摘要/Abstract
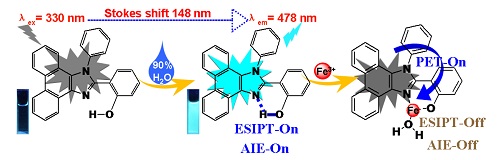
设计合成具有激发态分子内质子转移(ESIPT)和聚集诱导发光(AIE)特征的酚羟基菲并咪唑Fe3+荧光探针PIP-o-OH,对其结构进行了表征和确认,并通过单晶结构确认了探针PIP-o-OH中的O-H与咪唑N的分子内氢键.紫外和荧光光谱分析表明,探针PIP-o-OH与Fe3+形成络合物后实现Fe3+的选择性识别,并通过质谱和离散傅立叶变换(DFT)计算确定了探针PIP-o-OH与Fe3+的配位方式.探针PIP-o-OH与Fe3+络合前后的荧光变化成功应用于HeLa细胞和实际水样中Fe3+的检测.
关键词: 菲并咪唑, Fe3+, 荧光探针, 细胞成像, 水样
Selective detection of Fe3+ has considerable importance due to its active involvement in various biological processes. Based on the mechanism of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) plus aggregation induced emission (AIE), a fluorescence probe of phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole modified by the phenolic hydroxyl (PIP-o-OH) had been designed, synthesized and applied in the detection of Fe3+. The structure of PIP-o-OH was characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, HRMS and X-ray single diffraction. Furthermore, a clear intramolecular hydrogen bond was observed between hydroxyl O-H and imidazole N atom in X-ray single structure, which improved the impossibility of ESIPT activity. ESIPT and AIE activities of PIP-o-OH were adequately determined by absorption, emission spectra and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The aggregated PIP-o-OH in MeOH/H2O (V:V=1:9, Hepes 10 μmol/L, pH=7.4) exhibited a good sensitivity towards Fe3+ with "turn-off" fluorescence response just after 20 s. The limit of detection (LOD) was calculated as low as 0.49 μmol/L. So it could be utilized to detect Fe3+ in biology and environmental samples. In addition, the calculation of the density functional theory (DFT) confirmed the formation of PIP-o-OH-Fe3+ complex. Also, PIP-o-OH was successfully applied to monitor Fe3+ in HeLa cells by the fluorescence change and quantificationally detect Fe3+ in water samples.
Key words: phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole, Fe3+, fluorescence probe, cell imaging, water samples
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
