 ), 李伟健1
), 李伟健1 1 浙江师范大学心理与脑科学研究院, 金华 321004
2 阳光学院, 福州 350015
收稿日期:2018-02-07出版日期:2019-02-25发布日期:2018-12-24通讯作者:李锋盈E-mail:lfyfly@zjnu.cn基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(31871124)The influence of learner’s beliefs about processing fluency on font-size effect
CHEN Ying1,2, LI Fengying1( ), LI Weijian1
), LI Weijian1 1 Institute of Psychological and Brain Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua 321004, China
2 Yango College, Fuzhou 350015, China
Received:2018-02-07Online:2019-02-25Published:2018-12-24Contact:LI Fengying E-mail:lfyfly@zjnu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究考察个体关于加工流畅性的信念对学习判断(Judgment of learning, 简称JOL)的影响, 探讨字体大小效应的产生机制。研究通过两个实验分别考察个体关于“字体大小影响加工流畅性” (实验1)以及“加工流畅性影响记忆效果” (实验2)等信念对字体大小效应的影响。结果发现: 1)当人们相信大字体更流畅(实验1)或者越流畅越好记(实验2)时, 他们在大字体项目上的JOL值显著高于小字体项目上的JOL值; 2)当人们相信小字体更流畅(实验1)或者流畅性与记忆无关(实验2)时, 他们在大字体和小字体项目上的JOL值无显著差异, 字体大小效应消失。上述结果表明, 个体关于加工流畅性的信念是字体大小效应产生的重要原因, 是人们进行学习判断的重要线索。
图/表 5

图1词对呈现方式示意图
 图1词对呈现方式示意图
图1词对呈现方式示意图表1实验1三组中不同字体大小上词对的学习判断值和回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 组别 | JOL值 | 回忆正确率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | |
| 控制组 (N=25) | 45.96±14.04 | 44.08±13.00 | 0.39±0.21 | 0.37±0.22 |
| 大字体更流 畅组(N=22) | 44.97±17.36 | 40.00±15.40 | 0.32±0.21 | 0.34±0.24 |
| 小字体更流 畅组(N=22) | 39.99±15.63 | 40.20±17.08 | 0.34±0.22 | 0.30±0.17 |
表1实验1三组中不同字体大小上词对的学习判断值和回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 组别 | JOL值 | 回忆正确率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | |
| 控制组 (N=25) | 45.96±14.04 | 44.08±13.00 | 0.39±0.21 | 0.37±0.22 |
| 大字体更流 畅组(N=22) | 44.97±17.36 | 40.00±15.40 | 0.32±0.21 | 0.34±0.24 |
| 小字体更流 畅组(N=22) | 39.99±15.63 | 40.20±17.08 | 0.34±0.22 | 0.30±0.17 |
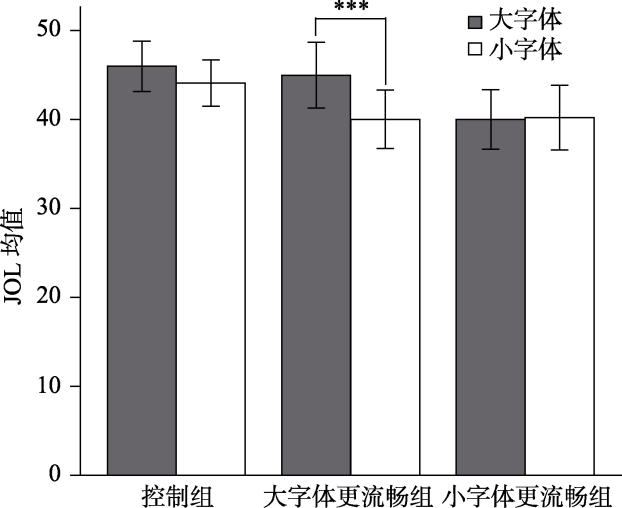
图2实验1字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001
 图2实验1字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001
图2实验1字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001表2实验2三组中不同字体大小上词对的学习判断值和回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 组别 | JOL值 | 回忆正确率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | |
| 控制组 (N=23) | 39.01±13.55 | 36.14±12.10 | 0.36±0.22 | 0.33±0.19 |
| 越流畅越 好记组(N=27) | 49.40±14.93 | 40.66±14.49 | 0.32±0.20 | 0.29±0.18 |
| 流畅性与记忆 无关组(N=27) | 40.64±20.39 | 40.36±19.44 | 0.39±0.25 | 0.39±0.23 |
表2实验2三组中不同字体大小上词对的学习判断值和回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 组别 | JOL值 | 回忆正确率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大字体 | 小字体 | 大字体 | 小字体 | |
| 控制组 (N=23) | 39.01±13.55 | 36.14±12.10 | 0.36±0.22 | 0.33±0.19 |
| 越流畅越 好记组(N=27) | 49.40±14.93 | 40.66±14.49 | 0.32±0.20 | 0.29±0.18 |
| 流畅性与记忆 无关组(N=27) | 40.64±20.39 | 40.36±19.44 | 0.39±0.25 | 0.39±0.23 |
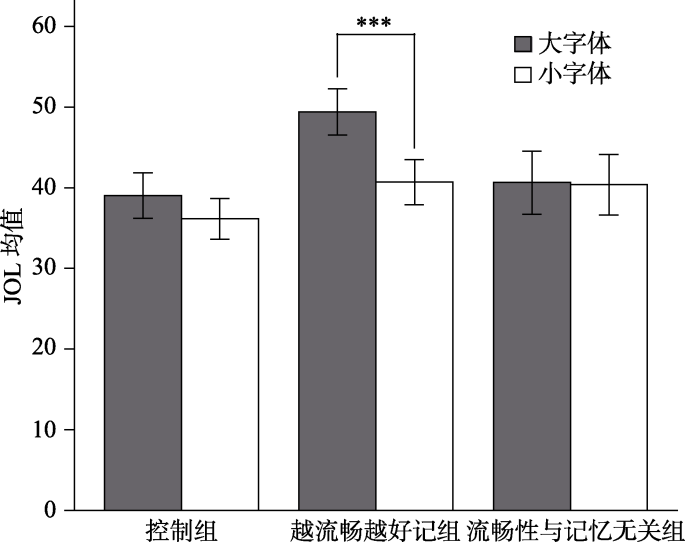
图3实验2字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001。
 图3实验2字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001。
图3实验2字体大小和组别的交互作用 注:图中误差线为标准误, ***表示p < 0.001。参考文献 31
| 1 | Alter, A.L., & Oppenheimer D.M, . ( 2009). Uniting the tribes of fluency to form a metacognitive nation. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 13( 3), 219-235. doi: 10.1177/1088868309341564URL |
| 2 | Besken, M., & Mulligan N.W, . ( 2013). Easily perceived, easily remembered? Perceptual interference produces a double dissociation between metamemory and memory performance. Memory & Cognition, 41( 6), 897-903. |
| 3 | Bjork R. A., Dunlosky J., & Kornell N . ( 2013). Self- regulated learning: Beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 417-444. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143823URL |
| 4 | Carpenter S. K., Wilford M. M., Kornell N., & Mullaney K. M . ( 2013). Appearances can be deceiving: Instructor fluency increases perceptions of learning without increasing actual learning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20( 6), 1350-1356. |
| 5 | Dunlosky, J., & Metcalfe J. ( 2009). Metacognition: A textbook of cognition, educational, life span, and applied psychology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. |
| 6 | Dunlosky J., Mueller M., & Tauber, S. K .( 2015) . The contribution of processing fluency (and beliefs) to people’s judgments of learning. In D. S. Lindsay, C. M. Kelley, A. P. Yonelinas, & H. L. Roediger, III (Eds.), Remembering: Attributions, processes, and control in human memory: Essays in honor of Larry Jacoby (pp. 46-64). New York: Psychology Press. |
| 7 | Dunlosky, J., & Rawson K.A, . ( 2012). Overconfidence produces underachievement: Inaccurate self evaluations undermine students’ learning and retention. Learning and Instruction, 22( 4), 271-280. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2011.08.003URL |
| 8 | Faul F., Erdfelder E., Lang A., & Buchner A . ( 2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39( 2), 175-191. doi: 10.3758/BF03193146URL |
| 9 | Finn, B., & Tauber S.K, . ( 2015). Erratum to: When confidence is not a signal of knowing: How students’ experiences and beliefs about processing fluency can lead to miscalibrated confidence. Educational Psychology Review, 28( 1), 205-205. |
| 10 | Hofer, B.K . ( 1999). Instructional context in the college mathematics classroom: Epistemological beliefs and student motivation. Journal of Staff Program & Organization Development, 16( 2), 73-82. |
| 11 | Hu X., Li T., Zheng J., Su N., Liu Z., & Liang L . ( 2015). How much do metamemory beliefs contribute to the font-size effect in judgments of learning? Plos One, 10( 11), e0142351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142351URL |
| 12 | Jia X., Li P., Li X., Zhang Y., Cao W., Cao L., & Li W . ( 2016). The effect of word frequency on judgments of learning: Contributions of beliefs and processing fluency. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1995. |
| 13 | Koriat, A. ( 2000). The feeling of knowing: Some metatheoretical implications for consciousness and control. Consciousness and Cognition, 9(2), 149-171. doi: 10.1006/ccog.2000.0433URL |
| 14 | Koriat, A. ( 2007). Metacognition and consciousness. In P. D. Zelazo, M. Moscovitch, & E. Thompson (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of consciousness (pp. 289-325). New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| 15 | Kornell, N., & Metcalfe J. ( 2006). Study efficacy and the region of proximal learning framework. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32( 3), 609-622. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.32.3.609URL |
| 16 | Kornell N., Rhodes M. G., Castel A. D., & Tauber S. K . ( 2011). The ease-of-processing heuristic and the stability bias: Dissociating memory, memory beliefs, and memory judgments. Psychological Science, 22( 6), 787-794. doi: 10.1177/0956797611407929URL |
| 17 | Li T., Hu X., Zheng J., Su N., Liu Z., & Luo L . ( 2016). The influence of visual mental imagery size on metamemory accuracy in judgment of learning. Memory, 25( 2), 244-253. |
| 18 | Miele D. B., Finn B., & Molden D. C . ( 2011). Does easily learned mean easily remembered? It depends on your beliefs about intelligence. Psychological Science, 22( 3), 320-324. doi: 10.1177/0956797610397954URL |
| 19 | Mueller, M.L., & Dunlosky J. ( 2017). How beliefs can impact judgments of learning: Evaluating analytic processing theory with beliefs about fluency. Journal of Memory and Language, 93, 245-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2016.10.008URL |
| 20 | Mueller M. L., Dunlosky J., & Tauber S. K . ( 2016). The effect of identical word pairs on people's metamemory judgments: What are the contributions of processing fluency and beliefs about memory? Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 69( 4), 781-799. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2015.1058404URL |
| 21 | Mueller M. L., Dunlosky J., Tauber S. K., & Rhodes M. G . ( 2014). The font-size effect on judgments of learning: Does it exemplify fluency effects or reflect people’s beliefs about memory? Journal of Memory and Language, 70, 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2013.09.007URL |
| 22 | Mueller M. L., Tauber S. K., & Dunlosky J . ( 2013). Contributions of beliefs and processing fluency to the effect of relatedness on judgments of learning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20( 2),378-384. |
| 23 | Nist, S.L., & Holschuh J.P . ( 2005). Practical applications of the research on epistemological beliefs. Journal of College Reading and Learning, 35( 2), 84-92. doi: 10.1080/10790195.2005.10850175URL |
| 24 | Rhodes, M.G., & Castel , . ( 2008). Memory predictions are influenced by perceptual information: Evidence for metacognitive illusions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 137( 4), 615-625. doi: 10.1037/a0013684URL |
| 25 | Rouder J. N., Speckman P. L., Sun D., Morey R. D., & Iverson G . ( 2009). Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16( 2), 225-237. |
| 26 | Simon, D.A., & Bjork R.A, . ( 2001). Metacognition in motor learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 27( 4), 907-912. |
| 27 | Susser, J.A., & Mulligan N.W, . ( 2015). The effect of motoric fluency on metamemory. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22( 4), 1014-1019. |
| 28 | Thiede K. W., Anderson M. C. M., & Therriault D . ( 2003). Accuracy of metacognitive monitoring affects learning of texts. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95( 1), 66-73. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.66URL |
| 29 | Wagenmakers E.-J., Love J., Marsman M., Jamil T., Ly A., Verhagen J., .. van Doorn J . ( 2018). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25( 1), 58-76. |
| 30 | Yang C., Huang T. S-T., & Shanks D. R . ( 2018). Perceptual fluency affects judgments of learning: The font size effect. Journal of Memory and Language, 99, 99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2017.11.005URL |
| 31 | Yue C. L., Castel A. D., & Bjork R. A . ( 2013). When disfluency is—and is not—a desirable difficulty: The influence of typeface clarity on metacognitive judgments and memory. Memory & Cognition, 41( 2), 229-241. |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 赵文博, 姜英杰, 王志伟, 胡竞元. 编码强度对字体大小效应的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(10): 1156-1167. |
| [2] | 陈功香, 张承芬,苏雅雯. 延迟学习判断的效应机制[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(07): 743-753. |
| [3] | 侯瑞鹤,俞国良. 加工流畅性和提取流畅性与学习不良儿童学习判断的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(09): 994-1001. |
| [4] | 张雅明,俞国良. 学习不良儿童元记忆监测与控制的发展[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(2): 249-256. |
| [5] | 陈功香,傅小兰. 内外部线索对学习判断的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2003, 35(02): 172-177. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4379
