 , 杨玉盛
, 杨玉盛
Application of GWR model in hyperspectral prediction of soil heavy metals
JIANGZhenlan , YANGYusheng
, YANGYusheng
通讯作者:
收稿日期:2016-09-27
修回日期:2016-12-13
网络出版日期:2017-03-15
版权声明:2017《地理学报》编辑部本文是开放获取期刊文献,在以下情况下可以自由使用:学术研究、学术交流、科研教学等,但不允许用于商业目的.
基金资助:
作者简介:
-->
展开
摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
-->0
PDF (1675KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章收藏文章
本文引用格式导出EndNoteRisBibtex收藏本文-->
1 引言
土壤是农业生产最重要的自然资源。随着农业集约化生产的发展以及城市化进程的加快,重金属通过污水灌溉、大气干湿沉降、污泥农用等途径进入土壤,重金属污染已成为当今土壤污染中污染面积最广、危害最大的环境问题之一[1-4]。解决土壤重金属污染问题首先需要摸清污染情况,2016年5月31日国务院印发关于《土壤污染防治行动计划》提出在2018年底前查明土壤污染的面积、分布[5]。高光谱遥感技术由于能同时获得精细的几乎连续的光谱,从而能够根据地物的光谱特征对地物进行反演和识别,为快速获取土壤重金属元素信息提供了新的途径[6-8]。土壤重金属高光谱预测的机理在于,高光谱遥感以其获取的连续、精细的反射光谱有可能捕捉到土壤重金属的光谱吸收特征,通过分析土壤重金属的光谱特征,筛选出土壤重金属响应的敏感波段,从而构建模型对重金属进行定量预测[9]。目前应用于高光谱土壤重金属的预测方法主要有多元线性回归[10-11]、偏最小二乘回 归[10, 12-13]、支持向量机[14]、人工神经网络[11, 15]、小波分析[16-17]、遗传算法[18]、随机森林[19]等,这些方法在特定的研究区均取得了较好的效果。但这些方法假定研究区内土壤重金属含量在不同空间位置上对光谱反射率的影响是相同的,即系数是不变的,忽视了土壤重金属含量与反射光谱之间关系的空间异质性。然而,土壤重金属元素含量由于受区域成土母质、土壤类型、地形、水文、小气候等自然因素以及城市建设、工业、农业、采矿等人为因素的影响,这些影响具有区域性和连续性,使重金属的分布表现出一定的空间变异特征[20-26]。而且,土壤光谱特征是土壤有关性质的综合反映,除重金属外,还受到土壤结构和成分、植被等环境变量影响,故在不同的研究区域,不同的位置,由于土壤类型、组分和污染水平不同,土壤重金属含量与光谱特征的关系也将发生变化[27-30],在前人研究中,关于研究区内土壤重金属含量对光谱反射率的影响是相同的假设条件与实际情况不相吻合,模型的预测精度也将受到影响。
由英国New Castle大学地理学家Fortheringham等[31]于1996年提出的地理权重回归(Geographically Weighted Regression, GWR)模型,是一种对不同空间子区域自变量和因变量之间关系随空间变化进行建模的非参数局部空间回归分析方法,被广泛应用于空间非平稳性关系探讨,已在土壤属性的空间预测中取得较好效果[32-34],但有关这类模型在土壤重金属高光谱预测研究中的应用尚未见文献报道。本文选择福建省福州市为研究区域,以土壤重金属镉(Cd)、铜(Cu)、铅(Pb)、铬(Cr)、锌(Zn)、镍(Ni)为对象,构建土壤重金属预测的GWR模型,并探讨GWR模型在区域土壤重金属高光谱研究中的适用性及局限性,为模型推广提供理论和技术支持。
2 研究区概况
研究区选择在福建省福州市。福州市地处中国东南沿海,背山面海,位于118°08′E~120°31′E、25°15′N~26°29′N之间,属于亚热带海洋性季风气候,年均温在16~20 ℃,年降水量为900~1200 mm。福州市所在地属于典型的河口盆地,盆地四周被群山峻岭包围,地貌以山地、丘陵为主,海拔多在600~1000 m之间,地势自西向东倾斜,盆地周边海拔较高处的地带性土壤为红壤。作为福建省的省会城市,福州市区内人口密度大、工农业较发达,土壤污染问题日渐突出,由于区内地形复杂破碎,使得土壤重金属在空间分布上呈现出异质性大的特点。3 数据来源及其处理
3.1 土壤样品采集和分析
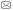
在研究区范围(除平潭县外),共采集132个0~20 cm土壤表层土样,样点分布较为均匀(图1)。采样的同时,利用手持GPS定位样点的经纬度坐标及高程。每个采样点混合后取500 g土样,经实验室风干,去除沙砾及动植物残体后研磨,过100目尼龙筛。每个样品分成两份(每份各约250 g),一份用来进行化学分析,另一份用来进行光谱分析。土壤重金属含量采用电感耦合等离子质谱(ICP-MS,美国Thermo Electron)进行测定。 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1研究区与采样点分布
-->Fig. 1Study area and sample sites
-->
3.2 土壤光谱测定及其预处理
土壤样品光谱测定采用美国ASD(Analytical Spectral Device)公司生产的地物光谱仪FieldSpec 3在室内测量,波段范围为350~2500 nm,在350~1100 nm和1000~2500 nm范围内的光谱采样间隔分别为1.4 nm和2 nm,光谱重采样后的间隔为1 nm,输出2151个波段。将经过预处理后的土样放在直径大于10 cm,深度大于5 cm的盛样器皿内,轻轻震动器皿使得土壤表面呈自然状态,以1000 W的卤光灯作为光源,采用15°的光源照射角度、15 cm的探头距离及30 cm的光源距离,从垂直于土壤表面的方向进行土壤反射光谱测量,并利用40 cm×40 cm的白板进行定标,获取绝对反射率。为消除测量的不稳定性,每个土样采集10条光谱曲线,利用ViewSpec Pro软件剔除异常曲线后取光谱反射率平均值作为样本的原始反射率光谱值[35]。光谱预处理主要包括:① 利用Savitzky-Golay平滑对曲线进行处理,以消除光谱曲线上存在的“毛刺”噪声;② 对平滑后的数据以10 nm为间隔进行算术平均运算进行重采样,得到10 nm光谱分辨率的土壤光谱反射率,以达到压缩波段,消除相邻波段间冗余信息的目的。3.3 土壤光谱变换与特征波段选取
为消除背景噪声,突出光谱的特征值,本文对土壤反射率(Reflectance, R)进行以下变换:一阶微分(First Derivative, FD)、二阶微分(Second Derivative, SD)、倒数变换(Reciprocal Transformation, RT)、倒数的一阶微分(RTFD)、倒数的二阶微分(RTSD)、倒数对数变换(吸光率,Absorbance Transform, AT)、倒数对数的一阶微分(ATFD)、倒数对数的二阶微分(ATSD)及连续统去除(Continuum Removal, CR)等。将土壤重金属含量与变换后的光谱数据进行相关分析,筛选出相关系数最大的光谱特征波段。在此基础上,以土壤重金属含量为因变量,各光谱特征值为自变量,通过逐步回归分析方法,筛选出共线性小的变量参与模型的构建。4 研究方法
GWR是由Fotheringham等[31]提出的一个空间变参数模型,是对普通最小二乘法回归(Ordinary Least Squares Regression, OLS)模型(式(1))的空间扩展,将数据的地理位置嵌入到回归参数之中,使得参数可以进行局部估计,扩展后的模型如式(2)。式中:yi为样点i的因变量;xik为第i个样点上第k个变量的观测值;
GWR模型中的
式中:
式中:Wij为由已知点j估计待测点i时的权重;dij为估算点i与样点j间的欧氏距离;h为带宽。其中带宽h由最小AIC信息准则(Akaike Information Criterion)确定。本文的GWR回归过程在Fotheringham等开发的GWR 4.0软件支持下完成,模型精度评价采用AIC准则、调节决定系数(Adj-R2)、残差平方和(RSS)等指标进行评价。此外,重金属的预测值与实测值间的相关系数、回归的调节决定系数(R2)和均方根误差也被用来比较GWR与OLS的预测效果。
5 结果分析
5.1 土壤重金属含量的统计分析
表1为福州市土壤采样实测的重金属统计特征值。从重金属的含量看,Cd均值为0.74 mg·kg-1,高于国家土壤环境质量二级标准;重金属Pb、Zn均值介于国家土壤环境质量标准的一级和二级之间;而重金属Cu、Cr和Ni则低于国家土壤环境质量一级标准[36]。说明研究区受重金属Cd的污染较为严重,受Pb、Zn元素轻度污染,受其他元素的影响则不大。从重金属的空间分布看,6种重金属的变异系数在50%~75%之间,属中等变异,说明这几种重金属在土壤中的分布不均匀,空间异质性较为显著。Tab. 1
表1
表1福州市土壤重金属描述性统计特征
Tab. 1Statistical values for measured content of soil heavy metals in Fuzhou City
| 重金属 | 最小值 (mg·kg-1) | 最大值 (mg·kg-1) | 平均值 (mg·kg-1) | 标准差 (mg·kg-1) | 偏度 (mg·kg-1) | 峰度 (mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.01 | 2.94 | 0.74 | 0.38 | 1.49 | 8.21 | 51.35 |
| Cu | 5.68 | 94.60 | 23.54 | 14.89 | 1.93 | 5.32 | 63.25 |
| Pb | 8.78 | 155.96 | 44.85 | 24.37 | 1.76 | 3.97 | 54.34 |
| Cr | 0.75 | 111.55 | 26.13 | 17.85 | 1.69 | 4.53 | 68.31 |
| Zn | 1.15 | 383.13 | 101.19 | 54.73 | 1.63 | 5.54 | 54.09 |
| Ni | 0.23 | 50.96 | 12.25 | 8.73 | 1.79 | 4.86 | 71.27 |
新窗口打开
5.2 土壤重金属含量与光谱变量的相关分析
经变换后的土壤光谱值与土壤重金属含量进行Pearson相关分析,筛选出最大相关系数及其对应的光谱特征波段如表2所示。从表2中可以看出:① 除了Pb元素与原始反射率及倒数对数变换值之间相关性不显著外,其他重金属含量与光谱变量间的最大相关系数均达到0.01的极显著性水平或0.05的显著性水平;② 不同重金属的光谱敏感特征波段是不同的,Cd、Pb、Zn元素的敏感特征波段主要在近红外波段,而Cu、Ni元素的敏感特征波段则主要在可见光波段;③ 不同光谱变换对重金属光谱特征的增强作用不尽相同,其中,倒数变换和倒数对数变换对土壤重金属光谱特征的增强作用最明显,表现为这两种变换与重金属的最大相关系数(除Cr元素外)均大于原始反射率与重金属含量间的最大相关系数;④ 对于不同重金属来说,光谱变换对Cd和Pb元素的光谱特征的增强作用最大,变换后的光谱特征值与Cd和Pb之间的最大相关系数均大于原始反射率与它们的最大相关系数。Tab. 2
表2
表2福州市土壤重金属含量与光谱变量的最大相关系数
Tab. 2Maximum correlation coefficients between soil heavy metal content and spectral variables in Fuzhou City
| 重金属 | R | FD | SD | RT | RTFD | RTSD | AT | ATFD | ATSD | CR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 特征波段 相关系数 | 1040 -0.211* | 2420 0.347** | 1990 0.329** | 1040 0.230** | 2420 -0.327** | 1990 -0.352** | 1040 0.220** | 2420 -0.345** | 1250 0.354** | 2170,2190 0.251** |
| Cu | 特征波段 相关系数 | 420 -0.478** | 470 -0.426** | 940 0.330** | 380,390,400 0.519** | 510 -0.534** | 450 0.480** | 410 0.511** | 1150 -0.371** | 410 -0.353** | 410 -0.337** |
| Pb | 特征波段 相关系数 | 2500 -0.164 | 2490 -0.212* | 1940 -0.240** | 2500 0.182* | 2500 0.234** | 2490 0.237** | 2500 0.171 | 2500 0.222** | 2490 0.218** | 1630 0.190* |
| Cr | 特征波段 相关系数 | 520 0.415** | 2230 -0.434** | 1440 0.351** | 360 0.357** | 410 -0.337** | 430 0.319** | 2010 0.411** | 1440 -0.327** | 1440 -0.327** | 2210 0.310** |
| Zn | 特征波段 相关系数 | 2240 -0.469** | 390 -0.437** | 440 0.332** | 2150,2160 0.497** | 1050 -0.359** | 2100 0.335** | 2150,2160 0.483** | 2170 -0.313** | 2080 -0.322** | 1480 0.212* |
| Ni | 特征波段 相关系数 | 2410 -0.430** | 390 -0.374** | 560 0.300** | 2470 0.438** | 480 -0.399** | 780 0.410** | 2470 0.436** | 600 0.325** | 780 0.294** | 450 -0.293** |
新窗口打开
5.3 土壤重金属预测模型的最佳光谱因子组合
为消除光谱变量间的多重共线性,以土壤重金属含量为因变量,特征波段的光谱值为自变量,利用逐步线性回归分析筛选因子的最佳组合,标准为回归结果的调节R2最大,自变量间的方差膨胀因子(Variance inflation factor, VIF)小于7.5,结果如表3所示。Tab. 3
表3
表3利用光谱变量对福州市土壤重金属进行逐步线性回归的结果
Tab. 3Results of stepwise linear regression between soil heavy metals and spectral variances in Fuzhou City
| 重金属 | 模型变量 | 调节R2 | 估计误差 | F | 显著性水平 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 常量, SD_1990, RT_1040 | 0.179 | 0.343 | 15.413 | 0.000 |
| Cu | 常量, FD_470, RT_380, RTSD_450 | 0.300 | 12.442 | 19.658 | 0.000 |
| Pb | 常量, FD_2490, SD_1940, RTSD_2490, CR_1630 | 0.141 | 22.430 | 7.781 | 0.000 |
| Cr | 常量, SD_1440, RTSD_430 | 0.226 | 15.685 | 20.170 | 0.000 |
| Zn | 常量, RT_2150, RTFD_1050 | 0.312 | 45.235 | 30.706 | 0.000 |
| Ni | 常量, RT_2470, RTFD_480 | 0.180 | 7.874 | 15.427 | 0.000 |
新窗口打开
从表3可以看出,原始反射率均未作为最佳因子出现在回归方程中,说明在土壤重金属的高光谱预测中,采用变换后的光谱特征波段参与模型构建的效果比利用原始光谱进行预测的效果要好。其中,以光谱的倒数变换在预测模型构建中的作用最为突出,分别参与了Cd、Cu、Zn和Ni元素预测模型的构建,说明倒数变换不仅有利于突出重金属的光谱特征,还可很好地提高模型预测的精度。其次为二阶微分变换和倒数变换的二阶微分,分别参与了Cd、Pb、Cr元素和Cu、Pb、Cr预测模型的构建。光谱的一阶微分变换和倒数变换的一阶微分在模型的构建中也有较好的表现,分别参与了其中两种元素的预测模型构建。而对土壤重金属光谱特征有明显增强作用的倒数对数变换,在本文的高光谱预测中则表现不佳,这说明了虽然倒数对数变换可以更好地突出土壤重金属的光谱信息,但不能提高模型预测的精度。
5.4 土壤重金属的OLS与GWR分析
为尽量保证建模样本与验证样本范围一致,将样本数据按土壤重金属含量从大到小排列,每隔两个样品取一个作为验证样本,共44个(33%),其余的88个(67%)作为建模样本。逐步回归筛选后的光谱因子作为自变量,分别利用OLS和GWR模型对重金属进行回归分析,回归的AIC、调节R2及残差平方和以及验证样本预测值与实测值回归的调节R2、均方根误差(RMSE)等统计量如表4所示。Tab. 4
表4
表4福州市土壤重金属OLS及GWR预测模型的精度检验
Tab. 4Prediction accuracy of OLS and GWR regression models in Fuzhou City
| 重金属 | 建模样本 | 验证样本 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIC | 调节R2 | 残差平方和 | 调节R2 | 均方根误差 | |||||||
| OLS | GWR | OLS | GWR | OLS | GWR | OLS | GWR | OLS | GWR | ||
| Cd | 75.807 | 78.544 | 0.181 | 0.196 | 10.986 | 10.330 | 0.167 | 0.192 | 0.302 | 0.294 | |
| Cu | 730.248 | 698.162 | 0.323 | 0.649 | 13758.666 | 4141.423 | 0.217 | 0.613 | 11.658 | 8.192 | |
| Pb | 1204.227 | 1199.618 | 0.141 | 0.216 | 64334.784 | 55866.254 | 0.083 | 0.213 | 24.700 | 22.884 | |
| Cr | 742.016 | 720.703 | 0.266 | 0.716 | 21484.197 | 5441.275 | 0.090 | 0.396 | 15.487 | 12.463 | |
| Zn | 925.785 | 916.964 | 0.281 | 0.525 | 194869.446 | 92018.520 | 0.247 | 0.456 | 39.781 | 31.934 | |
| Ni | 602.693 | 605.455 | 0.212 | 0.219 | 5406.102 | 5179.912 | 0.094 | 0.117 | 7.392 | 7.292 | |
新窗口打开
从模型的回归效果看,土壤重金属的OLS预测效果总体上不太理想,其中Cu元素的预测效果相对较好,解释度(调节R2)为32.3%,其后为Zn(解释度为28.1%)、Cr(解释度为26.6%)、Ni(解释度为21.2%),而Cd和Pb预测的解释程度则小于20%。在GWR预测模型中,则以Cr元素的预测效果最好,解释度为71.6%,其次为Cu,解释度64.9%,其后依次为Zn、Pb、Cd和Ni。
GWR方法对不同重金属预测精度的提高作用是不同的。对于Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn 4种重金属来说,GWR预测精度提高显著,表现为:Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn 4种重金属的GWR预测AIC值分别减少了32.09、4.61、21.31和8.82,均大于3(不同模型中的AIC值若能减少3个单位,认为模型有显著改善[37]),说明该4种元素的GWR方法对重金属预测的效果改善明显。其中,Cr元素的GWR预测精度提高的效果最为显著,调节R2从OLS模型的0.266提高到GWR的0.716,即利用GWR模型对Cr预测的解释程度比OLS提高了45%,为OLS模型的2.69倍,而残差平方和减少了16042.92,仅为OLS的25.33%;其次为Cu元素,GWR模型的调节R2从OLS模型的0.323提到0.649,提高了32.6%,为OLS模型的2.01倍,而残差平方和减少了9617.24,仅为OLS的30.09%。其后依次为Zn元素和Pb元素,GWR模型的解释程度比OLS分别提高了24.4%和7.5%,而残差平方和分别减少了52.78%和13.16%。对于Cd和Ni元素来说,GWR回归的调节R2较OLS模型略有增加(分别从0.181和0.212提到0.196和0.219),残差平方和略有降低(分别降低了5.97%和4.18%),但GWR的AIC值较OLS模型却略有上升(差值小于3),说明GWR模型对该两种元素预测精度改善效果不明显。
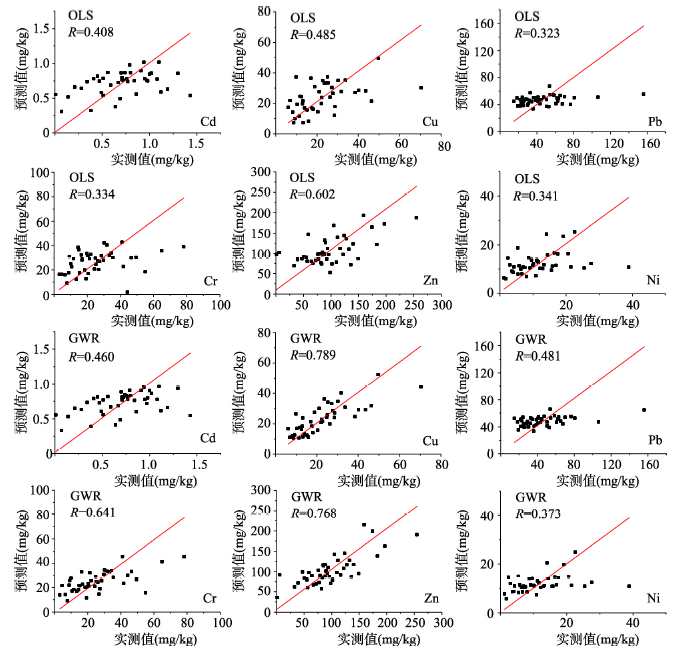
模型的验证效果也进一步证实了以上结果,Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn 4种重金属的GWR预测值与实测值回归的调节R2较OLS模型有了很大提高,而均方根误差则有明显的降低。为了更好地说明这一问题,绘制验证样本土壤重金属的OLS和GWR的预测值与实测值散点图(图2)。从图2可以直观看出,OLS模型的土壤重金属预测精度普遍不高,除了Zn预测值与实测值之间的相关系数为0.602外,其余元素的预测值与实测值之间的相关系数均小于0.5。GWR模型的预测结果与实测值的吻合程度要优于OLS模型。其中,Cu、Cr、Zn、Pb的GWR模型预测结果较OLS模型有了较大的改善,预测值与实测值之间呈现出较好的吻合度,相关系数分别为0.789、0.641、0.768和0.481,较OLS模型分别提高了0.304、0.307、0.166和0.158。但Cd和Ni的GWR模型的预测值与实测值之间的相关系数较OLS提高不明显。不论是OLS模型还是GWR模型,实测值较低时,其预测值与实测值的吻合度较好,但当实测值较大时,预测效果有所偏低(图2),说明模型的误差主要来自土壤重金属含量较高的样点,这主要是由于本文的样本点有限,采集样点的重金属含量以低值为主,而少量的高值样本点成为相对的极值样点,故其预测精度偏低。本文所构建的GWR模型可用于含量较低区域的土壤重金属预测,可推广至土壤重金属的普查工作中,在条件许可下,适当加大重金属含量较高的样本点,有利于改善模型的预测精度及适用性。
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2福州市土壤重金属含量的OLS和GWR模型的预测值与实测值散点图
-->Fig. 2Scatter plot of measured and predicted soil heavy metal contents in OLS and GWR models in Fuzhou City
-->
5.4 土壤重金属含量与光谱变量间的空间非平稳性分析
对模型参数进行统计,通过GWR模型局部参数的上四分位数(upper quartiles, UQ)与下四分位数(lower quartiles, LQ)的值范围与OLS模型全局参数的两倍标准误差(standard errors, SE)进行比较分析,判断土壤重金属与相应变量间相关关系是否存在空间非稳定性(表5)。当GWR模型变量参数的UQ-LQ值大于OLS相应变量参数的SE值两倍(2×SE)时,土壤重金属与相应光谱变量的关系存在明显的空间非平稳性,反之,则空间非平稳性不明显。Tab. 5
表5
表5福州市土壤重金属与变量间关系的空间非平稳性检验
Tab. 5Test of spatial non-stationarity of the relationship between soil heavy metal and variables in Fuzhou City
| 重金属 | 常量 | 变量1 | 变量2 | 变量3 | 变量4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UQ-LQ | SE | UQ-LQ | SE | UQ-LQ | SE | UQ-LQ | SE | UQ-LQ | SE | |||||
| Cd | 0.04 | 0.18 | 3286.93 | 2440.54 | 0.03 | 0.09 | ||||||||
| Cu | 27.71 | 11.23 | 24251.91 | 10698.67 | 2.51 | 0.82 | 15446.67 | 3914.22 | ||||||
| Pb | 252.90 | 287.82 | 1035.71 | 978.55 | 323742.57 | 155253.07 | 1329.4 | 1314.67 | 234.69 | 289.44 | ||||
| Cr | 15.78 | 3.60 | 277645.03 | 51064.04 | 6360.06 | 1981.41 | ||||||||
| Zn | 153.11 | 31.68 | 80.30 | 17.37 | 17108.15 | 6167.21 | ||||||||
| Ni | 6.39 | 5.03 | 2.39 | 2.32 | 61.63 | 70.43 | ||||||||
新窗口打开
从表5可知,Cr、Cu、Zn元素GWR预测模型各参数的UQ-LQ值均大于OLS模型的2×SE值,说明该3种重金属预测的各参数在空间上均呈现出显著的空间非平稳性;Pb元素的只有变量2(SD_1940)的UQ-LQ值大于OLS模型的2×SE值,说明只有变量SD_1940与Pb之间的关系具有显著的空间非平稳性,而其它参数则呈现出相对的空间同质性;Cd和Ni元素模型各参数的UQ-LQ值均小于OLS模型的2×SE值,该2种元素预测的各参数在空间上呈现出较强的空间同质性。
由此可见,相较于OLS模型,GWR对土壤重金属的预测精度的提高程度取决于土壤重金属与各光谱变量间关系的空间非平稳性程度,对于Cr、Cu、Zn等元素,由于模型的各光谱变量参数均具有明显的空间非平稳性,GWR模型预测效果较OLS提高显著;而对于Pb元素,仅有部分光谱变量参数具有显著空间非平稳性,GWR模型较OLS模型改善较为明显;而对于Cd和Ni等元素,由于各光谱变量参数具有相对的空间同质性特征,GWR预测效果较OLS模型则没有明显提高。
6 结论
(1)与OLS模型相比较,利用GWR模型进行土壤重金属预测,由于充分考虑了重金属与光谱变量间相关关系的空间非平稳性,对重金属的预测精度有了一定的提高。但由于GWR模型应用的前提是变量间关系的空间非平稳性,故GWR模型对土壤重金属的预测效果提高的作用大小取决于土壤重金属与各变量间相关关系的空间非平稳性程度:① 对于Cr、Cu、Zn、Pb等预测模型参数具有显著空间非平稳性的元素,GWR模型预测精度较OLS改善明显。该4种元素GWR回归的调节R2分别为OLS模型的2.69倍、2.01倍、1.87倍和1.53倍,提高至0.716、0.649、0.525和0.216;而AIC值和残差平方和则明显降低,GWR预测的AIC值为720.703、698.112、916.964和1199.618,较OLS模型分别减少了21.31、32.09、8.82和4.61,而残差平方和则分别为5441.275、4141.423、92018.520和55866.254,仅为OLS模型的25.33%、30.09%、47.22%和86.84%。② 对于Cd和Ni等预测模型参数不具有显著空间异质性的元素,GWR预测效果较OLS则改善不明显。该两种元素GWR回归的调节R2较OLS模型略有提高(分别提高了0.015和0.007),残差平方和略有下降(分别降低了5.97%和4.18%),但GWR的AIC值较OLS模型却略有上升(分别增加了2.737和2.762)。(2)由于土壤重金属含量低,反映在土壤光谱信息很微弱,直接利用原始反射光谱进行模型构建效果较差,可通过不同的光谱变换进行重金属光谱特征的增强。其中,光谱的倒数变换效果最好,不仅可以有效增强土壤重金属的光谱特征,而且该变换及其微分形式,在各重金属的预测模型构建中均有较好的表现,很好地提高土壤重金属的预测效果。而光谱的倒数对数变换,虽然可以有效地增强土壤重金属的光谱特征,但对于预测模型的构建作用却不大。
(3)由于本批采样点的重金属含量以低值为主,而少量的高值样本点成为相对的极值样点,使得实测值较低样点的预测效果好,实测值较大样点的预测值偏低,从而影响模型的预测精度。在今后的研究中,应适当加大重金属含量较高的样本点数,进一步验证该模型是否适用于含量较高区域的土壤重金属反演,为GWR模型在土壤重金属的高光谱研究中推广提供理论和技术支持。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | . ABSTRACT Both general and specific investigations of soil and crop heavy metal contamination were carried out across China. The former was focused mainly on Cd, Hg, As, Pb, and Cr in soils and vegetables in suburbs of four large cities; the latter investigated Cd levels in both soils and rice or wheat in contaminated areas throughout 15 provinces of the country. The results indicated that levels of Cd, Hg, and Pb in soils and some in crops were greater than the Governmental Standards (Chinese government limits for soil and crop heavy metal contents). Soil Cd ranged from 0.46 to 1.0465mg kg611, on average, in the four cities and was as high as 14565mg kg611 in soil and 765mg kg611 in rice in the wide area of the country. Among different species, tuberous vegetables seemed to accumulate a larger portion of heavy metals than leafy and fruit vegetables, except celery. For both rice and wheat, two staple food crops, the latter seemed to have much higher concentrations of Cd and Pb than the former grown in the same area. Furthermore, the endosperm of both wheat and rice crops had the highest portion of Cd and Cr. Rice endosperm and wheat chaff accumulated the highest Pb, although the concentrations of all three metals were variable in different parts of the grains. For example, 8.3, 6.9, 1.4, and 0.665mg kg611 of Pb were found in chaff, cortex, embryo, and endosperm of wheat compared with 0.11, 0.65, 0.71, and 0.1965mg kg611 in the same parts of rice, respectively. Untreated sewage water irrigation was the major cause of increasing soil and crop metals. Short periods of the sewage water irrigation increased individual metals in soils by 2 to 80% and increased metals in crops by 14 to 209%. Atmospheric deposition, industrial or municipal wastes, sewage sludge improperly used as fertilizers, and metal-containing phosphate fertilizers played an important role as well in some specific areas. |
| [2] | . <h2 class="secHeading" id="section_abstract">Abstract</h2><p id="">This paper reviews quite a few heavy metal contamination related studies in several cities from China over the past 10 years. The concentrations, sources, contamination levels, sample collection and analytical tools of heavy metals in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils were widely compared and discussed in this study. The results indicate that nearly all the concentrations of Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb, Zn, As, Hg and Cd are higher than their background values of soil in China. Among the cities, the contamination levels of the heavy metals vary in a large range. The geoaccumulation index shows that the contamination of Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd is widespread in urban soils and urban road dusts of the cities. Generally, the contamination levels of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd are higher than that of Ni and Cr. Agricultural soils are also significantly influenced by Cd, Hg and Pb derived from anthropogenic activities. The integrated pollution index (IPI) indicates that the urban soils and urban road dusts of the developed cities and the industrial cities have higher contamination levels of the heavy metals. The comparison of the IPIs of heavy metals in urban soils and urban road dusts of Shanghai, Hangzhou, Guangzhou and Hongkong reveals that the contamination levels of the metals in urban road dusts are higher than that in urban soils in the cities. Moreover, the main sources of the metals in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils are also different.</p> |
| [3] | . Heavy metal pollution has pervaded many parts of the world, especially developing countries such as China. This review summarizes available data in the literature (2005-2012) on heavy metal polluted soils originating from mining areas in China. Based on these obtained data, this paper then evaluates the soil pollution levels of these collected mines and quantifies the risks these pollutants pose to human health. To assess these potential threat levels, the geoaccumulation index was applied, along with the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) recommended method for health risk assessment The results demonstrate not only the severity of heavy metal pollution from the examined mines, but also the high carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks that soil heavy metal pollution poses to the public, especially to children and those living in the vicinity of heavily polluted mining areas. In order to provide key management targets for relevant government agencies, based on the results of the pollution and health risk assessments, Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Hg, As, and Ni are selected as the priority control heavy metals; tungsten, manganese, lead-zinc, and antimony mines are selected as the priority control mine categories; and southern provinces and Liaoning province are selected as the priority control provinces. This review, therefore, provides a comprehensive assessment of soil heavy metal pollution derived from mines in China, while identifying policy recommendations for pollution mitigation and environmental management of these mines. (C) 2013 Published by Elsevier B.V. |
| [4] | . |
| [5] | |
| [6] | . The aim of this study is to derive parameters from spectral variations associated with heavy metals in soil and to explore the possibility of extending the use of these parameters to hyperspectral images and to map the distribution of areas affected by heavy metals on HyMAP data. Variations in the spectral absorption features of lattice OH and oxygen on the mineral surface due to the combination of different heavy metals were linked to actual concentrations of heavy metals. The ratio of 610 to 500 nm (R |
| [7] | . A new method was put forward to assess the cadmium pollution of soil by hyperspectra technology.175 soil samples were collected using a FieldSpec 3 spectrometer in mine and factory area.All samples were divided randomly into 2 groups,one group with 135 samples used as calibration set,and another with 40 samples used as prediction set.The samples data were pretreated with the methods of wavelet denoising and standard normalization variate(SNV),and then analyzed by principal component analysis(PCA).The top 5 principal components of PCA were used as the new variables,and modeling by fisher linear discrimination,Bayes multi-types stepwise discrimination,fuzzy pattern recognition,back-propagation artificial neural network(ANN-BP) and support vector machine(SVM) algorithms.Then,the 40 unknown samples in the prediction set were predicted,and the result showed that the discriminating accuracy rate was 77.5% with the methods of fisher linear discrimination,80.0% with the method of Bayes multi-types stepwise discrimination and fuzzy pattern recognition,82.5% with the method of BP-ANN model,and 85.0% with the method of SVM model.Therefore,the feasibility of assessment the cadmium pollution of soil in rapid and non-invasive way by hyperspectra technology was proved,and PCA combined with SVM was confirmed as a preference method. |
| [8] | . Soil contamination by heavy metals is an increasingly important problem worldwide. Quick and reliable access to heavy metal concentration data is crucial for soil monitoring and remediation. Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy, which is known as a noninvasive, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly technique, has potential for the simultaneous estimation of the various heavy metal concentrations in soil. Moreover, it provides a valid alternative method for the estimation of heavy metal concentrations over large areas and long periods of time. This paper reviews the state of the art and presents the mechanisms, data, and methods for the estimation of heavy metal concentrations by the use of visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. The challenges facing the application of hyperspectral images in mapping soil contamination over large areas are also discussed. (C) 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. |
| [9] | . <p>利用高光谱遥感数据进行了南京郊外土壤重金属元素铅的含量反演,由于高光谱数据波段众多,波段选择或变换至关重要。比较了基于次贪婪的前向选择模型的最小角度拟合和基于遗传算法进行波段选择的最小二乘和偏最小二乘拟合,结果发现基于遗传算法的偏最小二乘反演结果优于全波段的偏最小二乘,表明波段选择在高光谱反演重金属中是有益的。尽管采取了波段选择后的各方法在反演时均能达到70%以上的训练精度,但因遗传算法搜索的解空间范围更宽广,使得基于遗传算法的偏最小二乘优于前向选择模型的最小角度拟合。最后还比较了基于遗传算法的普通最小二乘和偏最小二乘拟合,结果表明偏最小二乘更优,因此在高光谱反演重金属含量当中,偏最小二乘精度较高,而在波段选择方法中,遗传算法更优。</p> . <p>利用高光谱遥感数据进行了南京郊外土壤重金属元素铅的含量反演,由于高光谱数据波段众多,波段选择或变换至关重要。比较了基于次贪婪的前向选择模型的最小角度拟合和基于遗传算法进行波段选择的最小二乘和偏最小二乘拟合,结果发现基于遗传算法的偏最小二乘反演结果优于全波段的偏最小二乘,表明波段选择在高光谱反演重金属中是有益的。尽管采取了波段选择后的各方法在反演时均能达到70%以上的训练精度,但因遗传算法搜索的解空间范围更宽广,使得基于遗传算法的偏最小二乘优于前向选择模型的最小角度拟合。最后还比较了基于遗传算法的普通最小二乘和偏最小二乘拟合,结果表明偏最小二乘更优,因此在高光谱反演重金属含量当中,偏最小二乘精度较高,而在波段选择方法中,遗传算法更优。</p> |
| [10] | . Heavy metals contaminated soils and water will become a major environmental issue in the mining areas. This paper intends to use field hyper-spectra to estimate the heavy metals in the soil and water in Wan-sheng mining area in Chongqing. With analyzing the spectra of soil and water, the spectral features deriving from the spectral of the soils and water can be found to build the models between these features and the contents of Al, Cu and Cr in the soil and water by using the Stepwise Multiple Linear Regression (SMLR). The spectral features of Al are: 48002nm, 50002nm, 56502nm, 61002nm, 68002nm, 75002nm, 100002nm, 143002nm, 175502nm, 188702nm, 192002nm, 195002nm, 221002nm, 226002nm; The spectral features of Cu are: 48002nm, 50002nm, 61002nm, 75002nm, 86002nm, 130002nm, 143002nm, 192002nm, 215002nm, 226002nm; And the spectral features of Cr are: 48002nm, 50002nm, 61002nm, 71502nm, 75002nm, 86002nm, 130002nm, 143002nm, 175502nm, 192002nm, 195002nm. With these features, the best models to estimate the heavy metals in the study area were built according to the maximal R 2 . The R 2 of the models of estimating Al, Cu and Cr in the soil and water are 0.813, 0.638, 0.604 and 0.742, 0.584, 0.513 respectively. And the gradient maps of these three types of heavy metals’ concentrations can be created by using the Inverse distance weighted (IDW).The gradient maps indicate that the heavy metals in the soil have similar patterns, but in the North-west of the streams in the study area, the contents are of great differences. These results show that it is feasible to predict contaminated heavy metals in the soils and streams due to mining activities by using the rapid and cost-effective field spectroscopy. |
| [11] | . Heavy metal contamination from anthropogenic sources is a threat to human health. To assess the feasibility of predicting surface soil arsenic (As) concentration from hyperspectral reflectance measurement, three different regression algorithms are compared in this paper, i.e., multiple linear regression (MLR), partial least squares regression (PLSR), and adaptive neural fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) modeling. Soil samples were taken from three study sites in mining/agricultural areas after reclamation. As concentration was determined by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HG-AFS) analysis, and the reflectance was measured with an analytical spectral devices (ASD) field spectrometer covering the spectral region of 350-2500 nm. First, after preprocessing of the original reflectance spectroscopy, the correlation coefficients between the As concentration and spectral reflectance measurement were derived. Characteristic bands were then chosen for the quantitative retrieval model. Finally, all of the 30 samples were divided into a calibration set and a validation set of 18 and 12 samples, respectively. When compared with the MLR and PLSR algorithms, the ANFIS model was the best retrieval model, with a coefficient of determination (R-2) of 0.94 and a root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 0.88. ANFIS model and reflectance spectroscopy therefore have the potential to map the spatial distribution of As abundance, with the aim of improving public health. |
| [12] | . ABSTRACT During the past decades, large amounts of diffuse cadmium (Cd) and zinc (Zn) contaminated soil material have been deposited in the floodplains of the river Rhine in the Netherlands. As spatial information on soil quality is required at different scale levels covering the whole area, characterisation exclusively based on soil sampling and analysis is time-consuming and very expensive. A quicker method is developed based on a multivariate calibration procedure using partial least squares (PLS) regression to establish a relationship between reflectance spectra in the visible–near-infrared (VNIR) region and spec-trally active soil characteristics (organic matter and clay content) that are inter-correlated with concentration levels of Cd and Zn. Several spectral pre-processing methods (normalisation, multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), derivation, standard normal variate (SNV) transform) were employed to improve the robustness and performance of the calibration models. No pre-processing gave the best results for Cd and Zn with RMSECV equal to 0.676 and 80.97 mg kg 611 , respectively. Application of the calibration models for soil quality characterisation in river floodplains is promising. The future possibilities of multi-variate calibration and pre-processing in remote sensing have to be explored. 08 2001 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. |
| [13] | . <h2 class="secHeading" id="section_abstract">Abstract</h2><p id="">Due to rapid economic development, high levels of potentially harmful elements are continuously being released into the suburban soils of the Nanjing area, China. Conventional methods for investigating soil potentially harmful element contamination based on raster sampling and chemical analysis are time consuming and relatively expensive. Reflectance spectroscopy within the visible-near-infrared region has been widely used to predict soil constituents due to its rapidity, convenience and accuracy. The objective of this study was to examine the possibility of using soil reflectance spectra as a rapid method to simultaneously assess contaminant metals (Ni, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) and As in the suburban soils of the Nanjing area. One hundred and twenty soil samples were collected for chemical analyses and spectral measurements. Prediction of contaminant elements was achieved by a partial least-square regression (PLSR) approach. According to their relationships with Fe, the seven contaminant elements could be categorized into two groups. The results showed that the prediction accuracy for Group II (Ni, Cr, Cu and Hg) was higher than that for Group I (Pb, Zn and As). This finding was consistent with the fact that the correlation coefficients between Group II and Fe were higher than that between Group I and Fe. It was concluded that element-sorption by spectrally active Fe oxides was the major mechanism by which to predict spectrally featureless contaminant elements. This conclusion was strengthened by the fact that the PLSR regression coefficients, which revealed the most important wavelengths for prediction, were attributed to absorption features of Fe oxides. Future study with real remote sensing data and field measurements are strongly recommended.</p> |
| [14] | . The development of rapid techniques, such as hyperspectral spectrophotometry, for investigating arsenic (As) soil contamination could be of great value with respect to conventional methods. This study was conducted to detect As concentrations in artificially polluted soils (from 25 to 1045 mg kg(-1)) through hyperspectral visible-near infrared spectrophotometry and to compare two multivariate statistical regression analyses: partial least squares and support vector machines. The correlation coefficient r is greater in the partial least squares in both model (0.93%) and test (0.87%) with respect to support vector machines (0.88% for the model and 0.82% for the test). The most important model variables extracted from the variable importance in projection scores resulted the absorption peaks at 580, 660, 715, and 780 nm. Bands in the visible spectra are not directly associated to As, but the metalloid can interact with the main spectrally active components of soil permitting to multivariate statistical models to screen As concentrations. |
| [15] | . A generalized dynamic fuzzy neural network (GDFNN) was created to estimate heavy metal concentrations in rice by integrating spectral indices and environmental parameters. Hyperspectral data, environmental parameters, and heavy metal content were collected from field experiments with different levels of heavy metal pollution (Cu and Cd). Input variables used in the GDFNN model were derived from 10 variables acquired by gray relational analysis. The assessment models for Cd and Cu concentration employed five and six input variables, respectively. The results showed that the GDFNN for estimating Cu and Cd concentrations in rice performed well at prediction with a compact network structure using the training, validation, and testing sets (for Cu, fuzzy rules=9, R 2 greater than 0.75, and RMSE less than 2.5; for Cd, fuzzy rules=9, R 2 greater than 0.75, and RMSE less than 1.0). The final GDFNN model was then compared with a back-propagation (BP) neural network model, adaptive-network-based fuzzy interference systems (ANFIS), and a regression model. The accuracies of GDFNN model prediction were usually slightly better than those of the other three models. This demonstrates that the GDFNN model is more suitable for predicting heavy metal concentrations in rice. |
| [16] | ABSTRACT Remote sensing allows monitoring heavy metal pollution in crops for agricultural production and food security. This paper presents an approach to wavelet-fractal analysis for exploring a set of sensitive spectral parameters to monitor the heavy metal pollution levels in rice crops from hyperspectral reflectance data. Hyperspectral and biochemical data were collected from three study farms in Changchun, Jilin Province, China. Our study explored the fractal dimension of reflectance with wavelet transform (FDWT) that demonstrated a better performance than other existing methods. Our results obtained in this study show that the red edge position (REP) was the most sensitive indicator for monitoring the heavy metal pollution levels in rice crops among common indices. As compared with REP, the FDWT is more sensitive to biochemical composition, namely with respect to chlorophyll concentrations, N, Cu and Cd. The established linear models showed a correlation coefficient (R2) above 0.70, model efficiency (ME) above 0.65 and a root mean square error (RMSE) below 3.5. Minimum FDWT values occurred in rice with Level II pollution followed by Level I pollution, and finally the safe level. This study suggests that wavelet transform is well suited as a spectral analysis method to eliminate noise and amplify the stress information from heavy metals. The wavelet transform in conjunction with fractal analysis is promising for detecting heavy metal-induced stress in rice crops. |
| [17] | . Accurate detection of heavy metal-induced stress on the growth of crops is essential for agricultural ecological environment and food security. This study focuses on exploring singularity parameters as indicators for a crop's Zn stress level assessment by applying wavelet analysis to the hyperspectral reflectance. The field in which the experiment was conducted is located in the Changchun City, Jilin Province, China. The hyperspectral and biochemistry data from four crops growing in Zn contaminated soils: rice, maize, soybean and cabbage were collected. We performed a wavelet transform to the hyperspectral reflectance (350-1300 nm), and explored three categories of singularity parameters as indicators of crop Zn stress, including singularity range ( S), singularity amplitude ( S) and a Lipschitz exponent ( ). The results indicated that (i) the wavelet coefficient of the fifth decomposition level by applying Daubechies 5 (db5) mother wavelets proved successful for identifying crop Zn stress; the Sof crop concentrated on the region was around 550-850 nm of the spectral signal under Zn stress; (ii) the Sstabilized, but Sand had developed some variations at the growth stages of the crop; (iii) the S, Sand were found among four crop species differentially; and moreover the Sincreased in relation to an increase in the Sof crop species; (iv) the had a strong non-linear relationship with the Zn concentration ( R:0.7601-0.9451); the Shad a strong linear relationship with Zn concentration ( R:0.5141-0.8281). Singularity parameters can be used as indicators for a crop's Zn stress level as well as offer a quantitative analysis of the singularity of spectrum signal. The wavelet transform technique has been shown to be very promising in detecting crops with heavy metal stress. |
| [18] | . In order to monitor the accumulation of heavy metals effectively and avoid the damage to the health of agricultural soils, a promising approach is to predict low concentrations of heavy metals in soils using visible and near-infrared (VNIR) reflectance spectroscopy coupled with calibration techniques. This study aimed to (i) compare the performance of a combination of partial least squares regression with genetic algorithm (GA-PLSR) against a general PLSR for predicting low concentrations of four heavy metals (i.e., As, Pb, Zn and Cu) in agricultural soils; (ii) explore the transferability of GA-PLSR models defined on one subset of land-use types to the other types; and (iii) to investigate the predictive mechanism for the prediction of the metals. One hundred soil samples were collected in the field locating at Yixing in China, and VNIR reflectance (350-2500 nm) spectra were measured in a laboratory. With the entire soil samples, GA-PLSR and PLSR models were calibrated for the four heavy metals using a leave-one-out cross-validation procedure. The GA-PLSR models achieved better cross-validated accuracies than the PLSR models. For the transferability of GA-PLSR models, the soil samples were divided into three pairs of training sets and test sets from different land-use types. Three GA-PLSR models defined on the training sets had good transferability to the test sets, but nine GA-PLSR models were not successful. As for the predictive mechanism, besides the widely-used correlation analysis between OM and the metals, the relationship between the content of OM and the prediction accuracy of the metals was investigated and the similarity of the important wavelengths for OM and the metals was compared. The three methods verified that OM had a significant correlation with the predictions of the spectrally-featureless metals (Pb, Zn and Cu) from VNIR reflectance. We conclude that GA-PLSR modeling has a better capability for the prediction of the low heavy metal concentrations from VNIR reflectance, and it has a potential of transferability between different land-use types, and its accuracy is fundamentally influenced by OM. (C) 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. |
| [19] | . 矿山开采普遍存在土壤重金属污染问题,有效的进行尾矿区农田土壤重金属含量估算迫在眉睫。以陕西金堆城矿区尾矿为研究区,采集土壤样本,测量土壤可见光近红外光谱,测试分析土壤铜元素含量。将Isomap(Isometrio mapping)和LLE(locally linear embedding)流形学习方法应用于土壤高光谱降维,基于随机森林构建估算模型,反演土壤铜含量。结果表明:降维后的高光谱数据反演精度更高,Isomap降维后模型预测结果均方根误差为30.50,R2=0.76,优于LLE降维结果。研究为尾矿区土壤Cu元素含量的快速反演估算提供了理论依据。 . 矿山开采普遍存在土壤重金属污染问题,有效的进行尾矿区农田土壤重金属含量估算迫在眉睫。以陕西金堆城矿区尾矿为研究区,采集土壤样本,测量土壤可见光近红外光谱,测试分析土壤铜元素含量。将Isomap(Isometrio mapping)和LLE(locally linear embedding)流形学习方法应用于土壤高光谱降维,基于随机森林构建估算模型,反演土壤铜含量。结果表明:降维后的高光谱数据反演精度更高,Isomap降维后模型预测结果均方根误差为30.50,R2=0.76,优于LLE降维结果。研究为尾矿区土壤Cu元素含量的快速反演估算提供了理论依据。 |
| [20] | . The development and formation of chemical elements in soil are affected not only by parent material, climate, biology and topology factors, but also by human activities. The pollution sources of heavy metals in the environment are mainly derived from anthropogenic sources, and heavy metal elements in soil have been considered to be powerful tracers for monitoring the impacts of human activities. The present study attempts to analyze whether and how a connection can be made between macroscopical control and microcosmic analysis, to estimate the impacts of human activities on heavy metals in soil, and to determine a way to describe the spatial relationship between heavy metals in soil and human activities, by means of landscape geochemical theories and methods. In addition, the disturbances of human activities on Zn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Hg, Cd, Ni and Ag are explored through the analysis of the spatial relationship between human disturbed landscapes and element anomalies, thereby determining the diversified rules of the effects. The study results show that the rules of different landscapes influencing heavy metal elements are diversified, and that the Zn, Ni, Pb, Hg and Ag elements are closely related with city landscapes, but Cu and Cd are not significantly affected by city landscapes; furthermore, the elements Ni, Pb, Hg, Ag and Cd are shown to be closely related with river landscapes, while evidently Zn is not affected by river landscapes; the relationships between mine landscapes and the elements Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni and Hg are apparent, among which Zn is not included; the relationships between the elements Zn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Hg, Cd, Ni and Ag and road landscapes are quite close, which shows that road landscapes have significant effects on these elements. Therefore, the conclusion is drawn that the response mechanism analysis of-human disturbance and soil chemical element aggregation is feasible, based on the landscape geochemical theories and methods. The results of the study provide the possibility for applying spatial information techniques, such as remote sensing and geographic information systems, to study chemical elements in soil, thereby realizing the effective combination of macroscopic spatial information and microscopic mechanism of soil element migration research. (C) 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. |
| [21] | . The present paper aims to map pollution and assess the risk for agricultural soils in a wider lignite opencast mining and industrial area. Geochemical data related to environmental studies show that the waste characteristics favor solubilization and mobilization of inorganic contaminants and in some cases the generation of acidic leachates.<br/>The spatiotemporal distribution of soil contamination is studied by the application of the Bayesian Maximum Entropy (BME) theory which allows merging spatial and temporal estimations in a single model.<br/>Results reveal a correlation range of contaminant concentrations up to 5000 m and indicate a potential forecasting range up to 4 years. Inspection of the produced spatiotemporal maps indicates that the whole study area is contaminated by As and various heavy metals, a situation which seems to be more or less stable over time. (C) 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. |
| [22] | . ABSTRACT Soil heavy metal concentrations exhibit significant space-time trends due to their accumulation along the time axis and the varying distances from the pollution sources. Thus, concentration trends cannot be ignored when performing spatiotemporal soil heavy metal predictions in an area. In this work, datasets were used of soil cadmium (Cd) concentrations in the Qingshan district (Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China) sampled during the period 2010-2014. Spatiotemporal Kriging with four Trend models (STKT) and non-separable space-time correlation was implemented to assimilate multi-temporal data in the mapping of Cd distribution within the contaminated soil area. Soil Cd trends were represented by four different space-time polynomial functions, and a non-separable power function-exponential variogram model of Cd distribution was assumed. Plots of the predicted space-time Cd distributions revealed a marked tendency of the Cd concentrations over time to spread from the southwest part to the entire study area (higher soil Cd concentrations are found in the southwest part of the Qingshan area, whereas the temporal Cd trend is characterized by a constant increase from 2010 to 2014). Thus, the maps indicate that the entire study area is contaminated by Cd, a situation that seems to be stable over time. STKT can reduce prediction errors in practically and statistically significant ways. A numerical comparison of the STKT technique vs. the mainstream Spatiotemporal Ordinary Kriging (STOK) technique showed that STKT can perform better than STOK when the trend model's goodness of fit to the Cd data was satisfactory (producing minimal data fit error statistics), implying that adequate trend modeling is a key issue for space-time prediction accuracy purposes. In particular, quantitative results obtained at the Qingshan region showed that, by incorporating local Cd values and distance-based dependence structures the STKT techniques produced the best prediction error statistics, resulting in considerable prediction error reductions (the level of which depend on the trend model specification; e.g., in the case of STKT with trend model 3 the improvement comparing to STOK was almost 30%). Future studies of Cd contamination in the region (sampling design optimization) can benefit from the results of the geostatistical analysis of the present paper (variogram and trend modeling, etc.). |
| [23] | . <p>With rapid economic and social development, soil contamination arising from heavy metals has become a serious problem in many parts of China. We collected a total of 445 samples (0-20 cm) at the nodes of a 2 km×2 km grid in surface soils of Rizhao city, and analyzed sources and risk pattern of 10 heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn). The combination of Multivariate statistics analysis and Geostatistical methods was applied to identify the sources and hazardous risk of heavy metals in soils. The result indicated that Cr, Ni, Co, Mn, Cu, and As were mainly controlled by parent materials and came from natural sources. Cd and Hg originated from anthropogenic sources. Pb and Zn, belonging to different groups in multivariate analysis, were associated with joint effect of parent materials and human inputs. Ordinary Kriging and Indicator Kriging suggested that single element and elements association from the same principal components had similar spatial distribution. Through comprehensive assessment on all elements, we also found the high risk areas were located in the populated urban areas and western study area, which could be attributed to the higher geological background in the western part and strong human interference in the eastern part.</p> |
| [24] | . . |
| [25] | . 为了定量分析土壤重金属含量的影响因素,以长沙城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd为例,采用传统回归模型(ordinary least squares, OLS)和地理加权回归模型(geographically weighted regression, GWR)分析比较了土壤Pb、Cd含量与影响因素间的相关关系。结果表明:长沙城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd含量存在空间自相关性,Pb、Cd的GWR模型拟合度较OLS模型高,残差不存在空间自相关,GWR模型能更好地解释土壤Pb、Cd与影响因素变量的空间异质性。土壤Pb与Cd含量呈极显著正相关;土壤pH值、有机质、氮磷含量是影响土壤Pb、Cd含量的重要因素;离河流、城镇、工矿建设用地的距离对于城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd含量也有一定影响,土壤Pb、Cd的"高-高"集聚区(土壤Pb或Cd含量高的区域被Pb或Cd含量高的其他区域所包围,区域土壤Pb或Cd含量水平较高,且空间差异程度较小)和离河流、城镇、工矿建设用地较近的农田是Pb、Cd污染风险防控的重点区域。该研究可为定量分析区域土壤重金属含量的空间结构与影响因素提供参考,为长沙城郊农田土壤重金属污染的防控提供参考。 . 为了定量分析土壤重金属含量的影响因素,以长沙城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd为例,采用传统回归模型(ordinary least squares, OLS)和地理加权回归模型(geographically weighted regression, GWR)分析比较了土壤Pb、Cd含量与影响因素间的相关关系。结果表明:长沙城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd含量存在空间自相关性,Pb、Cd的GWR模型拟合度较OLS模型高,残差不存在空间自相关,GWR模型能更好地解释土壤Pb、Cd与影响因素变量的空间异质性。土壤Pb与Cd含量呈极显著正相关;土壤pH值、有机质、氮磷含量是影响土壤Pb、Cd含量的重要因素;离河流、城镇、工矿建设用地的距离对于城郊农田土壤Pb、Cd含量也有一定影响,土壤Pb、Cd的"高-高"集聚区(土壤Pb或Cd含量高的区域被Pb或Cd含量高的其他区域所包围,区域土壤Pb或Cd含量水平较高,且空间差异程度较小)和离河流、城镇、工矿建设用地较近的农田是Pb、Cd污染风险防控的重点区域。该研究可为定量分析区域土壤重金属含量的空间结构与影响因素提供参考,为长沙城郊农田土壤重金属污染的防控提供参考。 |
| [26] | . 土壤重金属或其他生态环境属性在时间和空间上均存在连续性和变异性,而目前的研究忽略了它们在时间维的变异。为了在预测时使用多时期采样数据,该文提出使用时空克里格方法对土壤重金属进行时空建模及预测,着重介绍了经验半方差值的计算、理论变异模型的形式及参数拟合、时空克里格估值算法、估值方差和精度随邻近点数量的变化及时空克里格制图。以武汉市青山区土壤重金属为例介绍了时空克里格建模及预测的流程。结果表明,时空克里格方法能够很好地描述土壤重金属在空间、时间和时空上3个部分的变异特征,能够利用其他时期的数据对预测时间点的属性进行插值,而多时期的属性空间分布图能够很好地反映土壤重金属的分布变化规律。该研究可为资源环境生态时空建模及预测研究提供参考。 . 土壤重金属或其他生态环境属性在时间和空间上均存在连续性和变异性,而目前的研究忽略了它们在时间维的变异。为了在预测时使用多时期采样数据,该文提出使用时空克里格方法对土壤重金属进行时空建模及预测,着重介绍了经验半方差值的计算、理论变异模型的形式及参数拟合、时空克里格估值算法、估值方差和精度随邻近点数量的变化及时空克里格制图。以武汉市青山区土壤重金属为例介绍了时空克里格建模及预测的流程。结果表明,时空克里格方法能够很好地描述土壤重金属在空间、时间和时空上3个部分的变异特征,能够利用其他时期的数据对预测时间点的属性进行插值,而多时期的属性空间分布图能够很好地反映土壤重金属的分布变化规律。该研究可为资源环境生态时空建模及预测研究提供参考。 |
| [27] | . Soil contamination is an ever-growing concern and demands efficient methods for diagnosis of areas under suspected contamination. Spectroscopy reflectance vis-NIR has been shown to be a reliable and environmentally friendly method for the rapid detection and monitoring of soil properties. Despite the use of vis-NIR it is necessary to test the effectiveness of other wavelengths (mid-IR 4000-400 cm(-1)). We aim with this study to (1) evaluate the contamination of Cr applied by tannery sludge and CrCl3 center dot 6H(2)O in tropical soils through sequential extraction procedures and spectroscopy techniques; (2) identify parameters of soil spectral variation (vis-NIR-mid) associated with Cr and explore their viability in the evaluation of contaminated soils; and (3) investigate the feasibility of using soil spectral data and chemometrics methods to predict Cr in soils. Results indicate that metal adsorption to soil constituents caused expressive changes in soil spectral curves, showing differentiation between highly contaminated soils and those that are relatively contaminant-free. Cr content can be predicted by spectroscopy reflectance in vis-NIR-mid data. The mid-IR models of Cr outperformed vis-NIR. Organic matter played a more important role in determining soil spectral signatures than the mineralogical characteristics of soils, especially in those with high organic carbon content. |
| [28] | . This study explored the spatial pattern of heavy metals in Beijing agricultural soils using Moran's I statistic of spatial autocorrelation. The global Moran's I result showed that the spatial dependence of Cr, Ni, Zn, and Hg changed with different spatial weight matrixes, and they had significant and positive global spatial correlations based on distance weight. The spatial dependence of the four metals was scale-dependent on distance, but these scale effects existed within a threshold distance of 13 km, 32 km, 50 km, and 29 km, respectively for Cr, Ni, Zn, and Hg. The maximal spatial positive correlation range was 57 km, 70 km, 57 km, and 55 km for Cr, Ni, Zn, and Hg, respectively and these were not affected by sampling density. Local spatial autocorrelation analysis detected the locations of spatial clusters and spatial outliers and revealed that the pollution of these four metals occurred in significant High-high spatial clusters, Low-high, or even High-low spatial outliers. Thus, three major areas were identified and should be receiving more attention: the first was the northeast region of Beijing, where Cr, Zn, Ni, and Hg had significant increases. The second was the southeast region of Beijing where wastewater irrigation had strongly changed the content of metals, particularly of Cr and Zn, in soils. The third area was the urban fringe around city, where Hg showed a significant increase. |
| [29] | . Heavy metal contamination in crops is a worldwide problem that requires accurate and timely monitoring. This study is aimed at improving the accuracy of monitoring heavy metal stress levels in rice utilizing remote sensing data. An assimilation framework based on remote sensing and improved crop growth model was developed to continuously monitor heavy metal stress levels over the entire period of crop growth based on the growth law of crops and the stress mechanism. Compared with other physiological indices, dry weight of rice roots (WRT) was selected as the best indicator to estimate heavy metal stress levels. The World Food Study (WOFOST) model, widely used for the description of crop growth, was improved by incorporating stress factors with overall consideration for the changes in physiological status under heavy metal stress. Three scenarios were put forward based on the stress factors f DTGA and f CVF , which, respectively, correspond to the daily total gross assimilation of CO 2 and carbohydrate-to-dry matter conversion coefficient, and were analyzed for their efficiency of simulating WRT. A method of assimilating the leaf area index (LAI) retrieved from remotely sensed data into the improved WOFOST model was applied to optimize f DTGA and f CVF . The results suggested that the scenario using both factors can simulate WRT under heavy metal stress more accurately, with a relative percent error (RPE) lower than 14%. Based on the RS-WOFOST assimilation framework, continuous spatial-temporal evaluation of heavy metal stress levels based on WRT can be accomplished. |
| [30] | . <h2 class="secHeading" id="section_abstract">Abstract</h2><p id="">Open-focused microwave-assisted extraction and ICP-OES determination of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn from surface sediments of the estuary of Bilbao (Basque Country, North of Spain) was carried out. All the samples were collected at three different tributaries of the estuary (Asua, Galindo and Nerbioi-Ibaizabal) every two months during 1999. The digestion procedure was proposed from the conclusions of a fractionated factorial design, and the precision and accuracy of the method was verified using a certified reference sediment (RTC008-050). The results of the analysis were statistically treated by means of principal component analysis and correlation analysis. The principal component analysis of sediment data (32 samples × 9 metals) indicated different patterns of contamination regarding the tributary and sampling station. The two main patterns observed were a steady increment of the metal concentration along all the campaigns in the samples collected in the Galindo River and a seasonal variation in the Nerbioi-Ibaizabal River, with higher metallic content during summertime and lower content during wintertime.</p> |
| [31] | . Abstract included in text. |
| [32] | . This study aimed at comparing the effectiveness of the global aspatial multiple linear regression (MLR) using ordinary least squares (OLS) and local spatial geographically weighted regression (GWR) for producing a map showing the spatial variations in soil organic carbon (SOC) in Amman-Zarqa Basin (about 3,583km 2 )—a typical semi-arid watershed in Jordan—using Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) data. After normalizing the SOC data (the dependent variable) using Box-Cox power transformation and removing the multicollinearity of TM bands 1 to 5 and 7 (the independent variables) by applying principal component analysis, both regression techniques developed maximum likelihood best linear unbiased estimators in which the residuals had close-to-normal and random independent distributions with almost common variances and close-to-zero means. However, the GWR model had smaller Akaike’s information criterion (corrected) (AIC c ) (2,534.0 versus 2,560.5), larger adjusted multiple coefficient of determination \( \left({\overline{\mathbf{\mathcal{R}}}}^2\right) \) (0.31 versus 0.22), and larger Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient ( r ) between measured and observed values (0.63 versus 0.51). Thus, applying map algebra using the developed GWR model generated a raster map with 3065×6530m 2 cell size. The map showed that SOC composition to 20cm depth varied from 3.5 to 85.0 metric tons per hectare (ton/ha) with a mean and standard deviation of about 23.9 and 9.3ton/ha, respectively. The spatial pattern of surface SOC reflected partly the spatial variability of land cover and agricultural management practices in the basin. The results demonstrate the potential and superiority of GWR over MLR as a practical tool for conducting further spatial and temporal analyses of SOC stocks and implementing best land management practices in semi-arid environments using TM data. |
| [33] | . ABSTRACT Accurately mapping the spatial distribution of soil total nitrogen is important to precision agriculture and environmental management. Geostatistical methods have been frequently used for predictive mapping of soil properties. Recently, a local regression method, geographically weighted regression (GWR), got the attention of environmentalists as an alternative in spatial modeling of environmental attributes, due to its capability of incorporating various auxiliary variables with spatially varied correlation coefficients. The objective of this study is to compare GWR and ordinary cokriging (OCK) in predictive mapping of soil total nitrogen (TN) using multiple environmental variables. 353 soil Samples within the surface horizon of 0-20 cm in a study area were collected, and their TN contents were measured for calibrating and validating the GWR and OCK interpolations. The environmental variables finally chosen as auxiliary data include elevation, land use types, and soil types. Results indicate that, although OCK is slightly better than GWR in global accuracy of soil TN prediction (the adjusted R2 for GWR and OCK are 0.5746 and 0.6858, respectively), the soil TN map interpolated by GWR shows many details reflecting the spatial variations of major auxiliary variables while OCK smoothes out almost all local details. Geographically weighted regression could account for both the spatial trend and local variations, whilst OCK had difficulties to capture local variations. It is concluded that GWR is a more promising spatial interpolation method compared to OCK in predicting soil TN and potentially other soil properties, if a suitable set of auxiliary variables are available and selected. |
| [34] | . The spatial information of soil organic matter (SOM) is crucial for precision agriculture and environmental modeling. It is, however, difficult to obtain the regional details of SOM by dense sampling due to the high cost. Although a variety of interpolation methods are available for mapping SOM at regional scales, accurate prediction usually needs densely distributed samples and requires the interpolated variable to meet some constraints such as spatial stationarity. This paper introduces the Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) technique as an alternative approach for SOM mapping. We interpolated the spatial distribution of SOM based on a limited number of samples with the incorporation of multiple independent variables. We also compared GWR with the ordinary least squares regression approach in mapping SOM. Results indicated that GWR could capture more local details and improve the prediction accuracy. However, more attention should be paid to the selection of independent variables. |
| [35] | . 高光谱遥感技术已成为当前遥感领域的前沿技术,因其高分辨率的特 点,可利用地物反射光谱特征定量反演地物的物理化学性质。目前土壤环境质量愈来愈受到关注,土壤重金属含量与土壤环境质量安全密切相关,以往土壤高光谱遥 感技术研究多注重于土壤有机成分如土壤碳氮的光谱反演模型,对土壤重金属含量的高光谱反演研究普遍较少。土壤重金属污染已经成为影响土壤质量安全的关键因 素,对土壤重金属尤其是污染元素普查是当务之急。传统土壤重金属的测试方法要求条件较高,测试周期较长,试图建立土壤高光谱与土壤铬元素(ICP-MS测 定)含量之间的定量预测模型,以实现土壤铬元素的快速准确预测。采集福州市土壤样品135个,对土壤样品在350~2500 nm的光谱反射率进行倒数、对数、微分等六种变换,筛选出对土壤总铬含量敏感的光谱波段,最后获得福州土壤铬元素高光谱反演优化模型。研究结果表明:亚热 带红壤总铬的敏感光谱波段为:可见光520~530 nm和近红外1440~1450,2010~2020,2230~2240 nm;亚热带地区土壤总铬-高光谱反演的优化模型为:y=120.768e-7.037x(相关系数R为0.568,均方根误差为0.619μg·g- 1,检验相关系数R为0.484,均方根误差为1.426μg·g-1),该模型可以用于福州地区土壤全铬的光谱快速监测。 . 高光谱遥感技术已成为当前遥感领域的前沿技术,因其高分辨率的特 点,可利用地物反射光谱特征定量反演地物的物理化学性质。目前土壤环境质量愈来愈受到关注,土壤重金属含量与土壤环境质量安全密切相关,以往土壤高光谱遥 感技术研究多注重于土壤有机成分如土壤碳氮的光谱反演模型,对土壤重金属含量的高光谱反演研究普遍较少。土壤重金属污染已经成为影响土壤质量安全的关键因 素,对土壤重金属尤其是污染元素普查是当务之急。传统土壤重金属的测试方法要求条件较高,测试周期较长,试图建立土壤高光谱与土壤铬元素(ICP-MS测 定)含量之间的定量预测模型,以实现土壤铬元素的快速准确预测。采集福州市土壤样品135个,对土壤样品在350~2500 nm的光谱反射率进行倒数、对数、微分等六种变换,筛选出对土壤总铬含量敏感的光谱波段,最后获得福州土壤铬元素高光谱反演优化模型。研究结果表明:亚热 带红壤总铬的敏感光谱波段为:可见光520~530 nm和近红外1440~1450,2010~2020,2230~2240 nm;亚热带地区土壤总铬-高光谱反演的优化模型为:y=120.768e-7.037x(相关系数R为0.568,均方根误差为0.619μg·g- 1,检验相关系数R为0.484,均方根误差为1.426μg·g-1),该模型可以用于福州地区土壤全铬的光谱快速监测。 |
| [36] | 把屯昌县发展为菜篮子保障基地、热带水果和特色南药生产基地,带动农民增收致富,实现在国际旅游岛背景下把资源 建设国家热带现代农业基地: 海南国际旅游岛建设发展规划纲要解读之十九[N]. 海南日报. 中华人民共和国多目标区域地球化学调查报告海南岛[R]. 海口: 海南省地质调查院 把屯昌县发展为菜篮子保障基地、热带水果和特色南药生产基地,带动农民增收致富,实现在国际旅游岛背景下把资源 建设国家热带现代农业基地: 海南国际旅游岛建设发展规划纲要解读之十九[N]. 海南日报. 中华人民共和国多目标区域地球化学调查报告海南岛[R]. 海口: 海南省地质调查院 |
| [37] | . 准确了解土壤有机质的空间分布是合理施肥的重要前提,也是水土流失控制及保护环境的重要基 础。利用113个土壤有机质样点数据,以海拔高度、土壤侵蚀强度、土地利用、比值植被指数、样点至河流的欧氏距离、亚铁矿物指数及坡度为参考因子,来尝试 利用GWR(Geographically Weighted Regression)模型探索多重因素作用下的土壤有机质空间分布,并通过与普通线性回归(ordinary least squares,OLS)相比较,来了解GWR模型的精度,进而进行了土壤有机质的空间制图,并对其制图效果进行了评价。结果表明,与OLS模型相 比,GWR预测模型它能显著降低AIC(Akaike Information Criterion)值,较大程度地提高模型的决定系数,并有效地减少模型的回归残差值。从制图的总体效果看,GWR模型的预测结果与实测值的吻合程度要 优于OLS模型。文章还对利用GWR模型进行回归时的样点数量、因子筛选及因子定量化等方面进行了相应的讨论。 . 准确了解土壤有机质的空间分布是合理施肥的重要前提,也是水土流失控制及保护环境的重要基 础。利用113个土壤有机质样点数据,以海拔高度、土壤侵蚀强度、土地利用、比值植被指数、样点至河流的欧氏距离、亚铁矿物指数及坡度为参考因子,来尝试 利用GWR(Geographically Weighted Regression)模型探索多重因素作用下的土壤有机质空间分布,并通过与普通线性回归(ordinary least squares,OLS)相比较,来了解GWR模型的精度,进而进行了土壤有机质的空间制图,并对其制图效果进行了评价。结果表明,与OLS模型相 比,GWR预测模型它能显著降低AIC(Akaike Information Criterion)值,较大程度地提高模型的决定系数,并有效地减少模型的回归残差值。从制图的总体效果看,GWR模型的预测结果与实测值的吻合程度要 优于OLS模型。文章还对利用GWR模型进行回归时的样点数量、因子筛选及因子定量化等方面进行了相应的讨论。 |
