摘要/Abstract
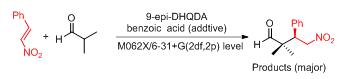
通过密度泛函方法(DFT)研究了(9S)-9-氨基-10,11-二氢-6'-甲氧基奎宁(9-epi-DHQDA)及辅助催化剂苯甲酸催化1-硝基-2-苯基乙烯与2-甲基丙醛的不对称Michael加成反应的机理.对反应通道上的反应物、中间体、过渡态和产物进行了结构优化,通过能量和振动频率分析及内禀反应坐标(IRC)计算证实了中间体过渡态的合理性,并通过自然键轨道(NBO)理论和原子轨道(AIM)分析了分子轨道的相互作用及成键特点.机理如下:苯甲酸辅助9-epi-DHQDA与羰基化合物2-甲基丙醛发生缩合反应形成亚胺离子中间体,随后亚胺离子作为亲电试剂与1-硝基-2-苯基乙烯进行加成反应,生成的复合物从胺基团到1-硝基-2-苯基乙烯发生了质子转移.该阶段决定了整个反应的立体选择性,也是速率决速步骤,最后水分子参与水解过程和碳氧双键的形成得到了最终产物.
关键词: 密度泛函, 金鸡纳碱衍生伯胺, Michael加成, 机理, 立体选择性
The theoretical study is presented for the Michael addition reaction between trans-1-nitro-2-phenylethylene and 2-methylpropionaldehyde catalyzed by (9S)-9-amino-6'-methoxy-10,11-dihydrocinchonan (9-epi-DHQDA) and benzoic acid. All structures, including the reactants, intermediates, transition states and products were optimized. Transition states have been confirmed by the corresponding vibration analysis and intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC). In addition, nature bond orbital (NBO) and atoms in molecules (AIM) theories have been used to analyze orbital interactions and bond natures. Calculations indicate that the benzoic acid might undergo a proton step to the 9-epi-DHQDA to produce the iminium intermediate. Then the iminium serves as a reactive acceptor to participate in the subsequent nucleophilic addition. Next, a proton transfer process from the tertiary amine to nitronate carbon is found to be rate-determining step, and the enantioselectivity of the catalyzed Michael reaction is also controlled by this step. Finally, one water molecule participates in hydrolysis and C=O bond formation, and results in the formation of product and recovery of catalyst.
Key words: cinchona alkaloid derived primary amine, density functional theory, Michael addition, mechanism, enantioselectivity
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
