摘要/Abstract
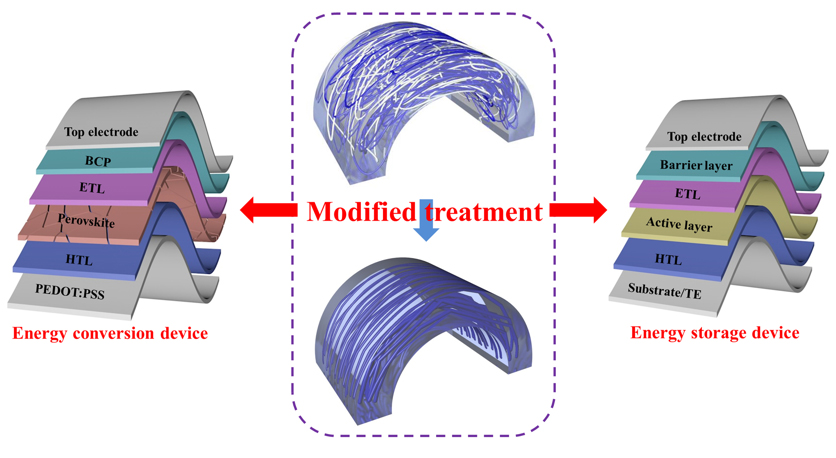
近年来, 柔性有机和钙钛矿光伏器件、有机薄膜晶体管和医用传感器等因其具有可穿戴性、柔性、半透明性等优点, 成为科学研究的热门领域. 利用具有优异力学性能的导电聚合物是实现这些高性能器件的有效途径之一. 在导电聚合物中, 3,4-亚乙基二氧噻吩(PEDOT)及其水性分散液3,4-亚乙基二氧噻吩:聚苯乙烯磺酸盐(PEDOT:PSS)已经被证明是最有前途替代传统金属氧化物的柔性材料, 其在器件中可作为透明电极、空穴传输层、互连器、电活性层或运动传感导体等. 综述了PEDOT及PEDOT:PSS应用柔性器件的研究现状, 包括提高电导率、机械耐受性和长期稳定性的各种策略, 揭示了性能增强的潜在机理. 最后, 论述了导电聚合物在器件制备中亟待解决的问题和未来发展方向. 本工作讨论了导电聚合物薄膜形貌的重要性, 并展望了它们在下一代柔性电子器件中的广阔前景.
关键词: PEDOT/PEDOT:PSS, 电导率, 透明电极, 柔性能源电子, 可拉伸器件
In recent years, flexible organic and perovskite photovoltaic devices, organic thin-film transistors and medical sensors have been become popular fields of scientific research due to their advantages of wearable, flexible and semi-transparent properties. Employing conductive polymer with excellent mechanical properties is one of the effective pathways to realize these high-performance devices. In conducting polymers, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and its aqueous dispersion poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) have been demonstrated to be the most promising alternative flexible materials of conventional metal oxides. It can be used as transparent electrode, hole transport layer, interconnects, electroactive layer, or motion sensing conductor in the device. This review focused on recent research advances of flexible devices for PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS applications, including various strategies to improve electrical conductivity, mechanical tolerance and long-term stability, and reveals the potential mechanisms of performance enhancement.
Key words: PEDOT/PEDOT:PSS, electrical conductivity, transparent electrode, flexible energy electronics, stretchable device
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
