全文HTML
--> --> --> 2019年,中国粗钢产量达到9.963×108 t,比2018年增长8.3%,在全球粗钢产量中的份额上升到53.3%[1]。钢铁行业发展迅猛,其原料之一的铁矿石虽现储量十分丰富,但大多数已探明的铁矿石品位较低,只有经过选矿和富集处理后才能使用[2];而且,大多常规选矿方法只针对高品位铁矿石,大量低品位铁尾矿被废弃。虽然这些铁尾矿的铁平均品位较低,但是由于其历史存量非常大,如果按铁尾矿总量计算,铁元素的总含量十分庞大;加之随着选矿技术的发展和铁矿石价格的上涨,低品位的铁尾矿又被赋予了利用价值。然而,低品位铁尾矿粒度细、易泥化,常规选矿方法成本高,难以有效回收利用[2]。从铁尾矿中富集铁的方法有很多,主要包括直接还原法[3-5]、微波焙烧[6-7]、悬浮磁化焙烧[8-9]和浮选[10]等方法。其中,还原焙烧结合磁选工艺已被证明可获得高铁品位,并可从贫矿中回收铁元素,获得高品位的铁精矿[11-14]。磁化焙烧是将弱磁性铁矿石还原焙烧成强磁性的铁精矿,利用低强度磁选设备进行简单回收的一种焙烧工艺。反应机理可用方程式(1)和式(2)表示。在磁化焙烧过程中,需要大量的还原剂,若将煤作为磁化焙烧的主要还原剂[13],不仅会增加生产成本,而且在加热过程中会产生二氧化硫。因此,寻找低成本、少污染的绿色还原剂成为铁尾矿磁化焙烧技术工业化应用的关键。
有研究[15]发现,生物质热解产生的固体碳和各种烃类气体等可以作为磁化焙烧的还原剂。生物碳是生物质热解的固体产物,可以由农业废弃物如鸡粪、猪粪、木屑、秸秆以及工业有机废弃物、城市污泥等得来[15]。生物质碳化过程降解了部分生物质,但保留了大部分含碳物质,使得产物的碳含量更高,因此更容易用作技术流程的替代品[16];并且该工艺还具有减少温室气体排放、降低SOx和NOx生成等环境友好特性[17]。NAYAK等[18]研究了废椰壳在铁矿还原焙烧中的应用,在焙烧温度为800 ℃、生物质投料比为20%和焙烧时间为60 min的焙烧条件下,将铁品位从49%提高到63%。ZHANG等[19]研究发现,以秸秆为还原剂时,铁尾矿的磁性得到了有效提升,焙烧后的饱和磁化强度为60.13 emu·g?1。RATH等[20]利用木屑和花生壳混合而成的生物质作为还原剂,研究包头低品位褐铁矿的磁化焙烧情况,当温度为750 ℃、生物质投加量为10%和焙烧时间为40 min时,在磁选后能得到回收率为64%、品位为65%的铁精矿。以往的研究大多使用椰壳、花生壳等不同生物质做还原剂,在磁化焙烧后,均能在一定程度上还原矿中的铁元素,将弱磁性铁还原成强磁性铁,但以木屑生物质作为磁化焙烧-磁选过程还原剂的研究还比较少。我国每年产生的木材加工类废弃物108 t[21],其中包括锯木厂、木器加工厂、伐木场等企业排放的大量锯木屑。将木屑用于铁尾矿中铁回收,既能解决目前铁精矿供应不足的问题,也能解决大量木屑废弃物堆积的环境问题。
本研究为探究木屑生物质作为还原剂在铁矿石磁化焙烧磁选工艺中应用的可能性,在焙烧温度650、750、850和950 ℃,木屑与铁尾矿的配比为5、10、15和20%的条件下,将掺入木屑的铁尾矿在管式炉内分别焙烧20、40、60和80 min后,采用低强度磁选法对这些焙烧矿进行分离。研究木屑的掺入对铁精矿品位及回收铁的影响,通过XRD与热重分析研究焙烧过程中的机制,对铁尾矿焙烧前后的表面形貌变化及磁性性能进行了测定,为分析铁的回收效率提供参考。
1.1. 实验原料
本研究以广东省韶关市大宝山铁尾矿为研究对象,尾矿样品经过自然风干后,用球磨机磨细过200目标准筛,置于干燥器中干燥待用。X射线荧光光谱分析仪(XRF)用于测定铁尾矿的化学组成。本研究样品中主要由Fe、Si、Al等元素的氧化物构成。其中,总铁(TFe)占比为31.79%,是主要的有用元素;其次是占20.70%的SiO2和7.43%的Al2O3;此外,尾矿中还含有少量铜、铅、锌。
本研究所用还原剂为木屑,将其烘干、磨碎后过200目标准筛,干燥保存待用。参考《煤的工业分析方法》(GB/T 212-2008)[22]测定木屑的挥发分、水分及灰分,计算后得出固定碳的含量。经测定及计算,组分含量最大的是固定碳,占比为50.12%,其次是灰分,占比为28.20%,挥发分占比为21.34%,水分占比为0.34%。
1.2. 实验方法
实验室规模的管式炉用于磁化焙烧实验。将木屑与铁尾矿按一定质量比在球磨机里研磨30 min,充分混合后,将20 g混合样品放入管式炉中,通入氮气,防止焙烧矿在降温过程中发生再氧化反应,以5 ℃·min?1的升温速度加热。在焙烧温度为650、750、850和950 ℃,木屑与铁尾矿的比例为5、10、15和20%的条件下,将掺入木屑的铁尾矿在管式炉内分别焙烧20、40、60和80 min。将焙烧矿研磨过200目筛后,在湿法磁选法在磁选管中分离焙烧矿,工作电流为3 A。磁选后,分选铁精矿和非铁精矿部分,干燥并称重。用化学分析法测定铁品位,以式(3)计算铁回收率。式中:
1.3. 分析方法
X射线荧光光谱(XRF)用于分析铁尾矿样品的主要组成成分。X射线衍射仪(XRD)用于分析矿物组成,测定条件为Cu Kα靶,扫描电压为40 kV,电流为100 mA,扫描速度为5 (°)·min?1,扫描角度为10°~80°。扫描电镜(SEM)用于观察铁尾矿样品焙烧前后的形貌变化。原尾矿、焙烧矿和铁精矿经磨细后,取1 g样品加入6 mL 65%硝酸(AR,HNO3)、2 mL 35%浓盐酸(AR,HCl)和2 mL 40%氢氟酸(AR,HF)于微波反应仪中,进行消解后赶酸,用纯水稀释至50 mL,火焰原子吸收光谱仪(AAS)用于测定总铁含量。热重(TG)用于测定原铁矿与15%木屑与铁尾矿混合物的热重变化,氮气氛围,升温速率为10 ℃·min?1。振动样品磁强计(VSM)用于研究样品焙烧前后的磁性。随着磁场强度的增加,磁化强度增加并达到最大值,此时的磁化强度记为Ms。Ms值与样品磁性有关,Ms值大,表明样品的磁性强,便于通过弱磁选对样品进行分离。1.4. 实验仪器
管式炉(SK2-2-130,天津中环电炉股份有限公司);行星式球磨机(QM-3SP2,南京南大仪器有限公司);磁选管(XCGS-50,江西龙中机械设备有限公司);微波反应仪(COOLPEX,上海屹尧有限公司);X射线荧光光谱(EDX-7000,日本Shimadzu公司);X射线衍射仪(D8 ADVANCE,德国Bruker公司);场发射扫描电子显微镜(SU8220,日本Hitach公司);火焰原子吸收光谱仪(Z200,日本日立公司);热重分析仪(209F1,德国NETZSCH公司);振动样品磁强计(7410,美国Lake Shore公司)。2.1. 木屑还原铁尾矿的优化
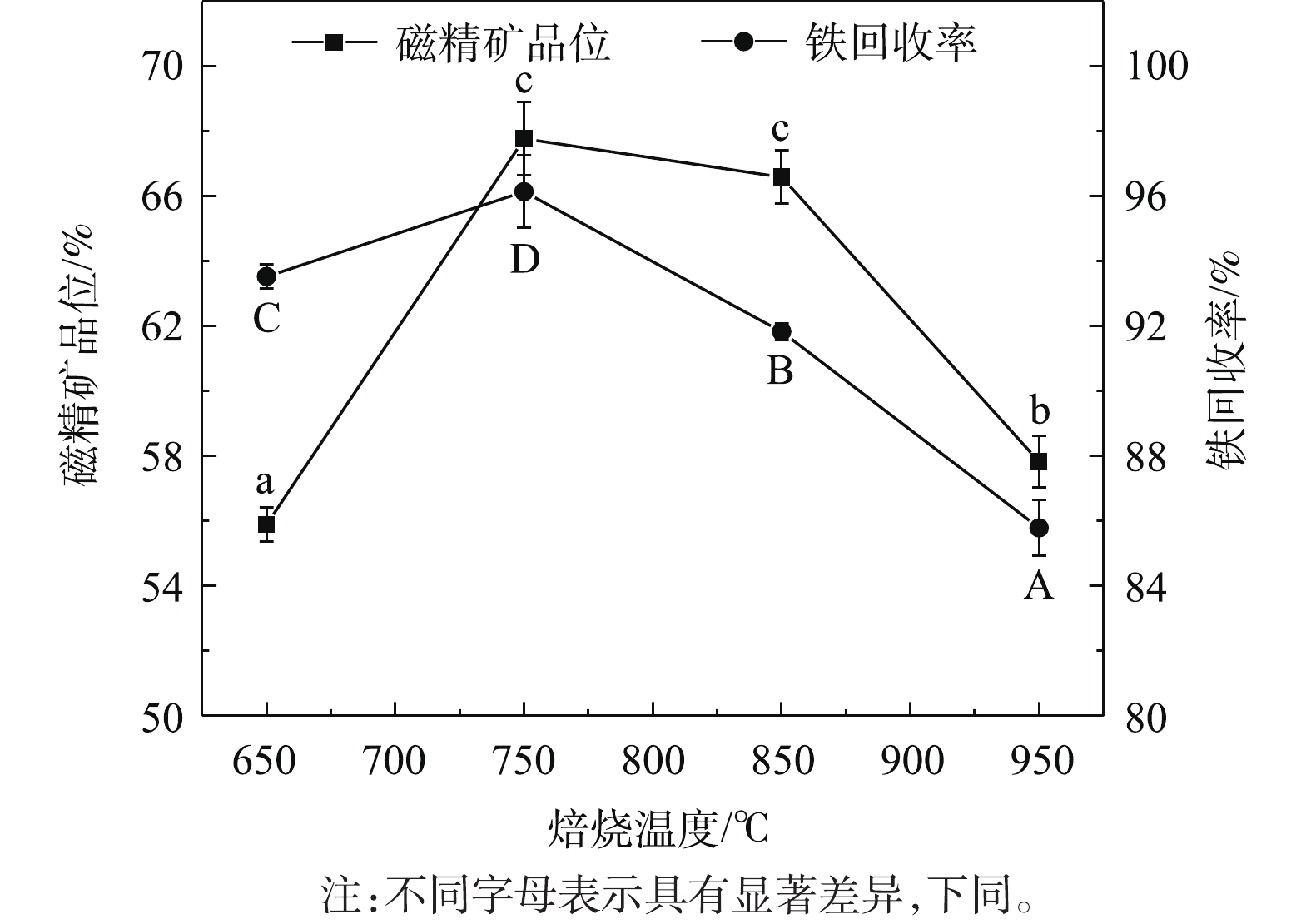
焙烧温度对磁化还原过程有着重要影响。本研究参考RATH等[20]的实验条件,初步固定木屑添加量为10%、焙烧时间为40 min,探究不同焙烧温度对铁回收率、铁精矿品位的影响,结果如图1所示。可以看出,随着焙烧温度的增加,铁精矿品位先升高而后降低,值得注意的是,750 ℃及850 ℃对应的磁精矿品位均大于65%,且无显著差异;在750 ℃时铁精矿品位达到(67.77±1.14)%,相比于原矿的31.79%,得到显著提高。而后,随着焙烧温度继续增加,铁精矿品位开始出现下降趋势。这可能是因为在升温过程中,Fe3O4进一步与脉石矿物SiO2反应,转化成弱磁性的铁橄榄石Fe2SiO4[23]。铁回收率在不同焙烧温度下得到的回收率差异显著(P<0.05)。当焙烧温度为750 ℃时,铁回收率最高,为(96.14±1.12)%。因此,最优焙烧温度为750 ℃。木屑添加量是影响磁化焙烧效果的重要因素之一,木屑添加量太少会导致铁矿物还原不完全,而过多又会发生过还原反应[24]。因此,进行了木屑添加量条件实验。在固定焙烧温度为750 ℃、还原焙烧时间为40 min的条件下,研究木屑添加量对磁化焙烧的影响。实验结果如图2所示。由图2可知,随着木屑添加量的增加,铁精矿品位和铁回收率都呈先升高后降低趋势。这可能是在焙烧过程中,由于较高的木屑添加量导致短时间内木屑碳化成的生物质含量高,部分强磁性Fe3O4还原成弱磁性FeO,发生过还原现象[25]。不同木屑添加量焙烧条件下的铁精矿品位差异显著(P<0.05),且在添加量为15%时,铁品位达到最高值,为(62.84±0.59)%。此时铁回收率也达到最大值,高达(94.58±0.36)%。综合考虑,最优的木屑添加量为15%。
焙烧时间对磁化焙烧效果影响较大。在焙烧温度750 ℃、木屑添加量为15%的条件下,考察焙烧时间对磁化焙烧的影响,结果如图3所示。由图3可知,随着焙烧反应时间的增加,铁精矿品位和铁回收率均呈持续上升的趋势。20 min与其他焙烧反应时间所得到的铁精矿品位和铁回收率均有显著差异(P<0.05)。其中,40、60和80 min焙烧后得到的铁精矿品位及铁回收率均无显著差异(P>0.05),即再延长焙烧时间并不能获得更高的铁回收率和铁精矿品位。焙烧时间为40 min时,铁精矿品位为(62.84±1.02)%,铁回收率为(94.03±0.78)%。出于能耗及经济角度的考虑,选取40 min为最佳焙烧时间。木屑还原铁尾矿的最优焙烧条件为:焙烧温度750 ℃、木屑添加量15%、焙烧时间40 min。
2.2. 焙烧前后的表征分析
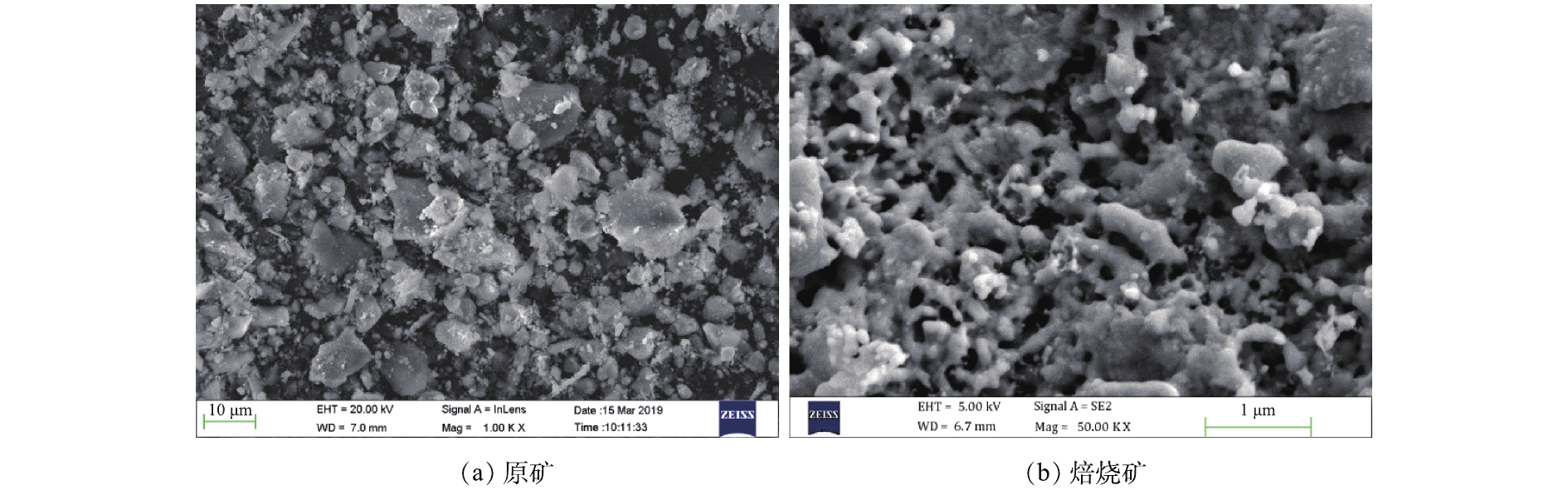
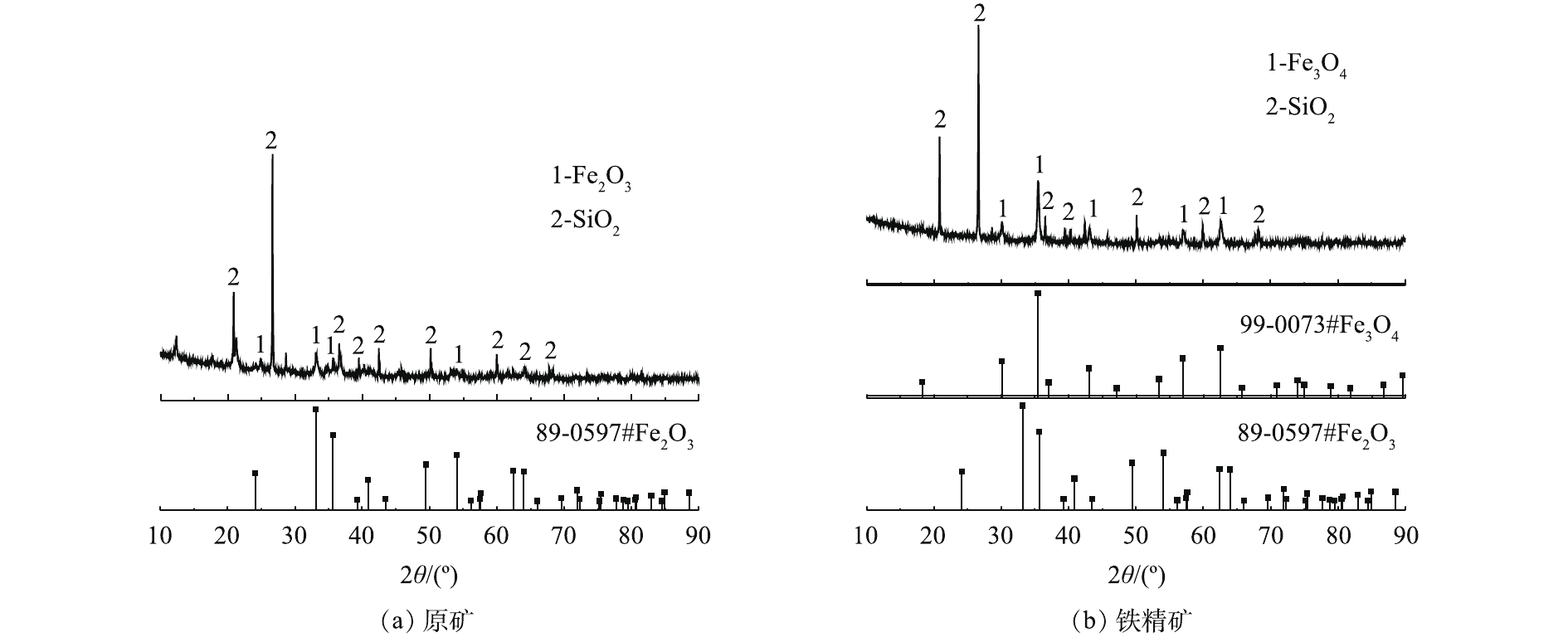
为观察最佳焙烧条件(焙烧温度为750 ℃、木屑添加量为15%、焙烧时间为40 min)下得到的焙烧矿在焙烧前后的形貌差异,对原矿及焙烧矿进行SEM分析,结果如图4所示。从图4(a)中可以看出,原矿主要以块状为主,表面呈光滑状态。与原矿的块状结构相比,焙烧矿(图4(b))的结构主要以骨架为主。这可能是在焙烧过程中,木屑在高温下碳化成生物碳后与铁尾矿发生还原反应所致;另外,焙烧矿的骨架结构相比于原铁尾矿的块状结构更加容易研磨,可有效减轻磁选前的研磨工作量。利用X射线衍射(XRD)对铁尾矿样品进行矿物组分分析。如图5(a)所示,含铁矿物以赤铁矿(Fe2O3)为主,而脉石矿物主要以石英(SiO2)为主。在XRD图谱中没有出现Al2O3特征峰,可能是由于Al2O3含量太低。与原矿的XRD图谱(图5(a))相比,铁精矿的XRD图谱(图5(b))中Fe2O3的特征峰消失,出现了Fe3O4的特征峰[19, 23]。这表明,在加入木屑焙烧后,铁尾矿中的Fe2O3转化成Fe3O4,即用木屑作为还原剂进行还原焙烧后回收铁尾矿中的赤铁矿是可行的。
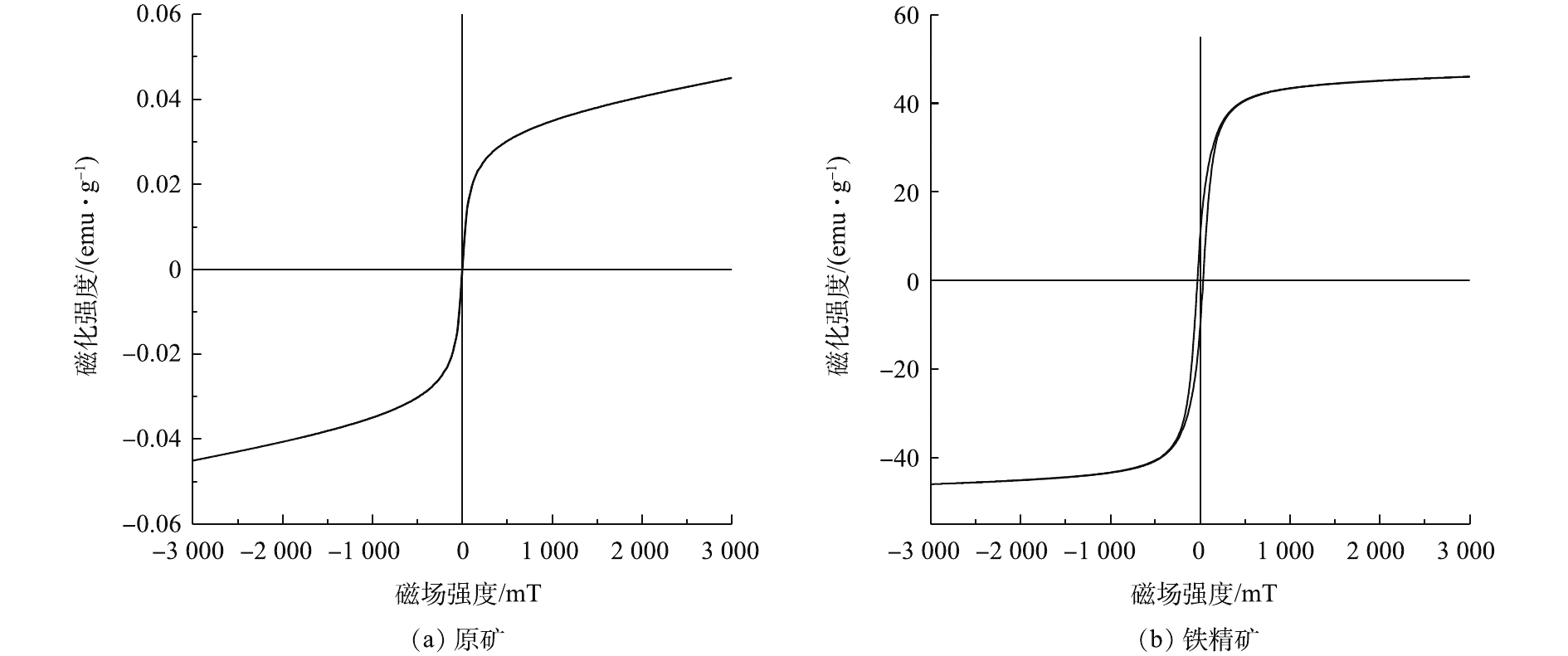
通过磁化曲线分析结果(图6)发现,原矿(图6(a))的饱和磁化强度(Ms)为0.04 emu·g?1,其磁性相对较弱,无法直接进行磁选,需要在磁选之前提高铁尾矿的磁性。铁尾矿经过还原焙烧后,铁精矿的饱和磁感应强度从0.04 emu·g?1提高至46.01 emu·g?1(图6(b))。通过还原焙烧能明显提高焙烧矿的磁性,利于磁选过程中铁精矿和非磁性矿的有效分离。这说明,添加木屑生物质为还原剂进行焙烧,能得到磁性能更佳的铁精矿。该结果与前面提到的物相分析得到弱磁性Fe2O3消失,出现强磁性Fe3O4的结果符合。
原铁矿与铁尾矿和15%木屑的混合物的热重(TG)曲线如图7所示。通过图7(a)可知,原铁矿中的针铁矿主要在200~400 ℃发生脱水,生成Fe2O3[19]。从图7(b)中可知,样品的失重主要有3个阶段[26]:第1个阶段在30~200 ℃,主要是由于木屑和铁尾矿中的游离水挥发所致;第2个阶段是200~400 ℃,主要是由于原矿中的针铁矿脱水生成赤铁矿,以及木屑中纤维素、半纤维素和木质素热解,有机物受热分解生成气体溢出[27],与木屑的挥发分、水分含量相当;第3个阶段发生在400~800 ℃,主要可能是木屑残留物缓慢分解,最后形成生物碳,与铁尾矿发生反应。图7说明赤铁矿在400~800 ℃与木屑生成的生物碳发生还原反应生成Fe3O4,与前面提到的铁精矿物相分析结果吻合。当使用煤作为还原剂时,需要850 ℃以上的焙烧温度,才能将Fe2O3转化成Fe3O4[27-29]。而本研究中使用木屑为还原剂时只需要750 ℃的焙烧温度即可完成还原反应,在代替了煤为还原剂的同时还能降低焙烧反应所需的温度。
2)铁尾矿经过磁化焙烧-磁选后,饱和磁化强度从0.04 emu·g?1提升至46.01 emu·g?1,磁性大大增加,为后续弱磁选提供了良好的条件。
3)原铁尾矿中含铁矿物主要为赤铁矿,添加木屑焙烧后的焙烧矿,经弱磁选后所得的铁精矿主要以磁铁矿为主,实现了铁元素的有效回收。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 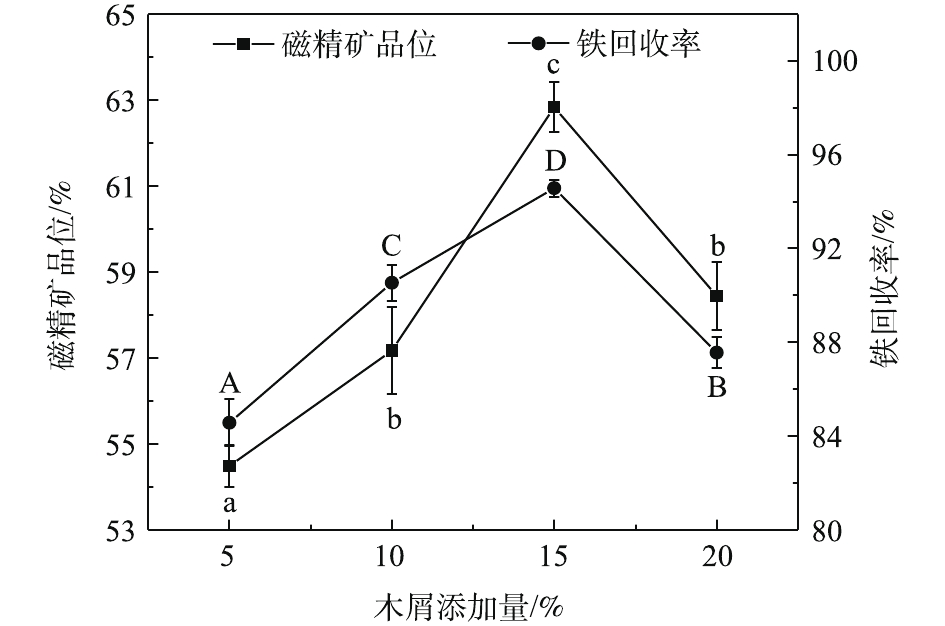


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图