HTML
--> --> -->In this paper, we analyze the
This article is organized as follows. In Sec. 2, we present the theoretical formalism used in the calculations. Numerical results and discussion are presented in Sec. 3, followed by a summary in the last section.
$ \begin{split}(a) \quad K^+ p \to pK^{*+}( \to K^0 \pi^+), \\ (b)\quad K^+ n \to pK^{*0}( \to K^+ \pi^-). \end{split} $  |
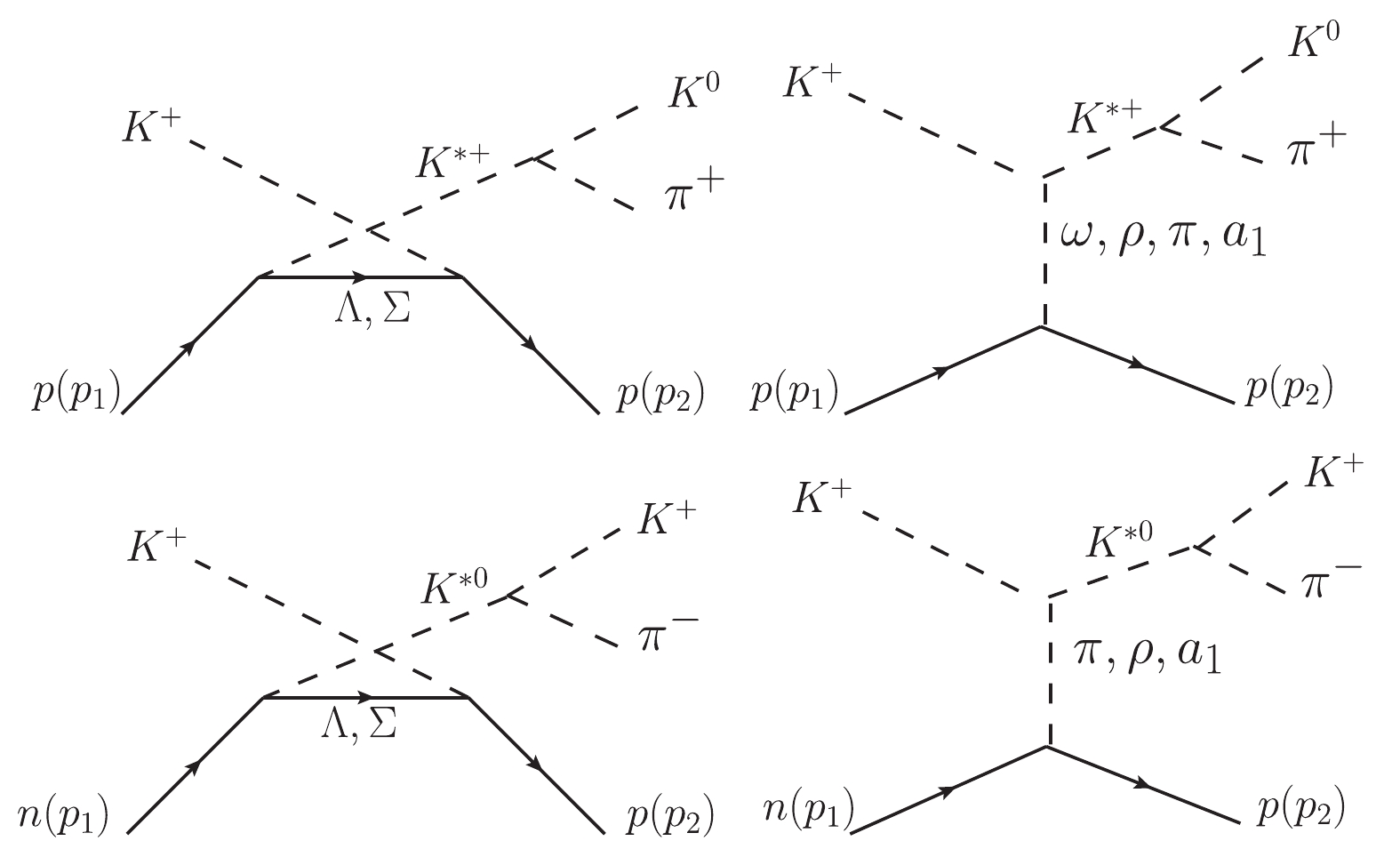 Figure1. Model of the reactions
Figure1. Model of the reactions $ \begin{split} {\cal L}_{K^* K \pi} = & {\rm i} G_V\{(\partial_\mu{\bar{K}})\vec{\tau}K^{*\mu}\cdot\vec{\pi} -{\bar{K}}\vec{\tau}K^{*\mu}\cdot(\partial_\mu\vec{\pi})\}+{h.c.}, \end{split} $  | (1) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal L}_{K^* K V} =& g_{K^*K V}\varepsilon^{\mu\nu\alpha\beta} (K^-\partial_{\alpha}K^{*+}_\beta\partial_{\mu}V_\nu \\ & +K^+\partial_{\mu}K^{*-}_\nu\partial_{\alpha}V_\beta), \end{split} $  | (2) |
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_{NNV} = -g_{NNV}\bar{N}\left(\gamma_\mu-\dfrac{k_V}{2 m_N}\sigma_{\mu\nu}\partial^\nu\right)V^\mu N , \end{array} $  | (3) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal L}_{NY K^*} = -g_{NY K^*}\bar{N}\left(\gamma_\mu Y K^{*\mu}-\frac{\kappa_{Y}}{2m_N}\sigma_{\mu\nu}Y\partial^{\nu}K^{*\mu}\right) +{h.c.}, \end{split} $  | (4) |
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_{NYK} = -g_{NYK}\bar{N}\gamma_5 Y K+{h.c.}, \end{array} $  | (5) |
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_{NN\pi} = -{\rm i} g_{NN\pi}\bar N \gamma_5 \vec{\tau}\cdot\vec{\pi} N, \end{array} $  | (6) |
$ \begin{split} \sigma_{\mu\nu} = \frac{\rm i}{2}(\gamma_\mu\gamma_\nu-\gamma_\nu\gamma_\mu). \end{split} $  | (7) |
| vertex | CD-Bonn model [24] | |
g[  |   | |
  | 15.85(0.0) | 1.5 |
  | 3.25(6.1) | 1.31 |
  | 13.07 | 1.72 |
Table1.Parameters of the N-N-meson vertices.
| vertex |   | Ref. | vertex | g(  | Ref. |
  | 7.45 GeV?1 | [25] |   | ?13.24 | [21] |
  | 7.45 GeV?1 | [25] |   | 3.58 | [21] |
  | 3.02 | [26] |   | ?4.26 (2.66) | [27] |
  | ?2.46 (?0.47) | [27] |
Table2.Coupling constants of the K*-K-meson and K*(K)-N-Y vertices used in this work.
The general invariant scattering amplitude for the reactions under study can be written as
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal M}_i = \bar u(p_2)\; {\cal A}_i\; u(p_1), \end{array} $  | (8) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal A}_V =& \sqrt{2}G_V\; g_{NNV}g_{KK^*V} \frac{-p^{K^0}_\nu+p^{\pi^+}_\nu}{p_{K^*}^2-m_{K^*}^2+{\rm i} m_{K^*}\Gamma}\varepsilon^{\mu\nu\alpha\beta} \\ &\times p^{K^*}_\mu p^V_\alpha\frac{1}{p_V^2-m_V^2} \left(\gamma_\beta-{\rm i} \frac{k_V}{2m_N}\sigma_{\beta\gamma}p^\gamma\right), \end{split} $  | (9) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal A}_Y =& {\rm i} \sqrt{2}G_Vg_{YNK}g_{K^*NY}\gamma_5(-p^\alpha_{\pi^+}+p^\alpha_{K^0}) \frac{{\not\!\!\!p }_Y+m_Y}{p^2_Y-m^2_Y} \\&\times \frac{-g_{\mu\alpha}+\frac{p_\mu^{K^*}p_\alpha^{K^*}}{m^2_{K^*}}}{p^2_{K^*}-m^2_{K^*}+im_{K^*}\Gamma} \left(\gamma^\mu-{\rm i}\frac{\kappa_{Y}}{2m_N}\sigma^{\mu\nu}p_\nu^{K^*}\right), \end{split} $  | (10) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal A}_P =& g_{NNP}\sqrt{2}G_V g_{K^*KP}(p_{K^0}^\mu-p_{\pi^+}^\mu) \\ &\times \frac{-g_{\mu\nu}+\frac{p^{K^*}_\mu p^{K^*}_\nu}{p_{K^*}^2}}{p_{K^*}^2-m_{K^*}^2+{\rm i} m_{K^*}\Gamma}\cdot\frac{p_{k^+}^\nu-p_P^\nu}{p_P^2-m_P^2}\gamma_5, \end{split} $  | (11) |
To take into account the finite extension of hadrons, we also introduce the form factors in the amplitudes. For the N-N-meson vertex, we adopt the form factors used in the Bonn model [24],
$ \begin{array}{l} F^\alpha_N(q_{\rm ex}^2,M_{\rm ex}) = \dfrac{\Lambda_\alpha^2-M_{\rm ex}^2}{\Lambda_\alpha^2-q_{\rm ex}^2}\, , \end{array} $  | (12) |
$ \begin{split} F_Y(q_{\rm ex}^2,M_{\rm ex}) = {\Lambda^4_Y\over \Lambda^4_Y+(q_{\rm ex}^2-M_{\rm ex}^2)^2}\, , \end{split} $  | (13) |
$ \begin{array}{l} F^\alpha_{K^*}(q_{\rm ex}^2,M_{\rm ex}) = \dfrac{{\Lambda^{*}_\alpha} ^2-M_{\rm ex}^2}{{\Lambda^{*}_\alpha}^2-q_{\rm ex}^2}\, . \end{array} $  | (14) |
The differential cross-section for this reaction can be represented by
$ \begin{split} {\rm d}\sigma =& {m_N \over 4F}\sum\limits_{s_i}\sum\limits_{s_f}|{\cal M}|^2{m_N {\rm d}^3p_2 \over E_2}{{\rm d}^3p_{K} \over E_{K}}{{\rm d}^3p_{\pi} \over E_{\pi}} \\ & \times\delta^4(p_1+p_{K^+}-p_2-p_{K}-p_{\pi}), \end{split} $  | (15) |
The spin density matrix elements (SDMEs) of
$ \begin{split} \rho_{ { {{mm'}}}} = \frac{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{ { {{s_i,s_f}}}}M(K^+p_{ { {{s_i}}}}\to K^*_{ { {{m}}}}p_{ { {{s_f}}}})M^*(K^+p_{ { {{s_i}}}}\to K^{*}_{ { {{m'}}}}p_{ { {{s_f}}}})}{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{ { {{s_i,s_f,m}}}}|M(K^+p_{ { {{s_i}}}}\to K^{*}_{ { {{m}}}}p_{ { {{s_f}}}})|^2},\\ \end{split} $  | (16) |
$ \begin{split} {\cal M} =& {\cal M}_\omega + {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\pi} {\cal M}_\pi+ {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\rho} {\cal M}_\rho + {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\Lambda} {\cal M}_\Lambda \\&+ {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\Sigma} {\cal M}_\Sigma+ {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_{a_1}} {\cal M}_{a_1}, \ \end{split} $  | (17) |
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal M} = 2{\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\pi}{\cal M}_\pi+2 {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\rho} {\cal M}_\rho+ {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\Lambda} {\cal M}_\Lambda - {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_\Sigma} {\cal M}_\Sigma+2 {\rm e}^{{\rm i}\phi_{a_1}} {\cal M}_{a_1}, \ \end{array} $  | (18) |
2
3.1.Model I
In this section, we only consider the  |   |   |   |   |
  |   |   |   | 5.18 |
Table3.Fit results for the parameters in Model I.
The fit results for the angular distributions and SDMEs are shown by the black dashed lines in Fig. 2, which shows that the model gives just a rough description of the experimental data. It is interesting to compare our results with previous studies. In Ref. [13], the authors analyzed the
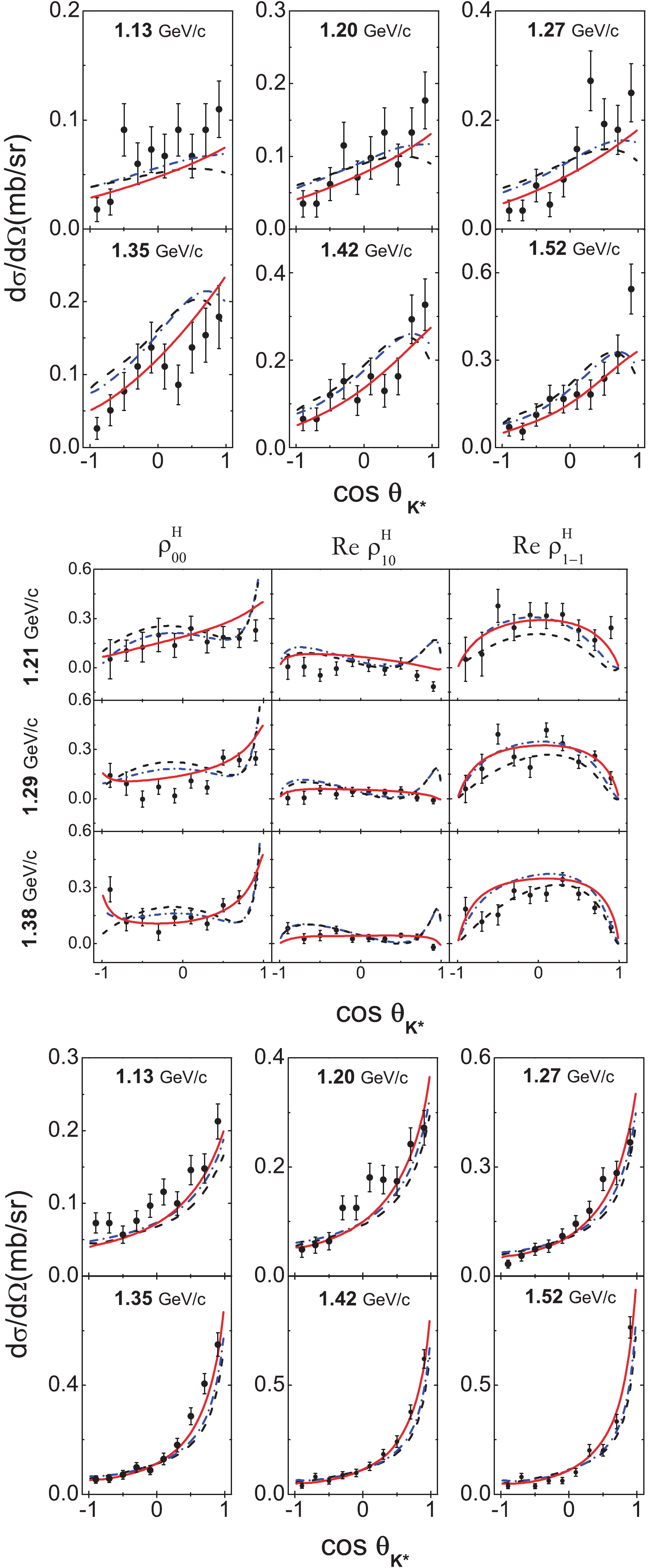 Figure2. (color online) Fit results for the angular distributions (top) and SDMEs (middle) of
Figure2. (color online) Fit results for the angular distributions (top) and SDMEs (middle) of To illustrate why the present model cannot reproduce the data very well, we study the contribution of the individual Feynman diagrams. In Fig. 3 and Fig. 4, we plot the angular distributions and SDMEs of
 Figure3. (color online) Contribution of the individual meson exchange diagrams in the
Figure3. (color online) Contribution of the individual meson exchange diagrams in the 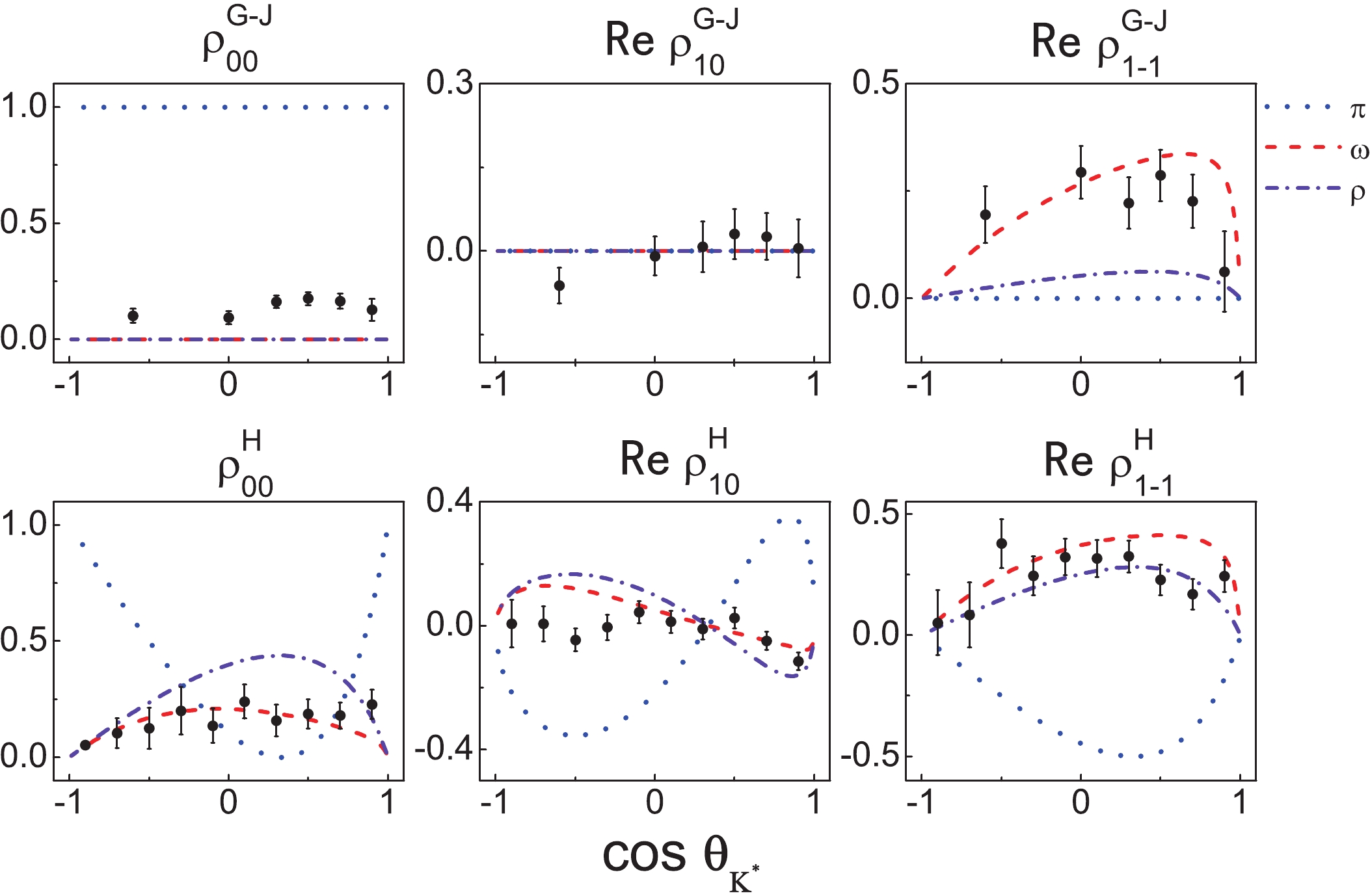 Figure4. (color online) Density matrix elements induced by the individual diagrams for pK+ = 1.2 GeV and the experimental data [31].
Figure4. (color online) Density matrix elements induced by the individual diagrams for pK+ = 1.2 GeV and the experimental data [31].2
3.2.Model II
In Model I, it was shown that by only considering theWe include the contribution of these new diagrams in two steps to show their effect on improving the model. First, we only include the hyperon exchange diagrams (Model IIA). In this case, to evaluate the amplitudes, the coupling constants and cutoff parameters of the
| parameter | value | parameter/GeV | value |
  | 1.18±0.16 |   | 0.65±0.01 |
  | 0.56±0.22 |   | 2.50±0.13 |
  | 3.20±0.14 |   | 1.69±0.07 |
  | 5.10±0.12 |   | 0.52±0.01 |
  | 1.11±0.03 |
Table4.Fit parameters obtained with Model IIA (
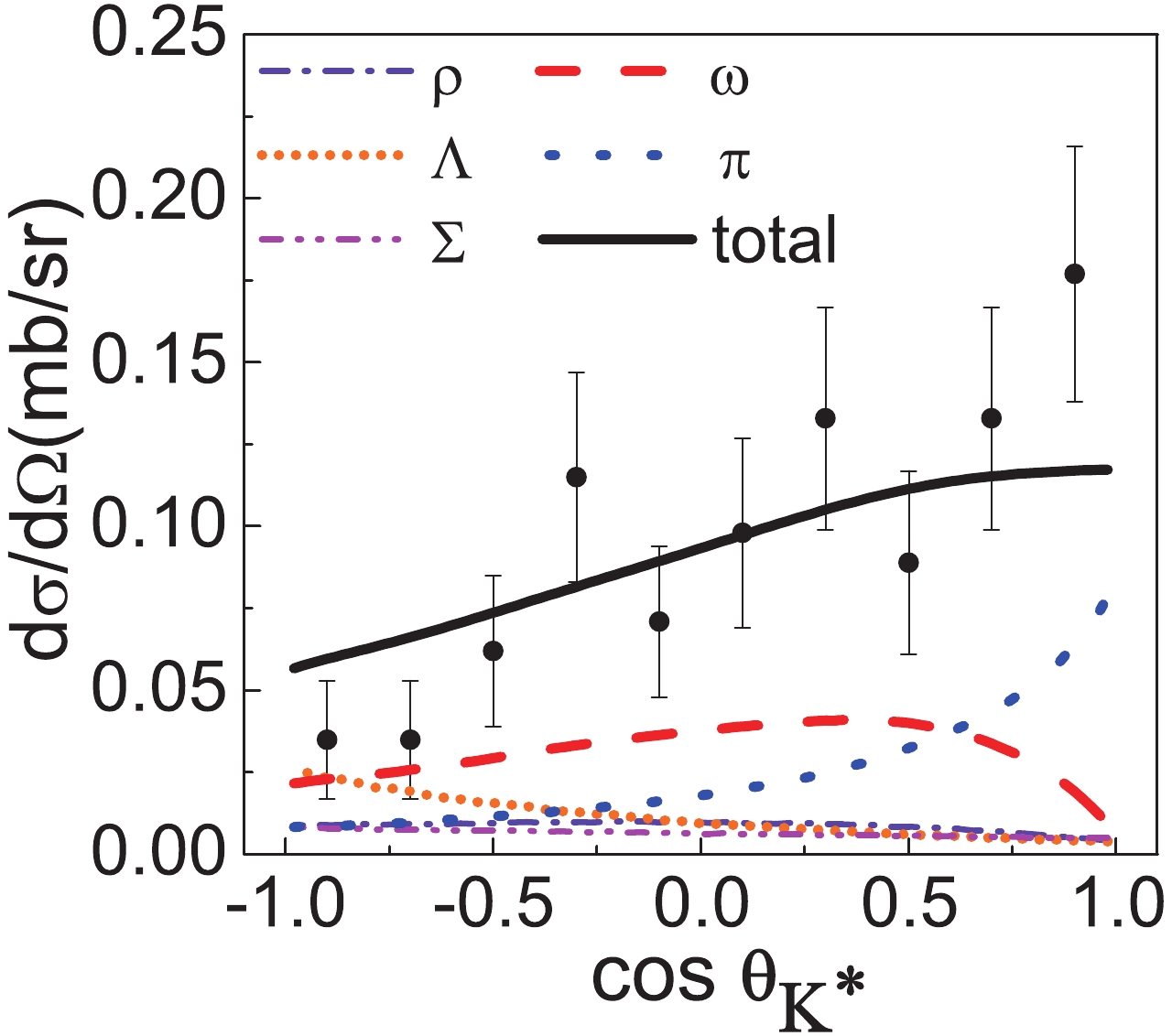 Figure5. (color online) Contribution of the individual diagrams in the
Figure5. (color online) Contribution of the individual diagrams in the As a next step, we include the contribution of the
| parameter | value | parameter | value |
  | 2.06±0.19 |   | 2.04±0.08 |
  | 2.79±0.14 |   | 1.48±0.09 |
  | 2.44±0.19 |   | 0.55±0.04 |
  | 2.05±0.40 |   | 1.04±0.05 |
  | 3.86±0.15 |   | 0.58±0.02 |
  | 3.59±0.76 |   | 2.50±0.11 |
  | 18.26±2.23 |
Table5.Fit parameters obtained with Model IIB (
The individual contributions in Model IIB are shown in Fig. 6. It is found that in this model the
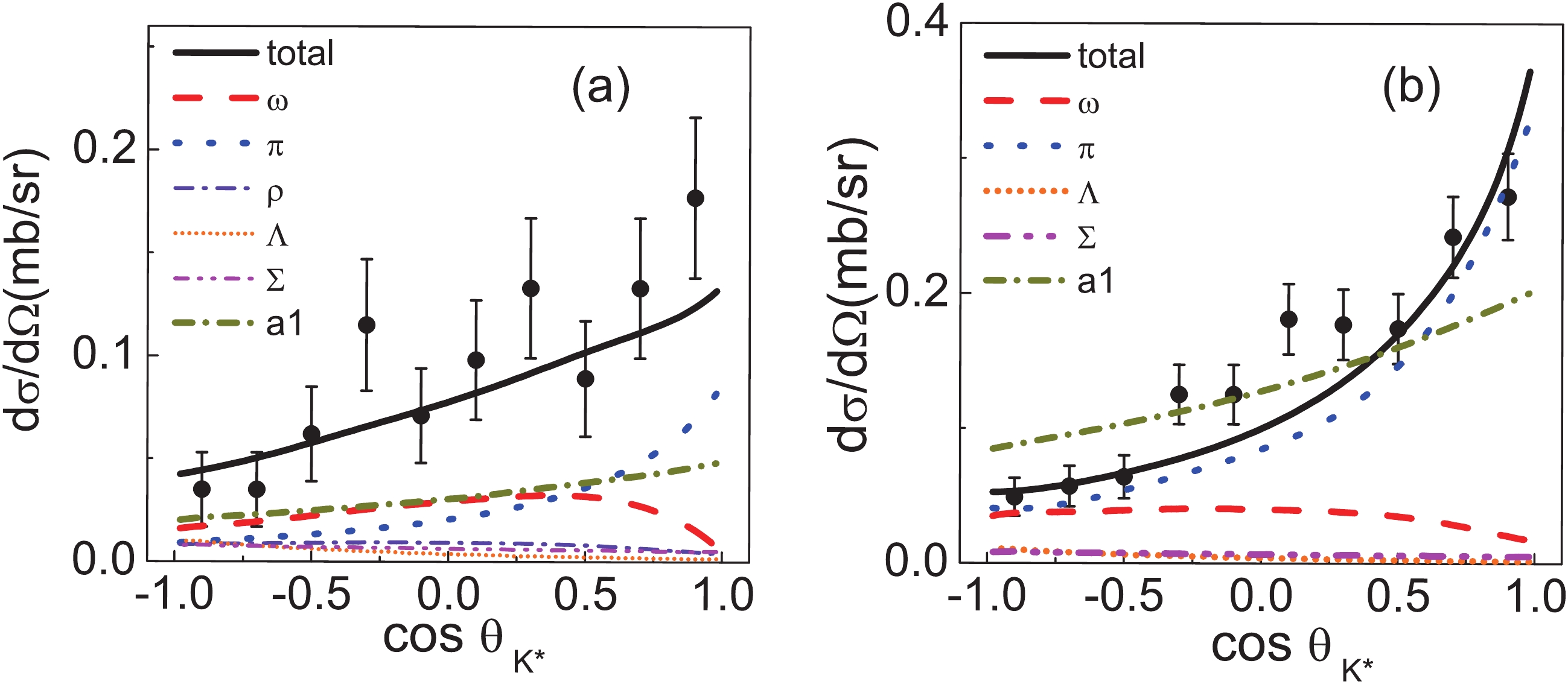 Figure6. (color online) Contribution of the individual diagrams in the reactions
Figure6. (color online) Contribution of the individual diagrams in the reactions It is interesting to note that compared to
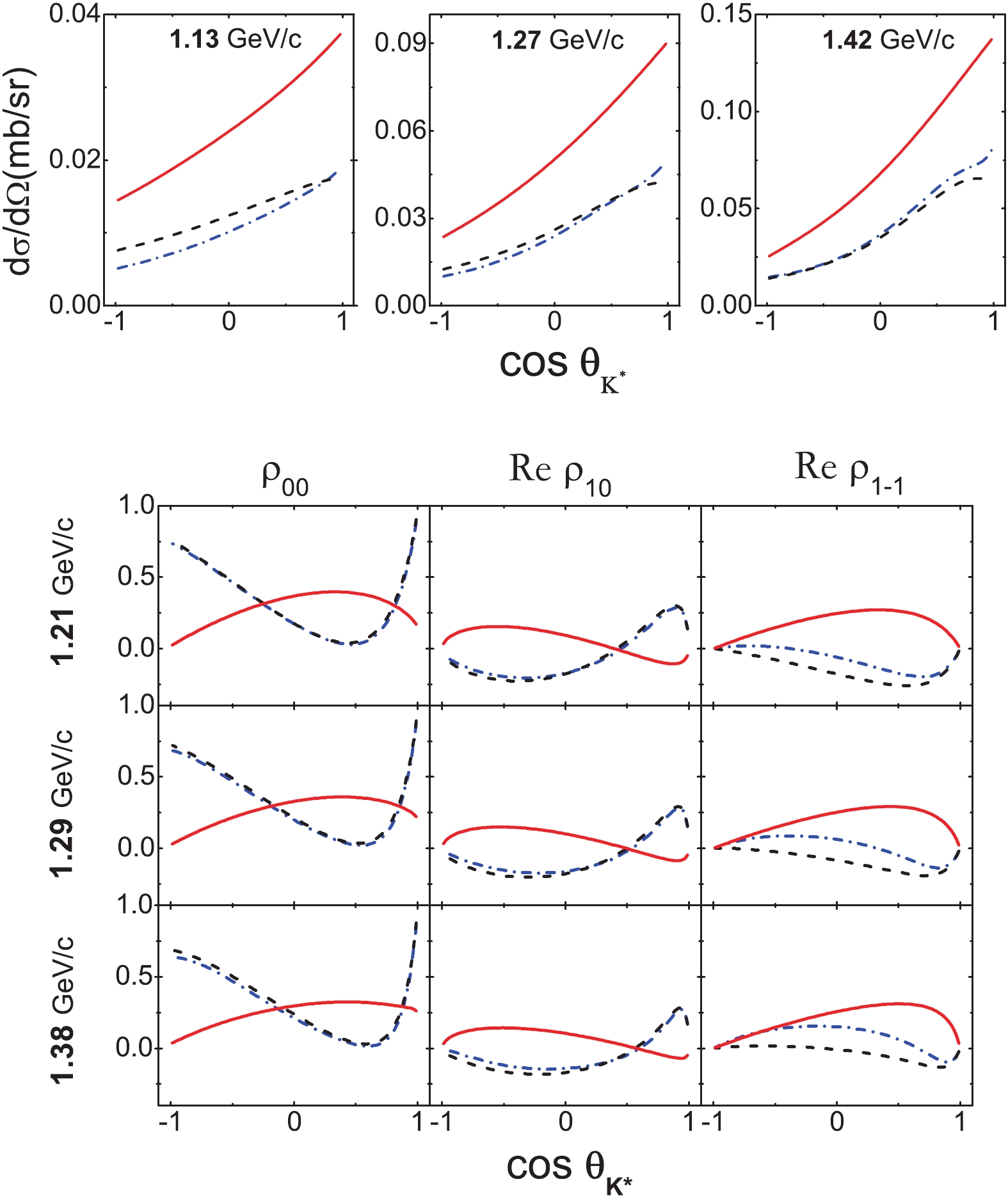 Figure7. (color online) Predictions of the angular distributions and SDMEs (Helicity frame) of
Figure7. (color online) Predictions of the angular distributions and SDMEs (Helicity frame) of $\tag{A1} \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_{NNa_1} = g_{NNa_1}\bar{N}\gamma_\mu \gamma_5 N a_1^\mu . \end{array} $  |
The Lagrangian for the
$\tag{A2} \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_{a_1KK^*} = \frac{g_{a_1KK^*}}{\sqrt{2}}({\cal L}_1 \cos\theta_{a_1}+{\cal L}_2 \sin\theta_{a_1}) , \end{array} $  |
$ \begin{array}{l} {\cal L}_1 = \partial^\nu \bar{K} a_1^\mu K^*_{\mu\nu}+h.c.,\\ {\cal L}_2 = \bar{K} \partial^\mu a_1^\nu K^*_{\mu\nu}+h.c., \end{array} $  |
$\tag{A3} \begin{split}{{\cal A}_{{a_1}}} =&{ - \sqrt 2 {G_V}{g_{{a_1}NN}}{g_{{a_1}K{K^*}}}\frac{{ - {g_{\mu \nu }} + \frac{{{p_{{K^*},\mu }}{p_{{K^*},\nu }}}}{{p_{{K^*}}^2}}}}{{p_{{K^*}}^2 - m_{{K^*}}^2 + {\rm i}{m_{{K^*}}}\Gamma }}}\\&\times{\left[ {\left( {p_{{K^*}}^\alpha p_K^\nu {\rm cos}\theta + p_{{K^*}}^\alpha p_{{a_1}}^\nu {\rm sin}\theta } \right)\frac{{ - {g_{\alpha \beta }} + \frac{{{p_{{a_1},\alpha }}{p_{{a_1},\beta }}}}{{p_{{a_1}}^2}}}}{{p_{{a_1}}^2 - m_{{a_1}}^2}}} \right.}\\&{\left. { {\left. { - ({p_{{K^*}}} \cdot {p_K}{\rm cos}\theta + {p_{{K^*}}} \cdot {p_{{a_1}}}{\rm sin}\theta } \right)\frac{{ - {g_{\nu \beta }} + \frac{{{p_{{a_1},\nu }}{p_{{a_1},\beta }}}}{{p_{{a_1}}^2}}}}{{p_{{a_1}}^2 - m_{{a_1}}^2}}} } \right]}\\&\times{( - p_{{\pi ^ + }}^\mu + p_{{K^0}}^\mu ){\gamma _\beta }{\gamma _5}.}\end{split}$  |
Since
$\tag{A4} \begin{split} \Gamma_{a_1\to KK^*} =& \frac{1} {\pi^2}\int {\rm d}s_{ { {{a_1}}}} {\rm d}s_{ { {{K^*}}}} \\ &\times {\rm Im}\left(\frac{1}{s_{ { {{K^*}}}}-M_{ { {{K^*}}}}^2+{\rm i}M_{ { {{K^*}}}}\Gamma_{K^*}}\right) {\rm Im}\left(\frac{1}{s_{ { {{a_1}}}}-M_{ { {{a_1}}}}^2+{\rm i}M_{ { {{a_1}}}}\Gamma_{ { {{a_1}}}}}\right) \\ &\times\Gamma_{ { {{a_1KK^*}}}}(\sqrt{s_{ { {{a_1}}}}},\sqrt{s_{ { {{K^*}}}}}) \Theta(\sqrt{s_{ { {{a_1}}}}}-\sqrt{s_{ { {{K^*}}}}}-M_{ { {{K}}}}), \end{split} $  |
$\tag{A5} \begin{array}{l} \Gamma_{a_1KK^*} = \frac{q}{12\pi M_A^2}\sum|M_{a_1\rightarrow KK^*}|^2 \end{array} $  |
$\tag{A6} \begin{array}{l}\left(\frac{\Lambda_{a_1}^2}{\Lambda_{a_1}^2+|s_A-m_{a_1}^2|}\right)^2\cdot \left(\frac{\Lambda_{K^*}^2}{\Lambda_{K^*}^2+|s_V-m_{K^*}^2|}\right) \end{array} $  |
To obtain the results presented in the text, we use









