 ,*, 邓飞
,*, 邓飞 ,*四川农业大学 / 农业农村部西南作物生理生态与耕作重点实验室 / 四川省作物生理生态及栽培重点实验室, 四川温江 611130
,*四川农业大学 / 农业农村部西南作物生理生态与耕作重点实验室 / 四川省作物生理生态及栽培重点实验室, 四川温江 611130Effects of sowing date on eating quality of indica hybrid rice in Sichuan Basin
LI Bo, ZHANG Chi, ZENG Yu-Ling, LI Qiu-Ping, REN Hong-Chao, LU Hui, YANG Fan, CEHN Hong, WANG Li, CHEN Yong, REN Wan-Jun ,*, DENG Fei
,*, DENG Fei ,*College of Agronomy, Sichuan Agricultural University / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology, Ecology, and Cultivation in Southwest China, Ministry of Agriculture and Rual Affairs / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology, Ecology, and Cultivation in Sichuan Province, Wenjiang 611130, Sichuan, China
,*College of Agronomy, Sichuan Agricultural University / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology, Ecology, and Cultivation in Southwest China, Ministry of Agriculture and Rual Affairs / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology, Ecology, and Cultivation in Sichuan Province, Wenjiang 611130, Sichuan, China通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-08-11接受日期:2020-12-1网络出版日期:2021-01-04
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-08-11Accepted:2020-12-1Online:2021-01-04
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (584KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李博, 张驰, 曾玉玲, 李秋萍, 任洪超, 卢慧, 杨帆, 陈虹, 王丽, 陈勇, 任万军, 邓飞. 播期对四川盆地杂交籼稻米饭食味品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(7): 1360-1371. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.02053
LI Bo, ZHANG Chi, ZENG Yu-Ling, LI Qiu-Ping, REN Hong-Chao, LU Hui, YANG Fan, CEHN Hong, WANG Li, CHEN Yong, REN Wan-Jun, DENG Fei.
随着经济的发展和消费结构的改变, 市场对优质稻米的需求日益增大[1,2,3], 而稻米品质, 特别是蒸煮食味品质一直深受消费者和科研工作者的关注[4,5]。目前我国评价米饭食味品质主要采用感官评价法, 或通过测定衡量蒸煮品质的主要理化指标, 如直链淀粉含量、糊化温度、胶稠度等, 间接反映稻米食味品质[6,7]。近年来, 由于感官评价法需要耗费大量的时间、人力和物力, 而且每个人的评价标准都不一样, 因此越来越多的****开始使用可见光/近红外光谱仪器(米饭食味计)来替代传统感官评价法来鉴定米饭食味品质[7,8,9]。而稻米品质形成是品种遗传特性、环境条件和栽培条件综合作用的结果[10]。适宜的环境条件是稻米品质形成的基础, 其中水稻灌浆结实期的气候条件是影响稻米品质的主要环境因子[11,12]。前人研究指出, 灌浆结实期高温会导致稻米品质变差[13,14]。因此, 在水稻生产中, 往往通过合理调节播期使水稻结实期处于较佳光温条件, 以确保稻米品质的提高。合理的播期可以有效利用温光资源[15]; 适宜播期内, 晚播有利于优质稻米的形成, 随着播期的延迟, 稻米加工品质有规律地提高, 垩白粒率和垩白度降低, 外观品质有所改善, 直链淀粉含量降低[12,16-17]。四川盆地属我国典型的弱光稻区, 具有“弱光、寡照、高湿”的生态特点[18], 关于播期对稻米产量的影响前人已有一定研究[19], 但播期对弱光稻区稻米食味品质, 特别是米饭食味品质的影响尚不明确, 仍需进一步研究。因此, 本研究以3个杂交籼稻品种宜香优2115、F优498和川优6203为试验材料, 在四川大邑、南部、射洪设置播期试验, 研究弱光稻区播期对杂交籼稻米饭食味品质的影响及其与气象因子的关系, 以期为四川盆地水稻的优质生产提供理论和实践依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料和地点
以四川省近年来主推的3个杂交籼稻品种宜香优2115 (国标二级米)、F优498 (国标三级米)与川优6203 (国标二级米)为供试材料。试验于2018年和2019年分别在四川省成都市大邑县(30°30′30′′N, 103°36′15′′E)、南充市南部县(31°15′49′′N, 105°58′ 26′′E)和遂宁市射洪市(30°49′30′′N, 105°26′41′′E) 3个地点实施, 大邑地处四川盆地西平原区, 南部属四川盆地东北丘陵区, 射洪属四川盆地中部丘陵区。各试验点土壤基础肥力资料见表1, 各试验点生育期气象资料见图1。Table 1
表1
表13个地点试验田土壤理化性质
Table 1
| 试点 Location | pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g kg-1) | 全氮 Total N content (g kg-1) | 全磷 Total P content (g kg-1) | 全钾 Total K content (g kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大邑Dayi | 6.04 | 32.97 | 2.94 | 0.77 | 13.81 | 97.74 | 32.11 | 112.67 |
| 南部Nanbu | 7.39 | 31.95 | 1.28 | 0.36 | 10.62 | 55.97 | 50.88 | 96.32 |
| 射洪Shehong | 7.52 | 26.69 | 1.40 | 0.60 | 12.20 | 62.04 | 85.83 | 128.52 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
1.2 试验设计
各试验点均采用二因素裂区设计, 主因素为播期, 根据当地种植习惯, 大邑设置第1播期(A1): 3月25日播种, 第2播期(A2): 4月4日播种, 第3播期(A3): 4月24日播种, 第4播期(A4): 5月4日播种; 南部设置第1播期(A1): 3月20日播种, 第2播期(A2): 3月30日播种, 第3播期(A3): 4月19日播种, 第4播期(A4): 4月29日播种; 射洪设置第1播期(A1): 3月22日播种, 第2播期(A2): 4月1日播种, 第3播期(A3): 4月22日播种, 第4播期(A4): 5月2日播种。副因素为不同杂交籼稻品种(B1: 宜香优2115, B2: F优498, B3: 川优6203), 各试验点共12个处理, 每处理3次重复, 共36个试验小区, 小区面积12.6~18.0 m2。由于播栽期不同, 因此主区间用塑料薄膜包埂隔离, 以减少侧渗、窜流, 小区田埂筑高30 cm, 埂基30 cm, 设立相互独立的排灌系统, 进行单独肥水管理。各试验点采用当地育秧方式培育机插壮秧, 秧龄30 d, 机插栽培, 行穴距30 cm ×21 cm, 每穴2~4株苗。施肥按照氮肥后移高产高效施肥管理, 施氮量150 kg hm-2, 氮磷钾比例为2∶1∶2, 氮肥分基肥、分蘖肥、促花肥和保花肥按3.5∶1.5∶3∶2施用, 磷肥作基肥一次施用, 钾肥分基肥和穗肥1∶1施用。其他管理措施同当地常规高产栽培大田管理。图1
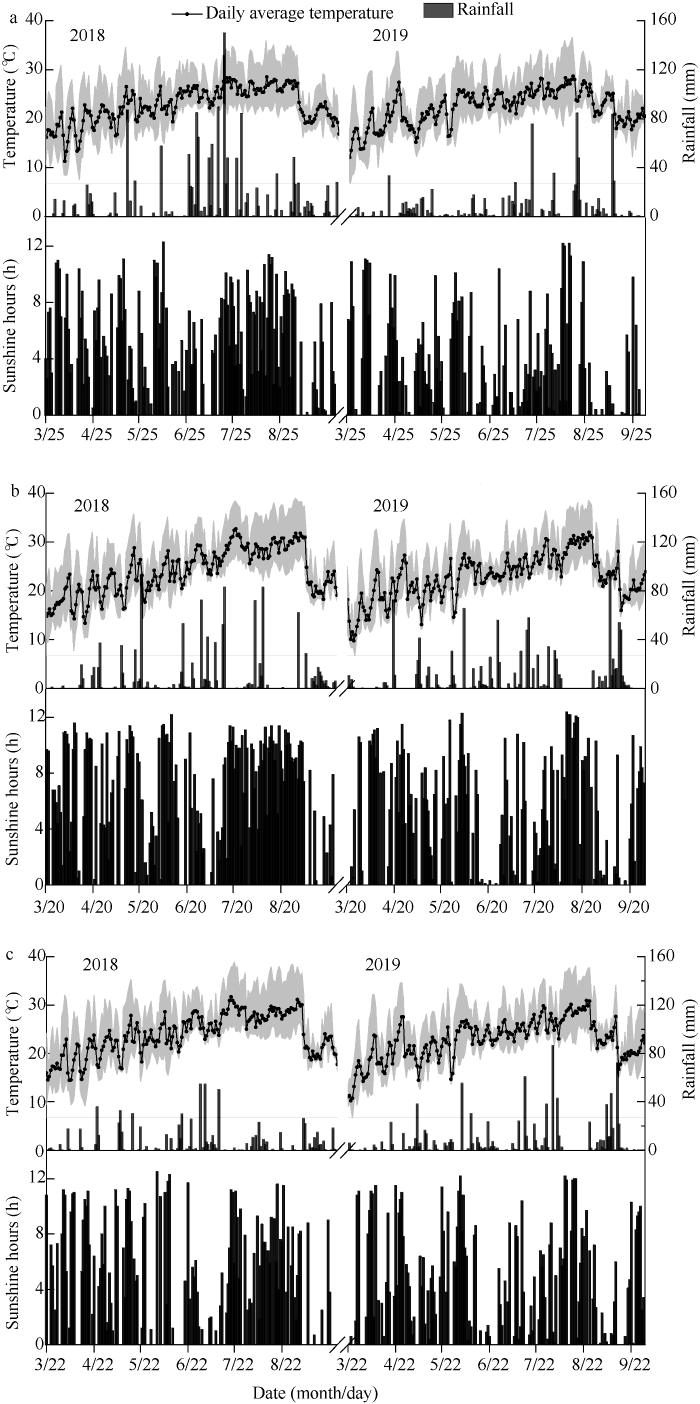 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图13个地点2018-2019年气象数据
a: 大邑; b: 南部; c: 射洪。本试验水稻生长季大邑点2018年为3月25日至10月1日, 2019年为3月25日至10月3日; 南部点2018年为3月20日至9月25日, 2019年为3月20日至9月30日; 射洪点2018年为3月22日至9月27日, 2019年为3月22日至10月1日。
Fig. 1Meteorological data of three locations from 2018 to 2019
a: Dayi, b: Nanbu, c: Shehong. The rice growing seasons in this experiment were from 25 March to 1 October in 2018, from 25 March to 3 October in 2019 at Dayi; from 20 March to 25 September in 2018, from 20 March to 30 September in 2019 at Nanbu, and from 22 March to 27 September in 2018 and 22 March to 1 October in 2019 at Shehong.
1.3 测定项目与方法
水稻成熟期分小区人工收获, 各小区取稻谷约2.0 kg, 在室温下保存3个月, 使其理化特性趋于稳定后, 用水稻砻谷机去壳得到糙米, 将糙米按中华人民共和国国家标准(GB/T 1354-2009)用碾米机制备成一等精度的大米备用。用天平称取精米30 g, 放入不锈钢罐中, 用流水冲洗直到洗米水不混浊为止, 然后沥尽余水, 按照米水质量比为1.0∶1.6加入48 g的水, 浸泡30 min后盖上滤纸。将不锈钢罐放入电饭锅内的蒸架上, 盖好电饭锅盖, 蒸煮30 min, 保温10 min。用饭勺搅拌煮好的米饭, 然后放到冷却箱冷却30 min, 冷却好的米饭盖上盖子, 放置2 h后进行指标测定。使用米饭食味计(STA-1A型, 日本佐竹公司)测定综合评分、外观、口感, 硬度黏度仪(RHS-1A型, 日本佐竹公司)测定硬度和黏度。取冷却到室温的米饭7.0 g装入直径30 mm、高9 mm不锈钢圆环内, 再用专用的压饭器压成饭饼作为测定饭样。将测定饭样放到测定槽中插入食味计测定, 然后再放入硬度黏度仪测定。一个饭样的正反面各测1次, 重复3次。
1.4 统计分析
用Microsoft Excel 2016录入和整理数据。用SPSS 25.0系统软件分析数据, 用Origin 2018作图, 用LSD (least significant difference test)进行样本平均数的差异显著性比较, 基于R语言的RStudio软件的GGE BiplotGUI软件包进行GGE模型分析[20]。2 结果与分析
2.1 地点、播期、品种及其互作对米饭食味品质的影响
由表2可知, 杂交籼稻的米饭食味品质是地点、播期、品种及其互作共同作用的结果, 且不同年份间存在一定差异。不同年份间, 外观、口感、综合评分均受地点、播期、品种及其互作的显著或极显著影响; 硬度和黏度则受品种, 以及地点与品种和地点与播期(除2018年硬度)互作的显著影响; 此外, 地点显著影响2018年黏度和2019年硬度, 而播期则显著影响2019年硬度和黏度。Table 2
表2
表2米饭食味值联合方差分析(F值)
Table 2
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 综合评分 Comprehensive score | 外观 Appearance | 口感 Taste | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度 Viscosity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| 地点 Location | 234.23** | 133.68** | 89.05** | 69.83** | 9.73** | 10.96** | 2.46 | 17.54** | 13.12** | 2.46 |
| 播期 Sowing date | 61.42** | 30.92** | 58.45** | 42.87** | 38.43** | 13.34** | 1.75 | 5.68** | 1.15 | 6.15** |
| 品种 Variety | 1181.41** | 464.29** | 586.89** | 173.56** | 467.00** | 136.24** | 181.53** | 113.86** | 64.95** | 9.15** |
| 地点×播期 Location × sowing date | 20.35** | 6.32** | 14.86** | 8.64** | 10.55** | 2.71* | 3.61** | 3.91** | 2.66* | 55.89** |
| 地点×品种 Location × variety | 23.39** | 20.80** | 21.06** | 18.27** | 14.19** | 13.91** | 0.51 | 5.34** | 2.80* | 3.67** |
| 播期×品种 Sowing date × variety | 13.05** | 27.72** | 21.50** | 18.53** | 19.53** | 10.89** | 2.99* | 1.67 | 1.06 | 1.29 |
| 地点×播期×品种 Location × sowing date × variety | 15.72** | 34.42** | 27.48** | 16.60** | 13.28** | 12.05** | 1.69 | 1.73 | 1.24 | 1.39 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 播期对米饭食味品质的影响
由表3可知, 不同播期导致米饭食味品质各项指标的明显变化, 且年份间差异明显。2018年, 较第1播期而言, 第3播期显著提高了外观、口感和综合评分; 第2和第4播期则导致外观、口感和综合评分显著降低, 同时增加了硬度值; 此外, 较第2播期, 第4播期显著降低了综合评分。2019年, 较第1播期, 第2播期下口感、硬度、黏度和综合评分无显著差异; 第4播期的外观、口感和综合评分显著高于其他3个播期, 第3播期则显著增加了硬度值, 同时降低了黏度值。Table 3
表3
表3播期对米饭食味品质的影响
Table 3
| 播期 Sowing date | 综合评分 Comprehensive score | 外观 Appearance | 口感 Taste | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度Viscosity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| A1 | 77.10 b | 81.45 b | 6.66 b | 7.07 b | 6.49 b | 7.00 b | 3.09 b | 2.43 b | 0.23 a | 0.34 a |
| A2 | 77.01 b | 81.41 b | 6.48 c | 6.89 c | 6.39 c | 6.98 b | 3.19 ab | 2.47 b | 0.22 a | 0.37 a |
| A3 | 78.14 a | 80.58 c | 6.91 a | 7.01 b | 6.60 a | 6.99 b | 3.19 ab | 2.75 a | 0.20 a | 0.29 b |
| A4 | 75.19 c | 82.80 a | 6.49 c | 7.39 a | 6.37 c | 7.25 a | 3.32 a | 2.68 a | 0.21 a | 0.27 b |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 地点和播期互作对米饭食味品质的影响
不同地点间米饭食味品质各项指标差异明显(表4)。2年试验结果表明, 大邑外观和综合评分显著低于南部和射洪; 2018年外观、口感和综合评分均以南部最高, 硬度和黏度则以射洪最高; 2019年射洪外观、口感和综合评分则显著增高, 硬度显著降低, 进而具有较好的米饭食味品质。地点和播期互作对米饭食味品质相关指标的影响存在明显差异。2018年, 较第1播期, 大邑和南部第3播期的外观、口感、黏度和综合评分无显著差异, 第4播期则导致外观、口感和综合评分显著降低; 在射洪, 第2播期的综合评分无显著变化, 第3播期则显著提高了外观、口感和综合评分, 降低了黏度, 而第4播期显著降低了综合评分。2019年, 与其他3个播期相比, 第4播期则有效提高了大邑、南部和射洪的外观、口感和综合评分, 降低了黏度; 第3播期综合评分显著低于第1、第2和第4播期, 并且显著增加了大邑的硬度, 降低了黏度; 在射洪, 较常规第1播期, 第2和第3播期则导致外观、口感和综合评分呈降低趋势。整体看来, 不同地点下, 播期间米饭食味品质各项指标差异显著, 而同一播期的特征指标因生态条件的改变而变化。因此将播期和综合评分作为一个因素进行GGE模型分析, 把各个方向上距离最远的点用直线连接起来, 构成一个多边形, 通过中心对每条边做垂线, 将双标图分为几个扇区, 地点在扇区内分布。位于扇区内环境中, 多边形顶角的综合评分最高[20]。由图2-a可知, 多边形被分割成3个扇形, DY-2018和SH-2018在第3播期综合评分最高, NB-2018在第2播期综合最好, 而DY-2019、NB-2019、SH-2019则在第4播期综合评分最好, 这与表4的分析结果一致。Table 4
表4
表4地点和播期对米饭食味品质的影响
Table 4
| 地点 Location | 播期 Sowing date | 综合评分 Comprehensive score | 外观 Appearance | 口感 Taste | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度 Viscosity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| 大邑 Dayi | A1 | 75.16 a | 80.16 a | 6.58 a | 6.79 b | 6.51 ab | 6.96 bc | 3.29 ab | 2.44 c | 0.16 a | 0.36 a |
| A2 | 74.23 b | 80.17 a | 6.30 b | 6.81 b | 6.41 bc | 7.07 ab | 2.98 b | 2.73 bc | 0.19 a | 0.36 a | |
| A3 | 75.71 a | 77.96 b | 6.60 a | 6.66 b | 6.59 a | 6.84 c | 3.08 b | 3.32 a | 0.19 a | 0.22 b | |
| A4 | 73.93 b | 80.93 a | 6.39 b | 7.12 a | 6.31 c | 7.20 a | 3.50 a | 2.79 b | 0.20 a | 0.24 b | |
| 平均Average | 74.76 C | 79.80 C | 6.47 C | 6.84 C | 6.46 B | 7.02 B | 3.21 AB | 2.82 A | 0.18 B | 0.30 B | |
| 南部 Nanbu | A1 | 79.62 b | 80.88 c | 7.01 a | 6.97 b | 6.71 a | 6.86 b | 2.70 b | 2.60 a | 0.23 a | 0.37 a |
| A2 | 80.57 a | 81.83 b | 6.81 b | 6.99 b | 6.50 b | 6.92 b | 3.17 a | 2.54 a | 0.20 a | 0.43 a | |
| A3 | 79.10 b | 81.51 bc | 7.03 a | 7.02 b | 6.76 a | 6.96 b | 3.26 a | 2.58 a | 0.21 a | 0.29 b | |
| A4 | 76.31 c | 82.91 a | 6.66 c | 7.46 a | 6.39 b | 7.18 a | 3.25 a | 2.64 a | 0.20 a | 0.26 b | |
| 平均Average | 78.90 A | 81.78 B | 6.88 A | 7.11 B | 6.59 A | 6.98 B | 3.10 B | 2.59 B | 0.21 B | 0.34 A | |
| 射洪 Shehong | A1 | 76.52 b | 83.31 b | 6.39 b | 7.47 ab | 6.23 c | 7.19 b | 3.28 a | 2.25 b | 0.29 a | 0.30 a |
| A2 | 76.23 b | 82.23 c | 6.33 b | 6.87 c | 6.26 c | 6.96 c | 3.42 a | 2.13 b | 0.28 a | 0.33 a | |
| A3 | 79.61 a | 82.27 c | 7.10 a | 7.34 b | 6.92 a | 7.17 b | 3.22 a | 2.35 ab | 0.22 b | 0.35 a | |
| A4 | 75.33 c | 84.56 a | 6.42 b | 7.60 a | 6.40 b | 7.38 a | 3.21 a | 2.61 a | 0.21 b | 0.31 a | |
| 平均Average | 76.93 B | 83.09 A | 6.56 B | 7.32 A | 6.45 B | 7.17 A | 3.28 A | 2.34 C | 0.25 A | 0.32 AB | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图2
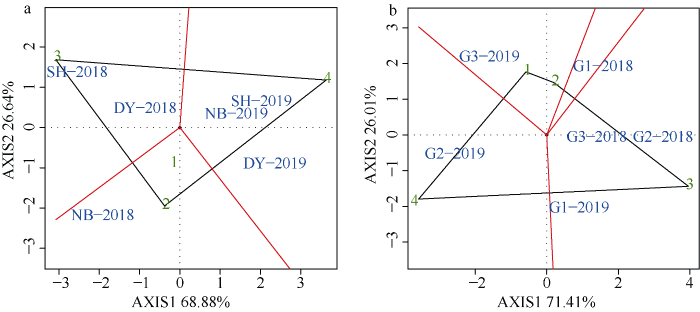 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2GGE双标图分析播期-地点(a)和播期-品种(b)适应性
图中数字1、2、3、4分别代表第1、第2、第3、第4播期; DY: 大邑; NB: 南部; SH: 射洪。G代表品种, 后面的数字1、2、3分别代表宜香优2115、F优498、川优6203。图a、b中2018、2019代表年份。
Fig. 2Adaptability analysis of sowing date-location (a) and sowing date-variety (b) based on GGE biplot
The numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the figure represent the first, second, third, and fourth sowing dates, respectively; DY: Dayi; NB: Nanbu; SH: Shehong. G represents the variety, and the numbers 1, 2, and 3 at the back represent Yixiangyou 2115, F you 498, and Chuanyou 6203, respectively. In this figure, a and b represent in 2018 and in 2019.
2.4 播期和品种对米饭食味值的影响
表5表明, 品种对米饭食味品质具有调控作用, 不同品种间米饭食味品质的各项指标存在显著差异。3个水稻品种米饭食味计和硬度黏度仪2年间变化趋势一致, 综合评分、外观和口感均表现为, 宜香优2115>川优6203>F优498; 硬度值则为F优498>川优6203>宜香优2115; 黏度值则表现为, 川优6203>宜香优2115>F优498。综合看来, 宜香优2115的米饭食味品质显著优于其他2个水稻品种。播期和品种互作显著影响米饭食味值的各项指标。较常规第1播期, 2018年, 宜香优2115的外观、口感和综合评分在第3播期差异不显著, 第4播期导致外观、口感和综合评分显著降低, 而硬度在第4播期达到最大, 黏度值没有差异, F优498和川优6203在第3播期差异显著, 第2和第3播期降低了这3个指标的评分, F优498的硬度和黏度则在4个播期之间差异不显著, 而川优6203的硬度值差异不显著, 第3、第4播期降低了这2个品种的黏度值, 黏度值在第2播期达到最大。2019年, 宜香优2115的综合评分在第3播期达到最大, 而外观、口感以及硬度则在第4播期达到最大, 从而导致黏度值降低; 对于F优498, 第4播期显著提高了外观、口感、黏度和综合评分, 降低硬度值; 对于川优6203, 第3播期显著降低了、外观、口感、黏度和综合评分, 显著增加了硬度值。从GGE双标图(图2-b)中可以得到, G1-2019、G3-2018、G2-2018在第3播期综合评分最高, G1-2018在第2播期综合评分最好, G3-2019、G2-2019分别在第1播期、第4播期综合评分最好, 这与表5的结果一致。Table 5
表5
表5播期和品种对米饭食味品质的影响
Table 5
| 品种 Variety | 播期 Sowing date | 综合评分 Comprehensive score | 外观 Appearance | 口感 Taste | 硬度 Hardness | 黏度 Viscosity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| 宜香优2115 Yixiangyou 2115 | A1 | 81.97 a | 82.68 b | 7.21 a | 7.19 b | 7.04 a | 7.12 b | 2.08 b | 1.89 b | 0.21 a | 0.33 ab |
| A2 | 82.11 a | 83.47 b | 7.30 a | 7.12 b | 7.16 a | 7.17 b | 2.55 a | 1.99 b | 0.25 a | 0.36 a | |
| A3 | 81.66 a | 85.40 a | 7.30 a | 7.70 a | 7.06 a | 7.60 a | 2.53 a | 2.03 ab | 0.22 a | 0.35 ab | |
| A4 | 78.94 b | 84.91 a | 6.96 b | 7.77 a | 6.76 b | 7.61 a | 2.81 a | 2.36 a | 0.21 a | 0.28 b | |
| 平均值Average | 81.17 A | 84.11 A | 7.19 A | 7.44 A | 7.00 A | 7.38 A | 2.49 C | 2.07 C | 0.22 B | 0.33 B | |
| F优498 F you 498 | A1 | 71.46 b | 78.34 b | 6.14 b | 6.73 b | 5.96 b | 6.63 b | 4.23 a | 3.06 b | 0.15 a | 0.25 ab |
| A2 | 72.07 b | 77.52 c | 5.67 d | 6.43 c | 5.54 d | 6.59 b | 3.93 a | 3.11 b | 0.14 a | 0.26 a | |
| A3 | 74.38 a | 76.27 d | 6.62 a | 6.50 c | 6.43 a | 6.52 b | 4.10 a | 3.58 a | 0.13 a | 0.17 c | |
| A4 | 69.81 c | 80.39 a | 5.91 c | 7.12 a | 5.79 c | 6.00 a | 4.10 a | 3.30 ab | 0.12 a | 0.18 bc | |
| 平均值Average | 71.93 C | 78.13 C | 6.09 C | 6.70 C | 5.93 C | 6.66 C | 4.09 A | 3.26 A | 0.13 C | 0.21 C | |
| 川优6203 Chuanyou 6203 | A1 | 77.88 a | 83.32 a | 6.62 b | 7.30 a | 6.46 b | 7.24 a | 2.97 a | 2.34 ab | 0.32 a | 0.45 a |
| A2 | 76.86 b | 83.24 a | 6.48 c | 7.11 b | 6.47 b | 7.19 a | 3.09 a | 2.30 b | 0.28 ab | 0.49 a | |
| A3 | 78.39 a | 80.07 b | 6.81 a | 6.82 c | 6.78 a | 6.84 b | 2.94 a | 2.64 a | 0.26 b | 0.35 b | |
| A4 | 76.82 b | 83.10 a | 6.60 bc | 7.29 a | 6.56 b | 7.24 a | 3.05 a | 2.39 ab | 0.28 ab | 0.36 b | |
| 平均值Average | 77.49 B | 82.43 B | 6.63 B | 7.13 B | 6.56 B | 7.13 B | 3.01 B | 2.42 B | 0.28 A | 0.41 A | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.5 GGE双标图分析播期和综合评分稳定性
可以通过GGE双标图揭示各个地点不同播期综合评分的稳定性。图中的小圆圈代表“平均环境”。带单箭头的直线是平均环境轴。它所指的方向是地点在所有播期环境下的近似综合评分, 越往箭头方向综合评分越高; 与平均环境轴垂直并通过原点的直线代表各品种与各播期相互作用的倾向性, 越偏离“平均环境轴”越不稳定[20]。由图3可以看出, 在大邑, 综合评分在DY1最高, DY2、DY4次之, DY3最低, 稳定性较好的依次是DY2、DY3、DY1、DY4, 由此可见DY2综合评分较高而且稳定。对于南部和射洪, 综合评分和稳定性均表现为第2和第3播期的高于第1和第4播期, 南部和射洪采用第2和第3播期具有较好的综合评分和稳定性。图3
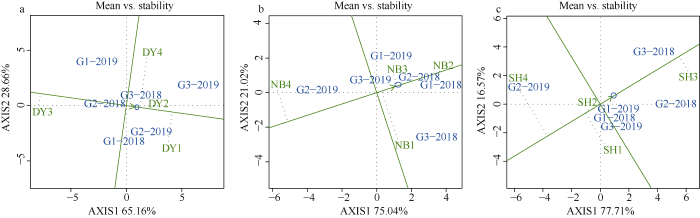 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3基于GGE双标图分析播期和综合评分的稳定性
图中G代表品种, 后面的数字1、2、3代表品种, 即宜香优2115、F优498、川优6203; 2018、2019代表年份; DY: 大邑(a); NB: 南部(b); SH: 射洪(c); 地点后面的数字1、2、3、4分别代表第1、第2、第3、第4播期。
Fig. 3Stabilities of sowing date and comprehensive score based on GGE biplot
In the figure, G represents the variety, and the numbers 1, 2, and 3 at the back represent the varieties, namely Yixiangyou 2115, F you 498, and Chuanyou 6203; 2018 and 2019 represent the year. DY: Dayi (a); NB: Nanbu (b); SH: Shehong (c); The number 1 2, 3, and 4 behind the location represent the first, second, third, and fourth sowing dates, respectively.
2.6 气象因子与米饭食味品质相关性分析
对3个生态点各播期气象因子与综合评分进行相关性分析(表6), 结果表明综合评分与气象条件密切相关。综合评分与南部和射洪播种至抽穗期的积温呈显著或极显著正相关, 在射洪和南部分别与播种至抽穗期日照时数、降雨量呈显著正相关和极显著负相关关系; 综合评分与南部和射洪全生育期日平均温度呈显著或极显著负相关关系; 综合评分与日照时数、降雨量在大邑呈显著或极显著负相关, 在射洪综合评分则与全生育期日照呈极显著正相关; 综合评分与抽穗至成熟期的积温在大邑达到显著水平, 在射洪呈极显著负相关, 与日照时数在大邑和射洪呈极显著负相关关系, 而南部都没有达到显著水平。3个地点综合起来和气象因子进行相关性分析, 结果表明, 综合评分与播种至抽穗期的积温和降雨量分别呈极显著正相关和显著负相关, 与抽穗至成熟期的积温、日照时数呈极显著负相关, 与全生育期的降雨量呈极显著负相关关系。对抽穗至成熟期的气象因子与综合评分进行通径分析(表7), 结果表明, 气象因子对综合评分的贡献情况因地点而异。大邑各气象因子通径系数绝对值大小排序为: 日照时数>积温>日平均温度>降雨量; 南部的日照时数的贡献率最大, 积温和降雨量次之, 日平均温度最小; 而射洪的积温贡献率则大于日照时数。综合3个地点分析, 贡献率最大的是积温, 日照时数次之, 最小的是日平均温度和降雨量。Table 6
表6
表6气象因子与综合评分相关性分析
Table 6
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 生态点 Location | 播种-抽穗期 S-H | 抽穗-成熟期 H-M | 全生育期 Whole growth period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日平均温度 Daily average temperature | 大邑Dayi | -0.037 | -0.224 | -0.237 |
| 南部Nanbu | -0.239 | -0.185 | -0.411* | |
| 射洪Shehomg | -0.148 | -0.328 | -0.512* | |
| 3个生态点 3 ecological points | -0.005 | -0.039 | -0.048 | |
| 积温 Accumulated temperature | 大邑Dayi | -0.040 | -0.464* | -0.131 |
| 南部Nanbu | 0.486* | -0.364 | 0.354 | |
| 射洪Shehomg | 0.587** | -0.646** | 0.099 | |
| 3个生态点 3 ecological points | 0.354** | -0.343** | -0.179 | |
| 日照时数 Sunshine hours | 大邑Dayi | -0.380 | -0.578** | -0.504* |
| 南部Nanbu | -0.181 | -0.378 | -0.295 | |
| 射洪Shehomg | 0.492* | -0.549** | 0.522** | |
| 3个生态点 3 ecological points | 0.001 | -0.275** | -0.130 | |
| 降雨量 Rainfall | 大邑Dayi | -0.520** | -0.141 | -0.597** |
| 南部Nanbu | -0.114 | 0.301 | 0.282 | |
| 射洪Shehomg | 0.330 | 0.506* | -0.051 | |
| 3个生态点 3 ecological points | -0.267* | -0.013 | -0.246* |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
3.1 生态条件对杂交籼稻米饭食味品质的影响
稻米品质是由品种遗传特性、气候生态环境和栽培管理措施等因素共同作用的结果[21,22,23]。温光资源作为影响食味品质的主要限制因子, 适温(21~26℃)有利于水稻灌浆和淀粉的充实与沉积, 过高或过低温度均不利于提高水稻品质[24]。进一步研究发现, 高温或低温胁迫下, 水稻生理生化活性下降, 光合功能降低, 抗逆性减弱, 干物质积累和运转受抑, 从而造成品质变劣[15,24-26]。本研究则发现, 不同地点间水稻生长季所处生态环境差异明显, 而综合评分与抽穗前积温呈极显著正相关, 与抽穗后积温则呈极显著负相关, 这与前人研究结果相似, 灌浆结实期高温导致籽粒灌浆加速, 过快消耗养分, 致使籽粒充实度差, 从而增加垩白度和垩白粒率,降低稻米蛋白质含量[27], 最终导致综合评分降低。此外, 王娇等[28]研究结果表明稻米品质性状与降雨量密切相关, 本研究中不同地点间, 综合评分还与抽穗前和全生育期降雨量呈显著负相关, 与抽穗至成熟期的日照时数呈极显著负相关。较南部和射洪, 大邑抽穗前和全生育期降雨量(2018年)以及抽穗后日照时数(2019年)明显较高, 从而使大邑的外观、口感、黏度和综合评分显著低于其他2个地点, 而硬度则高于其他2个地点。沈新平等[29]在江苏4个生态点的研究表明, 随着纬度的北移, 水稻的直链淀粉含量呈现先增加后减少的趋势, 而蛋白质含量呈现“小—大—小—大”的变化趋势。吉志军等[30]等进一步研究发现, 籼稻品种的外观品质以纬度较高的地区较优。本研究中, 随着纬度的升高, 综合评分、外观和口感评分变大, 黏度值升高, 而硬度值则变大。Table 7
表7
表7抽穗至成熟期气象因子对综合评分的作用
Table 7
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 通径系数 Path coefficient | 贡献率 Contribution rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接作用 Direct effect | 间接作用 Indirect effect | |||||
| 日平均温度 Daily average temperature | 积温 Accumulated temperature | 日照时数 Sunshine hours | 降雨量 Rainfall | |||
| 大邑 Dayi | ||||||
| 日平均温度Daily average temperature | 0.338 | -0.014 | -0.515 | -0.033 | 0.076 | |
| 积温 Accumulated temperature | -0.269 | 0.018 | -0.187 | -0.025 | 0.125 | |
| 日照时数 Sunshine hours | -0.748 | 0.233 | -0.067 | 0.005 | 0.432 | |
| 降雨量 Rainfall | -0.184 | 0.061 | -0.037 | 0.019 | 0.026 | |
| 南部 Nanbu | ||||||
| 日平均温度Daily average temperature | 0.311 | 0.030 | -0.383 | -0.143 | -0.058 | |
| 积温 Accumulated temperature | -0.221 | -0.042 | -0.049 | -0.053 | 0.077 | |
| 日照时数 Sunshine hours | -0.495 | 0.240 | -0.022 | -0.101 | 0.187 | |
| 降雨量 Rainfall | 0.222 | -0.200 | 0.053 | 0.266 | 0.067 | |
| 射洪 Shehong | ||||||
| 日平均温度Daily average temperature | -0.067 | -0.122 | -0.356 | 0.217 | 0.022 | |
| 积温 Accumulated temperature | -0.606 | -0.013 | -0.249 | 0.222 | 0.391 | |
| 日照时数 Sunshine hours | -0.411 | -0.058 | -0.367 | 0.287 | 0.226 | |
| 降雨量 Rainfall | -0.322 | 0.045 | 0.417 | 0.366 | -0.163 | |
| 3个地点 3 locations | ||||||
| 日平均温度Daily average temperature | 0.236 | -0.119 | -0.290 | 0.134 | -0.009 | |
| 积温 Accumulated temperature | -0.409 | 0.069 | -0.124 | 0.122 | 0.140 | |
| 日照时数 Sunshine hours | -0.397 | 0.173 | -0.128 | 0.077 | 0.109 | |
| 降雨量 Rainfall | -0.228 | -0.139 | 0.219 | 0.134 | 0.003 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3.2 播期对杂交籼稻米饭食味品质的影响
播期调节是优化稻米品质的重要栽培措施之一。随着播期推迟, 各品种拔节期、抽穗期和成熟期相应延迟, 全生育期缩短, 水稻抽穗到成熟期日平均温度逐渐降低, 日照时数逐渐缩短[19]。灌浆结实期是稻米品质形成的关键时期, 而播期能改变水稻各生育阶段的气候生态条件及其持续时间, 特别是通过调整水稻灌浆结实期的气象条件, 从而影响稻米品质[21,31]。关于播期对稻米品质的影响, 前人开展了较多研究, 但由于试验地点、试验材料和试验设计不同, 所得结果也不尽相同。朱镇等[16,32]研究表明, 随着播期的推迟, 稻米加工品质呈先升后降的变化趋势, 外观品质变优, 蒸煮食用品质下降。龚金龙等[24]研究指出, 随着播期推迟, 灌浆结实期日均温度呈有规律的下降, 灌浆速率更平缓, 合理分配灌浆物质, 缩小细胞孔隙籽粒充实较好, 质地紧密, 利于提升碾米品质和外观品质。而程方民等[12]研究表明, 适宜播期内, 晚播有利于优质稻米的形成。随着播期的推迟, 整精米率和直链淀粉含量增高, 蛋白质含量下降, 食味值有所改善[33,34]。本研究则发现, 播期显著影响米饭食味品质的各项指标, 2018年的第3播期和2019年的第4播期处理均显著提高了综合评分、外观和口感评分。此外, 播期和地点互作显著影响综合评分。在大邑, 综合评分与抽穗至成熟阶段积温、日照时数, 以及全生育期日照时数和降雨量呈显著或极显著负相关; 在南部和射洪, 综合评分则与全生育期日平均温度呈显著负相关与抽穗前积温呈显著正相关。因此, 应根据各地点不同的环境条件, 采取适宜的播期调节米饭食味品质。由GGE双标图分析播期和综合评分稳定性可知, 在南部和射洪, 第2和第3播期具有较好的综合评分和稳定性, 可以调节水稻生育进程, 改善水稻全生育期气候生态条件, 特别是抽穗后的田间气候条件, 提高效利用水稻生长季温光资源, 调节光合物质积累与转化过程, 优化籽粒灌浆动态进而提高稻米的食味品质[15,17,25,35]。对于大邑而言, 第2播期则具有较好的综合评分和稳定性。对于品种而言, 一般认为品种自身的遗传特性影响稻米品质的关键因素, 不同品种间差异明显[21,36]。对于本研究所选取的3个杂交籼稻品种, 在不同年份、地点、播期条件下, 综合评分均表现为, 宜香优2115>川优6203>F优498。前人研究指出, 播期与品种的合理搭配可以协调水稻的生育进程, 有利于充分利用水稻生长季的温光资源, 获得最大的光合生产量, 从而最大限度挖掘优良品种高产潜力, 促进稻米品质的形成[23]。从本试验可以看出, 在四川稻区不同生态条件下合理的播期设置与优质品种搭配, 可以有效改善米饭食味品质。本研究中宜香优2115在2年3个地点均具有最高的综合评分, 该品种可作为优食味品种在四川稻区进行推广。
4 结论
播期对四川盆地米饭食味品质具有显著影响。杂交籼稻的米饭食味品质是地点、播期、品种及其互作共同作用的结果, 应根据各地点不同的环境条件, 采取适宜的播期调节米饭食味品质。针对四川地区独特的温光资源和耕作种植制度, 要充分考虑前茬作物[麦(油)茬]收获时间的限制性, 本研究发现, 适度推迟播期可提高米饭食味品质。在大邑采用第2播期具有较好的综合评分且稳定性好; 在南部和射洪, 采用第2、第3播期具有较好的综合评分和稳定性。综合来看, 在四川盆地, 播期推迟10~20 d可以使水稻灌浆结实期处于较合理的温光环境, 进而有效改善杂交籼稻的米饭食味品质, 提高综合评分和稳定性。此外, 选择宜香优2115可以获得较好的食味品质。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1038/nplants.2017.31URLPMID:28319055 [本文引用: 1]

Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a staple food for more than half of the world's population. To meet the ever-increasing demand for food, because of population growth and improved living standards, world rice production needs to double by 2030(1). The development of new elite rice varieties with high yield and superior quality is challenging for traditional breeding approaches, and new strategies need to be developed. Here, we report the successful development of new elite varieties by pyramiding major genes that significantly contribute to grain quality and yield from three parents over five years. The new varieties exhibit higher yield potential and better grain quality than their parental varieties and the China's leading super-hybrid rice, Liang-you-pai-jiu (LYP9 or Pei-ai 64S/93-11). Our results demonstrate that rational design is a powerful strategy for meeting the challenges of future crop breeding, particularly in pyramiding multiple complex traits.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.085URLPMID:25442575 [本文引用: 1]

[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110497URLPMID:32540015 [本文引用: 2]

Appearance quality is an important determinant of rice quality. Many genes that affect grain appearance quality have been identified, but the regulatory mechanisms that contribute to this trait remain unclear. Here, two grains with chalkiness (gwc1) mutants, gwc1-1 and gwc1-2, were identified from an EMS-mutagenized population of indica rice cultivar Shuhui498 (R498). The gwc1 mutants had poor grain appearance quality consistent with the measured values for the percentage of grains with chalkiness, square of chalky endosperm, the total starch, amylose and sucrose contents. Milling quality and grain size were also affected in the gwc1 mutants. The gwc1-1 and gwc1-2 were found to be loss-of-function allelic mutants. GWC1 was mapped to the long arm of rice chromosome 8 using the MutMap strategy and incorrectly annotated in the reference genome for Nipponbare (MSU). The GWC1 gene corresponds to the WTG1/OsOTUB1 gene, which encodes an otubain-like protease with deubiquitinating activity that is homologous to human OTUB1. GWC1 transcripts accumulated to high levels in early endosperm after fertilization and developing inflorescences, and GWC1-green fluorescent protein (GFP) signal was detected in the nucleus and cytoplasm. GWC1 is likely to regulate grain appearance quality through genes involved in sucrose metabolism and starch biosynthesis. Overall, the present findings reveal that GWC1 is important for grain quality and yield due to its effects on grain chalkiness and size.
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.112URLPMID:26593544 [本文引用: 1]

