 , 周天航, 蔡顺, 陈硕, 刘毓阳, 陈美君
, 周天航, 蔡顺, 陈硕, 刘毓阳, 陈美君上海师范大学旅游学院地理系,上海 200234
The sedimentary record of Datong volcano eruption and its active stages
HUXiaomeng , ZHOUTianhang, CAIShun, CHENShuo, LIUYuyang, CHENMeijun
, ZHOUTianhang, CAIShun, CHENShuo, LIUYuyang, CHENMeijun收稿日期:2017-02-20
修回日期:2017-07-11
网络出版日期:2017-09-30
版权声明:2017《地理学报》编辑部本文是开放获取期刊文献,在以下情况下可以自由使用:学术研究、学术交流、科研教学等,但不允许用于商业目的.
基金资助:
作者简介:
-->
展开
摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
-->0
PDF (3125KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章收藏文章
本文引用格式导出EndNoteRisBibtex收藏本文-->
1 前言
火山活动是第四纪时期发生在大同盆地中的三个主要地质地貌事件之一(另两个是湖退—湖侵、古人类活动)[1-5]。在西自大同县陈庄—聚乐堡一线、东至神泉堡,北自阳高县下深井、南到六棱山山前这一东西长约30 km、南北宽约20 km的区域,共分布着31座大小不一的火山(图1)。早自20世纪30年代始,研究者们就开始关注这些火山的发生年代及其活动阶段性[6]。然而由于每位研究者所使用的测年手段不同,采集测年样品的层位不同(同一个火山往往有多期火山活动且每期又有多次火山喷发),已测出的区域火山年代数据、甚至是同一火山年代数据差异很大,尚不能清晰显示其活动的阶段性[7-11]。火山是地壳运动的一种形式,其活动在时间上应有活跃期和平静期之分。区域火山喷发会喷出大量玄武岩质的火山砾(渣)、火山砂、火山灰以及熔浆,颜色呈灰黑色。粗的火山砾(渣)、火山砂及熔浆会在火山口附近降落或停止运动,细的火山灰物质可随风漂移到远处降落。大同盆地第四纪期间长期为湖泊所占据形成大同古湖;区域的沉积特征显示,区内南区的火山一般位于湖水之中,北区的火山大多是处在当时湖岸之上的。因此,火山活跃期在区域湖相沉积和黄土沉积中都会留下其活动遗迹。本文拟根据大量的野外调查资料,从区域火山活动的湖相沉积和黄土沉积记录入手,查明和分析其活动期次;在此基础上,利用古地磁法、黄土—古土壤序列法对各活跃期的年代进行判定,以揭示其阶段性历史。
2 区域概况和研究方法
2.1 区域概况
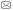
大同盆地是上新世开始形成的一断陷盆地,近东西向延伸。大同火山群位于盆地的东部,其南侧为六棱山,北侧是小北山。山地与盆地之间由正断层分界;盆地内部也发育了众多正断层,分割盆地产生了很多次级断块[2]。盆地内的断层走向有NE向、NW向、近EW向等,其中火山大多位于两组断层的交汇处。相对于南北两侧山地,整个盆地断块的沉降是不对称的,南部沉降幅度显著大于北部。这使得南部的地势低于北部,第四纪期间南部长时期为湖泊环境,而北部为气下环境(图1)。桑干河流淌于盆地的南部。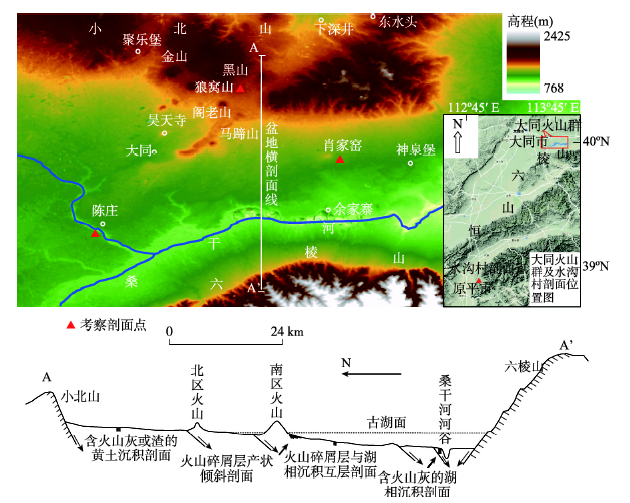 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1大同火山群区地貌及横剖面略图
-->Fig. 1The sketch map showing the landform and the cross section of Datong volcanic area
-->
2.2 研究方法
针对区域第四纪沉积环境的特点,为探查火山活动在区域湖相沉积和黄土沉积中的记录,研究团队野外选定了一些出露较完全的剖面。在盆地西南部选择了当时处在古湖深处、后由桑干河深切而出露的陈庄剖面;在盆地中部选择了当时处在湖滨及近岸附近的肖家窑火山东沟剖面;在盆地东北部选择了一直处在气下环境的黑山火山东南沟剖面。野外对剖面一方面进行沉积构造的调查分析,另一方面进行磁化率、化学成分、粒度和古地磁等样品的采集。磁化率、化学成分、粒度样按10 cm间距采集;古地磁样按1 m间距采集,关键层位加密至30 cm间距。磁化率等样品在室内经自然风干后,再轻微碾磨称重、备样、测定。磁化率的测试是使用Bartington MS2型磁化率仪对每个样品进行3次质量磁化率测试,取其算术平均值。粒度分析时,砾石和砂样品用过筛法测量,粉砂及黏土样品用LS13320型激光粒度分析仪测量。化学成分的测试是在Innov-X便携式X射线荧光光谱仪上完成。古地磁样品的测试是采用热退磁法,用TD-48型热退磁炉按50 ℃间距在100 ℃~650 ℃温度段中进行12步系统退磁;用美国2G-Enterprises公司生产的超导磁力仪对剩磁强度和方向进行测定。为保证古地磁测试结果的精度和可信度,本文对剖面进行了两次系统采样并进行统一测定(2015年取样品55块、2016年取123块)。
3 区域湖相沉积和黄土沉积剖面特征
3.1 肖家窑火山东沟剖面特征
本文调查了肖家窑火山锥东侧一羊尾沟沟头和沟口处的两个剖面点(40o01′57.3″N,113o46′33.2″E)。沟头处的剖面点位于火山锥的坡麓附近(海拔约1047 m),这里过去曾为大同古湖北侧的湖滨地带,每次火山喷发落入湖中的碎屑物都会在湖滨波浪作用下形成分选好、水平层理发育的碎屑沉积层。沟口处的剖面点(海拔约1025 m)在上一个剖面点以东600 m处,位处当时的古湖近岸地带,湖水有一定深度;这里也沉积了多套肉眼可识别的火山碎屑物,只不过粒度稍细、厚度变薄。3.1.1 沟头处剖面 一次火山喷发所产生的火山砾(渣)、火山砂、火山灰等碎屑物落入湖中经波浪分选后再沉积,会产生一套典型的韵律特征层。特征层的下半部为粒度较细的火山砂沉积,上半部为粗粒度的火山砾(渣)沉积(图2a)。特征层之下或之上与另一较早或较晚的火山喷发特征层之间是薄层灰绿色的粉砂黏土层,厚度7~40 cm,其中夹有零星的小块火山砾(渣)。这套韵律特征层可为本文提供判别火山喷发次数的线索。在一个火山活跃期内往往有多次火山喷发,形成多套这样的特征层叠加。特征层的形成机理如下。① 一次火山喷发后,火山砂粒度虽细但密度大,会最先沉积下来。② 火山砾(渣)粒度虽粗但气孔构造发育,因而密度低,落入湖中时往往是悬浮的;只有经过一段时间,火山砾(渣)中的气孔被水渗入或火山砾(渣)表面吸附一些黏土粉砂物质后,才会密度加大沉积下来;少数气孔特别发育的砾(渣)甚至会在水中悬浮很长时间后,才随后期的湖相粉砂黏土层一起沉积下来。
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2肖家窑火山东沟火山碎屑层沉积剖面图
-->Fig. 2The sedimentary profile of volcanic clastic layers along eastern gully of Xiaojiayao village
-->
具水平层理的火山碎屑沉积层产状都发生了倾斜,且位于底部、形成时代逾早的沉积层倾角越大(图2b)。同一活跃期内的多套特征层一般具有相同的倾角和倾向,而不同活跃期的沉积层之间往往呈角度不整合接触。根据实地测量,本文发现有4组具有不同倾角的活跃期沉积层。第一活跃期沉积层(最老的)产状是125o∠30o,出露的剖面显示其中包括3套特征层(未见底),指示该活跃期内至少有密集的3次火山喷发。第二活跃期沉积层产状是137o∠21o,其中包括6套特征层,指示该活跃期内有密集的6次火山喷发。第三活跃期沉积层产状45o∠9o,其中可见5套特征层,反映期间有密集的5次火山喷发。第四活跃期沉积层(最晚的)产状为95o∠4o,可见其中包含密集的3次火山喷发;经过该活跃期后,区域脱离了湖泊环境,火山沉积层之上接受L1黄土覆盖。火山沉积层的倾斜反映了地下岩浆喷出时,火山锥周围的地壳受岩浆顶托而发生了不等量抬升;越老的沉积层所经受的不等量抬升次数越多、抬升量越大,从而倾角也越大。
3.1.2 沟口处剖面 该剖面点距火山口稍远,但在约12 m高的剖面中仍可见四期火山碎屑层沉积(其中第一期火山碎屑层处在沟谷的沟床位置)。这里每一活跃期的碎屑层产状倾斜现象不太明显,可近似认为是水平的,但相邻两期碎屑沉积层之间是1.5~4 m厚度不等的质纯灰绿色粉砂黏土层(偶见小颗粒火山砾或渣散落其中),反映两个相邻活跃期期间的漫长火山平静期。在每一活跃期沉积层中,仍可分辨出每次火山喷发所形成的特征层及特征层之间的薄层灰绿色粉砂黏土层。图2c是该剖面中第三活跃期沉积层的微细沉积层理构造。该沉积层中每次火山喷发的特征层为细粒火山碎屑物,厚度7~11 cm,韵律变化不明显;相邻的上下碎屑层间的质纯灰绿色粉砂黏土层4~7 cm厚。特征层的数量显示该活跃期共发生过5次密集的火山喷发,与沟头处的剖面记录是一致的。
该处剖面也显示第四期火山碎屑层之上覆盖着L1黄土沉积,指示经过该活跃期后湖泊环境从这里消失。本文对剖面进行了磁化率采样分析,结果显示夹火山碎屑层的层位磁化率值非常高,达330,而不含火山碎屑层的层位该值只有60左右。
3.2 陈庄湖相沉积剖面特征
陈庄剖面(39°58′25.5"N,113°31′43.1"E)位于大同县陈庄村西侧200 m的桑干河支流沟谷中,剖面顶部海拔1007 m。该位置地处过去的大同古湖深处,接受了厚层湖相沉积(包括部分河流相沉积);出露的湖相沉积层序列厚度约42.4 m。一正断层(产状168°∠71°)横穿该剖面,错断地层,总错距达20 m。剖面顶部覆盖的L1黄土很薄,反映这里的风蚀强度很大。仔细比对上下盘对应的沉积层发现,下盘顶部多层沉积层已被剥蚀,但其下部出露了更老的沉积层。为此,本文对该剖面的采样采用如下方式:在上盘上采集年轻的沉积层(第1~16层);通过第13层、第16层两标志层连接到下盘,在下盘上继续往下采集年老的沉积层(第17~23层)。剖面的分层描述如下:1. 土黄色粉砂及黏土互层,较松软,直抵顶部地面;顶部有薄层L1黄土和耕作层,2.1 m。
2. 土黄色、锈黄色黏土层,其中夹两层淡褐色黏土层,2.2 m。
3. 杂色粉砂层、粉砂质黏土层,2.0 m。
4. 灰绿色黏土层,1.3 m(标志层)。
5. 土黄色、锈黄色黏土层,夹薄层绿黄色黏土层,1.4 m。
6. 锈黄色粉砂层,1.2 m。
7. 水平层理发育的土黄色、锈黄色黏土层,底部夹薄层粉砂,1.8 m。
8. 浅褐色、土黄色、杂色黏土层,中间夹粘土质粉砂层,2.5 m。
9. 土黄色细砂层,较硬,3.5 m。
10. 灰绿色黏土层,0.8 m(标志层)。
11. 土黄色、淡褐色黏土层,较硬,2.4 m。
12. 水平层理发育的土黄色粘土质粉砂层,下部为浅褐色黏土层和灰色粉砂层。2.3 m
13. 黄色砂层,含砾石(粒径1~2 cm),磨圆不好;下部有薄层淡绿色粉砂层;砂层中夹黑色的粉尘条带(取2份粉尘样)。4 m(标志层)。
14. 淡红色黏土层,2.6 m。
15. 灰绿色黏土层,夹两层淡褐色黏土,3.1 m。
16. 胶结较硬的呈灰白色的钙板层,0.05 m(标志层)。
17. 淡褐色黏土层,0.7 m。
18. 灰色黏土层,1.3 m。
19. 淡红色水平层理发育的黏土层(数条淡红色条带),0.9 m。
20. 灰绿色黏土层,夹两层褐色黏土,0.8 m。
21. 粘土质粉砂层,夹两层薄层钙板层,2.5 m。
22. 上部灰绿色黏土层(胶结较硬),下部杂色黏土层(胶结好),1.5 m(标志层)。
23. 黄色砂层,其中夹有黑色的粉尘物质(取了2份粉尘样),出露厚度1.4 m,未见底。
需特别注意的是剖面第13、23层里夹有肉眼可分辨的黑色粉尘物质。图3是该剖面的磁化率、化学成分、粒度参数曲线。磁化率曲线显示,第1、9、13和23层是峰值;尤其是第9、13、23层,磁化率正异常特别显著,其平均数值逾310,比其他层位的值(平均值60)要高出一个数量级。元素Ti、Fe含量显示,整个剖面的平均浓度值分别为0.36%、2.7%,但第1、9、13和23层中的数值都比其它层位高,呈峰值状态。研究团队在肖家窑火山锥坡麓处也取了一些火山砂样品进行了磁化率、化学成分的测定,并同从第13、23层提取的4份浓度较高的黑色粉尘物质测定结果进行了比较。结果显示火山砂样品的磁化率、Ti元素含量、Fe元素含量分别为350±、2.0%、8.3%;黑色粉尘物质的对应参数数值分别是430±、1.8%、7.6%,两者具有一定的相似性。
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3陈庄剖面系列沉积参数曲线
-->Fig. 3The curve of some sedimentary parameters of Chenzhuang section
-->
平均粒径曲线显示,剖面沉积包含了4个大的韵律变化序列,反映了古湖曾经历过4次湖退—3次湖侵变化过程。4个韵律沉积层的厚度界限范围分别是第一韵律层(最早的)42.4~27.5 m、第二韵律层27.5~18.0 m、第三韵律层18.0~2.1 m和第四韵律层2.1~0 m;其中第四韵律层中没有湖侵序列,反映这次湖退后区域古湖消失,盆底出露气下。同剖面磁化率曲线比对后发现,记录湖退的粗粒度沉积序列也都是磁化率峰值层位;而指示湖侵的细粒度沉积序列,磁化率值都很低。
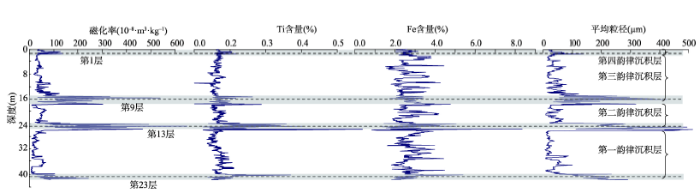
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4水沟村黄土剖面与黑山东南沟黄土剖面沉积参数曲线比较
-->Fig. 4The comparison of sedimentary parameters between Shuigoucun section and southeastern gully of Heishan
-->
4 黑山东南沟黄土剖面特征
该剖面(40o06′19.0″N,113o40′32″E,剖面顶部海拔1248 m)距黑山火山锥约1 km,是火山锥东南坡水流汇集后切割锥前黄土台地而暴露出来的。整个剖面为黄土沉积,高度近40 m,其中可见发育成熟的4条红色古土壤条带及剖面顶部一淡褐色古土壤条带。依据黄土古土壤条带的特征和序列判断,它们分别是S4、S3、S2、S1和S0(其中未见S5特征层)。在近火山锥的沟谷上游还可见在S1的上部、L1的底部有一层熔岩层夹于其间。为了诊断该剖面受火山活动影响是否产生一些沉积参数异常,本文在研究区西南距离约150 km的忻定盆地原平市境内(恒山南侧)选取了另一包含S5、S4、S3、S2和S1的黄土古土壤剖面—水沟村剖面(38o54′3.8″N,112o48′50.7″E);对两剖面分别进行了磁化率和化学成分采样,并对分析结果进行了比对。图4a、4b分别是两剖面的磁化率、Rb/Sr比值分布曲线。水沟村剖面的磁化率曲线与野外所见的黄土古土壤层位非常吻合(其中L1的上部被剥蚀了一部分;只采集了S5复合古土壤上部两个次级土壤层);Rb/Sr比值曲线也说明古土壤层形成时期风化作用较强烈,比值高,黄土层堆积时期的风化作用较弱,比值低[12]。黑山火山东南沟剖面的磁化率值普遍较低,一般小于100;与水沟村剖面相比,该剖面中磁化率峰值层位较多。除对应古土壤的层位磁化率、Rb/Sr比值为峰值外,在S3顶部或L3底部、L2底部或S2上部、L1底部或S1上部还出现了3个磁化率为峰值、但Rb/Sr比值却为谷值的层位;反映这3个磁化率为峰值的层位不是黄土强烈风化的结果。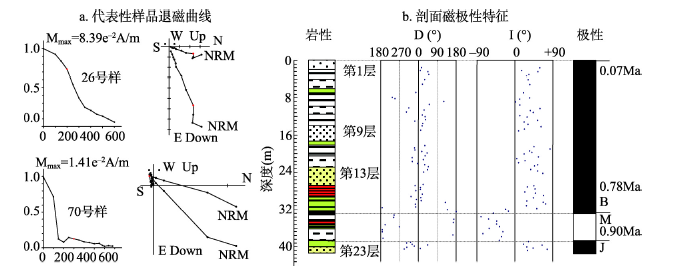 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5陈庄湖相沉积层剖面地层磁极
-->Fig. 5Magnetostratigraphic results of Chenzhuang lacustrine section
-->
5 陈庄湖相沉积剖面的年代标尺
对两次所采集的古地磁样品退磁结果显示,样品经200 ℃、300 ℃加热后基本上可消除稳定性差的次生组分,获得较可靠的原生剩磁。图5a是26号、70号样品的热退磁过程曲线。两次所采集样品的测试结果基本一致:深度0~32.6 m的样品显示为正极性,32.6~39.5 m的为负极性,39.5~42.4 m又为正极性;表明B/M界限位于深度32.6 m处,第17、18层位间,Jaramillo正极性亚带顶界位于深度39.5 m处,第21、22层位间(图5b)。考虑区域湖相沉积层之上普遍为L1黄土覆盖,本文以L1的底界年龄(0.07 Ma BP)、B/M界限年龄(0.78 Ma BP)和Jaramillo顶界年龄(0.90 Ma BP)为3个年龄控制点,并假定每一韵律沉积层的沉积持续时间正比于其厚度,则推断出每一韵律沉积层中的湖退序列开始堆积年代。第一韵律层中的湖退序列开始堆积年代要早于0.90 Ma BP,第二韵律层中的湖退序列开始于~0.47 Ma BP,第三韵律层中的湖退序列开始于~0.31 Ma BP,第四韵律层中的湖退序列开始于~0.09 Ma BP。
6 区域沉积对火山活动的记录及火山活动阶段性历史分析
6.1 区域沉积对火山活动的记录分析
在肖家窑火山东沟两剖面中,火山碎屑层特征明显指示区域火山活动曾经历过4个活跃期。在陈庄剖面中有4个层位的磁化率值特别异常,表明在湖相沉积层沉积的某些时段有一些高磁化率值的物质突然加入;第13、23层提取的高浓度黑色粉尘物质与火山锥附近的火山砂在系列特征参数上是近似的,反映它们在物源上具有相关性。而朱日祥的研究显示区域火山喷出物中的磁性矿物阻挡温度较低(约580 ℃),其类型应为磁铁矿[13];Xia等对冰岛火山的研究显示,含火山灰的一些沉积层,磁性参数常出现峰值、峰谷的变化[14]。据此,本文判断陈庄剖面中的4个高磁化率层位可能夹杂有火山灰物质,第13、23层中肉眼可见的黑色粉尘是火山灰高度富集的结果。在国内外的很多研究中都发现有一些可直接用肉眼识别的富含火山灰的剖面或层位[14-17]。陈庄剖面中4个高磁化率值的层位记录着区域过去曾有过4个火山活跃期。这与肖家窑火山东沟两剖面的记录是一致的。水沟村黄土剖面远离大同火山群,之间还有相对高差逾1000 m的恒山阻隔,且研究区盛行风向为北风或西北风,大同火山喷发后喷发物很难影响到这里;其磁化率值和Rb/Sr比值特征应是对区域过去古气候变化的正常响应。而在黑山火山东南沟黄土剖面中,除与湿热古气候阶段对应的数层古土壤层位外,仍存在3个磁化率为峰值、Rb/Sr比值为谷值的异常层位;这表明与水沟村剖面相比较在这3个层位中一定是加入了某些高磁化率值物质,整个剖面的磁化率特征曲线并不仅仅是区域过去古气候变化的结果。由此,本文推断黑山火山东南沟黄土剖面中的这3个层位磁化率异常可能是混入了火山灰物质所致,它们记录了区域3个火山活跃期。
6.2 区域火山活动阶段性历史分析
Lei的研究显示[18],大同火山群所在区域的地下深处存在明显低波速异常,指示可能存在地幔柱。虽然大同火山群中有很多不同的火山,它们的喷发年代和强度都各不相同,但在盆地地下深处为喷发提供岩浆的源头应是同一的,也就是说,区域众多火山的活动是受同一地下岩浆源头控制的。由此,地表所有的不同火山在喷发时间和强度上应该具有一定的同步性,并综合表现出区域火山活动的活跃期和平静期。陈庄湖相沉积剖面中记录火山活跃期的4个磁化率峰值层位也分别是沉积粒度较粗的湖退序列,因此,4个韵律层中的湖退序列堆积开始年代便指示着区域4个火山活跃期的开始年代。由前述可知,4个活跃期的开始年代应分别是早于0.90 Ma BP(第一活跃期)、~0.47 Ma BP(第二活跃期)、~0.31 Ma BP(第三活跃期)和~0.09 Ma BP(第四活跃期)。黑山东南沟黄土剖面记录了3个火山活跃期,层位分别在S3顶部或L3底部、L2底部或S2上部、L1底部或S1上部。根据文献[19]对黄土古土壤序列的估测年代,这几个层位的年龄分别为~0.28 Ma BP、~0.19 Ma BP和~0.07 Ma BP。对比两个剖面所记录的区域火山活跃期年代,可以发现:陈庄剖面所记录的最早两个活跃期(第一活跃期和第二活跃期)在黑山东南沟剖面中没有出现,但第三活跃期和第四活跃期与其~0.28 Ma BP和 ~0.07 Ma BP的两次记录是接近的;唯一例外的是黑山东南沟剖面中的~0.19 Ma BP这次记录在陈庄剖面中没有反映。本文判断,区域最早两个活跃期在黑山东南沟剖面中没有记录是因为该剖面的黄土出露厚度不够,只达到L5;而黑山东南沟剖面中的~0.19 Ma BP这次记录没被陈庄剖面所记录可能是因为这次火山活动强度较小且位于区域北部,陈庄剖面位处西南部的古湖深处,沉积响应不明显。
裴静娴用TL法测得黑山火山活动的年代约为19万年,中部余家寨火山年代约33万年[7]。李虎侯等采用同样方法获得盆地北部金山火山的喷发年龄为10万年左右,东部神泉堡、东北部东水头火山年龄为20万年左右,余家寨火山年龄约30万年[8]。陈文寄等利用K-Ar法对北部黑山、金山、昊天寺火山测年结果是35万年左右[9];对册田水库南边的一熔岩层测年结果是51万年左右[10]。赵华等用OSL法对东水头火山和余家寨火山的测年结果分别是8.5万年和17万年[11]。周昆叔等已识别出区域火山活动有两个活跃期:距今约20万年和距今10万年或不到10万年[20]。这些物理测年结果和识别出的活跃期与本文的火山活跃期划分时段是大致吻合的,而早于0.90 Ma BP的第一活跃期熔岩层可能是深埋地下,尚未被关注到。
此外,陈庄湖相沉积剖面所记录的4个火山活跃期都出现在区域湖退时期,平静期出现在湖侵时期。4个火山活跃期与4个区域湖退期在发生时间上的吻合可能不是巧合,反映着它们间有某种成因上的关联。文献[21]、[22]对陕(西)山(西)断陷盆地湖退—湖侵循环发生机制的阐释是对它们间成因上联系的一种解释:火山活跃期是盆地地壳深处上地幔物质强烈地向地表隆升时期,这会导致盆底地壳被抬升而引发湖退。
7 结论
依据区域湖相沉积和黄土沉积特征、古地磁测年结果及黄土古土壤序列,本文对大同火山活动的区域沉积记录和活动的阶段性历史有如下一些认识:(1)湖相沉积剖面中的磁化率显著正异常层位、黄土沉积中的高磁化率-低Rb/Sr比值层位可能是混入了大量火山灰物质;它们是区域火山活跃期的良好记录。
(2)出露的湖相沉积剖面、黄土沉积剖面和火山碎屑层产状变形等记录了区域火山活动曾经历4个活跃期,每个活跃期期间有多次密集的火山喷发。4个活跃期的开始年代大约为早于0.90 Ma BP(第一活跃期)、~0.47 Ma BP(第二活跃期)、~0.31 Ma BP(第三活跃期)和~0.09 Ma BP(第四活跃期)。黄土沉积剖面中还记录了区域北部有一个发生于~0.19 Ma BP的活跃期。
致谢:研究工作中的样品古地磁测试由南京大学地球科学与工程学院李永祥、胡旭芝两位老师帮助完成,特表谢意!感谢两位评审专家对论文的细心审阅和提出的建设性修改意见!
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | . 本文通过大同-阳原盆地古湖岸线遗迹的分析,阐述第四纪古泥河湾湖的出现、发展和消亡,指出湖泊变迁是构造运动和气候变化等因素共同作用的结果,构造运动是主要因素。 . 本文通过大同-阳原盆地古湖岸线遗迹的分析,阐述第四纪古泥河湾湖的出现、发展和消亡,指出湖泊变迁是构造运动和气候变化等因素共同作用的结果,构造运动是主要因素。 |
| [2] | |
| [3] | . The timing of early human dispersal to Asia is a central issue in the study of human evolution. Excavations in predominantly lacustrine sediments at Majuangou, Nihewan basin, north China, uncovered four layers of indisputable hominin stone tools. Here we report magnetostratigraphic results that constrain the age of the four artefact layers to an interval of nearly 340,000?yr between the Olduvai subchron and the Cobb Mountain event. The lowest layer, about 1.66 million years old (Myr), provides the oldest record of stone-tool processing of animal tissues in east Asia. The highest layer, at about 1.32?Myr, correlates with the stone tool layer at Xiaochangliang, previously considered the oldest archaeological site in this region. The findings at Majuangou indicate that the oldest known human presence in northeast Asia at 40 N is only slightly younger than that in western Asia. This result implies that a long yet rapid migration from Africa, possibly initiated during a phase of warm climate, enabled early human populations to inhabit northern latitudes of east Asia over a prolonged period. |
| [4] | . The Xujiayao site in the Nihewan Basin (North China) is one of the most important Paleolithic sites in East Asia. Twenty Homo fossils, which were previously assigned to an archaic Homo sapiens group, have been excavated along with more than 30,000 lithic artifacts and 5000 mammalian fossil specimens. Dating of the Xujiayao hominin has been pursued since its excavation in the 1970s, but its age has remained controversial because of limitations of the dating techniques that have been applied to available materials. Here, we report new ages for the Xujiayao hominin based on combined electron spin resonance (ESR) dating of quartz in the sediments and high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the fluvio-lacustrine sequence. The magnetostratigraphy suggests that the upper Matuyama and Brunhes polarity chrons are recorded at Xujiayao. The ESR dating results indicate a pooled average age of 260 370ka for the Homo -bearing layer, which is consistent with its position within the middle Brunhes normal polarity chron indicated by magnetostratigraphy. This age estimate makes the Xujiayao hominin among the oldest mid-Pleistocene hominins with derived Neanderthal traits in East Asia. This age is consistent with the time when early Denisovans, a sister group of Neanderthals, appeared and colonized eastern Eurasia. Our updated age and the Neanderthal-like traits of the Xujiayao Homo fossils, particularly the Denisovan-like molar teeth, make it possible that the Xujiayao hominin could represent an early Denisovan. |
| [5] | . 泥河湾盆地位于汾渭裂谷系的东北端,是裂谷系的重要组成部分。古近纪初恒山-大同一带发育软流圈上涌柱,导致岩浆喷发和地壳变薄,距今25~24 Ma,阳原-石匣一带开始沉陷形成盆地,北侧出现伸展造山带。受到挤压作用使盆地内地壳缩短并在盆地南侧形成台地。上新世末至早更新世为盆地沉陷最盛时期,泥河湾古湖形成。距今2.0~0.8 Ma,该地区为温和的温带气候环境,有的时段为亚热带气候,同时火山喷发的火山灰和风成沉积为盆地土壤提供了丰富矿物质养分,湖泊周边地区动植物繁盛,为早期古人类在此栖息提供了必要的条件。该裂谷型盆地是适于早期古人类生存和发展的地区,泥河湾盆地将是我国最有可能发现早期古人类化石的地点。 . 泥河湾盆地位于汾渭裂谷系的东北端,是裂谷系的重要组成部分。古近纪初恒山-大同一带发育软流圈上涌柱,导致岩浆喷发和地壳变薄,距今25~24 Ma,阳原-石匣一带开始沉陷形成盆地,北侧出现伸展造山带。受到挤压作用使盆地内地壳缩短并在盆地南侧形成台地。上新世末至早更新世为盆地沉陷最盛时期,泥河湾古湖形成。距今2.0~0.8 Ma,该地区为温和的温带气候环境,有的时段为亚热带气候,同时火山喷发的火山灰和风成沉积为盆地土壤提供了丰富矿物质养分,湖泊周边地区动植物繁盛,为早期古人类在此栖息提供了必要的条件。该裂谷型盆地是适于早期古人类生存和发展的地区,泥河湾盆地将是我国最有可能发现早期古人类化石的地点。 |
| [6] | . |
| [7] | . . |
| [8] | . . |
| [9] | . Ar is attri-buted to the surface contamination of the sample grain. . Ar is attri-buted to the surface contamination of the sample grain. |
| [10] | . 北京: 地震出版社, |
| [11] | . 对山西省大同市东水头村和于家寨两个点的第四纪火山玄武岩下伏烘烤层样品,进行了细颗粒石英光释光(OSL)测年研究。初步结果显示,对于大同火山烘烤层样品,应用简单多片OSL法能够获得有价值的火山活动年龄估计。光释光测年结果表明山西大同地区第四纪至少存在两期火山活动,一期发生的最小年龄为17万年,另一期发生在距今8.5万年左右。 . 对山西省大同市东水头村和于家寨两个点的第四纪火山玄武岩下伏烘烤层样品,进行了细颗粒石英光释光(OSL)测年研究。初步结果显示,对于大同火山烘烤层样品,应用简单多片OSL法能够获得有价值的火山活动年龄估计。光释光测年结果表明山西大同地区第四纪至少存在两期火山活动,一期发生的最小年龄为17万年,另一期发生在距今8.5万年左右。 |
| [12] | . 对洛川剖面中Rb和Sr分布规律的研究表明不同时代的黄土和古土壤中Rb和Sr分布特征存在明显差别 ,按Rb/Sr比值可以清晰地区别出剖面中的黄土层和古土壤层 ;在风化成壤过程中Rb是稳定组分 ,Sr是活动性组分 ,Rb/Sr比值的变化反映了风化成壤作用的强度 ,因而实际上记录了夏季风环流强度的大小 ;剖面中最近 80 0kaRb/Sr比值时间序列与SPECMAP十分吻合 ,揭示了全球冰量大小可能是控制夏季风环流强度变化的主要动力学因素 .更多还原 . 对洛川剖面中Rb和Sr分布规律的研究表明不同时代的黄土和古土壤中Rb和Sr分布特征存在明显差别 ,按Rb/Sr比值可以清晰地区别出剖面中的黄土层和古土壤层 ;在风化成壤过程中Rb是稳定组分 ,Sr是活动性组分 ,Rb/Sr比值的变化反映了风化成壤作用的强度 ,因而实际上记录了夏季风环流强度的大小 ;剖面中最近 80 0kaRb/Sr比值时间序列与SPECMAP十分吻合 ,揭示了全球冰量大小可能是控制夏季风环流强度变化的主要动力学因素 .更多还原 |
| [13] | . . |
| [14] | . A set of environmental magnetic parameters(i.e. magnetic susceptibility, xARM, IRMs, hysteresis loops and thermomagnetic curves) has been applied to two soil sections from SE Iceland. Results demonstrate that the main magnetic minerals in the tephras are ferrimagnetic minerals (e.g.magnetite) and canted antiferromagnetic minerals (e.g.haematite), with abundant paramagnetic material also present. Cross plots of Mrs/Ms vs. (B0)cr/(B0)c and xfd% vs.xARM/SIRM indicate that the main magnetic grain sizes in tephras are pseudo single domain (PSD) and multidomain(MD). Initial correlation of tephra layers was achieved, usingall the measured magnetic parameters, by use of the multi-variate statistical measures of Similarity Coefficient (SC) andEuclidean Distance (ED). This demonstrates that magnetictechniques can potentially assist in the identification andcorrelation of distal tephra. |
| [15] | . The synthesis of paleoclimatic archives provided by loess and alluvial sequences of central Argentina has been hindered by the lack of a cohesive lithostratigraphic framework extending across the Chaco Pampean plains and catchments of the Rios Desaguadero, Colorado, and Negro. This condition originates in part from the dearth of absolute chronological controls. The occurrence of discrete tephra layers across this region may provide an opportunity to address this deficiency if a tephrochronological framework can be established. The potential of such a project is assessed within the context of a pilot study constrained within alluvial sequences of central western Argentina proximal to potential source vents in the Southern Volcanic Zone. The intersite discrimination and correlation of tephra layers on a geochemical basis is examined, with indirect chronological control for the eruption of each generated by optical dating. Alluvial sediments on either side of each of five tephra units at a type site were dated using the optically stimulated luminescence of fine-silt-sized quartz, thus providing an age control on each tephra (ca. 24,000, 30,000, 32,000, 39,000, and 48,000 yr). The geochemical composition of each tephra was derived. Using these data, tephra layers at other sites in the study area were geochemically analyzed and in instances of statistical concordance in major oxide structure, correlated to the type site and therefore ascribed ages. This methodology identified a further sixth volcanic event between ca. 24,000 and 30,000 yr not registered by type-site tephras. The extension of this initial tephrochronological framework beyond the alluvial sequences of central western Argentina is encouraged by the occurrence of geochemically distinct tephra verified and dated in this study. |
| [16] | . This paper describes the initial stages of the development of a tephrochronology for the region of the Michoacán–Guanajuato volcanic field (MGVF) in central Mexico. There are two elements to this: the geochemical characterisation of volcanic glass and the linkage of tephra deposits to eruptions of known age. The MGVF is dominated by cinder cones and shield volcanoes which erupt only once. There are only two stratovolcanoes (multiple eruptions) which are common elsewhere in the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. Tephras were sampled from sub-aerial sites close to cones of known age and from lake sediment cores from the Zirahuén, Pátzcuaro and Zacapu basins in the State of Michoacán. Multiple samples were collected to ensure that each tephra was well represented. The glass was analysed by electron microprobe and found to be calc-alkaline in composition. SiO 2 abundances varied from 52% to 75%. Full results are available at http://www.geo.ed.ac.uk/tephra/ . The ages of the dated cones ranged from the 20th century AD to ca 17,000 14 C years BP. Tephras from eruptions of El Jabali (3840 14 C years BP), Jorullo (1759–1774) and Paricutín (1943–1952) have been identified in lake cores. These provide a means of correlating between basins and have the potential to provide a basis for understanding the volcanic history of this area and for dating a wider range of sediment sequences. |
| [17] | . Tephra-fall deposits from Cook Inlet volcanoes were detected in sediment cores from Tustumena and Paradox Lakes, Kenai Peninsula, Alaska, using magnetic susceptibility and petrography. The ages of tephra layers were estimated using 21 14C ages on macrofossils. Tephras layers are typically fine, gray ash, 1u20135u00a0mm thick, and composed of varying proportions of glass shards, pumice, and glass-coated phenocrysts. Of the two lakes, Paradox Lake contained a higher frequency of tephra (0.8 tephra/100 yr; 109 over the 13,200-yr record). The unusually large number of tephra in this lake relative to others previously studied in the area is attributed to the lake's physiography, sedimentology, and limnology. The frequency of ash fall was not constant through the Holocene. In Paradox Lake, tephra layers are absent between ca. 800u20132200, 3800u20134800, and 9000u201310,300u00a0cal yr BP, despite continuously layered lacustrine sediment. In contrast, between 5000 and 9000u00a0cal yr BP, an average of 1.7 tephra layers are present per 100 yr. The peak period of tephra fall (7000u20139000u00a0cal yr BP; 2.6 tephra/100 yr) in Paradox Lake is consistent with the increase in volcanism between 7000 and 9000 yr ago recorded in the Greenland ice cores. |
| [18] | . A high-resolution tomographic model of the upper mantle beneath the North China Craton (NCC) is determined using a large number of precisely hand-picked teleseismic P wave arrival times. The results are generally consistent with previous results but high-quality arrivals provide new insights into the dynamics beneath the NCC. Obviously north-south trending low-velocity (low-V) zones are revealed down to 300-400 km depth under the Shanxi rift and Tanlu fault zone, while a north-south trending high-velocity (high-V) zone representing the remainder of detached lithosphere is visible down to 200 km depth under the western portion of eastern NCC. High-V anomalies representing the detached lithosphere are detected at 200-400 km depth under central and eastern NCC. Under the Ordos block high-V anomalies are visible above 400 km depth, indicating intact lithosphere. Broad high-V anomalies representing the stagnant Pacific slab are imaged with a low-V anomaly from Datong volcano to the edge of Bohai Sea in the mantle transition zone beneath eastern and central NCC, suggesting that the Pacific slab has subducted to central NCC but with a gap. A continuously Y-shaped low-V structure is clearly imaged under Datong volcano and Bohai Sea from the lower mantle through this gap in the mantle transition zone to the upper mantle, indicating the existence of a lower mantle plume. These results suggest that in addition to the subduction of the Pacific plate, the plume has also played an important role in lithospheric destruction by thermal erosion of the asthenosphere and detachment of the lithosphere beneath the NCC. |
| [19] | . In this study, we analyzed the grain size of the Baoji loess-soil sequence at 10 cm intervals. Results show that grain size variations are very sensitive to loess-soil alternations, with loess units being much coarser than soils. Such a change in loess-soil grains is interpreted as the result of the glacial-interglacial cyclic variations in the intensity of the winter monsoon winds out of Siberia. The grain size record is thus employed as a proxy indicator of the winter monsoon circulation and tuned to the orbital records calculated recently by Berger and Loutre (1991) under the control of major magnetic reversals. The tuning is independent of any correlation with O signals in the deep-sea sediments. The resulting grain size time scale is tightly constrained, as suggested by the following facts: (1) the filtered obliquity and precession components from the grain size data on the orbital time scale closely match the theoretical orbital records; (2) ages of the major magnetic reversals estimated from the grain size time scale are in good agreement with the {K}/{Ar}-dated ages; (3) there is close coherence between the Baoji grain size time series and the orbital variations at the orbital frequency bands over the entire 0-2.5 Ma period; and (4) the grain size record on the orbital time scale shows a close similarity to the orbitally-tuned DSDP Site 607 and ODP Site 677 未O records. Examination of time-dependent characteristics of the grain size record suggests that there are two major shifts of dominant periodicities in the long-term monsoonal cycles, one occurring at about 0.8 Ma BP and the other around 1.7 Ma BP. |
| [20] | . . |
| [21] | . 依据汾渭地堑系列湖盆地貌与沉积特征对其阶段性演化历史进行了研究。野外调查发现,在第四纪中晚期,各湖盆内曾发生过3次大幅快速的湖退或河流强烈下切事件; 从渭河盆地至临汾太原盆地,再至大同阳原盆地,每一次事件的出现在各盆地中都有时间序次上的差异。以黄土-古土壤序列作为时间坐标系,渭河盆地中的3次湖退或河流下切分别发生在L<sub>9</sub>,L<sub>6</sub>和L<sub>2</sub>黄土堆积期; 临汾太原盆地分别发生在S<sub>8</sub>,S<sub>5</sub>和S<sub>1</sub>古土壤发育时期; 大同阳原盆地分别发生在L<sub>8</sub>,L<sub>5</sub>和L<sub>1</sub>黄土堆积期。也即是,第一次事件在几个盆地中出现的时间序次是L<sub>9</sub>-S<sub>8</sub>-L<sub>8</sub>,第二次事件是L<sub>6</sub>-S<sub>5</sub>-L<sub>5</sub>,第三次为L<sub>2</sub>-S<sub>1</sub>-L<sub>1</sub>。事件出现的时间序次差异显示: 距青藏高原越远的盆地,事件出现的时间越晚。根据早期对区域湖退-湖侵发生机制的研究成果并结合上述这些发现,本文认为正是受到青藏高原挤压隆升的影响,而非西太平洋板块俯冲的影响,才产生了区域系列湖盆第四纪中晚期地貌与沉积阶段性演化的这种时间序次差异。 . 依据汾渭地堑系列湖盆地貌与沉积特征对其阶段性演化历史进行了研究。野外调查发现,在第四纪中晚期,各湖盆内曾发生过3次大幅快速的湖退或河流强烈下切事件; 从渭河盆地至临汾太原盆地,再至大同阳原盆地,每一次事件的出现在各盆地中都有时间序次上的差异。以黄土-古土壤序列作为时间坐标系,渭河盆地中的3次湖退或河流下切分别发生在L<sub>9</sub>,L<sub>6</sub>和L<sub>2</sub>黄土堆积期; 临汾太原盆地分别发生在S<sub>8</sub>,S<sub>5</sub>和S<sub>1</sub>古土壤发育时期; 大同阳原盆地分别发生在L<sub>8</sub>,L<sub>5</sub>和L<sub>1</sub>黄土堆积期。也即是,第一次事件在几个盆地中出现的时间序次是L<sub>9</sub>-S<sub>8</sub>-L<sub>8</sub>,第二次事件是L<sub>6</sub>-S<sub>5</sub>-L<sub>5</sub>,第三次为L<sub>2</sub>-S<sub>1</sub>-L<sub>1</sub>。事件出现的时间序次差异显示: 距青藏高原越远的盆地,事件出现的时间越晚。根据早期对区域湖退-湖侵发生机制的研究成果并结合上述这些发现,本文认为正是受到青藏高原挤压隆升的影响,而非西太平洋板块俯冲的影响,才产生了区域系列湖盆第四纪中晚期地貌与沉积阶段性演化的这种时间序次差异。 |
| [22] | . 野外对临汾、太原盆地第四纪中晚期所发育的湖积地貌-沉积特征调查发现,湖盆在对应于S8、S5和S1古土壤开始发育时期(时代分别为0.77Ma BP、0.55Ma BP和0.13Ma BP)曾发生了三次强烈湖退,这三次湖退都是构造原因所致的 而在L11-S8、L8-S5、L5-S1黄土古土壤堆积发育期间(时代分别对应于0.96~0.77Ma BP、0.74~0.55Ma BP和0.47~0.13Ma BP)、以及S1古土壤发育以后的时期(时代为0.07Ma BP之后)出现的却是缓慢湖侵或盆地下沉。根据这些发现并结合地球物理学前期已获得的有关盆地深部上地幔结构及活动规律,本文提出了盆地湖侵-湖退过程的构造控制模式。在上地幔强烈上拱→减弱或渐趋稳定→再次强烈上拱的构造循环中,地表湖盆会以大幅快速湖退→缓慢湖侵→再大幅快速湖退这样的表现与之对应。盆地地表的地貌-沉积发育与地下的上地幔活动应具有因果关系。 . 野外对临汾、太原盆地第四纪中晚期所发育的湖积地貌-沉积特征调查发现,湖盆在对应于S8、S5和S1古土壤开始发育时期(时代分别为0.77Ma BP、0.55Ma BP和0.13Ma BP)曾发生了三次强烈湖退,这三次湖退都是构造原因所致的 而在L11-S8、L8-S5、L5-S1黄土古土壤堆积发育期间(时代分别对应于0.96~0.77Ma BP、0.74~0.55Ma BP和0.47~0.13Ma BP)、以及S1古土壤发育以后的时期(时代为0.07Ma BP之后)出现的却是缓慢湖侵或盆地下沉。根据这些发现并结合地球物理学前期已获得的有关盆地深部上地幔结构及活动规律,本文提出了盆地湖侵-湖退过程的构造控制模式。在上地幔强烈上拱→减弱或渐趋稳定→再次强烈上拱的构造循环中,地表湖盆会以大幅快速湖退→缓慢湖侵→再大幅快速湖退这样的表现与之对应。盆地地表的地貌-沉积发育与地下的上地幔活动应具有因果关系。 |
