 ,1,2,3, 程昌秀
,1,2,3, 程昌秀 ,3,4, 叶思菁3, 沈石3, 张红5,6
,3,4, 叶思菁3, 沈石3, 张红5,6The review and applications of spatial Boltzmann entropy
GAO Peichao ,1,2,3, CHENG Changxiu
,1,2,3, CHENG Changxiu ,3,4, YE Sijing3, SHEN Shi3, ZHANG Hong5,6
,3,4, YE Sijing3, SHEN Shi3, ZHANG Hong5,6通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-03-31修回日期:2021-03-25网络出版日期:2021-07-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-03-31Revised:2021-03-25Online:2021-07-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
高培超(1991-), 男, 河南人, 讲师, 中国地理学会会员(S110014357M), 主要从事信息地理学研究。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2329KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
高培超, 程昌秀, 叶思菁, 沈石, 张红. 空间玻尔兹曼熵的研究进展与应用. 地理学报[J], 2021, 76(7): 1579-1590 doi:10.11821/dlxb202107001
GAO Peichao, CHENG Changxiu, YE Sijing, SHEN Shi, ZHANG Hong.
1 引言
地理学通常被称为是研究世界的学科(The World Discipline/Subject)[1,2],旨在通过综合普适的或多个专门的定律、模型、指标等途径来刻画和理解地球关键带[3](陆地表层、河流湖泊、海岸带及近海海域等)的地理要素(包括自然与人文)及其综合体(即区域系统)的时空格局、演变过程、动力机制[4,5,6,7]。这些途径有著名的地理学三大定律、地理加权回归、地理探测器[8]等。熵作为热力学中解译世界变化的工具,也长期在地理学中扮演着重要角色。熵是复杂系统的核心指标,而地理学的新时代特征是复杂性[9,10],因此熵的研究愈发得到重视,对新时代地理学意义重大。当前,熵在地理学中主要有两大用途。首先,熵被用于关联地理学研究对象的时空变化表征与深层次的热力学机理。热力学中认为,封闭系统的熵自发地、不可逆转地渐增至最大值。这正是著名的热力学第二定律(又称熵定律)。同时,熵与热力学无序和系统不确定性有着紧密的内在联系。因此,熵作为联系热力学机理的“桥梁”,被长期、广泛地应用于地理系统(包括自然、人文系统、及其耦合系统)的研究中。例如,针对景观格局的应用可追溯至20世纪50年代,并形成了三大方向:刻画景观格局的空间异质性、尺度依赖性、不可预测性[11]。又如,学术界试图从热力学本质上理解系统可持续性和区域可持续发展,因此熵也用于构建可持续/高质量发展指数[12]、用于评估和指导城市建设[13]。其次,熵作为信息量的测度指标,被广泛地应用于地图制图学、地理信息科学与系统、遥感图像处理等领域。例如,熵被用于测度地图的信息量[14],进而对制图综合进行指导[15]。以熵为核心,地图制图学发展出地图信息论[16]的分支学科。在遥感图像处理领域,熵作为衡量图像信息量的标准指标[17],被用于降维[18]、融合[19]、配准[20]、分割[21]等。
尽管熵是源自热力学的概念,但在上述应用中的计算方法却几乎完全来自通信领域的信息论。具体而言,“熵”的概念是1851年由德国科学家Clausius首次引入[22],并于1872年由奥地利物理学家Boltzmann首次使用公式明确地表达(即玻尔兹曼熵、简称玻熵或称热力学熵)[23]。20世纪40年代始创的信息论中再次使用了“熵”的概念,并于1948年由美国数学家Shannon提出计算公式(即香农熵、信息熵)[24]。香农熵的公式简洁、变量含义明确且容易测定。相比之下,玻熵的计算困难重重。不过,多数****认为2种熵本质相同、数值可互换[25]。因此,在上述两大应用中,理论探讨时或采用玻熵或采用香农熵,但实际计算时均采用了香农熵算法。
然而,香农熵的使用带来了难以解决的困境。首先,通过香农熵而获得的热力学解译在近年来被严重质疑。例如,Vranken等****[11]发现:基于香农熵测定的空间异质性与热力学毫无关联、香农熵尺度依赖性的热力学解释与复杂理论相悖、基于香农熵的不可预测性只在特定条件下与热力学有关。美国地理学家Cushman将这些发现评论为“令人震惊”的,并呼吁重返玻熵[26]。其次,香农熵无法完整地刻画空间数据的信息量(或无序)。香农熵的设计初衷为刻画通讯信号(例如电报)的信息量,仅考虑了信号中不同成分的占比(或称为信源产生该成分的概率),因此也被广泛地称为统计信息量。在仅考虑统计信息时,香农熵和玻熵存在数值转换的可能性。而空间数据的信息量不仅在于成分的占比,更在于组分和配置。尽管学术界对香农熵算法做出了多种改进[27],但依然效果欠佳。因此,越来越多的****认为2种熵具有本质的不同。景观生态学界认为,2种熵仅是形式相似[11, 28],生物学界[29]和物理学界[30]均有类似观点。实际上,Shannon本人也曾明确其熵并非推导自玻熵[31],2种熵仅在特定条件下才可互转[32]。
因为上述困境和新的认识,最近5年学术界重新聚焦于古老的玻熵,见证了其长足的进步,实现了自1872年玻熵的概念提出后针对空间数据的首次计算,并形成实际应用。本文将从概念、模型、计算、应用4个方面对这些进展进行系统的综述。
2 玻熵的概念模型与计算难题
玻熵涉及两大概念:系统的宏观态(Macrostate)和微观态(Microstate)。前者指系统状态的宏观描述,通常使用若干可量测的宏观特性(称为状态函数、宏观参数,如压强、体积、温度)来实现[33]。后者指从微观的角度刻画系统的内部细节(如组分位置)。如在图1所示的封闭系统中,宏观态均为“容器中有3个气体分子”,微观态却不尽相同。图1
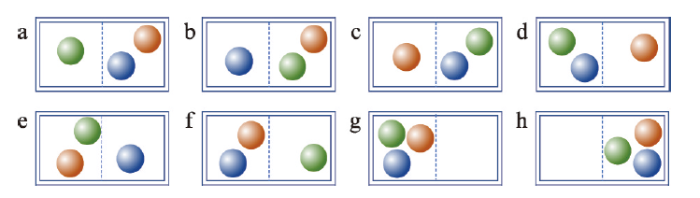 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1宏观态为内含3个不同类型气体分子的密闭容器及其8种微观态
Fig. 1A closed container and its 8 microstates (macrostate: it contains three gas molecules)
在宏、微观态概念的基础上,玻尔兹曼提出了玻熵的概念模型(玻尔兹曼公式):
式中:S即系统的玻熵;W是宏观态所对应微观态的个数;kB是玻尔兹曼常数取值为1.3807×10-23 J/K。图1中所示的密闭容器具有8种微观态,因此玻熵为kB log8。
玻尔兹曼公式简洁,但其在地理学中的应用长期停留在探讨层面[11, 26]。应用瓶颈在于计算困难,具体原因有:① 缺少通用、普适的宏观态定义方法,如美国社会学家Bailey所言“玻熵尽管重要,但物理学领域外的****缺少宏观态的定义方法,例如,如何定义一块景观格局的宏观态?”[34]② 即便宏观态有了良好的定义,微观态数的实验测定亦难实现,理论推导缺少方法[35]。
3 空间玻熵的计算模型
2016年起,学术界在空间数据的玻熵研究方面取得了系列进展。首要进展为计算模型实现了空间玻熵计算模型从无到有的突破(共计2类3种)。2类计算模型分别适用于定性型和定量型栅格数据。定性型是指以栅格形式存储的类别型空间数据,可细分为名义型和次序型。名义型中不同类别无顺序之分,例如土地利用/覆盖类型图、景观镶嵌体;次序型中不同类别有顺序之分,例如疫情风险等级地图。定量型是以栅格形式存储的连续型空间数据,包括间隔型和比率型2类。前者如地表摄氏温度梯度,后者如数字高程模型。与前者相比,后者支持乘除运算,但是实际应用中往往不严格区分二者,在地理学(尤其景观生态学)中通常将二者合并统称为景观梯度[36]。
3.1 针对定性型栅格数据的计算模型
空间玻熵的计算思想最早是针对定性型栅格数据提出的。2016年Cushman通过类比热力学中的算例,首次提出了针对景观镶嵌体的玻熵计算思想——基于边缘总长度(景观格局指数Total Edge, TE)的计算模型[37]。该模型使用了5项(组)宏观参数,分别是几何范围、细胞(景观镶嵌体的基本单元)的类型数、各类型的占比、分辨率(或细胞总数)、TE。微观态定义为细胞的空间配置,个数通过穷举法获得。以图2a中的景观镶嵌体为例,其几何范围为绿色和粉红色区域,共有2类、5个细胞。其中类型1的细胞有2个、类型2有3个,边缘总长度为2。微观态的穷举过程如下:首先,在保持除TE外的所有宏观参数不变的条件下,穷举细胞的空间配置方式,如图2b~2k所示。然后,统计与原景观镶嵌体具有相同TE的穷举结果个数,此处为3。此个数即微观态数,可代入玻尔兹曼公式求解玻熵,得到
图2
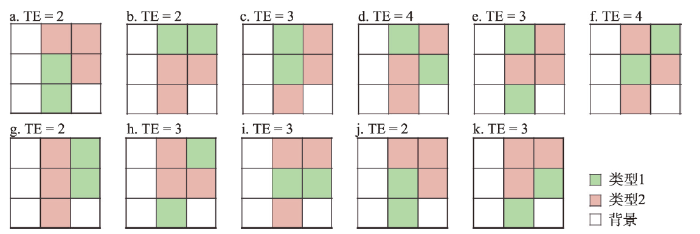 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2景观镶嵌体(a)、可能的空间配置方式(b~k)及其边缘总长度(TE)
Fig. 2A landscape mosaic (a), possible configurations (b-k), and the corresponding total edges (TE)
该计算模型的优点是宏观态的定义对所有定性型栅格数据具有普适性,宏观参数均可快捷地计算。其缺点是,微观态数的计算方法缺乏可操性。在栅格数据的尺寸较大时,穷举结果数可能是天文数字。例如,设栅格数据的大小仅为100行100列,且仅包括2类、每类个数相同的细胞,则穷举结果的理论个数高达
第二种计算思想为基于斑块的计算模型,由中国****于2019年提出[38]。首先,宏观参数被试验性地设置为栅格数据的细胞总数N以及各类型细胞的具体个数Ni。在此情况下,微观态数的计算可通过数学上的排列组合公式完成:
式中:m为类型数。将该微观态数带入玻熵公式并化简,得到:
然而,这种方式定义下的玻熵,只能刻画栅格数据的组分、无法刻画配置。因此,Zhao等[38]增加了对拓扑关系的考虑,将计算模型修正为:
式中:ni为类型i的细胞相互之间所形成的斑块数(细胞在上下左右的任一方向相连形成斑块);kij为类型i的细胞所形成的第j个斑块中所包含的细胞数。
该修正版在本文中被命名为基于斑块的计算模型,其优点是具有解析形式,缺点有:① 修正之后的计算模型所对应的宏观态定义不明确;② 在实际计算中容易因数值较大的阶乘运算产生数值溢出的问题,如假设栅格数据的大小仅为10行10列,公式(4)中首项中包括的阶乘数值高达9.3326×10157。
3.2 针对定量型栅格数据的计算模型
针对定量型栅格数据的计算模型于2017年提出[39],其核心思想是通过尺度变换建立宏观态与微观态之间的联系。该模型认为所有的定量型栅格数据均有普适的宏观态定义,即栅格数据的多尺度表达(图3)。同时认为,在热力学中微观态难以测定的本质原因是观测尺度可以无限细分,从而导致无穷尽。但对于栅格数据而言,其原分辨率即为最天然的观测尺度,因此限定了微观态的数量,使其测定成为可能。图3
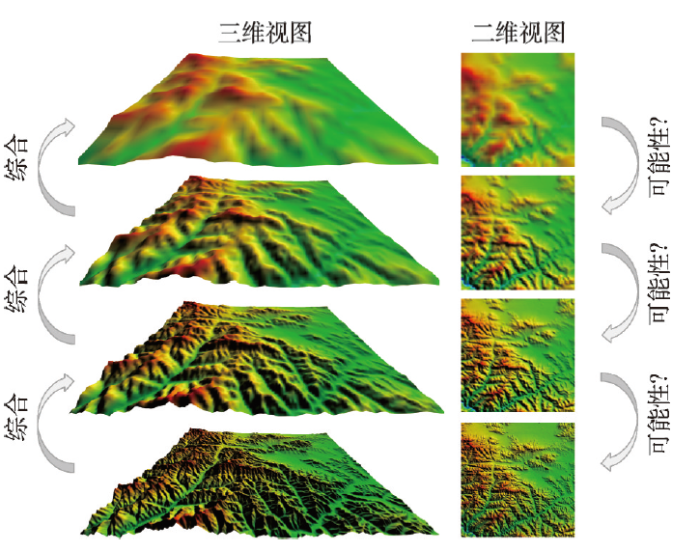 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3定量型空间栅格数据的多尺度层次表达结构
Fig. 3The multiscale hierarchy of a quantitative spatial raster data
具体而言,定量型栅格数据的宏观态定义为其多尺度层次表达结构中与原表达最相似的层次。多尺度层次表达结构通过制图综合中的升尺度(Up-scaling)操作获得。为了使层次尽可能得丰富,升尺度操作中采用大小为
图4
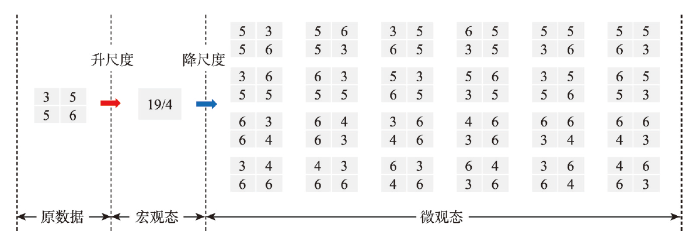 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4针对定量型空间栅格数据计算玻熵的核心思想
Fig. 4The core idea in computing the Boltzmann entropy of a quantitative spatial raster data
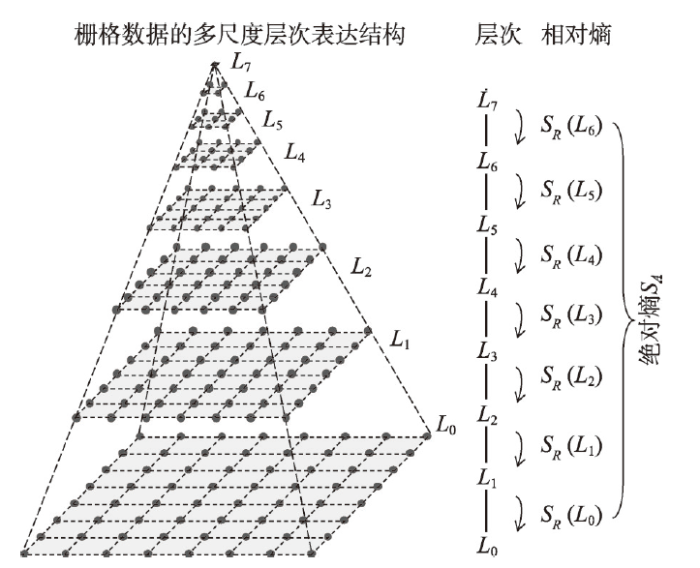
此外,该模型引入了相对和绝对玻熵的概念。将上述微观态数直接代入公式(1)得到的结果称为相对玻熵,因其刻画的是栅格数据相对于其宏观态的不确定性。在多尺度层次表达结构中,相对熵可在任意相邻的两层间计算(图5),所有层的相对熵之和称为绝对玻熵。其含义为,从栅格数据的最抽象状态逐层降尺度到原栅格数据的可能性大小;换言之,栅格数据相对于最抽象的状态(不确定性为零)的不确定性。
图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5相对玻熵(SR)与绝对玻熵(SA)
Fig. 5Relative (SR) and absolute (SA) Boltzmann entropies
4 空间玻熵的算法
以上述3种模型为蓝本,学术界分别发展了3类具体的计算途径:基于TE的算法[37, 40]、基于Wasserstein距离的算法[38, 41]、基于多尺度层次的算法[39, 41-45]。在实现过程中,由于技术考虑,有些算法甚至已经脱离了原模型的核心思想。4.1 基于TE的算法
实现TE计算模型困难的关键在于穷举数据趋近于无穷大,难以获得穷举结果的集合(即统计学中的整体)。因此,Cushman[40]提出使用样本集代替整体:不再测定整体中具有给定TE的个体数(W),而是通过测定样本集中具有给定TE的个体占比来估算假设栅格数据的行列数分别为
在获得上述样本集后,需统计与原栅格数据拥有相同TE的样本个数,并最终将个数转换为占比(
注意
基本算法中采用样本集代替了整体,降低了穷举的难度,但在栅格数据尺寸较大时穷举依然困难。Cushman在处理尺寸为
式中:
4.2 基于Wasserstein距离的算法
基于斑块的计算模型存在阶乘运算数值溢出的问题(3.1节),难以技术实现。为解决该问题,Zhao等提出了基于Wasserstein距离的算法[38]。具体算法如下:首先,舍弃公式(4)中的首项,仅使用第2项、第2项作为熵值的估算。其次,引入对数函数展开式,降低第2项、第2项中阶乘运算的数值大小。对数函数展开式如下:根据公式(7),公式(4)中的第2项、第2项将分别转换为以下形式:
由于
对于任何栅格数据,公式(4)中的第2项、第2项均能转换为如公式(8)所示的频率分布(分别记为分布
需要说明的是,首先,Wdis与玻尔兹曼公式已无关。此外,在Zhao等的原文中,斑块仅基于四邻域系统(von Neumann邻域)定义。实际上,斑块也可基于八邻域系统(Moore邻域)定义[47,48],并在后续研究中被证明效果更好[41]。
4.3 基于多尺度层次的算法
针对定量型栅格数据,学术界开发了2种基于多尺度层次的算法:重采样(Resampling-based)[39]和聚合(Aggregation-based)[44],分别是原计算模型(3.2节)的直接实现和改进实现。2种算法的核心原理相同,均基于大小为图6
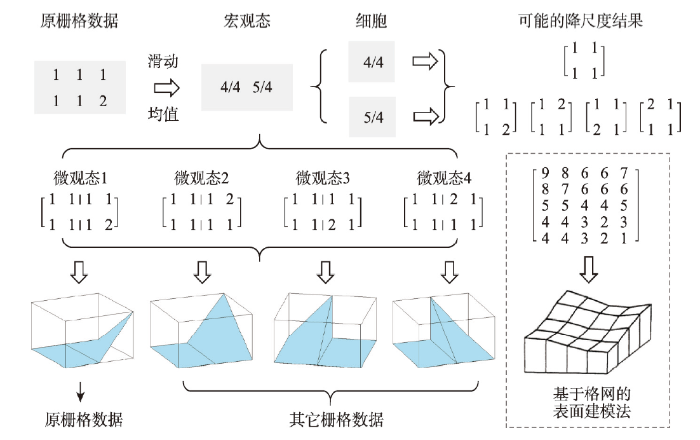 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6基于重采样技术的玻尔兹曼熵算法
Fig. 6Resampling-based algorithm for computing Boltzmann entropy
(1)重采样算法适用于计算任意大小栅格数据的相对熵和绝对熵。但在计算相对熵时,计算量较大(由重采样法生成的多尺度表达层次较多),且计算结果不具有完全的热力学一致性(Thermodynamic Consistency)[44]。
(2)使用聚合算法计算的熵均具有完全的热力学一致性,且绝对熵涉及的计算量较小(多尺度表达层次较少)。但在计算相对熵时,仅适用于长和宽均为偶数的栅格数据;在计算绝对熵时,栅格数据的长和宽均须为2的指数。
为解决上述2种算法存在的问题,学术界做出了诸多努力。例如,为提高算法效率,后续研究中推导了微观态数的解析解,并提供了并行算法[42]。也有****基于头尾分割法(Head/tail Breaks)发展了一种快速估算绝对玻熵的算法[49,50,51]。此外,Nowosad提出了滑动窗口中包括空值时的微观态数求解法[45],使得上述2种算法可适用于不规则的栅格数据、点格局(Point Patterns),例如空气质量监控站点的分布等。
5 空间玻熵的应用
随着计算难题的突破,空间玻熵已在遥感图像处理和地理学中得到应用,计算工具也相继被开发。目前开源的计算工具有3种,分别为针对定量型栅格数据的C#语言版软件[42]、R语言版软件[45];针对定性型数据的基于Matlab的软件[41]。典型应用如下。5.1 在图像处理中的应用
从理论上而言,玻熵在刻画空间信息时比香农熵具有绝对优势。该优势在图像处理中已得到证明。例如,2019年的研究基于玻熵刻画灰度图像的相似性,进而将玻熵应用于高光谱遥感图像的高效降维(波段选择)[52]。该研究获得以下结论:① 基于玻熵的指标能够完整地刻画图像相似性(同时刻画组分和配置),且效果优于目前所有基于香农熵的指标;② 基于玻熵的波段选择算法优于所有基于香农熵的算法。使用基于玻熵选择的波段进行图像分类实验时,分类精度比基于香农熵的算法最高可优化27%。即便与基于更先进、更复杂的波段选择算法相比,基于玻熵的算法也表现更优或具有很强的竞争力[53]。此外,玻熵被用于衡量遥感图像的信息量[54]。
5.2 在景观生态学的应用
空间玻熵的计算突破后,地理****迅速讨论了玻熵的景观生态学应用[40, 55-57]。中日两国****认为玻熵可用于日本里山(Satoyama)景观的生物多样性与生态系统服务评价[57]。2020年,Xu等[58]将玻熵用于中国黄土丘陵沟壑区的景观可持续性评价。其方法为:首先基于专家经验,并以土地利用类型、高程、坡度为自变量创建土地适宜性函数;而后利用该函数评价研究区的土地适宜性;进而分区(子流域)计算土地适宜性栅格数据的玻熵,熵值越大说明土地适宜性的空间分布越无序或数值波动越大,进而说明可持续性越低;最后,利用自然断点法将熵值分为5级,分级评价可持续性。评价结果说明,与2000年相比,2015年米脂县的景观可持续性有较大的改善。
6 讨论
通过前面的回顾,我们发现空间玻熵已形成初步的应用。实际上,正如引言中提及,玻熵对于地理学而言具有重要意义,其潜在的应用更加广泛。例如,由于玻熵刻画了尺度变换中的空间不确定性,而香农熵所刻画的不确定性正是信息论的基石[59],因此玻熵可作为香农熵的替代、并为空间或地图信息论等提供理论基础。值得一提的是,空间信息论正是地理信息科学领域的欠缺。例如,地理学第一定律提出者Tobler指出:信息论中的很多基本假设(如数据是空间无关的)在地理学中常不适用[60]。国内****同样质疑了信息论在测度空间信息时的适用性[61],并指出空间信息的测度研究“远没有达到以米计长度、以千克论质量、以安培量电流的定量程度,这与空间信息的重要地位极不相称”[17]。玻熵作为通往热力学的桥梁,应广泛地用于区域景观变化动力学的机理探究和土地利用可持续性的评价。例如,在中国2017年启动的第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究中,重点目标包括研究青藏高原环境演变背后的机理、探究人类活动对青藏高原的影响等。通过长时间序列地理数据的玻熵变化趋势计算,可为这些目标的实现提供不同的视角和新颖的观点。读者或许会疑惑:热力学的经典适用范围是与外界无能量交换的、独立封闭的系统,但青藏高原是非封闭系统、与外界存在着明显的能量交换,如何使用玻熵建立对青藏高原的热力学认知?实际上,诺贝尔奖获得者Prigogine[62]的耗散理论(Dissipative Theory)已将热力学的适应范围扩展至与外界存在频繁能量交换开放系统。从开放系统和熵的角度来看,实现可持续发展的青藏高原是指系统内部玻熵较低、能且持续保持的热力学系统,而实现高质量发展的青藏高原是指有能力接纳外部输入玻熵的热力学系统。
通过本文综述,我们发现尽管空间玻熵的计算已实现突破,并初步形成了概念、模型、计算、应用的4层研究体系,但依然处于萌芽阶段。回想与熵紧密相关的分形,其发展历程可能存在借鉴意义。在Mandelbrot发表《英国海岸线有多长?》,并正式提出分形维数的计算前,进行了数十载的修正、验算,此后分形又经过几十年的推广、应用与验证[63]。因此,空间玻熵的研究任重且道远,我们期待未来能有更多突破。
7 结语
最近5年地理学界在空间玻熵研究方面取得了系列进展,实现了自1872年玻熵的概念提出后、针对空间数据的首次计算,并形成实际应用。本文对这些进展进行了及时且系统综述。主要结论:① 目前的研究热点集中在空间栅格数据的玻熵,已研发出针对定性和定量型栅格数据的计算模型;② 算法百家齐放,已呈现出基于TE、Wasserstein距离、多尺度层次的3大类算法;③ 已形成景观生态学和遥感图像处理2类应用。未来研究中建议丰富空间玻熵的算法。空间数据可分为栅格数据和矢量数据,但目前缺少针对矢量数据的算法。其难点在于宏观态的定义和微观态数的测算,建议尝试本文中多尺度层次算法的思想。此外,空间玻熵的计算应适用于单要素数据(如景观生态学的廊道)和多要素数据(如土地利用类型图),只有这样才能更好地服务于地理要素耦合研究、促进对陆地表层各要素演化规律的探究[64]。在应用层面,建议将玻熵作为香农熵的重要补充、甚至在部分应用(热力学解译、空间信息测度等)中作为替代。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1111/area.2003.35.issue-1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00167487.2014.12094388URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201512001 [本文引用: 1]

Soil is an important natural resource that humans rely on and civilization is based upon. As the critical component of the Earth's critical zone, pedosphere is most active in Earth's surface system. Moreover, soil processes are considered as the control point for the flows and transformations of material, energy and information. In wake of the increasing attention to soil's multi-functions, traditional soil concept on its functions and roles is being challenged. Therefore, the concept of soil security is proposed, which is a strategic framework with the aim of soil sustainable development, and it can provide guidelines for the sustainable utilization and conservation of soil resources. In this review, the connotations of Earth's critical zone and soil security, and the difference and close relationship between each other are discussed. The ecosystem services in the framework of soil security are summarized. Finally, perspectives on future soil security research needs in the context of ecosystem services are proposed.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.002 [本文引用: 1]

A discipline has typically the following four key features, namely independent research objects, independent research questions, unique characteristics, and unique social services. This paper first discusses the nature of Geography from three aspects, to reveal the characteristics of modern Geography. First, the research object of Geography is changing from simple to complex evolution. In performing geographic research, we should well recognize the complexity of geographic systems. Second, the framework of geographic research questions is structured by the fusion among geographic features, space, and time. This paper explains the essential distinction between different geographic research questions, which promotes the development of the methods and technologies for answering these questions. Third, the philosophy of combining reductionism and holism is growing continuously. A new pattern of research has been formed based on new disciplines and technologies, which is the parallel development of the research on geographic features and that on systems. This paper then identifies the essential characteristics of geographic research, summarizes the key research questions in Geography, and discusses the multiple effects of driving mechanisms on the laws of Geography. An understanding of the fundamental characteristics and the modern value of Geography illustrated in this paper will be contribute to the societal development of Geography.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.08.939 [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject of "exploring the laws of nature, declaring the human essence", with characteristics of comprehensiveness and interactiveness. Since the 1980s, Geography plays an important role in global environmental change research programs. Theories, methods and techniques of Geography have become the basis for solving the problems of the sustainable development of human society is facing. Originated in the global environment change research, and combined with the social science research, The " Future Earth" research plan represents the direction of the development of Geography in the new period. In contemporary, Geography research methods have shift from survey, observation, and records, drawings and other traditional research methods to the modern scientific methods such as spatial statistics, earth observation, GIS, indoor and outdoor simulation and modeling, decision-making system, etc., and are gradually tend to comprehensive and quantitative. As the problems that Geography is facing are more complex and more comprehensive, the Geography research issues become more comprehensive and diverse, and attract more extensive subjects to participate in. In more and more field, the angle of Geography are considered. The discipline boundary that concepts and tools belonging to is blurring. In the new era, the geography, is heading for geographical science. China is an ideal geography test sites of studying the problem of the sustainable development of human society. The future development of Chinese Geography needs to deepen the comprehensive and integrated understanding of the complex man-land system, and strengthen the research of global problems. To achieve the goal of geographical science and social service value, the internationalization level of Chinese geographical science needs to be promoted, and the ability of using advanced technology to parse geographical phenomenon needs to be improved.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.01.001 [本文引用: 1]

Spatial differentiation of natural and human factors in the land surface system of the Earth is the main concern of Geography. Given the complexity of the land surface system, different research methods should be applied to different issues concerning the system. Based on past geographical research, four paradigms were generalized, including geographical empirical paradigm, geographical positivist paradigm, geographical system science paradigm, and geographical big data paradigm. Appropriate paradigms should be employed for different scientific questions, and multiple paradigms should be applied to some complicated questions.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001 [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010 [本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201807002 [本文引用: 1]

Since the 20th century, geography came into being with distinctive disciplinary characteristics by sustained effort of geographers. This paper puts forward predicament from cognitive and thought in the new era, and depicts new geographic characteristics from five aspects: new technology, new orders, new data, new approaches and new driving factors. According to new content of geo-regionality and new approaches of geo-comprehensiveness, the paper proposes that complexity research would be a successful new path in geography, and the complexity would be the third characteristic of geography. Then, the paper details some complex spatial patterns, complex time processes and complex spatio-temporal mechanisms in geography research. Based on the concept of a geographic complex system, this paper presents core issues and corresponding complex research tools. Finally, the paper puts forward new challenges and new requirements for geography in the new era.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808001 [本文引用: 1]

Since 2010, big data has played a significant role in various fields of science, engineering and society. The paper introduces the concepts of geographic big-data, the fourth paradigm and nonlinear complex geographic system, and discusses interactive relationships of these concepts. It is proposed that geographic big-data and the fourth paradigm would become a new opportunity to research on geography complexity. Then the paper discusses how to use the methods of geographic big-data and complexity science to examine geography complexity. For example, based on big-data, a series of indicators of statistical physics fields could be constructed to describe the complex nonlinear characteristics of the real geographic world. Deep learning, complex network and multi-agent methods can be used to model and simulate the complex nonlinear geographic systems. These methods are important for a better understanding of the complexity of geographic phenomena and processes, as well as the analysis, simulation, inversion and prediction of complex geographic systems. Finally, the paper highlights that the combination of geographic big-data and complexity science would be the mainstream scientific method of geography in the 21st century.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s10980-014-0105-0URL [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001 [本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.10.002URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/13658810210149416URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1109/JTEHM.2014.2299280URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1002/bltj.1948.27.issue-3URL [本文引用: 1]
PMID:12884539 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s10980-014-0108-xURL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3390/e20010019URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2012.06.004PMID:22796169 [本文引用: 1]

In the last century, jointly with the advent of computers, mathematical theories of information were developed. Shortly thereafter, during the ascent of molecular biology, the concept of information was rapidly transferred into biology at large. Several philosophers and biologists have argued against adopting this concept based on epistemological and ontological arguments, and also, because it encouraged genetic determinism. While the theories of elaboration and transmission of information are valid mathematical theories, their own logic and implicit causal structure make them inimical to biology, and because of it, their applications have and are hindering the development of a sound theory of organisms. Our analysis concentrates on the development of information theories in mathematics and on the differences between these theories regarding the relationship among complexity, information and entropy.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1538-4632.2010.00800.xURL [本文引用: 1]
[D].
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3390/ijgi8100466URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s10980-015-0305-2URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/s10980-019-00876-xURL [本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.3390/e20040298URL [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.3390/e22040381URL [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.1111/tgis.v22.5URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/s10980-019-00814-xURL
DOI:10.1007/s10980-019-00854-3URL [本文引用: 2]
URL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3390/ijgi9020103URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00330124.2012.700499URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/24694452.2017.1310022URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2018.2872358URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/01431161.2019.1711242URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1109/JSTARS.4609443URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3390/su10093300URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3390/su11030696URL
DOI:10.3390/su11020454URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3390/ijgi9020077URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
PMID:17837158 [本文引用: 1]

Geographical curves are so involved in their detail that their lengths are often infinite or, rather, undefinable. However, many are statistically "selfsimilar," meaning that each portion can be considered a reduced-scale image of the whole. In that case, the degree of complication can be described by a quantity D that has many properties of a "dimension," though it is fractional; that is, it exceeds the value unity associated with the ordinary, rectifiable, curves.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202001001 [本文引用: 1]

Coupling, as a classic physical concept, provides a suite of ideas and methods for describing interactions of multi-agents across disciplines. In contrast, the concept of integration is not from a certain discipline, but it is widely used in many natural and socioeconomic sciences fields due to its great generalization capacity. Both concepts are frequently mentioned in Earth science. Geography, as a multi-disciplinary research area between natural and socioeconomic sciences, owns regional, comprehensive, and complex characteristics. The understanding of coupling varies across geographic sciences. This paper presents an advanced understanding from six geographic perspectives based on different disciplines and scenarios, which is helpful to accurately explore patterns, processes, and mechanisms of land surface system. Firstly, this paper clarifies six perspectives on geographic coupling, and presents corresponding research cases, which include geographic spatial coupling, geographic features coupling, geographic interfaces coupling, geospatial scale coupling, geographic relationship coupling and geographic coupling interpretation. Secondly, the paper interprets the concept of integration from a geographic perspective, and introduces a pathway to achieving an integration in Heihe River Basin's research practice. Finally, the paper proposes intrinsic connections between geographic coupling and geographic integration.
[本文引用: 1]
