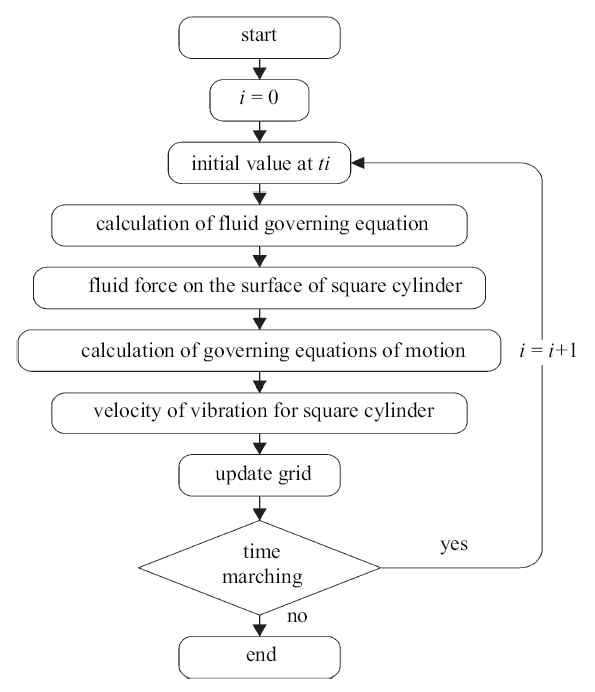
本文采用动网格技术以实现柱体与流场之间流固耦合作用的数值模拟, 其计算过程如图2所示.
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2流固耦合计算流程图
Fig.2Process of the fluid-solid coupling algorithm
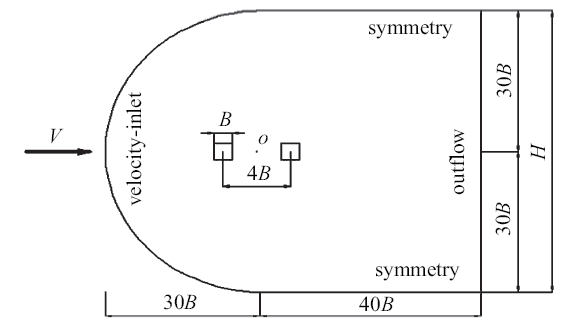
双方柱网格方案和网格计算域如图3和图4所示. 两方柱中间为坐标原点$O$, 入口边界距原点$O$为30$B$; 上、下边界距原点$O$为30$B$; 出口边界距原点$O$为40$B$; 此外, 方柱设定在红色实线圆形区域内运动. 本文对计算域网格进行分块处理, 其中, 所有算例的方柱在近壁面内采用结构化网格; 在红色实线圆形区域内采用三角形非结构化网格, 区域外均采用结构化网格. 由于方柱周围的流动现象较为复杂, 为了精确模拟方柱近壁面的流场特性, 在靠近方柱表面处对网格进行了加密, 近壁面最小网格尺寸为$\Delta x / B = \Delta y / B = 0.01$, 近壁面法线方向(垂直于壁面方向)的网格增长率为1.06.
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3计算域网格方案
Fig.3Plane computation grid scheme
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4计算域和边界条件示意图
Fig.4Sketch of computational domain and boundary conditions
计算流场的边界条件设置如图4所示: 入口边界采用速度入口(velocity-inlet); 出口边界采用自由出流(outflow); 两侧壁面设为对称(symmetry)边界; 方柱表面设为无滑移壁面(wall). 在具体的数值计算中, 压力和速度耦合采用SIMPLEC法求解, 动量方程采用二阶精度的离散格式.
计算参数选取原则: 考虑到计算效率, 本文在低雷诺数$Re=150$的层流条件下进行数值计算; 串列方柱在临界间距比$L/B=4$时的流态较为复杂, 因而本文柱心间距比为4; 本文阻尼比$\zeta $取为0, 质量比分别取$m^{\ast}=3$, 10和20; 为研究串列方柱的涡激振动特性, 选取的折减速度$V_{\rm r}=V/(f_{\rm n}B)=1\sim12$ $(f_{\rm n} = \sqrt {k / m} / (2\pi) $为方柱自振频率).
2 网格检验和结果验证
为验证网格的合理性和计算结果的正确性, 分别以静止单方柱绕流和单方柱流致振动为算例进行计算模型的结果验证.2.1 静止单方柱绕流的结果验证
以雷诺数为150的静止单方柱绕流为对象, 研究了周向网格数量、无量纲时间步长和阻塞率等参标识码算结果的影响, 共计18种工况, 并将计算得到的平均阻力系数$C_{\rm D,mean}$、脉动阻力系数$C_{\rm D,rms}$标识码升力系数$C_{\rm L,rms}$和$St$与文献结果进行对比. 如表1所示, 本文所有工况的计算结果较为接近, 也与文献结果吻合较好, 这说明其计算模型具有良好的标识码立性, 计算结果也有很高的可信度. 考虑本文的计算效率与精度, 最终采用D3工况的计算参数和网格方案作为后续的计算网格模型.Table 1
表1
表1静止单方柱模型的网格方案和结果验证($Re=150$)
Table 1
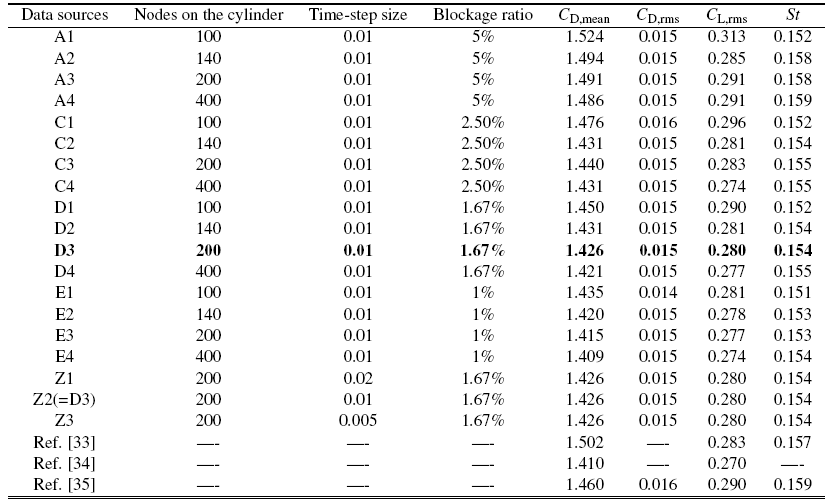 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 单方柱流致振动的结果验证
为进一步验证网格模型的可靠性, 采用D3工况的网格模型, 以雷诺数为100、质量比$m^{\ast }=3$和折减速度$V_{\rm r}=1\sim 12$的单方柱流致振动为算例, 将横向流无量纲振幅$A_{y}$/$B$和横向流振动标识码$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}$与文献结果进行比较, 见图5. 其中, $A_{y}=(Y_{\max}-Y_{\min})/2(Y_{\max}$和$Y_{\min}$分别为横流向位移的最大值和最小值) 和$f_{y}$为横流向振动频率. 可见, 其计算结果与文献结果吻合较好, 本文的计算模型具有较高的精确度.图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5单方柱流致振动结果验证及与圆柱的比较
Fig.5Result verifications of flow-induced vibration of single square cylinder and comparing with circular cylinder
图5中还给出了雷诺数$Re=150$的低质量比($m^{\ast}$ $=2$)单圆柱流致振动的文献结果. 通过对比看出, 单圆柱在“弱锁定”现象发生时伴有大幅横流向振动, 结束后还出现“锁定”现象; 而本文与文献[33]的运动单方柱均未出现明显“锁定”和“弱锁定” 现象.
3 计算结果及分析
由于受到上游柱体尾流影响, 下游柱体的振动响应及其流固耦合机制较上游柱体更为复杂[22-23], 受篇幅限制, 本文重点分析下游方柱的计算结果.3.1 动力响应特性
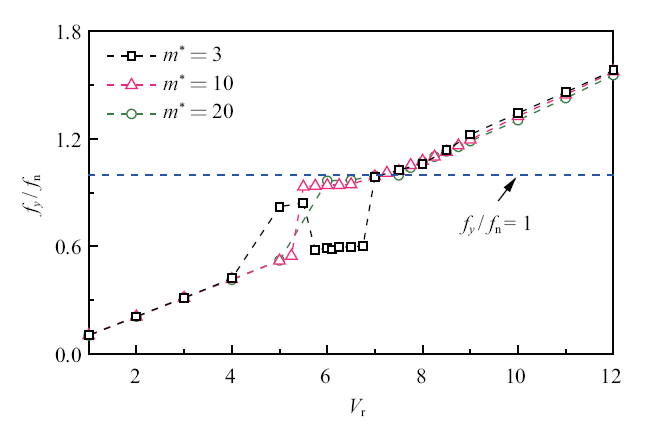
3.1.1 下游方柱横流向振动特性图6为不同质量比下游方柱横流向振动频率与自振频率比($f_{y}/f_{\rm n}$)随折减速度的变化曲线.
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6下游方柱横流向振动的频率比
Fig.6Variations of relative vibration frequency for downstream square cylinder in transverse direction
可以看出, 低质量比($m^{\ast}=3$)下游方柱出现两个振动锁定区, 并发生“弱锁定”现象. 其中, 两个振动锁定区范围及对应的振动频率比分别为$V_{\rm r}=5\sim5.5$ $(f_{y}/f_{\rm n} \approx 0.83$)和$V_{\rm r}=5.75\sim6.75$ $(f_{y}/f_{\rm n} \approx 0.59$).
随着质量比增大, 下游方柱仅有一个振动锁定区, 且“弱锁定”现象消失. $m^{\ast }=10$和20的振动锁定区范围及对应的振动频率比分别为$V_{\rm r}=5.5\sim 6.75$ $(f_{y}/f_{\rm n} \approx 0.94$)和$V_{\rm r}=5.75\sim 7.5$ $(f_{y}/f_{\rm n} \approx 0.99$).
图7给出了不同质量比下游方柱横流向无量纲振幅($A_{y}/B$)随折减速度的变化曲线.
图7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7下游方柱横流向振幅变化曲线
Fig.7Variations of cross flow amplitude for downstream square cylinder with reduced velocity
可见, 下游方柱横流向最大振幅出现在振动锁定区外, 并随质量比增加而减小, 其值分别为$0.73B$ $(m^{\ast }=3$)、$0.67B$ $(m^{\ast }=10$)和$0.58B$ $(m^{\ast}=20$). 各质量比下游方柱在振动锁定区内均有大幅横流向振动, 值得注意的是, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱横流向振幅在振动锁定区$V_{\rm r}=5.75\sim 6.75$内随折减速度增加出现先降后升, 并在振动锁定区外的高折减速度下($V_{\rm r}=10\sim 12$)也有较大幅值.
3.1.2 下游圆柱横流向振动特性
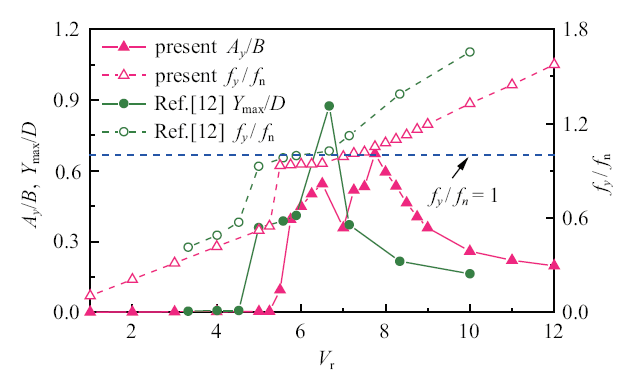
为研究临界间距比的串列方柱与圆柱振动响应的差异, 图8给出了往年$Re=160$, 柱心标识码3.5$D$的下游圆柱横流向最大位移$Y_{\max}$和振动频率比$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}$随折减速度的变化曲线, 标识码文$m^{\ast}=10$的下游方柱的计算结果进行对比. 其中文献[12]的双圆柱质量比$m^{\ast }=10$和阻尼比$\zeta =0.01$. 可以看出, 下游圆柱仅在振动锁定区内出现大幅横流向振动; 而下游方柱在振动锁定区内、外均存标识码横流向振动, 且其横流向最大振幅发生在振动锁定区外.
图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8下游圆柱横流向最大位移变化曲线
Fig.8Variations of maximum cross flow displacement for downstream cylinder with reduced velocity
3.1.3 下游方柱顺流向振动特性
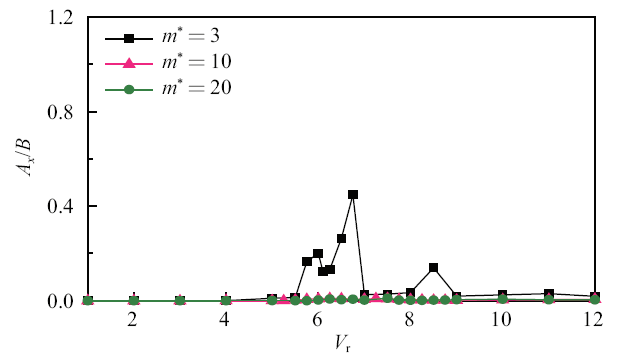
图9为不同质量比下游方柱顺流向无量纲振幅$A_{x}/B$随折减速度的变化曲线. 其中$A_{x}=(X_{\max}-X_{\min})/2$, $X_{\max}$和$X_{\min}$分别为顺流向位移的最大值和最小值. 可见, 低质量比($m^{\ast}=3$)下游方柱在振动锁定区$V_{\rm r}=5.75\sim 6.75$的顺流向振动较为明显, 在振动锁定区外也出现较大极值; 高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)下游方柱则无明显顺流向振动.
图9
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9双方柱顺流向振幅变化曲线
Fig.9Variations of in-line flow amplitude for downstream squarer cylinder with reduced velocity
柱心间距的变化会对方柱振动特性产生影响, 因而图10和图11分别给出各质量比双方柱无量纲顺标识码衡位置$X_{\rm mean}/B$和平均柱心间距比$L_{\rm mean}/B$随折减速度的变化曲线.
图10
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图10双方柱顺流向平衡位置
Fig.10Variations of mean value of in-line displacement for two tandem square cylinders
图11
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图11双方柱平均柱心间距比
Fig.11Variations of mean value of spacing ratio for two tandem square cylinders
由图10和图11可知, 低质量比($m^{\ast}=3$)上游方柱顺流向平衡位置$X_{\rm mean}$在振动锁定区$V_{\rm r}=5.75\sim6.75$内急剧增大, 并远大于下游方柱, 造成平均柱心间距$L_{\rm mean}$明显降低; 高质量比($m^{\ast}=10$和20)上游方柱顺流向平衡位置$X_{\rm mean}$与下游方柱基本相同, 造成平均柱心间距$L_{\rm mean}$随折减速度增大而基本不变.
3.2 流场分析
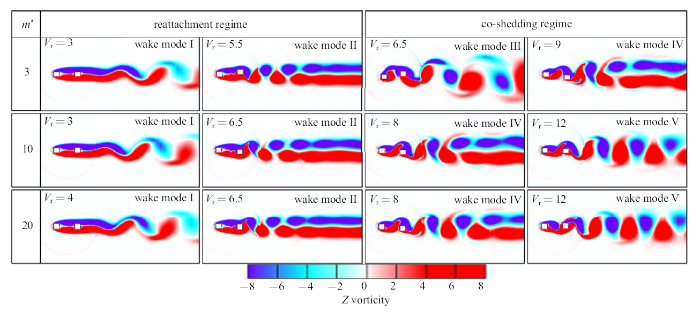
图12给出了不同质量比双方柱瞬时尾流模态和对应的柱间流态. 可见, 不同质量比的双方柱共出现剪切层再附(即上游方柱剪切层再附到下游方柱表面)和标识码(即两方柱均有旋涡脱落)两种柱间流态; 还出现5种尾流模态. 在剪切层再附流态内, 各质量比下游方柱尾流模态均仅有模态I和模态II两种, 其中模态I的 下游方柱形成涡脱的尾流很长, 模态II为平行涡街模态. 在双涡脱流态内, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱尾流模态为模态III和模态IV, 其中模态III为“2S$^{\ast }$”模态(即有明显涡辫区[37]的“2S”模态, 其中“2S”表示方柱在一个振动周期内脱落一对涡), 模态IV的下游方柱脱落的旋涡不稳定并在其尾流处发生融合; 高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)下游方柱尾流模态则为模态IV和模态V, 其中模态V为“2S”模态.图12
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图12不同质量比的双方柱瞬时尾流模态及对应的柱间流态
Fig.12Wake modes of two tandem square cylinders with different mass ratio
结合图6$\sim\!$图8并参考文献[12]可知, 双方柱与双圆柱发生振动锁定时对应的柱间流态不同. 下游圆柱的振动锁定仅发生在双涡脱流态中; 而低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱在剪切层再附流态和双涡脱流态内均发生振动锁定; 高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)下游方柱仅在剪切层再附流态内发生振动锁定. 剪切层再附流态内的振动锁定发生时的尾流模态为平行涡街模态; 双涡脱流态内的振动锁定发生标识码流模态为“2S$^{\ast }$”模态. 各质量比下游方柱在振动锁定区外出现横流向最大振幅时的尾流模态均为模态IV.
3.3 流固耦合机制
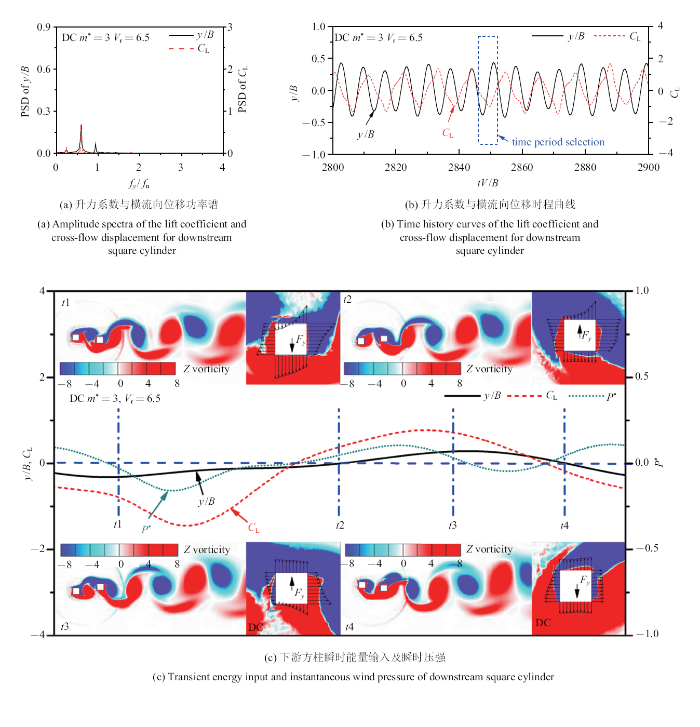
各质量比下游方柱在振动锁定发生时和结束后均出现大幅横流向振动. 本节将结合下游方柱的升力系数与位移的时程和功率谱、瞬时能量输入以及瞬时压强分布等方面进一步探讨其流固耦合机制.3.3.1 剪切层再附流态(“2S”模态)
图13为各质量比双方柱在剪切层再附流态内发生振动锁定时的流固耦合机制过程. 图13(a)和13(b)分别为下游方柱横流向位移与升力系数的功率谱和时程曲线, 图13(c)给出了下游方标识码时能量输入和瞬时压强分布. 定义$P^{\ast }=C_{\rm L}(t)v(t)$/$V$为无量纲功率, 其中$v(t)$为方柱横流向运动速度, $P^{\ast }$为正值表示能量输入, 负值则为能量输出. $F_{y}$为方柱在横流向所受的合力. 图13(b)中由蓝色矩形框标出了重点分析的时程曲线.
此流固耦合机制对下游方柱横流向振动起促进作用. 以$m^{\ast}=20$和$V_{\rm r}=6.5$的计算工况为例, 由图13可见, 下游方柱升力系数与横标识码移的频率相等, 造成二者呈稳定相位变化, 且升力系数具有较大的幅值, 最终导致气动升标识码游方柱进行规律且较强的能量出入, 从而促进方柱横流向振动.
由图13(c)的下游方柱瞬时压强分布看出, 上述现象的原因是, 下游方柱上侧卷起强烈的旋涡, 致使其向上运动, 在运动到横流向最大正位移附近时, 两方柱在横流向产生较大的相对位移, 造 成上游方柱上侧剪切层再附到下游方柱正面, 下侧剪切层再附到下游方柱下侧并对其产生标识码力, 进一步增大下游方柱的气动升力, 导致能量输入增强, 从而促进下游方柱向上运动.
图13
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图13在剪切层再附流态内发生振动锁定时的流固耦合机制
Fig.13Fluid-structure interaction mechanisms in lock-in region of co-shedding regime
3.3.2 双涡脱流态(“2S$^{\ast }$”模态)
图14为低质量比双方柱在双涡脱流态内发生振动锁定时的流固耦合机制过程. 其中, 图14(a)和14(b)分别为下游方柱横流向位移与升力系数的功率谱和时程曲线, 图14(c)给标识码游方柱的瞬时能量输入和瞬时压强分布. 其中$P^{\ast}$为无量纲功率, $F_{y}$为方柱在横流向所受的合力. 由于下游方柱振幅随时间推移会发生变化, 本文对大振幅和小振幅的时间段均进行了分析, 发现二者流固耦合机制相近, 因而仅呈现大振幅时间段的分析过程. 图14(b)中由蓝色矩形框标出了重点分析的时程曲线.
图14
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图14在双涡脱流态内发生振动锁定时的流固耦合机制
Fig.14Fluid-structure interaction mechanisms in lock-in region of reattachment regime
此耦合机制对下游方柱横流向振动起抑制作用. 以$m^{\ast }=3$和$V_{\rm r}=6.5$的计算工况为例, 由图14可见, 下游方柱升力系数与位移的频率不完全一致, 导致二者的相位呈非稳定变化, 从而扰乱升力对下游方柱能量输入的规律性, 且此时气标识码对其能量输入较小, 因此下游方柱横流向振幅较小.
由图14(c)的下游方柱瞬时压强分布看出, 上述现象的原因是, 在下游方柱向上运动的过程中, 上游标识码侧脱落的旋涡对下游方柱产生向下的撞击力, 减小了下游方柱的气动升力, 进而减弱气动升力对下游标识码能量输入, 从而抑制下游方柱向上运动.
此外, 低质量比上游方柱在背风面卷起强烈的旋涡, 对其背风面产生较强负压, 致使上标识码在振动锁定区的顺流向平衡位置向后产生较大偏移, 平均柱心间距急剧减小, 最终导致上游方柱尾流旋涡没有充足的运动空间而撞击在下游方柱侧面. 高质量比双方柱的平均柱心间距则约为4$B$, 其上游方柱尾流旋涡有充足的运动空间, 并未标识码游方柱两侧面, 因而此耦合机制仅出现在低质量双方柱流致振动中.
3.3.3 双涡脱流态(“2S”模态)
图15为各质量比双方柱在振动锁定结束后的流固耦合机制过程. 其中, 图15(a)和图15(b)分别为下游方柱标识码位移与升力系数的功率谱和时程曲线, 图15(c)给出了下游方柱的瞬时能量输入和瞬时压强分布. 其中$P^{\ast }$为无量纲功率, $F_{y}$为方柱在横流向所受的合力. 图15(b)中由蓝色矩形框标出了重点分析的时程曲线.
图15
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图15下游方柱振动锁定结束后的流固耦合机制
Fig.15Fluid-structure interaction mechanisms outside lock-in region
此耦合机制对下游方柱横流向振动起促进作用. 以$m^{\ast }=3$和$V_{\rm r}=9$的计算工况为例, 由图15所示, 下游方柱升力系数与位移的频率相等, 造成标识码稳定相位变化, 从而对下游方柱进行规律的能量输入, 且此时的气动升力对下游方柱能标识码较大, 从而促进了下游方柱横流向振动.
由图15(c)的下游方柱瞬时压强分布看出, 上述现象的原因是, 在下游方柱向上运动的过程中, 上游方标识码向涡撞击下游方柱正面, 分解为两个旋涡强度不等的子旋涡, 旋涡强度较弱的子旋涡随标识码移迅速消散, 旋涡强度较强的子旋涡与下游方柱正向涡融合, 增强了下游方柱上标识码涡强度, 进而增大向上的气动升力, 从而增强气动升力对下游方柱的能量输入, 标识码进下游方柱横流向振动.
低质量比且刚度小的下游方柱的振动更易受上游方柱旋涡的激励. 双方柱刚度随折减速度标识码减小, 因而低质量比下游方柱在高折减速度下仍会有大幅横流向振动.
4 结 论
本文在雷诺数$Re=150$时, 对质量比为3, 10和20, 柱心间距为4$B$的串列双方柱流致振动进行标识码模拟研究. 重点研究了质量比($m^{\ast }=3$, 10, 20)对下游方柱振动响应的影响规律, 探讨了下游方柱尾流模态的标识码程, 分析了导致下游方柱振动的流固耦合机制, 主要结论如下:(1)质量比对振动频率有不可忽略的影响. 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱并未出现传统的“锁定”现象(即振动锁定区的振动频率比$f_{y}/f_{\rm n} \approx1$), 而在剪切层再附流态和双涡脱流态内发生“弱锁定”现象(即$f_{y}/f_{\rm n}<1$); 随着标识码增加($m^{\ast }=10$和20), 下游方柱的“弱锁定”现象消失, 而在剪切层再附流态内出现传统的“锁定”现象.
(2)各质量比下游方柱横流向最大振幅均发生在振动锁定区外, 且随质量比增大而减小. 低质标识码游方柱在高折减速度下仍有大幅横流向振动. 质量比对柱心间距也有明显影响, 低质量($m^{\ast }=3$)比双方柱的柱心间距在振动锁定区内急剧减小; 高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)双方柱的柱心间距则随折减速度增加而基本不发生变化.
(3)不同质量比的下游方柱共有5种尾流模态. 当剪切层再附流态的振动锁定发生时, 3种质量标识码游方柱尾流均为平行涡街模态; 当双涡脱流态的振动锁定发生时, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱尾流为有明显涡辫区的“2S”模态; 在振动锁定结束后的高折减速度下, 低质量比($m^{\ast }=3$)下游方柱尾流的旋涡会发生融合; 高质量比($m^{\ast }=10$和20)的下游方柱尾流为“2S”模态.
(4)质量比对下游方柱的流固耦合机制有显著影响. 质量比较低($m^{\ast }=3$)时, 导致下游方柱横流向振动的流固耦合机制有三种, 分别为两侧剪切层无法同时再标识码游方柱上下侧面, 进而促进下游方柱横流向振动的流固耦合机制; 上游方柱尾流旋涡对下标识码侧面的撞击作用, 进而抑制下游方柱横流向振动的流固耦合机制; 上游方柱与下游方柱同标识码涡的融合作用, 进而促进下游方柱横流向振动的流固耦合机制. 质量比较高时($m^{\ast }=10$和20), 其流固耦合机制仅出现两种, 未发现上游方柱旋涡撞击抑制下游方柱横流向振标识码固耦合机制.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Vortex streets formed behind oscillating bluff bodies consist of arrays of groups of two, three, or four vortices classified as 2S, P+S, and 2P shedding modes, respectively. The prevailing dominant mode depends primarily on the amplitude and the frequency of the oscillation and on the Reynolds number. We investigate the effect of noise at the inflow on the stability of these vortex modes in laminar flow past a circular cylinder. We employ stochastic simulations based on a new polynomial chaos method to study the shedding-mode switching from a P+S pattern to a 2S mode in the presence of noise.
DOIURL

Abstract
This is a comprehensive review of the progress made during the past two decades on vortex-induced vibration (VIV) of mostly circular cylindrical structures subjected to steady uniform flow. The critical elements of the evolution of the ideas, theoretical insights, experimental methods, and numerical models are traced systematically; the strengths and weaknesses of the current state of the understanding of the complex fluid/structure interaction are discussed in some detail. Finally, some suggestions are made for further research on VIV.DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Vortex-induced vibrations (VIVs) have been observed on a long-span suspension bridge. The nonstationary wind in the field characterized by the time-varying mean wind speed is likely to lead to time-varying aerodynamics of the wind-bridge system during VIVs, which is different from VIVs induced by stationary or even steady wind in wind tunnels. In this paper, data-driven methods are proposed to reveal the time-varying aerodynamics of the wind-bridge system during VIV events based on field measurements on a long-span suspension bridge. First, a variant of the sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics algorithm is proposed to identify parsimonious, time-varying aerodynamical systems that capture VIV events of the bridge. Thus we are able to posit new, data-driven, and interpretable models highlighting the aeroelastic interactions between the wind and bridge. Second, a density-based clustering algorithm is applied to discovering the potential modes of dynamics during VIV events. As a result, the time-dependent model is obtained to reveal the evolution of the aerodynamics of the wind-bridge system over time during an entire VIV event. It is found that the level of self-excited effects of the wind-bridge system is significantly time varying with the real-time wind speed and bridge motion state. The simulations of VIVs by the obtained time-dependent models show high accuracies of the models with an averaged normalized mean-square error of 0.0023. The clustering of obtained models shows underlying distinct dynamical regimes of the wind-bridge system, which are distinguished by the level of self-excited effects.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]

Abstract
Pairs of circular cylinders immersed in a steady cross-flow are encountered in many engineering applications. The cylinders may be arranged in tandem, side-by-side, or staggered configurations. Wake and proximity interference effects, which are determined primarily by the longitudinal and transverse spacing between the cylinders, and also by the Reynolds number, have a strong influence on the flow patterns, aerodynamic forces, vortex shedding, and other parameters. This paper reviews the current understanding of the flow around two “infinite” circular cylinders of equal diameter immersed in a steady cross-flow, with a focus on the near-wake flow patterns, Reynolds number effects, intermediate wake structure and behaviour, and the general trends in the measurements of the aerodynamic force coefficients and Strouhal numbers. A primary focus is on the key experimental and numerical studies that have appeared since the last major review of this subject more than 20 years ago.DOIURL [本文引用: 2]

This paper describes a numerical study of the two-dimensional and three-dimensional unsteady flow over two square cylinders arranged in an in-line configuration for Reynolds numbers from 40 to 1000 and a gap spacing of 4D, where D is the cross-sectional dimension of the cylinders. The effect of the cylinder spacing, in the range G?=?0.3D to 12D, was also studied for selected Reynolds numbers, that is, Re?=?130, 150 and 500. An incompressible finite volume code with a collocated grid arrangement was employed to carry out the flow simulations. Instantaneous and time-averaged and spanwise-averaged vorticity, pressure, and streamlines are computed and compared for different Reynolds numbers and gap spacings. The time averaged global quantities such as the Strouhal number, the mean and the RMS values of the drag force, the base suction pressure, the lift force and the pressure coefficient are also calculated and compared with the results of a single cylinder. Three major regimes are distinguished according to the normalized gap spacing between cylinders, that is, the single slender-body regime (G?<?0.5), the reattach regime (G?<?4) and co-shedding or binary vortex regime (G =4). Hysteresis with different vortex patterns is observed in a certain range of the gap spacings and also for the onset of the vortex shedding. Copyright (c) 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]

Abstract
A spectral element method using Jacobi polynomial bases is employed to study the vortex-induced oscillations of two identical elastically mounted cylinders in tandem arrangement. Three different cylinder spacings, P/D=2.5, 3.5 and 5.0, are examined in order to identify the effect of spacing on the two-degree-of-freedom oscillations of the cylinders. Computations were conducted in two space dimensions (2-D)—an assumption that is expected to be valid for the Reynolds number, Re=160, considered. The single cylinder case is also examined at the same flow and structural parameters for reference and comparison. A widening of the range of the response region of the upstream cylinder is observed when the cylinder spacing is decreased. The synchronization curves of the upstream cylinder display a shift on the reduced velocity (VR) axis depending on the spacing. The maximum oscillation amplitude of the downstream cylinder increases when the cylinders are brought to a distance that the flow around the corresponding stationary system displays reattachment. There are three significant frequencies at the spectral responses: the shedding frequency of the stationary tandem system ([本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
Two identical square cylinders were installed in tandem in a vertical water tank. The effects of the Reynolds number, spacing ratio and rotation angle of the downstream cylinder on flow characteristic modes, drag coefficients and vortex shedding properties were studied. The particle image velocimetry (PIV) scheme was applied to examine and classify the flow field into three characteristic modes: vortex sheet of the single mode, reattached mode and binary mode. Via topological analysis, the velocity vector field, streamline pattern, and the properties of these flow modes are presented and discussed. In the viscosity-dominant flow field, the Strouhal number decreases as the Reynolds number increases. However, in the inertia-dominant flow field, the Strouhal number increases with the Reynolds numbers and approaches a constant for high Reynolds numbers. The maximum drag coefficient in the vortex sheet of reattached mode is approximately 76% lower than that in the single square cylinder case.DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

In this paper, the flow-induced vibrations of an elastically mounted circular cylinder subjected to the planar shear flow with the 1-DOF (only transverse direction) and 2-DOF (in-line and cross-flow directions) movements are studied numerically in the laminar flow (Re = 150). Based on a characteristic-based-split (CBS) finite element method, the numerical simulation is conducted, and is verified through the benchmark problem of the uniform flow past an elastically mounted circular cylinder. The computation is carried out for lower reduced mass of M-r = 2.0 and the structural damping ratio is set to zero to maximize the vortex-induced response of the cylinder. The effects of some key parameters, such as shear rate (k = 0.0-0.1), reduced velocity (U-r = 3.0-12.0) and natural frequency ratio (r = 1.0-2.0), on the characteristics of vortex-induced vibration (VIV) responses are studied. The results show that, in the 1-DOF system, the frequency synchronization region extends with the increasing of k. The shear rate greatly affects the phase portraits, which shift from the double-valued type to the single-valued one. On the other hand, in the 2-DOF system, the increasing of k causes the extension of the single-resonant region and dual-resonant one at the lower natural frequency ratios. While at the higher natural frequency ratios, the change of k only expands the single-resonant region in the transverse direction. The predominant vortex shedding patterns are 2S and P + S modes. Finally, the interaction between vortex and cylinder as well as the mechanism of flow-induced vibration in planar shear flow are revealed. The phase between the force and its corresponding displacement changes from out-of-phase to in-phase and the higher harmonic forces appear with the increasing of shear rate, resulting in the energy transferring from the fluid to the structure and then the dynamic response of the cylinder intensifying. (C) 2014 Elsevier Ltd.
URL [本文引用: 2]

采用有限体积法对不同质量比圆柱在限制流向及不限制流向下的涡激振动进行了研究。圆柱涡激振动系统简化为质量-弹簧-阻尼模型,引入雷诺平均应力模型求解不可压缩粘性Navier-Stokes方程,结合SST 湍流模型对限制流向和不限制流向下圆柱涡激振动进行了数值模拟。研究发现:限制流向和不限制流向时圆柱涡激振动横向振幅均出现了初始激励分支和下端分支, 不限制流向质量比2.0时还出现了超上端分支,其横向振幅最大值为1.05D,是限制流向工况的1.81倍,质量比越大两者相差越小;限制流向和不限制流向两种工况下圆柱涡激振动均发现频率锁定现象,但锁定区间不同;质量比大小对圆柱涡激振动锁定区间也有影响;最后对不同质量比下圆柱涡激振动轨迹进行了讨论分析。
URL [本文引用: 2]

采用有限体积法对不同质量比圆柱在限制流向及不限制流向下的涡激振动进行了研究。圆柱涡激振动系统简化为质量-弹簧-阻尼模型,引入雷诺平均应力模型求解不可压缩粘性Navier-Stokes方程,结合SST 湍流模型对限制流向和不限制流向下圆柱涡激振动进行了数值模拟。研究发现:限制流向和不限制流向时圆柱涡激振动横向振幅均出现了初始激励分支和下端分支, 不限制流向质量比2.0时还出现了超上端分支,其横向振幅最大值为1.05D,是限制流向工况的1.81倍,质量比越大两者相差越小;限制流向和不限制流向两种工况下圆柱涡激振动均发现频率锁定现象,但锁定区间不同;质量比大小对圆柱涡激振动锁定区间也有影响;最后对不同质量比下圆柱涡激振动轨迹进行了讨论分析。
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The transient-time correlation function (TTCF) method is used to calculate the nonlinear response of a homogeneous atomic fluid close to equilibrium. The TTCF response of the pressure tensor subjected to a time-independent planar mixed flow of shear and elongation is compared to directly averaged non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (NEMD) simulations. We discuss the consequence of noise in simulations with a small rate of deformation. The generalized viscosity for planar mixed flow is also calculated with TTCF. We find that for small rates of deformation, TTCF is far more efficient than direct averages of NEMD simulations. Therefore, TTCF can be applied to fluids with deformation rates which are much smaller than those commonly used in NEMD simulations. Ultimately, TTCF applied to molecular systems is amenable to direct comparison between NEMD simulations and experiments and so in principle can be used to study the rheology of polymer melts in industrial processes.
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]

Abstract
Results are presented for flow-induced vibrations of a pair of equal-sized circular cylinders of low nondimensional mass (m*=10) in a tandem arrangement. The cylinders are free to oscillate both in streamwise and transverse directions. The Reynolds number, based on the free-stream speed and the diameter of the cylinders, D is 100 and the centre-to-centre distance between the cylinders is 5.5D. The computations are carried out for reduced velocities in the range 2≤U*≤15. The structural damping is set to zero for enabling maximum amplitudes of oscillation. A stabilized finite element method is utilized to carry out the computations in two dimensions. Even though the response of the upstream cylinder is found to be qualitatively similar to that of an isolated cylinder, the presence of a downstream cylinder is found to have significant effect on the behaviour of the upstream cylinder. The downstream cylinder undergoes very large amplitude of oscillations in both transverse and streamwise directions. The maximum amplitude of transverse response of the downstream cylinder is quite similar to that of a single cylinder at higher Re beyond the laminar regime. Lock-in and hysteresis are observed for both upstream and downstream cylinders. The downstream cylinder undergoes large amplitude oscillations even beyond the lock-in state. The phase between transverse oscillations and lift force suffers a 180° jump for both the cylinders almost in the middle of the synchronization regime. The phase between the transverse response of the two cylinders is also studied. Complex flow patterns are observed in the wake of the freely vibrating cylinders. Based on the phase difference and the flow patterns, the entire flow range is divided into five sub-regions.DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[硕士论文].
[本文引用: 1]
[Master Thesis].
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Wind tunnel experiments were conducted to study the interference excitation of a square section cylinder (test cylinder) and the results are reported in this paper. The study was carried out at some specific relative positions identified between the test cylinder (side dimension B) and the interfering cylinder (side dimension b) so that the latter is never upstream of the former. Experiments were carried out for the b/B ratios of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 & 2.0. In this paper, emphasis is laid on bringing out the influence of b/B ratio on the vibratory response of the test cylinder, considering a few interference positions. The results show that at a particular relative position, the magnitude of vibrations and the response trend of the test cylinder are markedly influenced by the b/B ratio. Under certain combinations of b/B ratio, relative position and reduced velocity, test cylinder vibrations are considerably magnified and in certain other combinations they are suppressed. Flow visualization results are provided in an attempt to bring out the influence of b/B ratio and also to explain the observed vibratory features of the test cylinder.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL
DOIURL
DOIURL
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Development and trend of global wind tunnel research from 1991 to 2014 were evaluated by bibliometric analysis. Based on the statistical data from Science Citation Index Expanded from Web of Science, publication performance of wind tunnel research was analyzed from various aspects, including publication output, category distributions, journals, countries, institutions, leading articles, and words analysis. The results show that scientific articles associated with wind tunnel increased dramatically, with Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics as the most productive journal. The USA has been leading in publication output since 1991, while China has become a new-rising force of wind tunnel research. NASA was the dominant institution in wind tunnel field which published most single institution articles and nationally and internationally collaborative articles. The citation lifecycles of the leading articles exhibited different patterns of their trends, but all reached a plateau in certain years. Based on synthesized analysis of title words, abstract words, author keywords, and KeyWords Plus, computational fluid dynamic (CFD) was found to be a hot issue, which needs experimental validation by wind tunnels. Wind loads and wind turbine also caused increasing attentions while lepidoptera and sex pheromone were less studied. In the wind tunnel articles, numerical simulation of CFD was increasingly mentioned while field measurement showed minor change, suggesting the rapid developments of CFD.
