全文HTML
--> --> --> 镉是联合国环境规划署提出的12种全球性的危险化学物质中位于首位的有毒重金属,控制环境中尤其是水体中的镉含量十分重要[1]。当前,去除水体中Cd2+的常用方法包括化学沉淀法、离子交换法、膜处理等,但这些方法受到操作要求高、效率低、成本高等因素的制约,难以大面积推广[2]。吸附法因其具有绿色可行、便捷有效[3]的特点已成为当前研究的一个热点,但选取廉价、高效的吸附材料仍是目前面临的难题。生物炭是指由富炭生物质经热处理,在限氧条件下不完全燃烧生成的产物[4]。有研究[5]表明,生物炭具有比表面积巨大,表面能高等特性,这些特性决定了生物炭在吸附水体重金属方面具有巨大的潜力。当前,为了强化生物炭的吸附性能,增加其吸附容量,许多研究者通过改性的方法来增加生物炭对重金属的吸附效果。WU等[6]使用化学改性方法对椰子纤维炭进行修饰,增加其表面游离的羧基和羟基,研究结果表明,改性后生物炭的吸附容量较改性前可显著提高。马天行等[7]通过亲电芳香取代和还原反应在生物炭表面实现表面氨基化,再使用液相还原法在制备成功的氨基生物炭表面负载纳米零价铁,研究表明,制得的材料具有优良的吸附性能。王静等[8]利用活性炭与巯基乙酸的酯化反应,将巯基嫁接到活性炭上,改性后活性炭对汞的最大吸附容量为556 mg·L?1,远远优于原材料。陈维芳等[9]使用十六烷基三甲基氯化铵(CTAC)改性活性炭,结果表明,改性后活性炭对As5+的吸附能力显著提高,且在中性pH范围内,吸附效果最佳。在改性材料中,CTAB是一种价格低廉且应用范围较广的阳离子表面活性剂,由于生物炭表面多带负电荷,故CTAB通过静电吸附的作用很容易吸附于生物炭表面,同时插入材料表面的烷基基团在材料表面形成混合胶束,加大了与Cd2+的静电吸引力,从而提升了材料的吸附容量。
本研究采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)作为改性剂,椰壳炭(CSC)和竹炭(BC)作为改性材料,制备改性椰壳炭(CTAB-CSC)和竹炭(CTAB-BC),运用傅里叶红外变换光谱(FT-IR)、扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)和热稳定性分析(TGA)对材料进行了表征,研究了其吸附机理,并对其进行了动力学拟合和等温吸附曲线拟合,探究了2种改性材料对溶液中Cd2+的吸附机制。
1.1. 试剂与仪器
仪器:磁力搅拌器(MS200型,上海般特仪器制造有限公司)、电子天平(FA1004型,上海舜禹恒平科学仪器有限公司)、超声波清洗机(DTD-6R型,长沙皓嵘仪器设备有限公司)、高速冷冻离心机(ST-16R型,赛默飞世尔科技有限公司)、便携式pH计(PHBJ-260,仪电科学仪器股份有限公司)、恒温培养振荡器(NNY-21113,天津欧诺仪器仪表有限公司)、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES美国PEB00)。试剂:六偏磷酸钠(Na6O18P6)、氯化镉(CdCl2·2.5H2O)、十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(C19H42BrN)、盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)。这些试剂均为分析纯,去离子水为实验室自制。
1.2. 材料的制备
材料预处理:椰壳炭购自江苏艾格尼丝环境科技有限公司;竹炭购自浙江省农业科学院。将购买的椰壳炭和竹炭使用研磨机研磨,过0.180 0 mm筛;将过筛后的生物炭使用去离子水清洗3次,于80 ℃条件下,在烘箱中烘干备用,记做CSC(椰壳炭)和BC(竹炭)。改性材料的制备:称取20.00 g的材料(CSC和BC),置于100 mL烧杯中,在烧杯中按照固液比1∶2.5的比例加入质量分数为6%的六偏磷酸钠溶液50 mL,磁力搅拌30 min,然后超声分散30 min,按照1∶10的质量比(MCTAB∶M材料)在烧杯中加入CTAB(质量为2.000 0 g),于常温下搅拌10 h,静置沉淀,抽滤洗涤至没有泡沫产生,冷冻干燥得改性材料,记作CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC,密封保存待用。
Cd2+模拟废水配置:准确称取2.032 0 g CdCl2·2.5H2O,置于烧杯中,加500 mL的去离子水溶解,再将其转移至1 000 mL容量瓶中,定容摇匀后,配置Cd2+浓度为1 000 mg·L?1的母液。在后期使用中,所需不同浓度的废水均由母液按照浓度梯度稀释。
1.3. 材料的表征
2种材料的形态和外貌采用热场发射扫描电镜显微镜(QUANTA430,美国FEI公司)观测;CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC吸附前后的能谱图及元素含量由X射线显微分析系统(美国FEI公司)获得;CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC改性前后的傅里叶红外光谱由NICOLET 570 FTIR Spectrometer(美国热电尼高力仪器公司)获得;材料的热稳定性由热重分析仪(Q500,美国TA公司)测定。1.4. 材料吸附实验
1)吸附剂投加量对吸附效率的影响分析。称量0.050 0、0.100 0、0.200 0、0.350 0、0.500 0、0.600 0、0.700 0 g等7个不同质量梯度(每个梯度设置3个平行样)的CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC,置于50 mL的离心管中,在离心管中加入25 mL浓度为10 mg·L?1的Cd2+溶液,摇匀放置于气浴恒温振荡箱中振荡,直至吸附平衡,后于3 000 r·min?1离心10 min后取出再过滤,测定滤液中Cd2+浓度。2)pH对吸附效率的影响分析。准确称量18个0.200 0 g CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC样品,置于50 mL离心管中,在离心管中加入25 mL浓度为10 mg·L?1的Cd2+溶液,使用0.1 mol·L?1的NaOH和HCl调节溶液的pH,调节pH的梯度至2、3、4、5、6、7(每个梯度设置3个平行样),摇匀后,置于气浴恒温振荡箱振荡至吸附平衡,后于3 000 r·min?1离心10 min后,再取出过滤,测定滤液中Cd2+浓度。
3)吸附动力学实验。准确称量27个0.200 0 g CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC样品,置于50 mL离心管中,在离心管中加入30 mL浓度为100 mg·L?1的Cd2+溶液,调节溶液pH为7,根据时间梯度5、15、30、60、120、240、320、720、1 440 min(每个梯度设置3个平行样),分批次置于气浴恒温振荡箱中,振荡时间停止后,取出过滤,测定滤液中Cd2+浓度。
4)等温吸附模型实验。准确称量15个0.500 0 g CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC样品,置于50 mL离心管中,准确设置浓度梯度为30、60、120、250、500 mg·L?1的Cd2+溶液(每个梯度设置3个平行),在离心管中分别加入25 mL不同浓度的溶液,摇匀后,置于气浴恒温振荡箱中振荡至吸附饱和,振荡结束后,在3 000 r·min?1的条件下,离心10 min,离心结束后过滤,滤液稀释待测。
5)材料再生实验。将吸附饱和的材料通过抽滤进行固液分离,将分离出的材料用去离子水充分洗涤3~5次,烘干,分别放入0.01 mol·L?1的HCl溶液中,振荡24 h,振荡结束后,重复进行分离和干燥,将干燥的材料置于10 mol·L?1的Cd2+溶液中进行吸附,待吸附饱和后过滤,测定滤液中Cd2+浓度。重复吸附-脱附步骤3次,测定滤液中Cd2+浓度。
1.5. 数据分析
吸附材料的吸附效果分别用去除率和吸附量来衡量,其计算公式分别如式(1)和式(2)所示。式中:δ为去除率;C0为溶液初始浓度,mg·L?1;Ce为溶液吸附平衡时浓度,mg·L?1;V为溶液体积,mL;m为吸附剂质量,g。
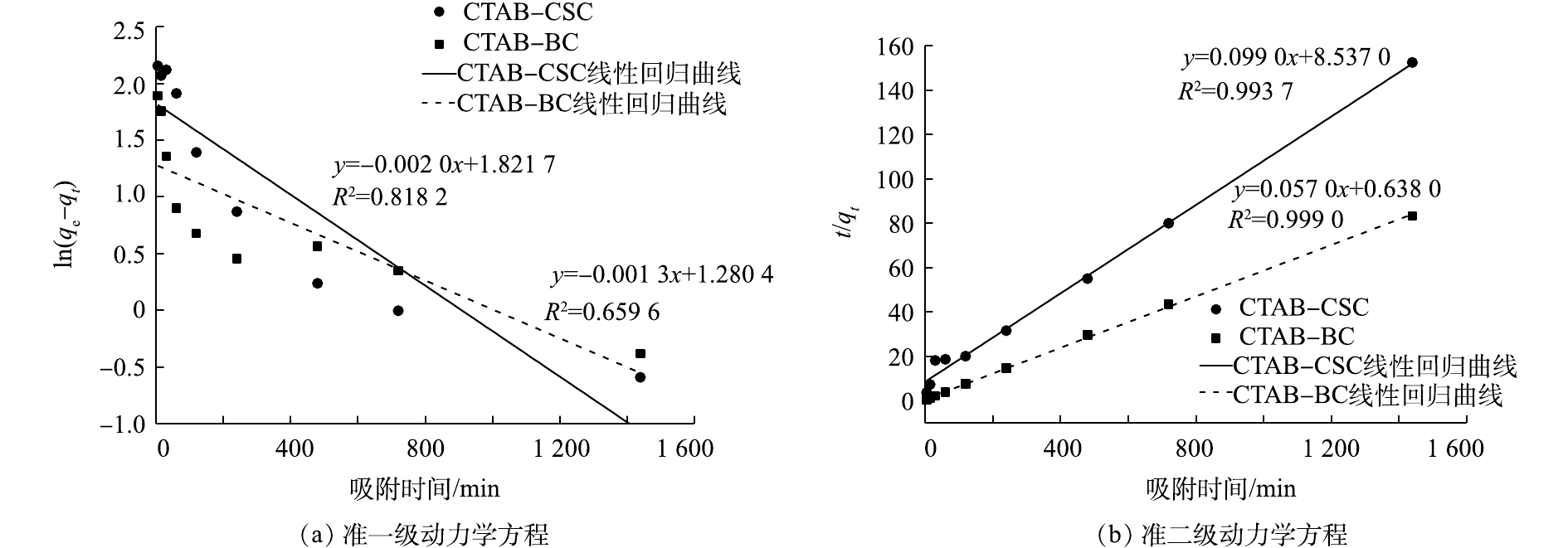
动力学模型拟合。为了研究CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC的吸附动力学,分别用一级动力学方程和二级动力学方程模型进行拟合。一级动力学方程和二级动力学方程[10]如式(3)和式(4)所示。
式中:qe为吸附剂吸附平衡时吸附容量,mg·g?1;qt为t时刻吸附剂的吸附容量,mg·g?1;K1为一级动力学吸附系数;K2为二级动力学吸附系数。
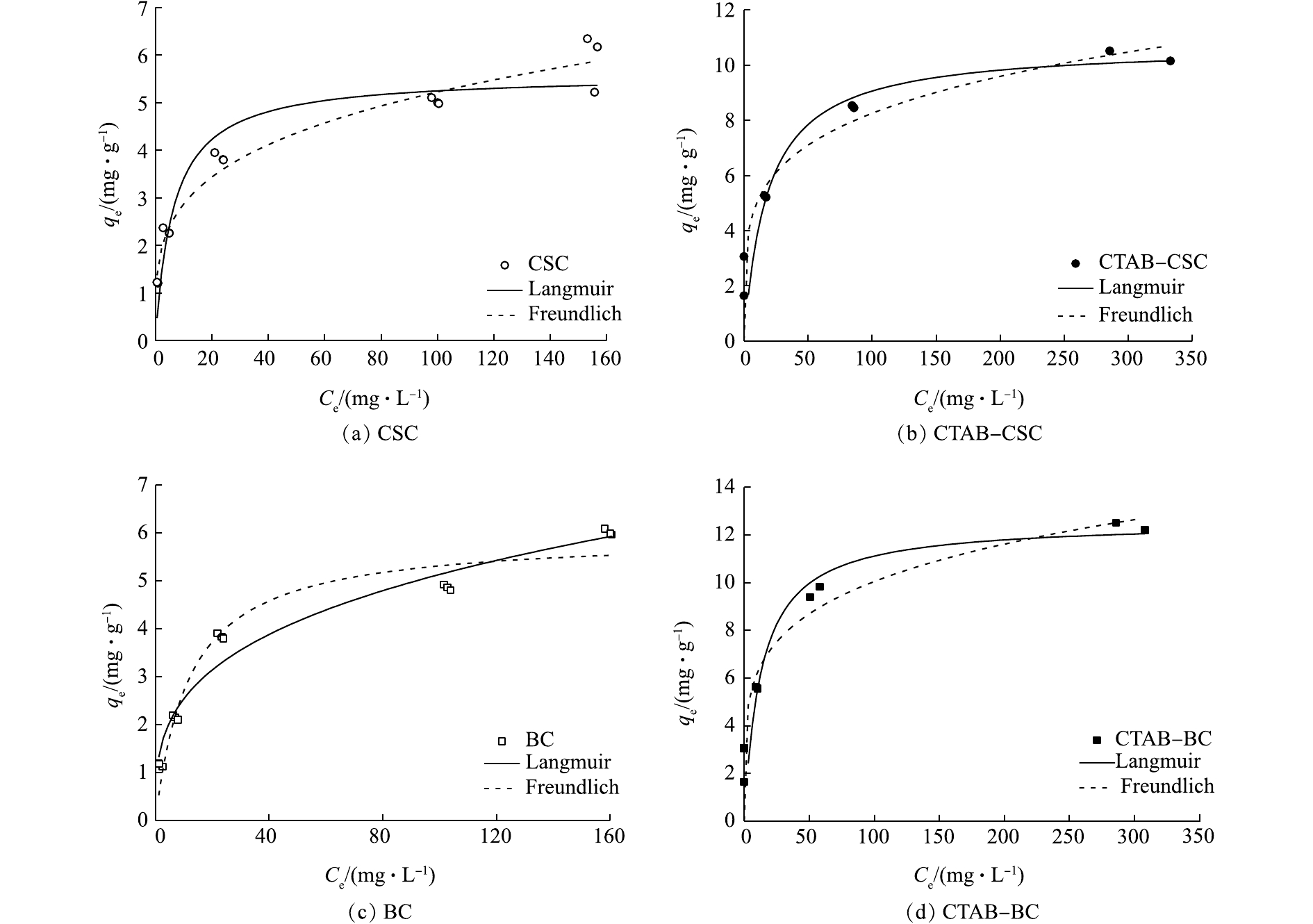
等温吸附模型拟合。本研究使用Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC等温吸附实验数据进行分析。其中,Langmuir模型属单分子层吸附,Freundlich模型属多分子层吸附,以参数分离因子来分析CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC 2种材料的吸附性能,其中Langmuir和Freundlich模型[10]如式(5)和式(6)所示。
式中:qmax为吸附剂的单层饱和最大吸附,mg·g?1;Ce为吸附平衡时溶液浓度,mg·L?1;KL为Langmuir吸附常数,L·mg?1,当0<KL<1,表示有利于吸附;KL>1,表示不利于吸附;KL =1,属于线性分配;KL趋于0,表示不可逆吸附。KF是Freundlich吸附常数;1/n是Freundlich模型中表示吸附强度的参数。
2.1. 材料的表征
2.1.1. 傅里叶红外光谱
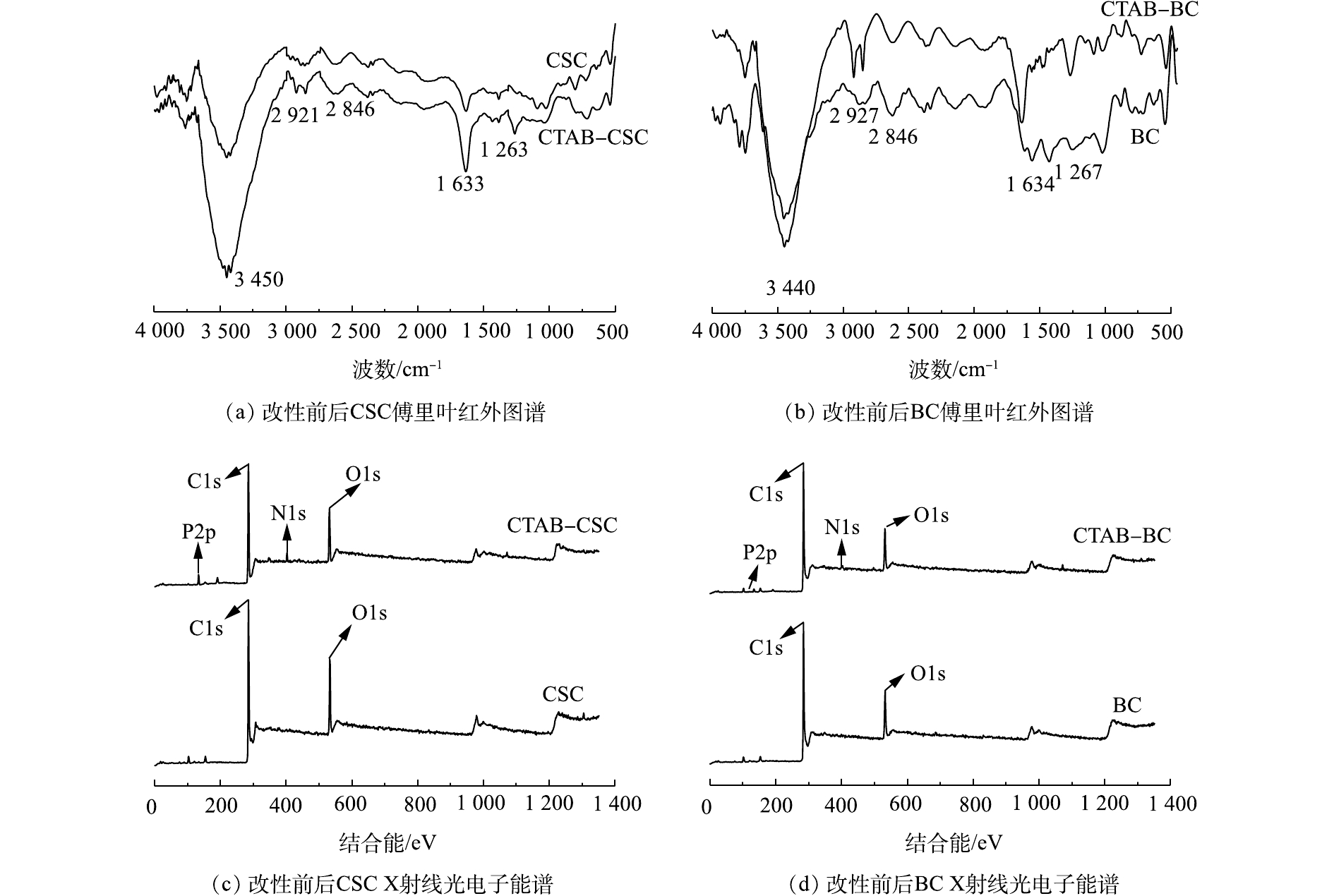
傅里叶红外图谱通过检测材料内部分子的振动和转动,从而可知材料中所含化合物的化学结构,包括各种官能团,如氨基、羧基和羰基等。生物炭改性前后的傅里叶红外图谱如图1(a)和图1(b)所示,从图1中可知,2种改性后的生物炭表面均含有更为丰富的官能团。由图1(a)可知,CTAB-CSC在3 440 cm?1处对应的是—NH伸缩振动引起的吸收峰[11];在1 634 cm?1处对应的是—NH弯曲振动引起的的吸收峰[12],这充分证明有氨基集团成功嫁接到生物炭表面[13]。氨基基团可以和Cd2+发生配合反应[14]。同时,在2 927 cm?1和2 846 cm?1处的2个峰可以归因于甲基和亚甲基中C—H的伸缩振动,在图1(b)中,也观察到类似的现象,这充分说明CTAB分子已成功嫁接在生物炭表面[15]。图1(c)和图1(d)是改性材料改性前后的XPS总谱,改性后,在400 eV左右出现了N1s的峰,亦可以证明材料改性后,其表面有氨基基团的存在。
2.1.2. 扫描电镜
改性前后的2种材料的冷场发射扫描电子显微镜观察结果如图2所示。由图2(a)可知,改性前,CSC表面棱角分明,表面较为平整;而经CTAB改性后,CSC(图2(b))表面有一定凸起,棱角较改性前更加圆滑。由图2(c)和图2(d)可知,改性后的CTAB-BC表面更加平滑,且材料表面还存在一些堆积状的颗粒,且在改性后表面颜色变浅,说明CTAB已经负载在材料的表面。2.1.3. X射线光电子能谱分析
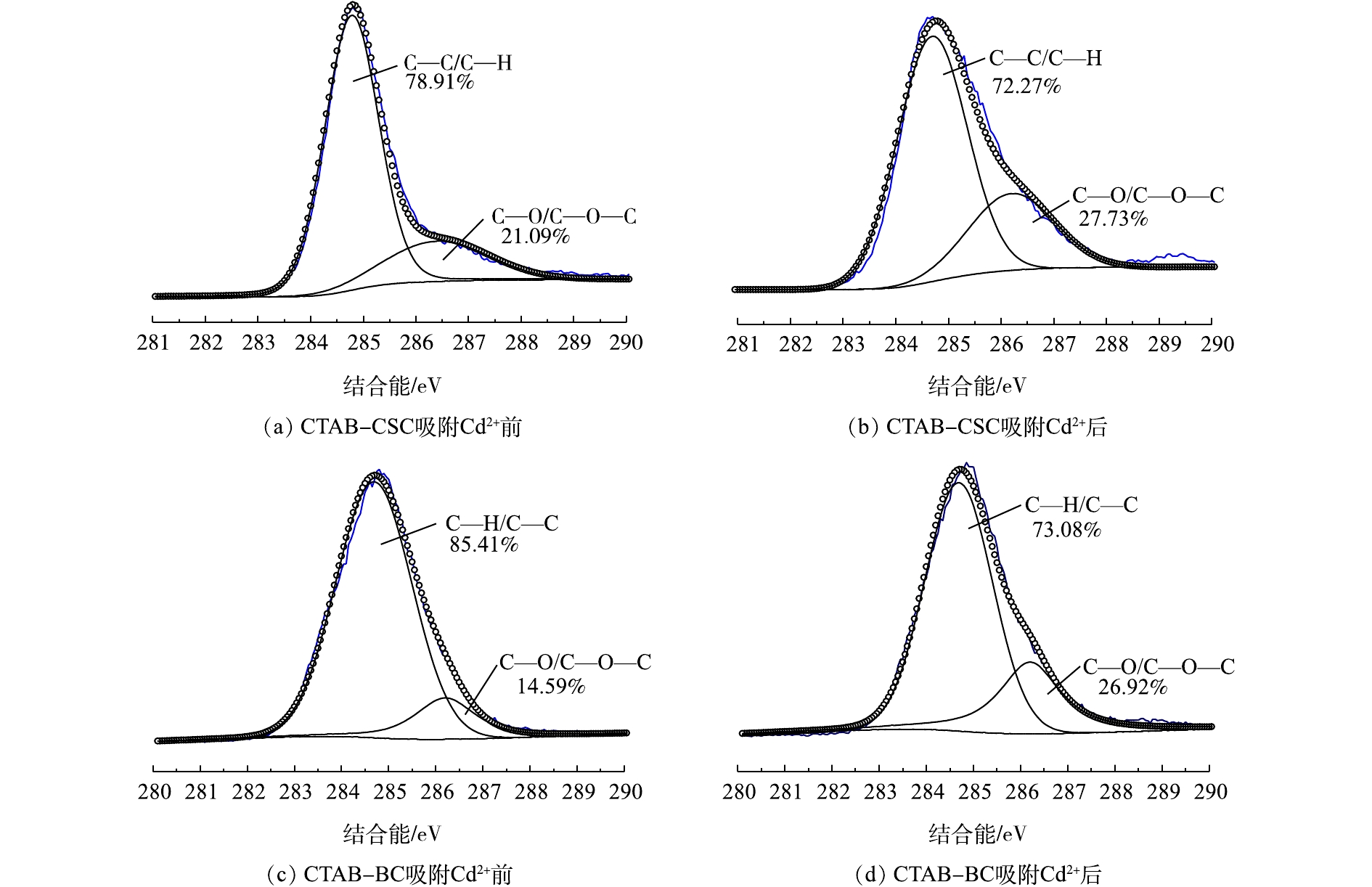
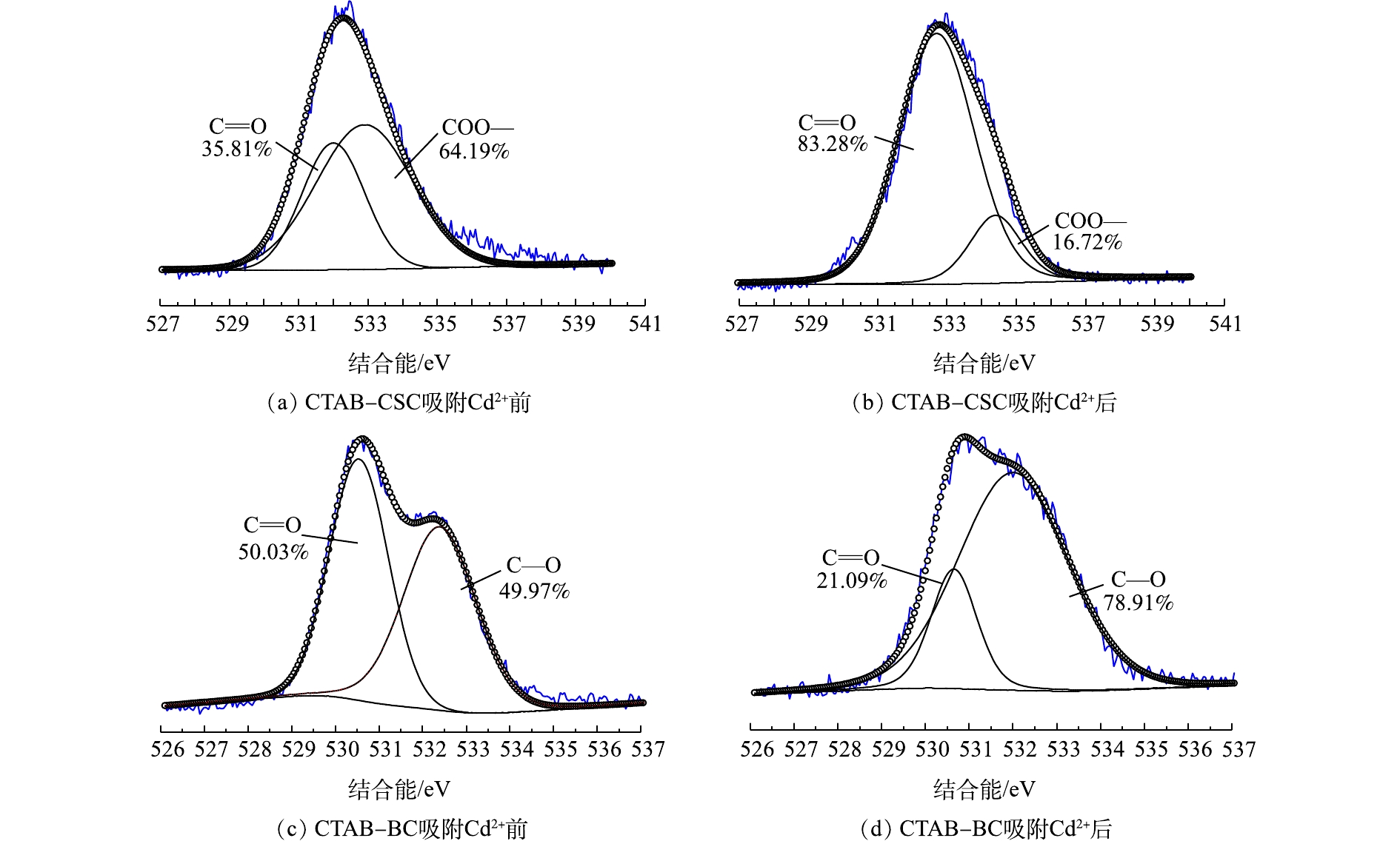
X-射线光电子能谱(XPS)具有比较高的表面灵敏度,通过比较吸附Cd2+前后的生物炭表面元素结合能的变化来进一步研究生物炭对Cd2+的吸附机理。图3(a)和图3(b)分别是CTAB-CSC的吸附Cd2+前后的C1s谱图。通过分峰处理,在284.7 eV和286.4 eV处捕捉到2个可见峰,可以将其归为C—C/C—H(芳香族)和C—O/C—O—C(醇式羟基和醚)[16-18]。利用XPS peak软件对RWA值及峰面积进行分析,发现C—C/C—H的峰未发生显著变化,这说明C—C/C—H形式的碳原子没有直接参与Cd2+的吸附;而C—O/C—O—C的峰面积发生了明显变化,这说明C—O/C—O—C形式的碳原子在一定程度上参与了生物炭对Cd2+的吸附。图3(c)和图3(d)分别是CTAB-BC吸附Cd2+前后的C1s谱图,通过分峰处理,得到了与CTAB-CSC同样的结论。图4(a)和图4(b)是分别是CTAB-CSC吸附Cd2+前后O1s谱图,峰值在532.0 eV和532.7 eV(Cd2+吸附前后)可归类为C=O,峰值在532.9 eV和534.4 eV(Cd2+吸附前后)可归类为COO—[19]。从图4(a)中可以观察到,吸附Cd2+后,C=O的峰面积从35.81%增加到83.28%;COO—的峰面积从64.19%降低到16.72%。图4(c)和图4(d)分别是CTAB-BC吸附Cd2+前后O1s谱图,峰值在530.5 eV和530.7 eV(Cd2+吸附前后)可归类为C=O,峰值在532.4 eV和532.0 eV(Cd2+吸附前后)可归类为C—O/C—O—C(醇羟基和醚)[20]。从图4(b)中可以观察到,吸附后,C=O的峰面积从50.03%减少到21.09%;C—O/C—O—C的峰面积从49.97%增加到78.91%。
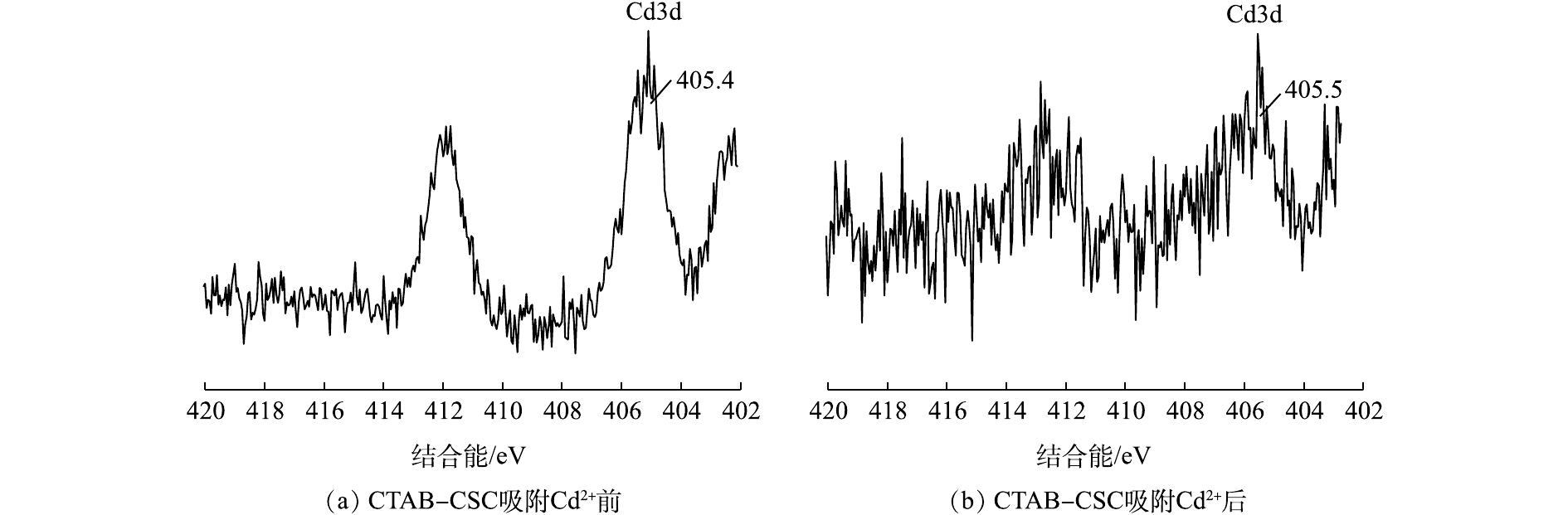
结合能的变化可能是因为Cd2+在吸附过程中与氧元素结合,导致氧元素的电子密度降低[21]。结合峰面积的变化,我们可以推断,氧原子是Cd2+的1个主要吸附点位,氧原子可以和Cd2+形成配位键。图5(a)和图5(b)分别为CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC吸附Cd2+后Cd3d谱图,经过XPS分析,发现Cd3d的峰出现在405.5 eV的位置,为CdCO3、Cd的氢氧化物以及—OCdOH。这表明生物炭对Cd的吸附机理主要为Cd与生物炭表面的羟基化表面(—OH)或其去质子化(—O—)络合[22],这与O1s谱图的结果一致。
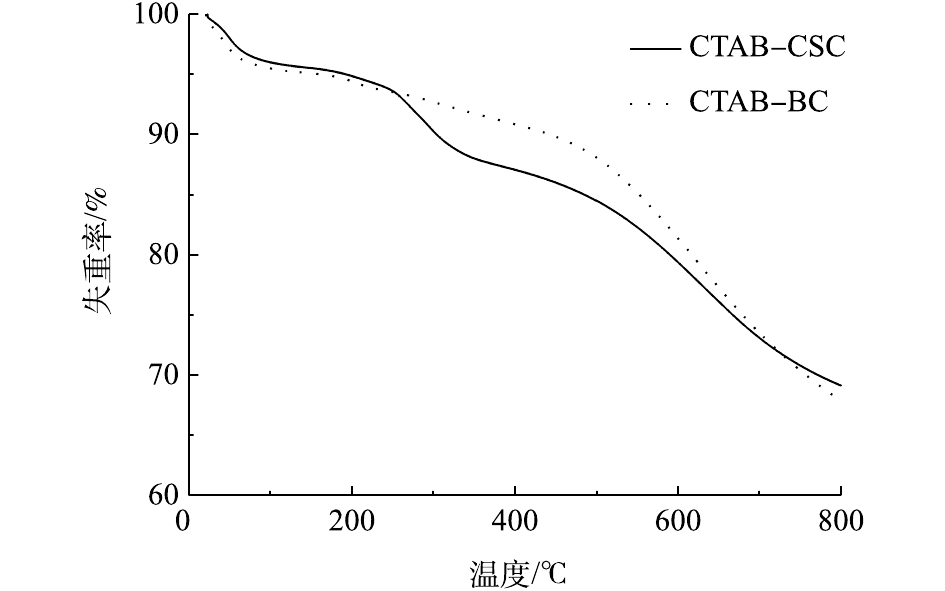
2.1.4. 热稳定性分析
TGA即热重分析,是指在程序控制温度下测量待测样品的质量与温度变化关系的一种热分析技术,用来研究材料的热稳定性和组分。图6是CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC的热重曲线。由图6可知,CTAB-CSC的热解过程主要分为4个阶段。室温到80 ℃为第1个阶段。此阶段为失水阶段,在此阶段中主要产生水分蒸发以及少量挥发性气体析出现象。80~250 ℃为第2个阶段。本阶段中样品质量变化很小,在此过程中主要产生秸秆的解聚和“玻璃化转变”现象[23],释放出H2O、CO、及CO2等小分子化合物。250~500 ℃为第3个阶段。秸秆类生物炭的3种主要成分为半纤维素、纤维素以及木质素,其热解难易程度为木质素>纤维素>半纤维素[24]。在此阶段中,较易热解的半纤维素和纤维素开始热解;同时,伴随着极少一部分的木质素的分解,主要生成挥发性物质和碳。500 ℃以后为炭化阶段。在本阶段中主要产生木质素缓慢分解现象。图6中CTAB-BC和CTAB-CSC相比,主要差异产生在第3个阶段。这可能是因为CTAB-BC的半纤维素的质量分数低于CTAB-CSC中的半纤维素质量分数,由于半纤维素的质量分数越高的生物质,越容易在该温度范围内出现转折现象[25]。由图6可知,当温度达到800 ℃时,CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC的质量损失率分别为30.96%和32.24%。2种材料的热稳定性能均较好,但CTAB-CSC的热稳定性优于CTAB-BC。
2.2. 吸附实验分析
2.2.1. 吸附剂投加量对吸附效果的影响
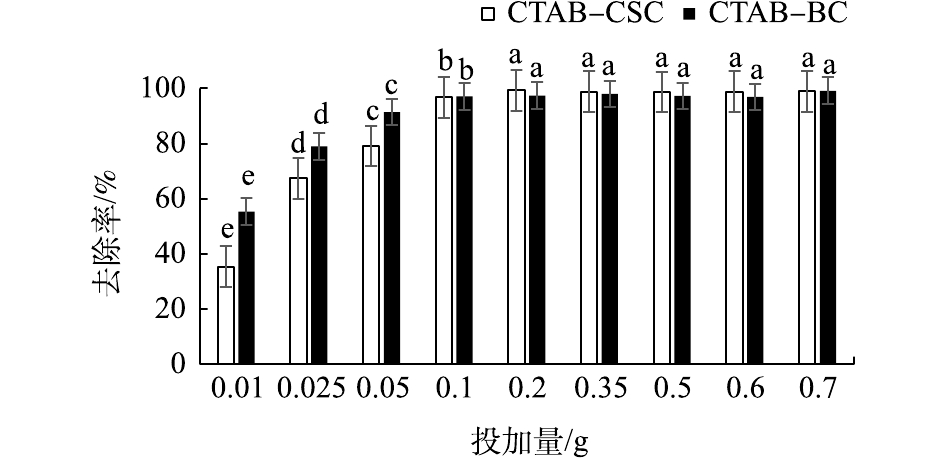
由图7可知,设置Cd2+废液初始浓度为10 mg·L?1时,溶液中的Cd2+的去除率随着材料的投加量的增加而升高。当投加量为0.200 0 g时,CTAB-CSC去除率达到98%以上,达到吸附饱和;当投加量为0.100 0 g时,CTAB-BC去除率达到98%以上,同时,由图7可知,CTAB-BC所有投加量的去除率均在90%以上,这可能是由于初始溶液中Cd2+浓度较低所致。综合考虑材料的制备以及原材料的利用率等因素,pH控制及吸附动力学实验的投加量均选为0.200 0 g。2.2.2. 溶液pH对吸附效果的影响
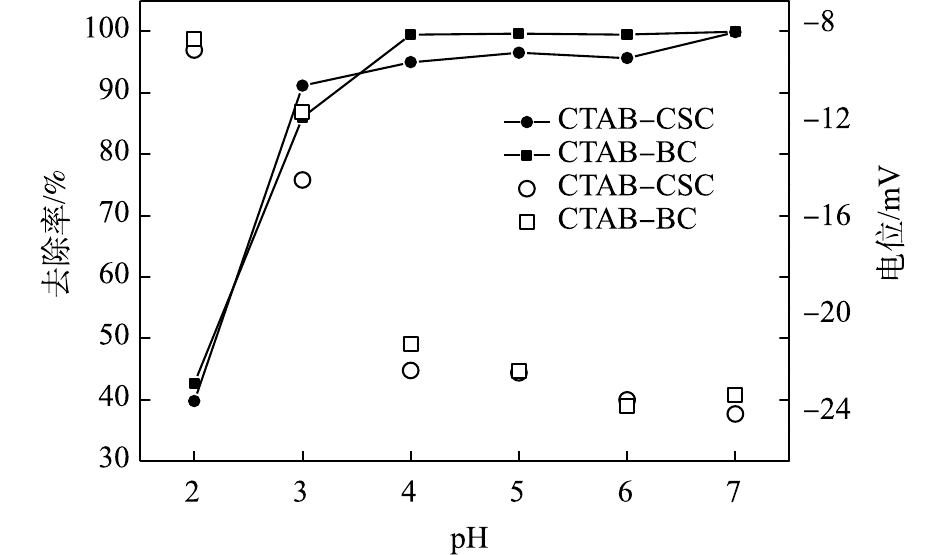
由图8可以看出,当Cd2+废液初始浓度为10 mg·L?1时,溶液中Cd2+的去除率随着溶液pH的增加而升高;在极端的酸环境下,2种材料对溶液中Cd2+的去除率均较低。当pH=2~3时,在CTAB-CSC处理过的溶液中,Cd2+去除率显著上升;当pH=3~7时,去除率缓慢上升;当pH=7时,去除率可达到最高。而CTAB-BC在pH=2~3时,对Cd2+的去除率显著升高;当pH=3~4时,缓慢上升;当pH=4~7时,溶液中Cd2+的去除率均达到98%以上。分析产生上述现象的原因,可能是在pH较低的情况下,溶液中存在大量与Cd2+形成竞争吸附的H+,其会占据有限的结合位点,降低Cd2+去除率[26];同时,这些H+会使材料表面的电荷分布改变,导致一部分有利于重金属吸附的有机官能团发生解离,从而抑制材料对Cd2+的吸附性能[27]。随着pH的升高,H+量减少,会暴露大量吸附剂表面结合位点,负电密度增大,则吸附容量也随之增加[28]。从图8中可以看出,随着pH的升高,体系中Zeta电位在逐渐下降,Zeta电位均处于负电势。这说明材料表面带负电荷,由此推测静电作用是吸附水中Cd2+的原因之一[29]。考虑到2种材料的吸附性能的影响,在后续实验中,设置溶液初始pH为7。2.2.3. 吸附动力学实验
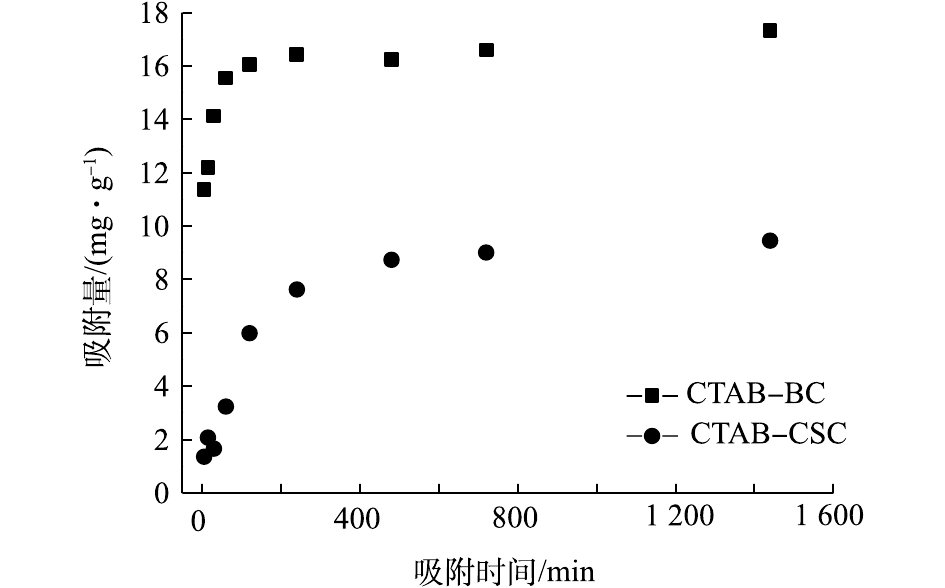
图9为吸附动力学实验结果。可以看出:2种改性材料CTAB-CSC、CTAB-BC对Cd2+的吸附量均随着时间的增加而增加;CTAB-BC在180 min处达到平衡,CTAB-CSC在240 min处达到吸附平衡,CTAB-BC的吸附性能明显优于CTAB-CSC。根据式(3)和式(4)拟合ln(qe-qt)-t和t/qt-t的线性关系,结果如图10所示,动力学拟合参数如表1所示。由拟合参数可得,在初始Cd2+浓度为100 mg·L?1时,CTAB-CSC的准二级动力学方程可决系数(0.993 7)大于准一级动力学方程可决系数(0.818 2),CTAB-BC的准二级动力学方程可决系数(0.999 9)大于准一级动力学方程可决系数(0. 659 6),这说明准二级动力学方程能更好地描述CTAB-CSC、CTAB-BC的吸附过程。通过准二级动力学方程拟合计算出CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC的理论最大吸附量分别为10.10 mg·g?1和17.54 mg·g?1,与等温吸附所得实验值较为接近。这也表明CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC对Cd2+的吸附主要受化学吸附作用的控制。
2.2.4. 等温吸附实验
表2是等温吸附模型的拟合参数;根据式(5)和式(6)拟合的Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型,结果如图11所示。通过分析4种材料的拟合度R2可知,改性前的CSC和BC 2种材料的吸附过程更符合Freundlich模型,由此可推测,改性前的CSC和BC这2种材料对溶液中Cd2+的吸附过程是一种非均匀的表面吸附过程,而经过改性后的材料CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC更符合Langmuir模型,故可推测CTAB-CSC、CTAB-BC 2种材料的表面具有有限的吸附位点,对Cd2+的吸附机制属于单分子层吸附[26]。Freundlich等温吸附方程是一个经验方程。该方程中的n值能反映材料的吸附性能,其中n值越大,表明材料的吸附性能越好。一般认为1/n为0.1~0.5,容易吸附;1/n大于2时,吸附较难进行。通过数据分析,2种材料的1/n均处于0.1~0.5,说明吸附过程是优惠吸附,材料的吸附性能较好。KF值与吸附剂吸附容量正相关,CTAB-BC的KF值大于CTAB-CSC,这表明CTAB-BC对Cd2+的吸附容量大于CTAB-CSC,与本研究结果一致。
CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC对Cd2+的最大吸附量分别为10.71 mg·g?1和12.56 mg·g?1,较改性前的吸附效果分别提升了92%和111%,改性效果明显提升,且CTAB-BC的吸附效果优于CTAB-CSC。
2.2.5. 材料再生实验
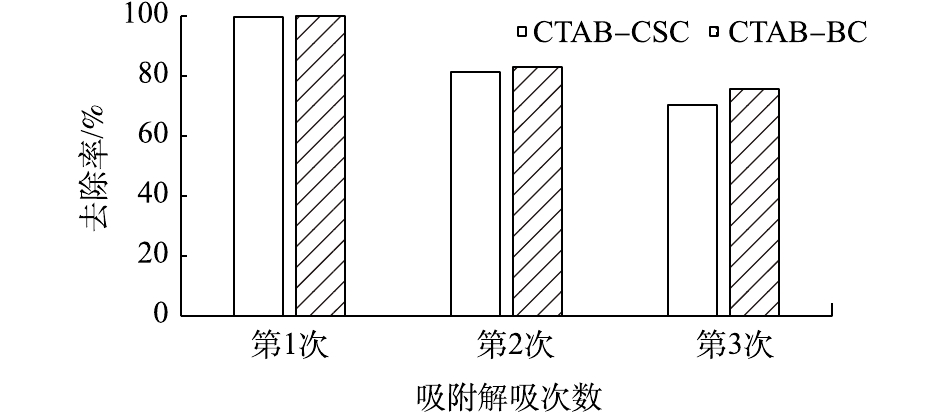
由图12可以看出,在Cd2+初始浓度为10 mg·g?1时,CTAB-CSC和CTAB-BC首次对Cd2+吸附去除率均在98%以上;经过2次重复的吸附-脱附实验后,CTAB-CSC、CTAB-BC对水中的Cd2+的去除率分别降低为70.33%和75.83%,较原材料对Cd2+的去除率分别减少了29.67%和24.17%。经过连续2次的吸附-脱附实验后,材料对水中Cd2+的去除率还保持在70%左右,且CTAB-BC的再生性能优于CTAB-CSC。以上结果表明2种材料均有较好的再生性。2) 2种改性材料的最佳投加量为0.100 0~0.200 0 g,CTAB-CSC的最适pH范围较窄,为6~7,CTAB-BC的pH范围较广,在4~7时均有较好的吸附效果。
3)通过动力学实验分析,准二级动力学方程能更好地描述CTAB-CSC、CTAB-BC 2种材料的吸附过程,R2均大于0.99,CTAB-BC在180 min时达到平衡,CTAB-CSC在240 min时达到吸附平衡。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图