 ,1,31.
,1,31. 2.
3.
Revaluation of ecosystem services in inland river basins of China: Based on meta-regression analysis
YAN Yan1, YAO Liuyang2, LANG Liangming1,3, ZHAO Minjuan ,1,31.
,1,31. 2.
3.
通讯作者:
收稿日期:2017-11-3修回日期:2019-02-26网络出版日期:2019-05-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2017-11-3Revised:2019-02-26Online:2019-05-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
颜俨(1991-),男,湖南攸县人,硕士,科研助理,主要从事自然资源价值评估与生态环境治理研究E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1414KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
颜俨, 姚柳杨, 郎亮明, 赵敏娟. 基于Meta回归方法的中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值再评估. 地理学报[J], 2019, 74(5): 1040-1057 doi:10.11821/dlxb201905015
YAN Yan.
1 引言
流域生态系统具备多重功能[1],持续为公众提供大量产品与服务[2,3]。尽管公众的生态保护意识日益增强,但由于流域生态系统具备生态敏感性和适应性[4],自然资源耗竭、生态破坏和环境污染等问题却愈发严重[5,6]。从经济学角度来说,流域生态系统服务属于公共物品,具有极强的外部性,其价值缺乏相关市场得以体现,在流域生态系统管理决策中往往被低估甚至被忽略[7,8]。生态系统服务的稀缺价值难以体现,使得私人成本向下偏离于社会成本,在这种情况下,理性的开发者会选择更多地开发资源或排放污染,由此产生的诸多问题是造成流域生态系统退化的关键因素[9]。在生态环境现代化治理中,经济价值是进行成本效益分析的重要实证依据与精细化数据基础,而此类数据的缺失是实现资源可持续配置的一大难题[10]。流域生态系统服务的价值评估,尤其是基于陈述偏好法的全价值评估[11],不仅有助于理解公众偏好,还能测算相关服务的经济价值[12],这种价值可促进政策制定者和利益相关者在竞争性使用资源时对其配置做出知情决策[9]。近年来,对生态环境的价值进行科学评估已成为各国学术研究者和政策制定者的热点问题[13]。其中,位于中国西北地区的中国内陆流域长期处于经济发展落后与生态环境脆弱的双重困境,该流域生态系统服务的价值评估一直受到****们重点关注[14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]。当前关于陈述偏好价值评估的文献,数量较多且呈逐年上升趋势。但由于评估研究的具体服务不尽相同(涉及水资源供给、防风固沙、休闲娱乐等各方面),且受到社会经济背景、评估方法、评估时间、评估价值类型等诸多因素的影响,其评估结果与结论呈现多样化[12, 23]。这种结论的不一致,一方面,使得在价值评估研究中越来越难以确定影响评估价值的关键因素,另一方面,使得研究成果往往难以被决策者采用,这与价值评估服务于决策的本意相背离。
Meta回归分析是综合一系列已有文献对具体研究指标的量化分析,由于具备严格统计性与较强客观性,能通过消除潜在因素的影响而纠正方程设定偏差,被认为是经济学实证研究发展的希望[24]。同理,对价值评估进行Meta回归,通过控制价值评估过程中的潜在影响因素,能更为深入地分析评估价值的影响因素。当前,除了关于Meta分析的方法介绍与研究范式以及对现有研究评述等[25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]研究外,在基于Meta回归的生态系统服务价值评估应用中,其研究范围涉及国家(如:西班牙[34]、英国[35]、美国[36]、中国[37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]、印度[45]等)、区域(如欧洲[46]、欧洲与北美[47,48]、东南亚[49]以及发展中国家[9]等)甚至全球[50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57];研究对象包含城市开放空间[58]、空气污染[59,60]、林地休闲[61]、户外休闲[62,63,64]、水上休闲[65]、地下水[66]、水质[36]、生物多样性[41]、珍稀濒危物种[67]、碳汇林[68]、森林[56, 69]、湿地[9, 47-48, 50, 53, 70]和湿地的具体分类(如珊瑚礁[51]、环礁湖[52]、红树林[49]、海岸[45, 71]、湖泊[38, 40, 57]、非湖泊湿 地[44]等)以及生态系统服务集合[12, 34, 55]等多方面;此外,在研究方法方面,涉及聚焦单一评估方法(如享乐价值法[59,60]、条件价值评估法[38, 47, 66, 72]等),以及综合两种及以上方法(包含旅行成本法、享乐价值法、条件价值评估法、重置成本法以及选择实验法等多种主流评估方法[9, 12, 34, 37, 41, 50, 53, 55-58, 44]);所有文献均明确划分研究对象所具备的休闲娱乐、淡水供给、水源涵养、防洪蓄水、生物栖息地等多维度价值。而且,大部分文献表明,评估对象面积、评估方法、受访者人均收入、是否发表等因素显著影响评估的价值。
现有Meta回归分析文献在生态系统服务价值评估以及评估价值的影响因素等方面提供了大量实证参考,但相关研究没有聚焦环境脆弱且发展落后的中国内陆河流域。在中国流域生态环境治理制约因素中,不仅包括现有文献普遍考虑的经济因素,还包括诸多社会因素,如祁毓等[73]关注的社会资本和制度环境等。这些被忽略的社会因素往往难以量化而不易纳入模型,因此,有必要聚焦社会因素较为同质的中国内陆河流域进行研究。为此,本文首次采用Meta回归分析评估中国内陆河流域的生态系统服务的经济价值,且通过当前较为前沿的n-1数据分割技术对Meta回归方程实施效益转移并进行检验。
2 研究区域概况
中国内陆河流域,地处欧亚大陆腹地、青藏高原北侧,远离海洋,介于73°40'E~120°03'E、33°09'N~48°N,流域覆盖面积250×104 km2,其中山区面积为98×104 km2,占流域面积的39.1%,流域地形复杂,地貌以高原和内陆盆地为主,这对流域内降水量的空间分布具有较大影响[74,75],流域受西北带气候、高原季风和东亚季风等气候系统的影响,气候复杂多变,由于地处干旱半干旱地区、蒸发十分强烈,水面蒸发量变化很大(最高值大于2400 mm,最低值小于700 mm)。除山区和北疆的伊犁、塔城等地区外,大部分地区的年降水量不足200 mm,水资源十分匮乏[75]。中国内陆河流域主要包括黑河、石羊河和塔里木河(水系)三大流域,均位于西北地区。流域的总面积占国土总面积的1/3,但水资源仅占全国的5.5%,为世界上最干旱的地区之一,水资源稀缺成为中国内陆河流域生态安全和经济发展面临的最大挑战[76]。随着国家西部大开发和“一路一带”倡议的实施,内陆河流域在中国西部资源开发和经济发展中的战略地位将愈发凸显。然而,经济发展、人口增长和城市化进程加快必然使得需水量增加,再加之全球气候变暖引发的近期北方蒸发量增大、降水量减少,中国内陆河流域面临的水资源形势将更加严峻,由此带来的生态环境问题也将更加突出[77]。
3 研究方法与数据
3.1 研究方法
3.1.1 Meta回归 Meta分析是对已有研究结果的统计分析,也是对具体问题的系统综述。在医学、教育学和社会科学的研究中,Meta分析是其循证实践的重要组成部分。不同于其他学科,在经济学中,Meta分析几乎完全是Meta回归分析[24],其最初是为了纠正已知的方程设定偏差,后来在计量经济学估计中流行开来[78]。Meta回归分析是多变量实证研究,使用多元回归,分析已有研究中回归估计值或回归估计值的转换形式(例如弹性,生态系统服务价值或偏相关性)之间的变异。由于计量经济学通常是观测性的(非实验性的),即使是最严格的计量经济学应用也不能消除所有潜在因素的影响。已有的大量Meta回归实证分析证明,实证经济学研究的所有领域均出现方程设定偏差,其中许多偏差都足以改变对有关现象的解释或对既定政策干预的评价[24]。Meta回归模型的具体形式通常为:
式中:yi是待研究的效应值;i表示第i个样本;βV、βS、βC分别为解释变量XVi(研究方法的特征)、XSi(研究对象的特征)、XCi(研究背景的特征)的系数向量;α是常数向量;εi是残差项。
3.1.2 效益转移 在生态环境价值评估实践中,受限于时间和成本等因素,研究者有时难以通过调研获取第一手价值评估资料,而且,有些价值评估由于调研成本与评估目的等因素并不一定需要通过调研来进行[37]。因此,****们开始利用效益转移法,尝试将研究地的价值转移到政策地[79],该方法不仅较为客观地综合已有研究成果进行分析,而且在操作上与成本上具有优势。
效益转移通常有3种方法:直接效益转移,效益方程转移和Meta回归分析[80,81],基于Meta回归的效益转移不仅具有充分利用已有文献的优势,而且在实际应用中也更为精确可靠[81,82,83]。尽管,基于Meta回归分析的效益转移是首选方法,但它在以下情形中可能产生实质性的转移误差:① Meta回归中的初始数据不能很好地表征政策地的基本特征;② 虚拟变量不能捕获变量的真实变异;③ 不同研究之间质与量的差异难以捕获;④ 初始文献的价值估计是错的[80]。
为此,本文将检验基于Meta回归效益转移方程的效益转移在中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值评估中的适用性,即模型样本外的预测能力[50]。本文采用n-1的数据分割技术,得到n个Meta回归效益转移方程。每个Meta回归效益转移方程都是基于n-1个样本量,来预测n-1之外的样本的价值。此外,本文以4种不同的方式来探讨预测效益转移的有效性[64, 80, 84],分别为:使用两个t检验,分别测试均值和相关性,计算效益转移的绝对(百分比)误差,以及对实际观测值和效益转移价值进行回归。
(1)进行配对t检验,效益转移价值的均值是否与实际观测值的均值显著不同。零假设为:
(2)进行另一个t检验来分析Pearson相关系数的显著性。Pearson相关系数
(3)通过计算绝对误差和均值绝对误差来评估效益转移的质量。其定义为:
(4)通过普通最小二乘(OLS)回归模型,研究实际观测到的价值与效益转移价值的线性关系:
在Meta回归效益转移方程完全预测的情况下,式(2)中的参数:
3.2 数据来源
Meta分析的第一步是精确提供有效且可比的现有生态系统服务价值评估[9]。本文的数据检索来源包括:中国知网(CNKI)、Web of Science和Google Scholar。在2017年2月24日,采用多种关键词进行检索:“支付意愿”“受偿意愿”“willingness to pay”或“WTP”“willingness to accept”或“WTA”,再结合以黑河、石羊河、塔里木河及其支流等中国内陆河名称①(①来源于中国数字科技馆—内陆河:http://amuseum.cdstm.cn/AMuseum/innerriver/nlhfb_nlh_1.html。)。基于文献检索,设定了文献选择的标准:① 使用陈述偏好法进行评估,包括条件价值评估法(CVM)和选择实验法(CE);② 评估的是流域生态系统服务价值;③ 评估单一或多个流域生态系统服务的价值;④ 评估对象位于中国内陆河流域;⑤ 报告了评估对象的面积等信息或这些信息可以从其他来源获取;⑥ 撰写语言为中文或英文。需要说明的是,在所有文献中,已发表和未发表的文献均包括在内。参照当前Meta分析的常规做法[24-25, 27-28],期刊论文归为发表文献,其他均归为“灰色”文献,具体包括工作论文、学术报告以及硕士论文和博士论文。
经进一步文献筛选,符合相关文献检索标准的文献共计22篇。然而,在实际统计中,关于受偿意愿的文献仅有2篇(共析出两个样本),若作为变量纳入模型可能会因为变异不足而无法有效估计,故未将这两篇文献并入Meta数据库。因此,本文编制了20篇文献的Meta数据库,共包括111个观测样本可供进行接下来的Meta回归与效益转移。
在这些中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值评估的研究中,最早的是徐中民等[96]使用支付卡式的条件价值评估方法(PC-CVM)对黑河流域下游额济纳旗的生态系统恢复进行总经济价值评估,最近的文献是徐涛等使用选择实验法(CE)对黑河流域生态系统恢复进行的价值评估。Meta数据库中包含黑河、石羊河以及塔里木河等3条中国内陆河(图1),涵盖甘肃、内蒙古和新疆等3个地区(省或自治区),具体特征详如表1所示。
图1
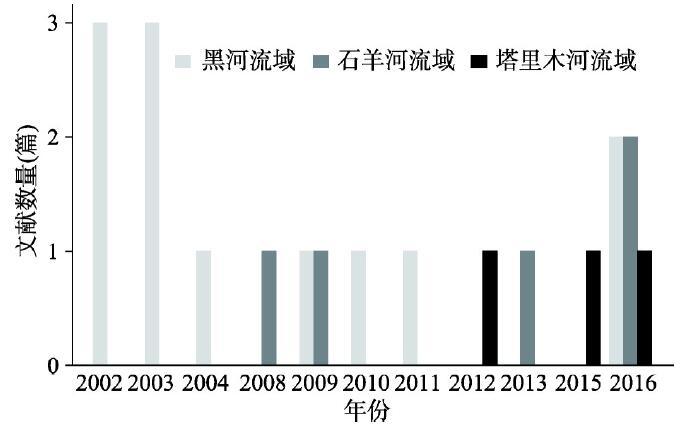 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1发表文献数量的时间与流域分布
Fig. 1Number of studies by year and basin
Tab. 1
表1
表1Meta回归文献的特征
Tab. 1
| 引用文献 | 样本 | 地区 | 流域 | 使用方法 | 调整价值(元) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahlheim等 [85] | 1 | 新疆 | 塔里木河 | CVM-二分式 | 1284.00 |
| Tang等[86] | 1 | 甘肃 | 石羊河 | CVM-二分式 | 1031.97 |
| 陈东景等[87] | 16 | 内蒙 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 47.40~75.73 |
| 樊辉等[88] | 1 | 甘肃 | 石羊河 | CE | 117.56 |
| 樊辉等[89] | 8 | 甘肃 | 石羊河 | CE | 86.73~456.93 |
| 李青等[22] | 6 | 新疆 | 塔里木河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 1112.61~1807.15 |
| 乔旭宁等[90] | 31 | 新疆 | 塔里木河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 17.34~199.21 |
| 尚海洋[91] | 1 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 13.26 |
| 石惠春等[92] | 1 | 甘肃 | 石羊河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 70.84 |
| 唐增[93] | 1 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-二分式 | 1201.21 |
| 王小鹏等[94] | 1 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 356.02 |
| 徐涛等[95] | 6 | 甘肃、内蒙 | 黑河 | CE | 42.08~124.59 |
| 徐中民等[96] | 1 | 内蒙 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 60.67 |
| 徐中民等[97] | 3 | 内蒙 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 44.88~56.14 |
| 徐中民等16] | 25 | 内蒙 | 黑河 | CVM-开放式 | 29.24~259.48 |
| 徐中民等[17] | 2 | 内蒙 | 黑河 | CE | 118.01~283.32 |
| 尹小娟等[98] | 1 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 78.88 |
| 张大鹏等[99] | 1 | 甘肃 | 石羊河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 147.43 |
| 张志强等[15] | 2 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-支付卡式 | 74.63~79.84 |
| 张志强等[100] | 2 | 甘肃 | 黑河 | CVM-二分式 | 225.21~252.26 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
Meta数据库中的内陆河流域生态系统呈多样化。最小的流域生态系统是位于黑河支流北大河中游的甘肃省酒泉市花城湖湿地,占地867 hm2;最大的流域生态系统是塔里木河流域,占地102万hm2;流域生态系统占地面积的中位数为6万hm2。流域生态系统服务价值的均值为每年每户257.66元(2016年价格,同下),中位数为每年每户79.84元。如预期,不同文献、不同流域和估价方法的生态系统服务价值差异较为明显。因此,有必要进行Meta回归分析。
3.3 变量选取
在本文的Meta回归中,被解释变量是中国内陆河流域生态系统服务的评估价值。在现有关于生态系统服务价值评估的Meta分析文献中,由于包含生产要素收入净额法(Net Factor Income)、机会成本法(Opportunity Cost)、重置成本法(Replacement Cost)与市场价格法(Market Prices)等无法获取支付意愿的诸多方法,研究往往无法将评估价值标准化为每人(或每户)的支付意愿[50],而不得不引入Meta数据库以外的数据(如年鉴)转化为单位面积的价值。然而,本文聚焦的是陈述偏好法,且Meta数据库中的研究均为支付意愿,故本文采用初始数据中大量使用的户均支付意愿的形式。这样做的好处有:不仅能避免引入外部数据、减少因再次计算而带来的偏差,还能立足于陈述偏好法的理论基础(效用最大化理论与随机效用理论的决策单元均为理性个体),使研究结论具备更直接的经济学含义。此外,在条件价值评估法得出的结果通常表示为平均值,而选择实验的结果表示为边际值。如果现状选项属于选择实验的可选方案,且边际值是基于现状的,可将边际值视为平均值[80]。但由于Meta回归数据库中的平均值与边际值的差异较大,若将二者近似等同会产生较大偏差,故在处理边际值时,采用现状至最佳状况的货币化价值,即此时的评估价值为:现状改善至最佳状态某属性的水平差值与边际值的乘积。
如前所述,Meta回归方程中的解释变量一般包括评估方法的特征、研究对象的特征、研究地域的特征等。文本结合陈述偏好法在生态系统服务价值评估研究中的各个环节(图2),将解释变量进一步拓展并细化,具体划分为以下4类:
图2
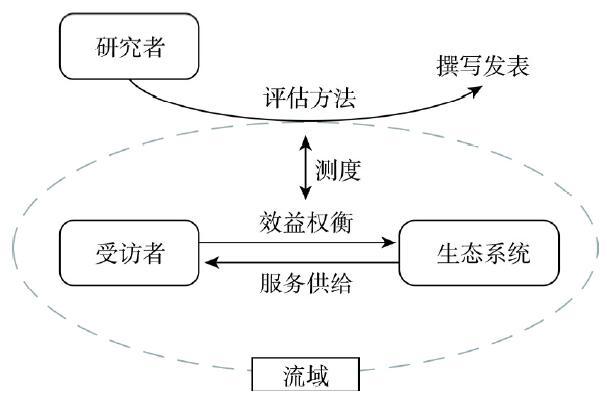 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2流域生态服务价值评估研究示意图
Fig. 2Research process of payment for ecosystem
(1)研究对象的特征。已有研究中尽管相关研究对象特征的划分存在多样性[9, 21, 40, 42],但基本依据千年价值评估(MA)的分类方法,即生态系统服务划分为供给服务、调节服务、文化服务和支持服务。由于近年来千年价值评估的分类体系受到很多质疑[101,102,103],本文依据欧洲环境署Haines-Young等所倡导建立的生态系统服务国际通行分类,使得生态系统服务的划分既无重叠亦无冗余[103]。具体来说,本文将内陆河流域生态系统服务划分为三大类:供给服务(Provsioning Services)、调节与维护(Regulating and Maintenance Services)、文化服务(Cultural Services)。此外,本文还加入流域类别(黑河、石羊河和塔里木河)、流域位置(上游、中游和下游)以及流域生态系统占地面积等已有研究中普遍采用的变量作为研究对象的特征变量。
(2)受访者的特征。该特征是针对本文所研究的陈述偏好法而设定的,由于陈述偏好法基于对受访者的问卷调查,受访者的社会人口特征不同所评估的价值(货币化的公众福利)也各异。现有文献中,大量研究纳入了受访者性别、年龄、受教育程度以及收入等影响因素[98, 104-106],此外,近年来越来越多的研究开始关注空间异质性的问题[89, 107-109]。因此,结合Meta回归数据库的实际情况,选取了每个样本受访者的男性比、年龄、受教育年限、家庭收入,以及受访者在流域的位置,即上游、中游和下游等3个虚拟变量。
(3)测度方法的特征。如前所述,陈述偏好法包含条件价值评估法和选择实验法,其中,条件价值评估法运用较早也较为普遍,具体包括投标博弈(Biding)、开放式(Opened)、支付卡式(Payment Card)以及当前较为前沿的二分式(Dichotomous)。依据Meta回归数据库的实际情况,本文选取支付卡式条件价值评估法、开放式条件价值评估法、选择实验法等3个虚拟变量。
(4)撰写发表的特征。发表偏差已成为Meta分析研究中公认的问题[110],本文为此设置期刊文献这一虚拟变量对其进行表征。此外,由于发表时间反映了文献的时代特征,体现出当时的主要观点、思想等因素[31],本文还加入了发表时间这一变量。
上述变量的基本特征如表2所示。
Tab. 2
表2
表2变量定义与描述性统计
Tab. 2
| 变量 | 解释 | 均值 | 标准误 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 被解释变量 | |||
| 评估价值 | 受访者每年户均支付意愿(元),以2016年人民币计 | 207.68 | 34.27 |
| 解释变量 | |||
| 研究对象特征 | |||
| 供给 | 评估的服务是否包含供给服务:是=1,否=0 | 0.92 | 0.03 |
| 调节与维护 | 评估的服务是否包含调节与维护服务:是=1,否=0 | 0.88 | 0.03 |
| 文化 | 评估的服务是否包含文化服务:是=1,否=0 | 0.87 | 0.03 |
| 石羊河 | 评估的流域是否为石羊河流域:是=1,否=0 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| 塔里木河 | 评估的流域是否为塔里木河流域:是=1,否=0 | 0.34 | 0.05 |
| 上游 | 评估的生态系统是否包含上游:是=1,否=0 | 0.44 | 0.05 |
| 中游 | 评估的生态系统是否包含中游:是=1,否=0 | 0.51 | 0.05 |
| 下游 | 评估的生态系统是否包含下游:是=1,否=0 | 0.87 | 0.03 |
| 面积 | 评估的生态系统面积(万hm2) | 12.20 | 2.23 |
| 受访者特征 | |||
| 性别 | 受访者的男性占比 | 0.69 | 0.01 |
| 年龄 | 受访者实际周岁 | 34.58 | 0.52 |
| 受教育程度 | 受访者的受教育层次:小学及以下=1;初中=2;高中=3;大学及以上=4 | 2.89 | 0.05 |
| 家庭收入 | 受访者的家庭年收入(万元) | 2.09 | 0.20 |
| 上游受访者 | 受访者是否包含上游居民:是=1,否=0 | 0.89 | 0.03 |
| 中游受访者 | 受访者是否包含中游居民:是=1,否=0 | 0.93 | 0.02 |
| 下游受访者 | 受访者是否包含下游居民:是=1,否=0 | 0.90 | 0.03 |
| 测度方法特征 | |||
| 支付卡式 | 评估的方法是否采用支付卡式CVM:是=1,否=0 | 0.58 | 0.05 |
| 开放式 | 评估的方法是否采用开放式CVM:是=1,否=0 | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| 选择实验 | 评估的方法是否采用选择实验法:是=1,否=0 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| 撰写发表特征 | |||
| 期刊 | 文献是否为公开发表的期刊论文:是=1,否=0 | 0.94 | 0.02 |
| 发表年份 | 文献公开发表时间,以2001年为基年 | 7.54 | 0.52 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3.4 参数估计
为了提高估计结果的质量[9, 40, 47],本文被解释变量采用取自然对数的形式。这使得本文的半对数线性模型为:式中:
在Meta回归中,加权回归模型、面板模型或多层线性模型通常用于解释单个研究效应[27]。由于本文Meta回归数据库中单个研究内解释评估价值差异的变动不足,面板模型或多层次模型并不适合本文的数据库[80]。因此,本文使用加权最小二乘法(WLS)估计,相较于已有Meta回归分析较多采用的最小二乘法(OLS),使用加权最小二乘法可有效避免可能存在的有偏估计[9]。在权重设置方面,Hedges等[111]表明方差的倒数是最优权重,即在理想情况下,更高精度的估值应该被赋予更大的权重。然而,与已有大部分相关文献类似,本文的Meta回归数据库中鲜有文献报告了评估价值的标准误,为此,本文依据Stanley等[112]的建议,使用样本量平方根的倒数来替代估计的标准误。
4 结果分析
4.1 Meta回归
本文采用Stata14软件运行Meta回归模型,结果如表3所示。模型1是纳入所有变量的加权最小二乘法的估计结果。F统计量通过了检验,调整R2为0.836,说明Meta回归模型能解释生态系统服务价值的83.6%的变异,总体来说具有较好的拟合优度。为了探索结果的稳健性,本文采用“一般到具体”(General-to-specific)的建模策略[9, 24]。本文删除了在模型1中p值大于0.3的两个变量得到模型2。尽管模型2具有较高的F统计值和调整R2,但F检验证明被删除的变量并非是冗余的(F = 7.32,p = 0.001)。此外,对比两个模型的估计结果,所有系数的方向一致、大小和显著性也基本一致,说明本文所采用的模型具有较好稳健性。由于未通过删除两个变量的F检验,以下主要依据模型1进行变量解释以及后续的效益转移估计。Tab. 3
表3
表3Meta回归模型结果
Tab. 3
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非标准化系数 | 标准误 | 非标准化系数 | 标准误 | ||
| 常数项 | 6.382*** | 0.809 | 6.350*** | 0.643 | |
| 研究对象特征 | |||||
| 供给 | 0.551*** | 0.187 | 0.549*** | 0.185 | |
| 调节与维护 | 0.555*** | 0.185 | 0.554*** | 0.183 | |
| 文化 | -0.765*** | 0.186 | -0.763*** | 0.184 | |
| 石羊河 | 1.389** | 0.333 | 0.820** | 0.326 | |
| 塔里木河 | 0.819* | 0.524 | 0.925* | 0.510 | |
| 上游 | 7.128*** | 1.619 | 7.224*** | 1.575 | |
| 中游 | -5.396*** | 1.159 | -5.473*** | 1.122 | |
| 下游 | -5.661*** | 1.139 | -5.685*** | 1.104 | |
| 面积 | 0.023*** | 0.005 | 0.023*** | 0.005 | |
| 受访者特征 | |||||
| 性别 | 0.055 | 0.517 | |||
| 年龄 | -0.003 | 0.009 | |||
| 受教育程度 | 0.095 | 0.080 | 0.095 | 0.079 | |
| 家庭收入 | 0.301** | 0.116 | 0.307*** | 0.114 | |
| 上游 | -7.475*** | 1.610 | -7.567*** | 1.568 | |
| 中游 | 5.290*** | 1.154 | 5.366*** | 1.119 | |
| 下游 | 5.086*** | 1.166 | 5.164*** | 1.130 | |
| 测度方法特征 | |||||
| 支付卡式 | -1.485*** | 0.159 | -1.489*** | 0.157 | |
| 开放式 | -1.437*** | 0.173 | -1.440*** | 0.170 | |
| 选择实验 | -0.446 | 0.329 | -0.457 | 0.323 | |
| 撰写发表特征 | |||||
| 发表年份 | -0.252*** | 0.070 | -0.256*** | 0.067 | |
| 期刊 | 1.291*** | 0.346 | 1.285*** | 0.332 | |
| F统计量 | 26.06 | 29.44 | |||
| 调整R2 | 0.836 | 0.840 | |||
| 样本量 | 111 | 111 | |||
新窗口打开|下载CSV
在模型中,研究对象特征的所有变量均显著。供给服务、调节和维护服务对支付意愿具有显著正向影响,这说明在中国内陆河流域生态系统中若存在供给服务、调节和维护服务倾向于获得更高的评估价值。文化服务具有显著负向影响,相较于其他服务,文化服务对支付意愿的影响恰好相反,该结论与张玲等[40]在研究中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值的研究结论相反。可能的原因是:与张玲等[40]的研究区域不同,本文聚焦的中国内陆河流域当前经济发展较为落后,公众对生态系统的文化服务的需求弹性较大,即当地公众对最基本食物和能源等物质供给需求最大,而较少关注文化休闲等主观需求[113]。与之类似,Chaikumbung等[9]在研究落后发展中国家的湿地生态系统价值评估中也出现文化服务对支付意愿为显著负向影响的结果。
生态系统所在的流域类别均正向显著,石羊河和塔里木河所评估的生态系统服务价值均显著高于黑河,从均值也可看出,石羊河和塔里木河的生态系统服务平均价值分别为265.24元和342.63元,而黑河流域的平均价值仅为112.30元。这表明,若其他条件保持不变,使用陈述偏好法评估中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值,石羊河和塔里木河得到的每年户均支付意愿要高于黑河。同理,上游生态系统具有显著正向影响,这说明包含流域上游生态系统的研究更倾向于获得较高的支付意愿。但中游和下游生态系统均显著为负,可能的原因是:在中国内陆河流域,上游一般属于是生态保护良好的山地,而中下游集中了流域大部分的城市和人口,因而受访者对中下游这种受到人类活动影响较大生态系统服务的支付意愿较小。面积对内陆河流域生态系统服务价值具有显著正向影响,这和已有文献的结论一致,如张玲等[40]、Chaikumbung等[9]。
本文受访者特征中的性别不显著,这与董冬等[104]、周晨等[105]、何可等[106]等研究结论一致;年龄和受教育程度的作用方向符合常理但并不显著,这与以上文献的研究结论不一致,但和尹小娟等[98]的结论相同,这可能是由于本文和尹小娟等[98]的研究区域均为中国内陆河流域,具有独特的社会经济与文化背景,在置于更大范围的研究中(如中国),这些特征很容易受到其他地区同类特征的主导而无法显现在模型估计中。这在一定程度上进一步支持本文聚焦中国西北内陆河流域的重要意义。家庭收入具有显著的正向影响,这符合常理且与已有研究结论一致。此外,文献是否包含上游、中游以及下游的受访者对中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值评估也均具有显著影响,且影响方向刚好与上述的生态系统所在流域上中下游位置变量的方向相反,其原因可能是由于中下游的生态系统受到人类活动影响较大,该地的受访者对于自然生态系统的诉求更强烈而具有更高支付意愿。
在测度方法特征中,相对于支付卡式和开放式条件价值评估法,二分式条件价值评估法得到的支付意愿显著较高。许多****均认为,二分式条件价值评估法比其他的条件价值评估法更具有激励性,特别是在非使用价值的评估中[114,115,116],这与本文中二分式条件价值评估法得到的价值较高的结论相一致。此外,通过二分式条件价值评估法测度的支付意愿与选择实验法相比并无显著差异,可能的原因是:二者均为当前较为前沿的陈述偏好法,其测度的价值均趋近于真实值。
撰写发表特征中的发表年份变量具有显著负向影响,这表明中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值每年下降2%~3%,原因可能是偏好在随时间改变,受访者为中国内陆河流域生态系统服务的付费意愿在降低,也可能是因为最有价值的生态系统在早前已经被评估了[48, 117],还有,Lehrer[118]认为可能的原因是较早的研究仅为了发表,后来的研究则使用更为精确的估计,从而造成一种随时间推移的“衰减效应”。但这个数值比Chaikumbung 等[9]得出的10%~13%要小,可能是由于研究区域的差异。此外,期刊变量具有显著正向影响,这说明期刊文献上所评估的价值相比其他文献显著较高,这与Enjolra等[52]和Chaikumbung等[9]的研究结论相反。再进一步将价值和价值的自然对数与期刊的影响因子进行Pearson相关分析发现,相关系数分别为0.047(p值为0.638)和0.005(p值为0.960)。
4.2 效益转移
运用Stata14软件,采用n-1数据分割技术,本文得出基于Meta回归效益转移方程公式(3)的效益转移结果。从图3可看出,由完整样本交互效应的模型1得到的效益转移价值(预测值),和实际观测价值(样本值)具有相同的变化趋势。表4中显示了有关效益转移质量的信息(左栏)。Meta回归效益转移方程的调整R2为0.699,效益转移价值和实际观测价值之间的差异均值(-29.65元)并不显著为0。此外,均值和中位数绝对误差之间的差异并不十分明显(最大百分比误差为470%,约为中位数百分比误差的10倍,低于Sundt等[53]的40倍差距)。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3全样本的流域生态系统价值效益转移
Fig. 3Value transfer for full sample
Tab. 4
表4
表4Meta回归效益转移的质量
Tab. 4
| 交叉检验技术 | 基于模型1交互效应模型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 全样本 | 黑河流域 | ||
| 效益转移均值 | 168.25 | 87.88 | |
| 效益转移方程的调整R2 | 0.699 | 0.552 | |
| 差异均值(效益转移价值-实际观测价值) | -29.65 | -22.08 | |
| Pearson相关系数 | 0.837 (p = 0.000) | 0.788 (p = 0.000) | |
| 绝对误差 | 均值 | 65.71 | 41.12 |
| 中位数 | 25.62 | 18.37 | |
| 百分比误差(%) | 均值 | 45.50 | 38.01 |
| 中位数 | 30.11 | 27.12 | |
| 接受 | 接受 | ||
| 接受 | 接受 | ||
| 效益转移样本量 | 110 | 60 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图4展示的是Meta回归方程对黑河流域的效益转移价值和实际观测价值,但效益转移方程的总体表现相较全样本稍有下降(表4、图3)。相较于图3,图4中效益转移价值变化相对较小。黑河流域Meta回归效益转移方程的调整R2是0.552,均值和中位数绝对效益转移误差分别是41.12元、18.37元,均值和中位数百分比效益转移误差是38%,27%。此误差与Salem等54]、Sundt等[80]的研究结果相近,且低于大多已有研究结果,如Brander等[50]的研究中均值绝对误差为58%,Brander等[119]则为186%,Brouwer[120]的研究为85%,Enjolras等[52]的为87%。故本文所得误差介于已有研究的误差范围内,是可以接受的。
图4
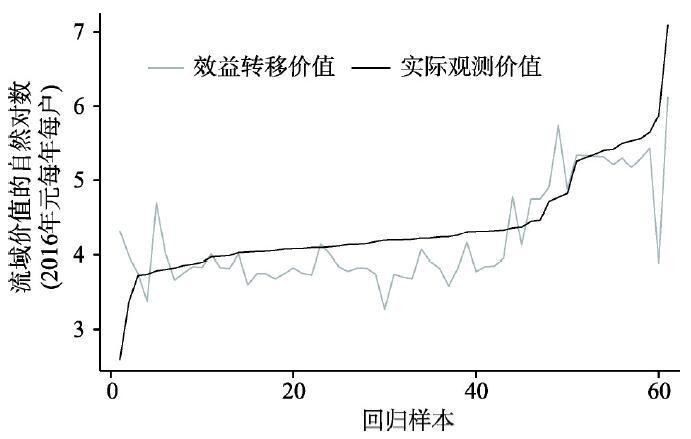 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4黑河流域生态系统价值效益转移
Fig. 4Value transfer for restricted sample
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
(1)研究对象特征在中国内陆河流域生态系统价值评估中具有显著影响,包含供给服务、调节和维护服务的流域生态系统倾向于获得更高价值,包含文化服务的流域生态系统则相反;石羊河和塔里木河所评估的价值高于黑河;此外,评估对象所在上、中、下游位置以及面积对价值评估均有显著影响。(2)受访者特征在价值评估中具有显著影响,受访者家庭收入越高所评估的价值越高,受访者包含流域上游居民倾向于获得更低的评估价值,受访者包含流域中游或下游居民则反之。
(3)测度方法特征在价值评估中具有显著影响,相较于支付卡式和开放式条件价值评估法,采用二分式条件价值评估法倾向于获得更高评估价值;而二分式条件价值评估法与选择实验法获得的价值无显著差异。
(4)撰写发表特征在价值评估中具有显著影响,中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值随时间推移具有“衰减效应”,每年下降2%~3%。此外,期刊文献所评估的价值显著高于其他文献。
(5)Meta回归方程结果运用到样本外效益转移中,得到均值和中位数效益转移误差分别为38.01%、27.12%,相较于现有研究,该结果处于可接受范围。
5.2 讨论
(1)Meta分析在中国经济学中的应用才刚刚起步,尤其在资源环境经济学方面。本文综合已有文献,分析了21个具体变量在陈述偏好法评估中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值中的作用关系,这不仅拓展了Meta回归分析在中国经济学方面的应用,也为中国内陆河流域的价值评估研究提供了归纳总结,可作为该地区后续相关价值评估研究的借鉴。(2)此外,本文中Meta回归效益转移方程的误差低于大多已有的Meta研究,这说明Meta回归效益转移在中国内陆河流域生态系统服务价值评估中具有适用性,这也为中国内陆河流域管理政策的发展和分析提供了低成本的政策工具。尽管如此,我们保有和Chaikumbung等[9]相似的态度,即:跨越不同空间、时间或其他维度进行效益转移,仍需十分谨慎。
(3)当然,本文尚有一些不足:本文和当前绝大部分Meta回归研究一样,纳入了较多虚拟变量,这可能会无法充分捕获生态系统服务提供的质量和数量差异,从而影响Meta回归的结果。另外,本文限于样本量,未对单个研究的多个样本进行群组分析,这样也可能在一定程度上对研究结果存在影响。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ejrh.2014.07.001URL [本文引用: 1]

India. India has a wealth of wetland ecosystems that support diverse and unique habitats. These wetlands provide numerous ecological goods and services but are under tremendous stress due to rapid urbanization, industrialization and agricultural intensification, manifested by the shrinkage in their areal extent, and decline in the hydrological, economic and ecological functions they perform. This paper reviews the wetland wealth of India in terms of their geographic distribution and extent, ecosystem benefits they provide, and the various stresses they are exposed to. The paper also discusses the efforts at management of these fragile ecosystems, identifies the institutional vacuum and suggests priority area where immediate attention is required in order to formulate better conservation strategies for these productive systems. It has been found that management of wetlands has received inadequate attention in the national water sector agenda. As a result, many of the wetlands are subject to anthropogenic pressures, including land use changes in the catchment; pollution from industry and households; encroachments; tourism; and over exploitation of their natural resources. Further, majority of research on wetland management in India relates to the limnological aspects and ecological/environmental economics of wetland management. But, the physical (such as hydrological and land use changes in the catchment) and socio-economic processes leading to limnological changes have not been explored substantially.
DOI:10.1007/s11769-005-0008-8URL [本文引用: 1]

US$/a for the total area of 1356700 ha, among which about 97% was provided by the wetlands. Effective conservation and management of wetlands are therefore crucial to Shanghai's sustainable development. The limitations of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value were also discussed in the present paper.
DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00164-6URL [本文引用: 1]

Wetlands all over the world have been lost or are threatened in spite of various international agreements and national policies. This is caused by: (1) the public nature of many wetlands products and services; (2) user externalities imposed on other stakeholders; and (3) policy intervention failures that are due to a lack of consistency among government policies in different areas (economics, environment, nature protection, physical planning, etc.). All three causes are related to information failures which in turn can be linked to the complexity and nvisibility of spatial relationships among groundwater, surface water and wetland vegetation. Integrated wetland research combining social and natural sciences can help in part to solve the information failure to achieve the required consistency across various government policies. An integrated wetland research framework suggests that a combination of economic valuation, integrated modelling, stakeholder analysis, and multi-criteria evaluation can provide complementary insights into sustainable and welfare-optimising wetland management and policy. Subsequently, each of the various components of such integrated wetland research is reviewed and related to wetland management policy.
DOI:10.1038/4351179aURLPMID:15988514 [本文引用: 1]

How China and the rest of the world affect each other.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.01.022URL [本文引用: 15]

This paper presents the first comprehensive synthesis of economic valuations of wetlands in developing countries. Meta-regression analysis (MRA) is applied to 1432 estimates of the economic value of 379 distinct wetlands from 50 countries. We find that wetlands are a normal good, wetland size has a negative effect on wetland values, and urban wetlands and wetlands that produce internationally traded goods and services are more valuable than other wetlands. Wetland values estimated by stated preferences are lower than those estimated by market price methods. The MRA benefit transfer function has a median transfer error of 17%. Overall, MRA appears to be useful for deriving the economic value of wetlands at policy sites in developing nations.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/3180269URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.07.005URL [本文引用: 4]

78 We screened over 300 case studies on the monetary value of ecosystem services. 78 The average value (market and non-market) of 10 main ecosystem types was calculated. 78 The total value ranged between 490 (Open Ocean) and 350,000 (Coral Reefs) Int$/ha/yr. 78 Most of the monetary value of ecosystem services is not captured in markets.
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文利用青岛市2008年商品住房交易数据,通过"特征价格法"估计商品住房购买者对于空气质量改善的边际意愿支付,发现了清洁空气的价值。估计结果显示,平均而言,空气污染每降低1个指数,消费者愿意为商品住房多支付99.785元/每平方米,相当于同期商品住房平均价格的1.74%。考虑到各类消费者支付意愿的差异,我们引入分位数回归得到了各分位数商品住房价格对应的边际意愿支付水平,并据此估计出商品住房价格和边际意愿支付之间的经验关系。我们还以案例方式,说明上述方法和结论在环境政策经济效益评估和公共环境治理融资规划中的应用。
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文利用青岛市2008年商品住房交易数据,通过"特征价格法"估计商品住房购买者对于空气质量改善的边际意愿支付,发现了清洁空气的价值。估计结果显示,平均而言,空气污染每降低1个指数,消费者愿意为商品住房多支付99.785元/每平方米,相当于同期商品住房平均价格的1.74%。考虑到各类消费者支付意愿的差异,我们引入分位数回归得到了各分位数商品住房价格对应的边际意愿支付水平,并据此估计出商品住房价格和边际意愿支付之间的经验关系。我们还以案例方式,说明上述方法和结论在环境政策经济效益评估和公共环境治理融资规划中的应用。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

青海湖,是我国最大的内陆高原湖泊,是镶嵌在青藏旅游国线上的一颗灿烂明珠。它浩瀚缥缈,迷离神奇,绚丽幽邃,是我国的旅游胜地之一,为海内外旅游者所向往。 青海湖,古藏语称“哧雪甲姆”,又称“赤秀洁莫”,意思是“万帐王母”、“女神湖”和“万户消失的地方”。蒙古语称“库库诺尔”,藏语称“错温波”,意思是“青色的海”,“蓝色的湖”,古称“西海”、“鲜水”、“卑禾羌海”。汉代名“仙海”,北魏起更名为“青海”。自古以来,不少文人墨客
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

青海湖,是我国最大的内陆高原湖泊,是镶嵌在青藏旅游国线上的一颗灿烂明珠。它浩瀚缥缈,迷离神奇,绚丽幽邃,是我国的旅游胜地之一,为海内外旅游者所向往。 青海湖,古藏语称“哧雪甲姆”,又称“赤秀洁莫”,意思是“万帐王母”、“女神湖”和“万户消失的地方”。蒙古语称“库库诺尔”,藏语称“错温波”,意思是“青色的海”,“蓝色的湖”,古称“西海”、“鲜水”、“卑禾羌海”。汉代名“仙海”,北魏起更名为“青海”。自古以来,不少文人墨客
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.06.013URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

以当前国际上流行的衡量环境物品经济价值的重要方法——条件价值评估法 ( CVM) ,针对黑河流域张掖地区生态系统恶化的现状 ,以支付卡的方法设计了 70 0份调查问卷 ,调查了黑河流域居民对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的支付意愿 ( WTP)。结果表明 ,黑河流域 96 .6 %的居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务存在支付意愿。对支付卡数据的非参数估计结果表明 ,黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年在 4 5 .9~ 6 8.3元之间。支付卡数据的参数估计分析表明 ,黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年为5 3.35元。按黑河流域现有家庭数量计算 ,恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济效益每年至少在 2 2 4 6 .2 8× 1 0 4 元以上。由于恢复张掖地区生态系统服务具有巨大的正外部效应 ,因此 ,仅就黑河流域居民家庭数量估计的恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济价值 ,只是对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济价值的最低估价。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.06.013URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

以当前国际上流行的衡量环境物品经济价值的重要方法——条件价值评估法 ( CVM) ,针对黑河流域张掖地区生态系统恶化的现状 ,以支付卡的方法设计了 70 0份调查问卷 ,调查了黑河流域居民对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的支付意愿 ( WTP)。结果表明 ,黑河流域 96 .6 %的居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务存在支付意愿。对支付卡数据的非参数估计结果表明 ,黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年在 4 5 .9~ 6 8.3元之间。支付卡数据的参数估计分析表明 ,黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年为5 3.35元。按黑河流域现有家庭数量计算 ,恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济效益每年至少在 2 2 4 6 .2 8× 1 0 4 元以上。由于恢复张掖地区生态系统服务具有巨大的正外部效应 ,因此 ,仅就黑河流域居民家庭数量估计的恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济价值 ,只是对恢复张掖地区生态系统服务的经济价值的最低估价。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.03.009URL [本文引用: 2]

中国科学院机构知识库(CAS IR GRID)以发展机构知识能力和知识管理能力为目标,快速实现对本机构知识资产的收集、长期保存、合理传播利用,积极建设对知识内容进行捕获、转化、传播、利用和审计的能力,逐步建设包括知识内容分析、关系分析和能力审计在内的知识服务能力,开展综合知识管理。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.03.009URL [本文引用: 2]

中国科学院机构知识库(CAS IR GRID)以发展机构知识能力和知识管理能力为目标,快速实现对本机构知识资产的收集、长期保存、合理传播利用,积极建设对知识内容进行捕获、转化、传播、利用和审计的能力,逐步建设包括知识内容分析、关系分析和能力审计在内的知识服务能力,开展综合知识管理。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.09.018URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

条件价值评估法是国际上衡量环境物品非利用经济价值的主要方法之一,其调查的问卷格式主要有开放式和封闭式两种类型。以黑河流域额济纳旗生态系统恢复为研究对象,在投标卡格式调查的基础上,以开放式、封闭式(单边界和双边界两分式)的问卷格式各设计了500份调查问卷,调查分析了黑河流域居民对额济纳旗生态系统服务恢复的支付意愿。分析结果表明,采用不同类型的调查方法得到的结论有较大差异,其中:开放式问卷的调查结果与投标卡式问卷的分析结果相差不大;封闭式问卷格式的调查结果是开放式问卷调查结果的3~4倍;同时,双边界两分式问卷比单边界两分式问卷更能逼近参与者的真实支付意愿。在综合比较多种不同的调查方法的基础上,认为以双边界两分式的评估结果作为额济纳旗生态系统服务恢复的总经济价值比较合适。因此,仅就黑河流域居民来说,用20a的时间将额济纳旗的生态系统恢复到20世纪80年代初的水平,其总经济价值的现值为3.674×108元。最后,讨论了条件价值评估的各种方法,并指出了今后研究中需加强的方面。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.09.018URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

条件价值评估法是国际上衡量环境物品非利用经济价值的主要方法之一,其调查的问卷格式主要有开放式和封闭式两种类型。以黑河流域额济纳旗生态系统恢复为研究对象,在投标卡格式调查的基础上,以开放式、封闭式(单边界和双边界两分式)的问卷格式各设计了500份调查问卷,调查分析了黑河流域居民对额济纳旗生态系统服务恢复的支付意愿。分析结果表明,采用不同类型的调查方法得到的结论有较大差异,其中:开放式问卷的调查结果与投标卡式问卷的分析结果相差不大;封闭式问卷格式的调查结果是开放式问卷调查结果的3~4倍;同时,双边界两分式问卷比单边界两分式问卷更能逼近参与者的真实支付意愿。在综合比较多种不同的调查方法的基础上,认为以双边界两分式的评估结果作为额济纳旗生态系统服务恢复的总经济价值比较合适。因此,仅就黑河流域居民来说,用20a的时间将额济纳旗的生态系统恢复到20世纪80年代初的水平,其总经济价值的现值为3.674×108元。最后,讨论了条件价值评估的各种方法,并指出了今后研究中需加强的方面。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.06.048URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

Costanza等提出的单位面积生态系统服务价值没有考虑生态系统服务的空间异质性,是与生态系统结构和功能有关的生态系统本身的价值,这里称为静态价值。在实际应用于指导以社会、经济、生态综合效益最大为目标的流域水土资源优化配置决策时,不能反映资源的稀缺程度和随社会经济发展水平变化的对生态价值的支付意愿,使得静态生态价值的研究成果难以得到应用。提出了动态生态价值的概念,某一特定区域生态系统服务的动态价值是指其相应的生态服务功能在特定人群一定支付意愿下的现实价值。在Costanza等人提出的单位面积生态价值的基础上,考虑生态类型的覆盖度等特点结合专家咨询法提出了林地、草地单位面积生态价值的修正系数,估算流域生态系统服务的静态生态价值;建立了基于发展阶段系数和资源紧缺度的生态价值动态估算方法。以甘肃河西走廊石羊河流域为例,估算出2000年流域生态系统服务的静态价值为4.17亿美元,相当于当年流域GDP的0.3657倍,且在空间上呈现从上游山区向下游荒漠区递减的规律;动态生态价值为2.35亿美元,下游和上游大,中游较小。动态生态价值的研究为生态价值研究成果进一步在资源合理配置中的应用提供了途径。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.06.048URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

Costanza等提出的单位面积生态系统服务价值没有考虑生态系统服务的空间异质性,是与生态系统结构和功能有关的生态系统本身的价值,这里称为静态价值。在实际应用于指导以社会、经济、生态综合效益最大为目标的流域水土资源优化配置决策时,不能反映资源的稀缺程度和随社会经济发展水平变化的对生态价值的支付意愿,使得静态生态价值的研究成果难以得到应用。提出了动态生态价值的概念,某一特定区域生态系统服务的动态价值是指其相应的生态服务功能在特定人群一定支付意愿下的现实价值。在Costanza等人提出的单位面积生态价值的基础上,考虑生态类型的覆盖度等特点结合专家咨询法提出了林地、草地单位面积生态价值的修正系数,估算流域生态系统服务的静态生态价值;建立了基于发展阶段系数和资源紧缺度的生态价值动态估算方法。以甘肃河西走廊石羊河流域为例,估算出2000年流域生态系统服务的静态价值为4.17亿美元,相当于当年流域GDP的0.3657倍,且在空间上呈现从上游山区向下游荒漠区递减的规律;动态生态价值为2.35亿美元,下游和上游大,中游较小。动态生态价值的研究为生态价值研究成果进一步在资源合理配置中的应用提供了途径。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.02.017URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

青海湖是我国最大的内陆高原咸水湖,是维系青藏高原东北部生态安全的重要水体。本文基于青海湖流域1977年MSS影像、1987年TM影像和2000年ETM影像,在地理信息系统(GIS)和遥感技术的支持下,采用景观格局分析方法,应用Costanza生态系统服务价值算法,揭示了青海湖流域景观生态服务价值的动态变化。结果表明,青海湖流域生态系统服务价值总体呈下降趋势,由1977年的423×10<sup>8</sup>元降低到2000年的364×10<sup>8</sup>元,年均损失2.57×10<sup>8</sup>元;从生态系统服务功能价值来讲,废物处理和水源涵养价值贡献率超过了58%,单项服务功能价值均呈下降趋势,其中气候调节功能缺失最明显减少达32%;就生态系统服务价值构型而言,草地、湿地和水域的价值贡献率超过了97%,成为构成青海湖生态系统服务价值的主体,湿地面积的大幅度减少可能是青海湖流域生态系统服务功能变化的主要原因。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.02.017URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

青海湖是我国最大的内陆高原咸水湖,是维系青藏高原东北部生态安全的重要水体。本文基于青海湖流域1977年MSS影像、1987年TM影像和2000年ETM影像,在地理信息系统(GIS)和遥感技术的支持下,采用景观格局分析方法,应用Costanza生态系统服务价值算法,揭示了青海湖流域景观生态服务价值的动态变化。结果表明,青海湖流域生态系统服务价值总体呈下降趋势,由1977年的423×10<sup>8</sup>元降低到2000年的364×10<sup>8</sup>元,年均损失2.57×10<sup>8</sup>元;从生态系统服务功能价值来讲,废物处理和水源涵养价值贡献率超过了58%,单项服务功能价值均呈下降趋势,其中气候调节功能缺失最明显减少达32%;就生态系统服务价值构型而言,草地、湿地和水域的价值贡献率超过了97%,成为构成青海湖生态系统服务价值的主体,湿地面积的大幅度减少可能是青海湖流域生态系统服务功能变化的主要原因。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<FONT face=Verdana>以石羊河流域下游民勤为主要研究范围,对民勤县1994-2005年12a间生态系统服务的价值进行了估算和对比分析. 结果表明,1994年区域生态系统服务的总价值为9.976×10<SUP>8</SUP>元,2005年区域生态系统服务的总价值为8.475×10<SUP>8</SUP>元, 12a来区域内的生态系统服务价值下降了近1.501×10<SUP>8</SUP>元. 由于缺乏对盐碱地、建筑用地等服务价值的相关研究信息, 该结果仅是对民勤生态系统服务价值的保守估算. 总的来说,研究区域生态系统服务价值呈现快速下降趋势. </FONT>
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

<FONT face=Verdana>以石羊河流域下游民勤为主要研究范围,对民勤县1994-2005年12a间生态系统服务的价值进行了估算和对比分析. 结果表明,1994年区域生态系统服务的总价值为9.976×10<SUP>8</SUP>元,2005年区域生态系统服务的总价值为8.475×10<SUP>8</SUP>元, 12a来区域内的生态系统服务价值下降了近1.501×10<SUP>8</SUP>元. 由于缺乏对盐碱地、建筑用地等服务价值的相关研究信息, 该结果仅是对民勤生态系统服务价值的保守估算. 总的来说,研究区域生态系统服务价值呈现快速下降趋势. </FONT>
URL [本文引用: 2]

张掖黑河湿地国家级自然保护区地处内陆干旱区,是西北典型的内陆河流湿地生态系统,具有多种重要的生态服务功能,其中湿地提供水源与调洪蓄水功能尤为显著。文中运用市场价值法和影子工程法,对黑河湿地自然保护区调洪蓄水和提供水源生态功能的价值进行估算。结果表明:研究区湿地调洪蓄水价值为10.86亿元,提供水源价值为3.82亿元。直观的货币价值使人们认识到该保护区的重要性,也为该地区水资源的分配、合理定价及湿地的保护与合理利用提供了科学依据和理论支持。
URL [本文引用: 2]

张掖黑河湿地国家级自然保护区地处内陆干旱区,是西北典型的内陆河流湿地生态系统,具有多种重要的生态服务功能,其中湿地提供水源与调洪蓄水功能尤为显著。文中运用市场价值法和影子工程法,对黑河湿地自然保护区调洪蓄水和提供水源生态功能的价值进行估算。结果表明:研究区湿地调洪蓄水价值为10.86亿元,提供水源价值为3.82亿元。直观的货币价值使人们认识到该保护区的重要性,也为该地区水资源的分配、合理定价及湿地的保护与合理利用提供了科学依据和理论支持。
DOI:10.18402/resci.2016.06.07URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

作为新疆南疆的核心区域,塔里木河流域居民的生态环境保护意识与参与意愿关系到当地环境演变态势。本文调查流域12个典型样本区,运用条件价值法、环境外部性与准公共物品理论分析1962户居民生态认知及支付行为。研究表明:①流域样本区60.30%的居民认为生态环境有所改善,67.30%的居民认为防护林的生态价值主要体现在保持土壤、涵养水源、调节气候与增加生物多样性,对生态系统服务功能的认知程度影响居民的最大支付意愿;②家庭禀赋、对环境价值的认知、对环境变化的心理感知的差异导致居民支付意愿影响因素存在异质性。下游居民有支付意愿的比重平均比上游高29.99%;且收入水平不影响居民对生态价值的理性、客观认知;③样本区居民参与环境保护呈现“零意愿”的比重平均为11.90%,其中“搭便车”心理与“对政府环境治理缺乏信任”的占比达到61.90%;流域下游居民作为环境改善的最直接受益者,对生态环境保护呈现“零意愿”的仅为5.30%;④考虑居民的异质性,并结合当地的经济社会条件、环境演变趋势、资源配置方式,是提高CVM理论评估环境价值有效性和可靠性的重要保障。
DOI:10.18402/resci.2016.06.07URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

作为新疆南疆的核心区域,塔里木河流域居民的生态环境保护意识与参与意愿关系到当地环境演变态势。本文调查流域12个典型样本区,运用条件价值法、环境外部性与准公共物品理论分析1962户居民生态认知及支付行为。研究表明:①流域样本区60.30%的居民认为生态环境有所改善,67.30%的居民认为防护林的生态价值主要体现在保持土壤、涵养水源、调节气候与增加生物多样性,对生态系统服务功能的认知程度影响居民的最大支付意愿;②家庭禀赋、对环境价值的认知、对环境变化的心理感知的差异导致居民支付意愿影响因素存在异质性。下游居民有支付意愿的比重平均比上游高29.99%;且收入水平不影响居民对生态价值的理性、客观认知;③样本区居民参与环境保护呈现“零意愿”的比重平均为11.90%,其中“搭便车”心理与“对政府环境治理缺乏信任”的占比达到61.90%;流域下游居民作为环境改善的最直接受益者,对生态环境保护呈现“零意愿”的仅为5.30%;④考虑居民的异质性,并结合当地的经济社会条件、环境演变趋势、资源配置方式,是提高CVM理论评估环境价值有效性和可靠性的重要保障。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2009.06.001URL [本文引用: 1]

生态补偿项目的成本是确定生态补偿标准的基础。在生态补偿项目评估中,全面、准确地计算损失者的直接成本、机会成本和发展成本比生态服务价值评估远为重要。生态补偿没有统一标准,最终结果取决于生态补偿项目中受损者和得益者双方的谈判能力。因此,动员各利益相关者参与能更准确地制定生态补偿标准,保护那些实实在在提供生态服务或遭受外部性损失的基层农民的利益;同时还可以充分利用地方性技术和制度知识,提高项目效益,监督项目管理者,减少寻租行为。生态补偿机制除政府和市场补偿外,还应包括社区内部补偿。在政府补偿中,中央和地方政府的分工是不同的。财政分权理论表明,由地方政府负责实施生态补偿是有效率的。因为地方政府更接近社会,更了解当地居民的偏好。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2009.06.001URL [本文引用: 1]

生态补偿项目的成本是确定生态补偿标准的基础。在生态补偿项目评估中,全面、准确地计算损失者的直接成本、机会成本和发展成本比生态服务价值评估远为重要。生态补偿没有统一标准,最终结果取决于生态补偿项目中受损者和得益者双方的谈判能力。因此,动员各利益相关者参与能更准确地制定生态补偿标准,保护那些实实在在提供生态服务或遭受外部性损失的基层农民的利益;同时还可以充分利用地方性技术和制度知识,提高项目效益,监督项目管理者,减少寻租行为。生态补偿机制除政府和市场补偿外,还应包括社区内部补偿。在政府补偿中,中央和地方政府的分工是不同的。财政分权理论表明,由地方政府负责实施生态补偿是有效率的。因为地方政府更接近社会,更了解当地居民的偏好。
[本文引用: 5]
DOI:10.2307/2074578URL [本文引用: 2]

When the first edition of The Handbook of Research Synthesis was published in 1994, it quickly became the definitive reference for researchers conducting meta-analyses of existing research in both the social and biological sciences. In this fully revised second edition, editors Harris Cooper, Larry Hedges, and Jeff Valentine present updated versions of the Handbook classic chapters, as well as entirely new sections reporting on the most recent, cutting-edge developments in the field. Research synthesis is the practice of systematically distilling and integrating data from a variety of sources in order to draw more reliable conclusions about a given question or topic. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis draws upon years of groundbreaking advances that have transformed research synthesis from a narrative craft into an important scientific process in its own right. Cooper, Hedges, and Valentine have assembled leading authorities in the field to guide the reader through every stage of the research synthesis process roblem formulation, literature search and evaluation, statistical integration, and report preparation. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis incorporates state-of-the-art techniques from all quantitative synthesis traditions. Distilling a vast technical literature and many informal sources, the Handbook provides a portfolio of the most effective solutions to the problems of quantitative data integration. Among the statistical issues addressed by the authors are the synthesis of non-independent data sets, fixed and random effects methods, the performance of sensitivity analyses and model assessments, and the problem of missing data. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis also provides a rich treatment of the non-statistical aspects of research synthesis. Topics include searching the literature, and developing schemes for gathering information from study reports. Those engaged in research synthesis will also find useful advice on how tables, graphs, and narration can be used to provide the most meaningful communication of the results of research synthesis. In addition, the editors address the potentials and limitations of research synthesis, and its future directions. The past decade has been a period of enormous growth in the field of research synthesis. The second edition Handbook thoroughly revises original chapters to assure that the volume remains the most authoritative source of information for researchers undertaking meta-analysis today. In response to the increasing use of research synthesis in the formation of public policy, the second edition includes a new chapter on both the strengths and limitations of research synthesis in policy debates and decisions. Another new chapter looks at computing effect sizes and standard errors from clustered data, such as schools or clinics. Authors also discuss updated techniques for locating hard-to-find ugitive literature, ways of systematically assessing the quality of a study, and progress in statistical methods for detecting and estimating the effects of publication bias. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis is an illuminating compilation of practical instruction, theory, and problem solving. This unique volume offers the reader comprehensive instruction in the skills necessary to conduct powerful research syntheses meeting the highest standards of objectivity. The significant developments included in the second edition will ensure that the Handbook remains the premier text on research synthesis for years to come.
DOI:10.1001/jama.2015.3656URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s10640-008-9253-5URL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1111/joes.12008URL [本文引用: 1]

Meta-regression analysis (MRA) can provide objective and comprehensive summaries of economics research. Their use has grown rapidly over the last few decades. To improve transparency and to raise the quality of MRA, the meta-analysis of economics research-network (MAER-Net) has created the below reporting guidelines. Future meta-analyses in economics will be expected to follow these guidelines or give valid reasons why a meta-analysis must deviate from them.
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 2]

Meta回归分析是一种以回归模型为基础的数量型文献综述方法,它能够科学地探究影响研究结果不一致性的因素,以及这些因素对研究结果不一致性的影响程度。Meta回归分析的应用主要从效应量选择、自变量选择和估计方法三个方面入手。Meta回归分析的价值主要在于,开创了经济学领域数量型文献综述方法的先河,分析了经济学领域存在的实证结果不一致及其原因问题,为经济学领域未来的实证研究设计提供了标准,为经济问题的研究进一步拓展了新的空间。
URL [本文引用: 2]

Meta回归分析是一种以回归模型为基础的数量型文献综述方法,它能够科学地探究影响研究结果不一致性的因素,以及这些因素对研究结果不一致性的影响程度。Meta回归分析的应用主要从效应量选择、自变量选择和估计方法三个方面入手。Meta回归分析的价值主要在于,开创了经济学领域数量型文献综述方法的先河,分析了经济学领域存在的实证结果不一致及其原因问题,为经济学领域未来的实证研究设计提供了标准,为经济问题的研究进一步拓展了新的空间。
DOI:10.1136/bmj.g7647URL [本文引用: 1]

Protocols of systematic reviews and meta-analyses allow for planning and documentation of review methods, act as a guard against arbitrary decision making during review conduct, enable readers to assess for the presence of selective reporting against completed reviews, and, when made publicly available, reduce duplication of efforts and potentially prompt collaboration. Evidence documenting the existence of selective reporting and excessive duplication of reviews on the same or similar topics is accumulating and many calls have been made in support of the documentation and public availability of review protocols. Several efforts have emerged in recent years to rectify these problems, including development of an international register for prospective reviews (PROSPERO) and launch of the first open access journal dedicated to the exclusive publication of systematic review products, including protocols (BioMed Central Systematic Reviews ). Furthering these efforts and building on the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) guidelines, an international group of experts has created a guideline to improve the transparency, accuracy, completeness, and frequency of documented systematic review and meta-analysis protocols RISMA-P (for protocols) 2015. The PRISMA-P checklist contains 17 items considered to be essential and minimum components of a systematic review or meta-analysis protocol. This PRISMA-P 2015 Explanation and Elaboration paper provides readers with a full understanding of and evidence about the necessity of each item as well as a model example from an existing published protocol. This paper should be read together with the PRISMA-P 2015 statement. Systematic review authors and assessors are strongly encouraged to make use of PRISMA-P when drafting and appraising review protocols.
DOI:10.1038/nature25753 [本文引用: 1]

1. The number of published meta-analyses in plant ecology has increased greatly over the last two decades. Meta-analysis has made a significant contribution to the field, allowing review of evidence for various ecological hypotheses and theories, estimation of effects of major environmental drivers (climate change, habitat fragmentation, invasive species, air pollution), assessment of... [Show full abstract]
DOI:10.1016/j.envsci.2015.10.001URL [本文引用: 3]

Highlights 61 We found a dissimilar spatial distribution of the economic valuation studies in Spain. 61 Coastal systems and forests are the most studied ecosystem types. 61 Cultural services are the most studied but those with lower economic values. 61 We provide evidence about the effect of methods and services on economic values. Abstract We analyzed the state of the art in research on the economic valuation of ecosystem services in Spain. A review of 150 publications was conducted and included 649 economic value estimates. The results showed an increase in the number of scientific studies on the economic valuation of ecosystem services and a dissimilar distribution across regions. Cultural ecosystem services received the most attention, and coastal systems and forested areas were the most studied ecosystem types. We found differences in the economic value estimates among categories of services and among economic valuation methods, with provisioning services and market-based methods as those that elicited the highest economic values, respectively. Our results provide an overview of past and current economic valuation studies in Spain. In addition the results depict patterns that help in understanding the effects of different factors on economic value estimates and in providing insights for future research on ecosystem services assessment in Spain. We conclude that although economic assessments remain important in scientific and policy forums, we should also recognize additional approaches that are able to incorporate the plurality of values attached to ecosystem services.
DOI:10.1007/s10640-013-9665-8URL [本文引用: 1]

A meta-analysis of studies valuing urban greenspace in the UK is undertaken to yield spatially sensitive marginal value functions. A geographical information system (GIS) is used to apply these functions to spatial data detailing the location of such greenspace resources in five British cities. Changes in monetary values are computed for the six future scenarios used in the UK National Ecosystem Assessment for the period 2010 2060. Different degrees of substitutability between urban greenspaces are considered. These findings are then extrapolated to all major British cities to obtain per household and aggregate valuation estimates for each scenario both with and without distributional weights. While subject to a number of shortcomings in both data availability and methodology, this represents the first systematic and comprehensive attempt to value marginal changes in urban greenspace while accounting for spatial heterogeneity.
DOI:10.1016/j.reseneeco.2007.01.002URL [本文引用: 2]

The literature estimating the economic value for water quality changes has grown considerably over the last 30 years, resulting in an expanded pool of information potentially available to support national and regional policy analysis. Using 131 willingness to pay estimates from 18 studies that use a similar definition of water quality, we performed a meta-regression analysis and found mixed results. We find that WTP varies in systematic and expected ways with respect to factors such as the size of the water quality changes, average household income, and use/nonuse characteristics of respondents. As a whole, we conclude that our meta-regression results provide a reasonable basis for estimating expected WTP values for defined changes in water quality. However, despite a large number of existing economic valuation studies, relatively few could be meaningfully combined through meta-analysis due to heterogeneity in the commodities being valued in the original studies. Based on these findings, we provide recommendations for future research, including suggestions regarding more standardized approaches for defining water quality and reporting information in valuation studies.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

国外对资源价值评估方法的研究正向系统化方向发展,但由于受到时间、成本等约束条件的影响,不可能对资源价值逐一进行现场调查和评价,因此效益转移方法(Benefit Transfer Method)应运而生,成为目前国外自然资源价值评价领域关注的热点。通过建立效益转移数据库,应用目前国外最流行的基于Meta分析的函数效益转移方法,对我国森林公园、风景名胜区、湿地、湖泊等在内的自然资源的价值进行评价。通过Meta函数效益转移的样本外有效性检验,平均效益转移误差为26.64%,转移值与“真实值”之间在统计上没有显著的差异。统计检验的结果表明,效益转移方法是一种有效的资源价值评价方法,在一定程度上可以作为我国自然资源开发与项目决策的有效参考,是对我国资源环境价值评价方法的有效补充和扩展。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

国外对资源价值评估方法的研究正向系统化方向发展,但由于受到时间、成本等约束条件的影响,不可能对资源价值逐一进行现场调查和评价,因此效益转移方法(Benefit Transfer Method)应运而生,成为目前国外自然资源价值评价领域关注的热点。通过建立效益转移数据库,应用目前国外最流行的基于Meta分析的函数效益转移方法,对我国森林公园、风景名胜区、湿地、湖泊等在内的自然资源的价值进行评价。通过Meta函数效益转移的样本外有效性检验,平均效益转移误差为26.64%,转移值与“真实值”之间在统计上没有显著的差异。统计检验的结果表明,效益转移方法是一种有效的资源价值评价方法,在一定程度上可以作为我国自然资源开发与项目决策的有效参考,是对我国资源环境价值评价方法的有效补充和扩展。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2013.03.015URL [本文引用: 3]

滇池是昆明市工业用水和生活用水的主要来源之一。应用国外较流行的Meta分析方法,通过搜集国内关于湖泊、河流的实证研究结果,构建效益转移数据库,建立Meta回归模型,对滇池水质改良的生态服务价值进行评价。结果表明,昆明市民每人每年对滇池水质改良的支付意愿为89.27元,滇池对昆明市民每年的生态服务价值为6.48亿元。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2013.03.015URL [本文引用: 3]

滇池是昆明市工业用水和生活用水的主要来源之一。应用国外较流行的Meta分析方法,通过搜集国内关于湖泊、河流的实证研究结果,构建效益转移数据库,建立Meta回归模型,对滇池水质改良的生态服务价值进行评价。结果表明,昆明市民每人每年对滇池水质改良的支付意愿为89.27元,滇池对昆明市民每年的生态服务价值为6.48亿元。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-575X.2013.04.005URL [本文引用: 1]

鉴于目前我国在构建价值转移模型中存在的限制因素,本文采用基于Meta分析的价值转移方法并尝试利用国外游憩活动价值评价的实证研究结果,构建基于Meta分析的国际间价值函数转移模型,估算了我国10种游憩活动的日平均消费者剩余。通过将价值转移模型估算的游憩活动价值"转移值"与国内97个游憩价值评价的"真实值"做比较,对价值转移模型的有效性和可靠性进行统计检验,平均转移误差为18.74%。最后,总结了提高我国Meta回归价值转移模型的具体、可操作性方法及途径。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-575X.2013.04.005URL [本文引用: 1]

鉴于目前我国在构建价值转移模型中存在的限制因素,本文采用基于Meta分析的价值转移方法并尝试利用国外游憩活动价值评价的实证研究结果,构建基于Meta分析的国际间价值函数转移模型,估算了我国10种游憩活动的日平均消费者剩余。通过将价值转移模型估算的游憩活动价值"转移值"与国内97个游憩价值评价的"真实值"做比较,对价值转移模型的有效性和可靠性进行统计检验,平均转移误差为18.74%。最后,总结了提高我国Meta回归价值转移模型的具体、可操作性方法及途径。
DOI:10.5846/stxb201403250552URLMagsci [本文引用: 7]

Meta分析价值转移方法作为资源价值评估的一种有效方法,在国外已经有大量的实证研究出现,但是在国内相应的实证研究非常稀少,有关该方法在湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估的应用研究还尚未见报道。通过收集有关中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估的实证研究文献的价值评估结果,建立价值转移数据库,应用Meta分析和多元回归分析方法构建中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务的Meta分析价值转移模型,并对该模型用于样本外价值转移的有效性做出评估,探讨Meta分析价值转移方法在中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估领域的可应用性及发展前景。研究结果表明:(1) 在样本文献中,通常洪水调蓄和水源涵养服务是湖沼湿地提供的经济价值最高的生态系统服务,而水质净化服务的经济价值最低;(2) 湖沼湿地面积、生态系统服务受益人口数量、不同生态系统服务之间的价值差异以及不同价值评估方法的使用会影响湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值的变化;(3) Meta分析价值转移模型用于样本外价值转移的有效性检验结果显示,样本外价值转移的转移误差范围在0.09%-234.61%之间,平均转移误差为19.99%,在自然资源价值转移的可接受误差范围内,因此Meta分析价值转移方法是评估湿地生态系统服务价值的一种可行且快速的方法。
DOI:10.5846/stxb201403250552URLMagsci [本文引用: 7]

Meta分析价值转移方法作为资源价值评估的一种有效方法,在国外已经有大量的实证研究出现,但是在国内相应的实证研究非常稀少,有关该方法在湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估的应用研究还尚未见报道。通过收集有关中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估的实证研究文献的价值评估结果,建立价值转移数据库,应用Meta分析和多元回归分析方法构建中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务的Meta分析价值转移模型,并对该模型用于样本外价值转移的有效性做出评估,探讨Meta分析价值转移方法在中国湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值评估领域的可应用性及发展前景。研究结果表明:(1) 在样本文献中,通常洪水调蓄和水源涵养服务是湖沼湿地提供的经济价值最高的生态系统服务,而水质净化服务的经济价值最低;(2) 湖沼湿地面积、生态系统服务受益人口数量、不同生态系统服务之间的价值差异以及不同价值评估方法的使用会影响湖沼湿地生态系统服务价值的变化;(3) Meta分析价值转移模型用于样本外价值转移的有效性检验结果显示,样本外价值转移的转移误差范围在0.09%-234.61%之间,平均转移误差为19.99%,在自然资源价值转移的可接受误差范围内,因此Meta分析价值转移方法是评估湿地生态系统服务价值的一种可行且快速的方法。
DOI:10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2016.01.023URL [本文引用: 3]

国内外已经在生物多样性价值评估方面开展了大量实证研究,但已有评估结果存在较大的差异性,增加了评估结果应用于生物多样性保护政策制定和实施的难度。采用Meta分析方法对国内外生物多样性价值研究结果进行再分析,总结已有研究的特征和趋势,分析和检验研究结果的影响因素。结果显示,评估价值类型、评估方法、评估时间、评估对象所在地的经济发展水平以及评估结果的发表类型等,都会显著影响生物多样性的人均价值量评估结果,而生物多样性的研究尺度以及文献来源对评估结果并无显著影响。建议在利用已有研究成果来评估生物多样性价值时,需要关注Meta分析所给出的评估结果差异性的来源;鉴于国内国际研究并无显著差异,在尚未开展独立价值评估的领域,可以适当借鉴国外已有研究成果。
DOI:10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2016.01.023URL [本文引用: 3]

国内外已经在生物多样性价值评估方面开展了大量实证研究,但已有评估结果存在较大的差异性,增加了评估结果应用于生物多样性保护政策制定和实施的难度。采用Meta分析方法对国内外生物多样性价值研究结果进行再分析,总结已有研究的特征和趋势,分析和检验研究结果的影响因素。结果显示,评估价值类型、评估方法、评估时间、评估对象所在地的经济发展水平以及评估结果的发表类型等,都会显著影响生物多样性的人均价值量评估结果,而生物多样性的研究尺度以及文献来源对评估结果并无显著影响。建议在利用已有研究成果来评估生物多样性价值时,需要关注Meta分析所给出的评估结果差异性的来源;鉴于国内国际研究并无显著差异,在尚未开展独立价值评估的领域,可以适当借鉴国外已有研究成果。
DOI:10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.026URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

<p align="justify">基于Meta-analysis方法, 分别建立耕地、林地、草地、园地、水域和未利用地 6 个地类的生态系统服务价值回归模型。除考虑年代和评估方法外, 还引入分区和社会经济因素(包括人口密度和人均GDP), 发现这两个变量在解释生态系统服务价值变化时较为重要。使用价值转移研究范式, 将所建模型应用到京津冀地区, 计算各类土地利用类型的生态系统服务价值。研究结果表明: 土地利用类型按照生态系统服务价值高低排序为水域、林地、草地、园地、耕地、未利用地; 京津冀地区不同市区各类土地利用提供的生态系统服务价值不同, 其中耕地、林地、草地、园地和水域的生态系统服务价值中, 北京和天津最高, 承德和张家口最低; 未利用地的生态系统服务价值中, 张家口和承德最高, 北京和天津最低。研究成果丰富了生态系统价值评估的方法和技术, 也可为京津冀地区土地持续管理提供科学依据。</p>
DOI:10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.026URLMagsci [本文引用: 2]

<p align="justify">基于Meta-analysis方法, 分别建立耕地、林地、草地、园地、水域和未利用地 6 个地类的生态系统服务价值回归模型。除考虑年代和评估方法外, 还引入分区和社会经济因素(包括人口密度和人均GDP), 发现这两个变量在解释生态系统服务价值变化时较为重要。使用价值转移研究范式, 将所建模型应用到京津冀地区, 计算各类土地利用类型的生态系统服务价值。研究结果表明: 土地利用类型按照生态系统服务价值高低排序为水域、林地、草地、园地、耕地、未利用地; 京津冀地区不同市区各类土地利用提供的生态系统服务价值不同, 其中耕地、林地、草地、园地和水域的生态系统服务价值中, 北京和天津最高, 承德和张家口最低; 未利用地的生态系统服务价值中, 张家口和承德最高, 北京和天津最低。研究成果丰富了生态系统价值评估的方法和技术, 也可为京津冀地区土地持续管理提供科学依据。</p>
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20160295URL [本文引用: 1]

采矿活动剧烈干扰了区域土地利用,对生态系统健康造成了严重影响。论文在综合国内若干资源型城市生态系统服务价值研究实例的基础上,提炼系列指标参数,运用Meta分析方法建立并验证了专门针对矿业城市耕地、林地、草地、水域的价值转移模型,并以河北省武安市为例估算了1987、2001和2014年的生态系统服务价值。研究结果表明:1)价值转移模型可以有效地评估矿业城市生态系统服务价值;2)武安市生态系统服务总价值呈现先增后减的趋势,2001年之后呈现快速下降状态;3)从地类面积来看,1987—2014年间武安市经济发展对生态用地产生的干扰程度为:耕地草地水域林地,从服务价值角度看,干扰程度为:耕地水域草地林地;4)在生态用地总面积减少的情况下,适当优化生态用地土地利用结构可以提高生态系统服务总价值。
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20160295URL [本文引用: 1]

采矿活动剧烈干扰了区域土地利用,对生态系统健康造成了严重影响。论文在综合国内若干资源型城市生态系统服务价值研究实例的基础上,提炼系列指标参数,运用Meta分析方法建立并验证了专门针对矿业城市耕地、林地、草地、水域的价值转移模型,并以河北省武安市为例估算了1987、2001和2014年的生态系统服务价值。研究结果表明:1)价值转移模型可以有效地评估矿业城市生态系统服务价值;2)武安市生态系统服务总价值呈现先增后减的趋势,2001年之后呈现快速下降状态;3)从地类面积来看,1987—2014年间武安市经济发展对生态用地产生的干扰程度为:耕地草地水域林地,从服务价值角度看,干扰程度为:耕地水域草地林地;4)在生态用地总面积减少的情况下,适当优化生态用地土地利用结构可以提高生态系统服务总价值。
DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.201704.025URL [本文引用: 3]

为了解青岛市各湿地类型生态系统服务价值,本文应用Meta分析构建青岛市湿地生态系统服务价值转移模型,估算了青岛市各湿地类型的价值水平,并对模型的影响因素及有效性进行了探讨.结果表明:构建的青岛市价值转移模型中,污染防治成本法、生态价值法、涵养水源以及侵蚀控制等自变量的回归系数为正,其对青岛市湿地价值为正效应;而影子价格法、碳税法、旅行费用法、沼泽湿地以及湿地面积的回归系数为负,其对青岛市湿地价值表现为负效应;2012年青岛市各湿地类型生态系统服务单位面积价值为近海与海岸湿地(3.29×104元·hm-2)>河流湿地(2.38×104元·hm-2)>人工湿地(2.27×104元·hm-2)>沼泽湿地(1.77×104元·hm-2);与1997年相比,2012年总服务价值减少了8.01×108元;生态系统服务价值评估方法的使用、不同生态系统服务以及湿地面积之间的差异是影响青岛市湿地生态系统服务价值变化的重要方面;人们的重视及保护程度、当地的消费水平以及政府的投入是单位价值不同的主要原因;近海与海岸湿地生态系统服务价值的减少是湿地生态系统服务总价值减少的关键原因;Meta分析价值转移模型的有效性检验结果说明,当人力和财力资源受到制约时或当估值数据缺乏时,其可以作为快速评估湿地生态系统服务价值的一种有效方法.
DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.201704.025URL [本文引用: 3]

为了解青岛市各湿地类型生态系统服务价值,本文应用Meta分析构建青岛市湿地生态系统服务价值转移模型,估算了青岛市各湿地类型的价值水平,并对模型的影响因素及有效性进行了探讨.结果表明:构建的青岛市价值转移模型中,污染防治成本法、生态价值法、涵养水源以及侵蚀控制等自变量的回归系数为正,其对青岛市湿地价值为正效应;而影子价格法、碳税法、旅行费用法、沼泽湿地以及湿地面积的回归系数为负,其对青岛市湿地价值表现为负效应;2012年青岛市各湿地类型生态系统服务单位面积价值为近海与海岸湿地(3.29×104元·hm-2)>河流湿地(2.38×104元·hm-2)>人工湿地(2.27×104元·hm-2)>沼泽湿地(1.77×104元·hm-2);与1997年相比,2012年总服务价值减少了8.01×108元;生态系统服务价值评估方法的使用、不同生态系统服务以及湿地面积之间的差异是影响青岛市湿地生态系统服务价值变化的重要方面;人们的重视及保护程度、当地的消费水平以及政府的投入是单位价值不同的主要原因;近海与海岸湿地生态系统服务价值的减少是湿地生态系统服务总价值减少的关键原因;Meta分析价值转移模型的有效性检验结果说明,当人力和财力资源受到制约时或当估值数据缺乏时,其可以作为快速评估湿地生态系统服务价值的一种有效方法.
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.09.014URL [本文引用: 2]

61Site similarity analyses in ecosystem service value transfer are limited.61A similarity index is proposed and integrated with meta-analytical value transfer.61The technique is tested on a tropical coastal wetland in India.61Using similarity weights produces narrower prediction intervals for transfer value.61Subsetting study sites based on similarity to policy site increases accuracy.
DOI:10.1007/s10640-011-9535-1URL [本文引用: 1]

AbstractThere is growing policy and academic interest in transferring ecosystem service values from existing valuation studies to other ecosystem sites at a large geographic scale. Despite the evident policy demand for this combined transfer and “scaling up” of values, an approach to value transfer that addresses the challenges inherent in assessing ecosystem changes at a national or regional level is not available. This paper proposes a methodology for scaling up ecosystem service values to estimate the welfare effects of ecosystem change at this larger geographical scale. The methodology is illustrated by applying it to value the impact of climate change on European wetlands for the period 2000–2050. The proposed methodology makes use of meta-analysis to produce a value function. The parameters of the value function include spatial variables on wetland size and abundance, GDP per capita, and population. A geographic information system is used to construct a database of wetland sites in the case study region with information on these spatial variables. Site-specific ecosystem service values are subsequently estimated using the meta-analytic value function. The proposed method is shown to enable the adjustment of transferred values to reflect variation in important spatial variables and to account for changes in the stock of ecosystems.
DOI:10.1007/s101130050007URL [本文引用: 4]

There is growing interest in the potential for producing generally applicable models for valuing non-market environmental services which do not rely upon expensive and time-consuming survey work, but rather extrapolate results from previous studies. This paper presents a meta-analysis for the use and non-use values generated by wetlands across North America and Europe. The study assesses the socio-economic values attributable to the hydrological, biogeochemical and ecological functions provided by such complex environmental assets. The clustering of multiple values derived from single studies is examined through the application of multilevel modelling methods allowing for the hierarchical structure of such data.
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.05.021URL [本文引用: 3]

http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0921800906003338
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.06.003URL [本文引用: 2]

78 We estimate the monetary value of mangrove ecosystem services in Southeast Asia. 78 We conduct a meta-analysis of mangrove values to estimate a value function. 78 Values are shown to be highly variable depending on biophysical and socioeconomic factors. 78 GIS data is used to define a spatially explicit baseline scenario for mangrove loss 2000–2050. 78 Estimated foregone annual benefits in 2050 are US$ 2.2 billion (95% prediction interval 1.6–2.8).
DOI:10.1007/s10640-005-3104-4URL [本文引用: 8]
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.11.002URL [本文引用: 2]

Coral reefs are highly productive ecosystems that provide a variety of valuable goods and services, including recreational opportunities. The open-access nature and public good characteristics of coral reefs often result in them being undervalued in decision making related to their use and conservation. In response to this, there now exists a substantial economic valuation literature on coral reefs. For the purposes of conducting a meta-analysis of this literature, we collected 166 coral reef valuation studies, 52 of which provided sufficient information for a statistical meta-analysis, yielding 100 separate value observations in total. Focusing on recreational values, we use US$ per visit as the dependent variable in our meta-analysis. The meta-regression results reveal a number of important factors in explaining variation in coral reef recreational values, notably the area of dive sites and the number of visitors. Different valuation methods are shown to produce widely different values, with the contingent valuation method producing significantly lower value estimates. Using a multi-level modelling approach we also control for authorship effects, which proves to be highly significant in explaining variation in value estimates. We assess the prospects for using this analysis for out-of-sample value transfer, and find average transfer errors of 186%. We conclude that there is a need for further high-quality valuation research on coral reefs.
DOI:10.1080/09640568.2010.495553URL [本文引用: 4]

Lagoons are naturally complex ecosystems whose dynamics are strongly influenced by anthropic factors. Therefore, their value depends not only on their characteristics but also on the nature of the interactions, whether positive or negative, between mankind and nature. Starting from a representative set of 31 original studies exclusively devoted to coastal lagoons valuation, we estimate a meta-analytic function of value transfer. Using a resampling technique, we then determine a transfer value and find a mean transfer error of 87% and a median error equal to 24%, between the predicted value and the original ones. This raises the problem of divergences between individual valuations for natural assets.
DOI:10.1029/2010WR009071URL [本文引用: 5]

Abstract The values of goods and services provided by wetland ecosystems are examined through a meta‐analysis of an expanded database of wetland value estimates and with a focus on human‐made wetlands. This study extends and improves upon previous meta‐analyses of the wetland valuation literature in terms of the number of observations, geographical coverage, wetland class and integrity, and the measurement of the effects of scarcity and anthropogenic pressure. We find that water quality improvement, nonconsumptive recreation, and provision of natural habitat and biodiversity are highly valued services. Substitution effects are observed through the negative correlation between values and abundance of other wetlands. Wetland values are found to increase with anthropogenic pressure. An extended metaregression model with cross effects shows that the valuation of specific services varies with the type of wetland producing them. Humanmade wetlands are highly valued for biodiversity enhancement, water quality improvement, and flood control.
DOI:10.3390/su4030359URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0148524URLPMID:26938447 [本文引用: 3]

Growing demand of resources increases pressure on ecosystem services (ES) and biodiversity. Monetary valuation of ES is frequently seen as a decision-support tool by providing explicit values for unconsidered, non-market goods and services. Here we present global value transfer functions by using a meta-analytic framework for the synthesis of 194 case studies capturing 839 monetary values of ES. For 12 ES the variance of monetary values could be explained with a subset of 93 study- and site-specific variables by utilizing boosted regression trees. This provides the first global quantification of uncertainties and transferability of monetary valuations. Models explain from 18% (water provision) to 44% (food provision) of variance and provide statistically reliable extrapolations for 70% (water provision) to 91% (food provision) of the terrestrial earth surface. Although the application of different valuation methods is a source of uncertainty, we found evidence that assuming homogeneity of ecosystems is a major error in value transfer function models. Food provision is positively correlated with better life domains and variables indicating positive conditions for human well-being. Water provision and recreation service show that weak ownerships affect valuation of other common goods negatively (e.g. non-privately owned forests). Furthermore, we found support for the shifting baseline hypothesis in valuing climate regulation. Ecological conditions and societal vulnerability determine valuation of extreme event prevention. Valuation of habitat services is negatively correlated with indicators characterizing less favorable areas. Our analysis represents a stepping stone to establish a standardized integration of and reporting on uncertainties for reliable and valid benefit transfer as an important component for decision support.
DOI:10.1007/s10640-010-9381-6URL [本文引用: 2]

Biodiversity loss is a problem of global concern affecting ecosystem functioning and services provided to humans. The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment is built on a conceptual framework that links biodiversity with the services ecosystems provide to society and human welfare. Numerous empirical studies have measured ecosystem goods and services in terms of economic values; however, less evidence is available of the indirect effect of biodiversity on these values. Based on this, we first compile market and non-market forest valuation studies and, secondly, explore the potential of an econometric modelling exercise by conducting a worldwide meta-analysis. This exercise aims to highlight the role of biodiversity indicators on valuation. In this way, we can study the underlying transmission mechanisms that explain to what extent biodiversity is related to human welfare. Furthermore, we also propose to evaluate the magnitudes of the respective distributional impacts, including the different ecosystem goods and services under consideration. Our results show that biodiversity indicators may have an underlying effect on forest ecosystem values, which also depend on the type of ecosystem services. Lastly, the results are discussed and analysed with respect to their policy implications concerning biodiversity conservation.
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.03.001URLPMID:5421154 [本文引用: 2]

This study presents the first meta-analysis on the economic value of ecosystem services delivered by lakes. A worldwide data set of 699 observations drawn from 133 studies combines information reported in primary studies with geospatial data. The meta-analysis explores antagonisms and synergies between ecosystem services. This is the first meta-analysis to incorporate simultaneously external geospatial data and ecosystem service interactions. We first show that it is possible to reliably predict the value of ecosystem services provided by lakes based on their physical and geographic characteristics. Second, we demonstrate that interactions between ecosystem services appear to be significant for explaining lake ecosystem service values. Third, we provide an estimation of the average value of ecosystem services provided by lakes: between 106 and 140 USD$2010 per respondent per year for non-hedonic price studies and between 169 and 403 USD$2010 per property per year for hedonic price studies. 61We conduct the first meta-analysis on the value of ecosystem services provided by lakes.61We analyze results of 133 studies, offering a total of 699 values.61We show that antagonisms and synergies across ecosystem services are perceived and valued by people. We conduct the first meta-analysis on the value of ecosystem services provided by lakes. We analyze results of 133 studies, offering a total of 699 values. We show that antagonisms and synergies across ecosystem services are perceived and valued by people.
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.019URLPMID:21763064 [本文引用: 2]

Urban open space provides a number of valuable services to urban populations, including recreational opportunities, aesthetic enjoyment, environmental functions, and may also be associated with existence values. In separate meta-analyses of the contingent valuation (CV) and hedonic pricing (HP) literature we examine which physical, socio-economic, and study characteristics determine the value of open space. The dependent variable in the CV meta-regression is defined as the value of open space per hectare per year in 2003 US$, and in the HP model as the percentage change in house price for a 10 m decrease in distance to open space. Using a multi-level modelling approach we find in both the CV and HP analyses that there is a positive and significant relationship between the value of urban open space and population density, indicating that scarcity and crowdedness matter, and that the value of open space does not vary significantly with income. Further, urban parks are more highly valued than other types of urban open space (forests, agricultural and undeveloped land) and methodological differences in study design have a large influence on estimated values from both CV and HP. We also find important regional differences in preferences for urban open space, which suggests that the potential for transferring estimated values between regions is likely to be limited.
DOI:10.1007/BF00418818URL [本文引用: 2]

This paper reports a meta analysis of how effectively hedonic property models have detected the influence of air pollution on housing prices. Probit estimates are reported describing how data, model specification, and local property market conditions in cities represented in thirty-seven studies influence the ability of hedonic models to uncover negative, statistically significant relationships between housing prices and air pollution measures.
DOI:10.1086/261981URL [本文引用: 2]

This paper reports the results of a statistical summary of estimates of the marginal willingness to pay (MWTP) for reducing particulate matter from hedonic property value models developed between 1967 and 1988. Results using both ordinary least squares and minimum absolute deviation estimators suggest that market conditions and the procedures used to implement the hedonic models were important to the resulting MWTP estimates. The interquartile range for these estimated marginal values (measured as a change in asset prices) lies between zero and $98.52 (in 1982-84 dollars) for a one-unit reduction in total suspended particulates (in micrograms per cubic meter). The mean MWTP is nearly five times the median ($109.90 vs. $22.40), suggesting that outliers are important influences to any summary statistics for these estimates.
DOI:10.2307/3146869URL [本文引用: 1]

The paper presents a variety of meta analysis models of woodland recreation benefit estimates, contrasting conventionally estimated models with those provided by novel, multi-level modeling (MLM) techniques (Goldstein 1995). Our conventional models suggest that studies carried out by certain authors are associated with unusually large residuals within our meta-analysis. However, the MLM approach explicitly incorporates the hierarchical nature of meta-analysis data, with estimates nested within study sites and authors. These residuals are not a significant determinant upon values, suggesting that, at least in this aspect, estimates may be more robust than indicated by less sophisticated models.
DOI:10.1029/2000WR900006URL [本文引用: 1]

The application of metaregression analysis models for the purpose of benefit transfer was investigated using in-sample convergent validity tests on average value transfers. The database on which the metaregression analysis models were developed is composed of empirical outdoor recreation use value studies conducted from 1967 through 1998. Results of the convergent validity tests suggest that th...
DOI:10.1017/S1074070800020563URL [本文引用: 1]

Statistical summarizations of literature review databases using meta-regression analysis provide insight into the differences in past estimates of economic variables such as benefits and price elasticities. The panel nature of the data is an issue that has not received adequate attention in past meta-analyses. This paper conceptually and empirically explores the complexity of stratifying data into panels that model the potential correlation and heterogeneity of past outdoor recreation benefit research. Although our tests of three stratifications of the data did not discern panel effects, the inherent complexity of the data maintains a strong presumption of heterogeneous strata.
DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00193-8URL [本文引用: 2]

The economic values of outdoor recreation are estimated using a benefit transfer approach in which one applies existing consumer surplus measures to value the resources at a new site. In this article, a benefit transfer study was conducted based on meta-analysis of existing research in outdoor recreation use values of the United States from 1967 to 1998. The meta-analysis method was used to estimate a meta-regression model, resulting in a benefit transfer function that could be applied to estimate a wide range of recreation activity values in other countries. The estimated meta-model was tested using original out-of-sample studies from countries around the world for international benefit transfer purposes. The tests reveal that there is mixed evidence in using meta-analysis of existing studies in outdoor recreation in the United States to value the recreational resources in other countries that are used by tourists. In the best case, 18 correlation coefficients between meta-predicted and out-of-sample values were positive and significant at the 5% level or greater, but nine of the 18 t-tests indicated a significant difference between the two sets of values at the 10% level. However, the absolute average percentage error of the meta-predictions was 28%, which may be acceptable for many benefit transfer applications.
DOI:10.1086/mre.21.1.42629492URL [本文引用: 1]

The use of estimated willingness to pay (WTP) to evaluate welfare associated with changes in the quality of recreational fishing presumes that WTP reflects variations in resource and policy attributes, and is not inappropriately influenced by attributes of applied non-market study methodology. This paper describes a meta-analysis conducted to identify systematic patterns in marginal WTP per fish among recreational anglers. Results establish the presence of systematic WTP variation associated with resource, context, and angler attributes, yet also indicate that WTP is subject to systematic variation associated with study methodology. While results are promising with regard to the ability of non-market research to provide insight regarding WTP for recreational fishery resources, they also suggest that researchers should consider the potential for methodological effects when conducting applied welfare analysis.
DOI:10.2307/1243391URL [本文引用: 2]

Evaluates the eight contingent-valuation studies of the benefits of groundwater protection in the United States. Statistical investigation using meta analysis; Inconsistency in the definition of groundwater contamination.
DOI:10.1016/0921-8009(96)00029-8URL [本文引用: 1]

The economic value of rare, threatened and endangered species to citizens of the USA has been measured using the contingent valuation method for 18 different species. Annual willingness to pay (WTP) range from a low of $6 per household for fish such as the striped shiner to a high of $95 per household for the northern spotted owl and its old growth habitat. A regression analysis of WTP values shows that over half of the variation in WTP is explained by the change in the size of the population, whether the payment is one-time or annual, whether the respondent is a visitor or non-user and whether the species is a marine mammal or bird. This illustrates that the contingent valuation method can provide meaningful estimates of the anthropocentric benefits of preserving rare and endangered species. Thus, economic techniques are available to perform broad-based benefit-cost analyses of species preservation. However, the Safe Minimum Standard approach is offered as an alternative for endangered species preservation decisions. The values reported in this paper are most useful to assess whether the costs are likely to be disproportionate to the benefits. To date, for even the most expensive endangered species preservation effort (e.g., the northern spotted owl) the costs per household fall well below the benefits per household found in the literature.
DOI:10.1016/j.envsci.2004.05.006URL [本文引用: 1]

Carbon terrestrial sinks are seen as a low-cost alternative to fuel switching and reduced fossil fuel use for lowering atmospheric CO. As a result of agreements reached at Bonn and Marrakech, carbon offsets have taken on much greater importance in meeting Kyoto targets for the first commitment period. In this study, meta-regression analysis is used to examine 981 estimates from 55 studies of the costs of creating carbon offsets using forestry. Baseline estimates of costs of sequestering carbon through forest conservation are US$ 46.62–US$ 260.29/t02C ($12.71–$70.99/t02CO). Tree planting and agroforestry activities increase costs by more than 200%. When post-harvest storage of carbon in wood products, or substitution of biomas for fossil fuels in energy production, are taken into account, costs are lowest – some $12.53–$68.44/t02C ($3.42–$18.67/t CO). Average costs are greater, between $116.76 and $1406.60/t02C ($31.84–$383.62/t CO), when appropriate account is taken of the opportunity costs of land. Peer review of the studies increases costs by a factor or 10 or more, depending on the model. The use of marginal cost estimates instead of average cost results in much higher costs for carbon sequestration, in the range of thousands of dollars per t02C, although few studies used this method of cost assessment.
DOI:10.1016/j.jfe.2008.03.006URL [本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a meta-analysis of forest recreation in Europe based on studies that have applied the travel cost method covering 26 studies in nine countries since 1979. We conduct the meta-regression with an increasing number of variables where level I includes only data available from the studies, level II aggregate socio-economic variables and level III site-specific characteristics such as diversity, fraction of open land and location. Data shows that consumer surplus varies between 0.66 per trip to 112 with a median of 4.52 per trip. Results of the model with the best overall summary indicate that the application of the individual travel cost method, inclusion of opportunity cost of time and average distance travelled lead to increasing benefits whereas the year of the study and estimations from theses and dissertations reduce welfare estimates. Including exogenous variables shows that site attributes, GDP per capita and population density play a significant role.
DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00276-7URL [本文引用: 1]

The number of studies quantify the value of wetlands and the services provided by these ecosystems is rapidly expanding. The time is ripe for an assessment of what has been learned from this literature. Using results from 39 studies, we evaluate the relative value of different wetland services, the sources of bias in wetland valuation and the returns to scale exhibited in wetland values. While some general trends are beginning to emerge, the prediction of a wetland's value based on previous studies remains highly uncertain and the need for site-specific valuation efforts remains large.
DOI:10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2013.02.017URL [本文引用: 2]

61We use remote sensing to assess distribution and areal extent of coastal wetlands.61All coastal wetlands in the area are included in the ecosystem services valuation.61Information to complete valuation for some ecosystems or services is needed.61Technical elements to simplify decision making on ecosystem services is given.
DOI:10.1006/jeem.1996.0045URL [本文引用: 1]

This paper considers the scope test proposed to judge the internal consistency of contingent valuation estimates. The test is shown to be quite sensitive to the maintained hypotheses required to derive fairly precise expectations for the properties of WTP functions, and, therefore, a different approach may be needed in gauging the reliability of CV. This paper describes an approach that relies on a weight-of-the-evidence criterion and uses meta-analysis to develop a systematic appraisal of what the economic values of changes in amenity resources are. The approach is illustrated for the case of estimating people's willingness to pay for improving (or maintaining) visibility at the national parks.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2015.12.006URL [本文引用: 1]

社会资本在多大程度上影响着公共事业的发展是一个悬而未决的重要理论命题和政策困惑.而越来越多的证据表明社会资本对增长、公平、贫困和环境可持续发展等有重要影响,本文以中国日趋加剧和受关注的环境问题为研究对象,提出了社会资本、制度环境与环境治理绩效之间关系的三个基本假说。采用结构方程中的MIMIC方法测算了2004-2011年186个地级及以上城市宏观层面的社会资本水平,实证考察了社会资本对环境治理绩效的影响程度和两者间的非线性关系以及制度异质效应。稳健性检验也进一步证明了结论的可靠性。研究发现:全国层面的社会资本呈现出较稳定的上升趋势。在地区分布上。东部地区的社会资本最高.西部地区其次.中部地区最后;社会资本总体上有利于环境治理。尤以社会信任和社会沟通的效应最为明显;社会资本与环境治理之间确实呈现倒U型的非线性关系,社会资本存在着一个适度水平;政府质量和市场化程度越高.社会资本的环境治理效应越大,改善政府质量所带来的社会资本边际环境治理效应更高.目前中国环境治理困局是多方面原因造成的,绝大部分城市面临着社会资本不足所导致的社会机制不全的困境;社会资本水平并不是越大越好。特别是当所处的制度环境尤其是政府部门难以满足社会资本的“需求”时,社会资本反而会引致环境治理的低效;但是如果政府部门努力提升公共服务水平和自身的运行效率,引导和沟通机制顺畅,实现与社会资本的匹配.会更有利于提升环境治理绩效。本文建议,重视社会机制尤其是社会资本在环境治理过程中的作用.发挥政府质量和市场机制在形塑和提升社会资本环境治理效应中的作用,促进社会资本与制度环境的匹配与衔接。对社会资本不同类型地区而17
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2015.12.006URL [本文引用: 1]

社会资本在多大程度上影响着公共事业的发展是一个悬而未决的重要理论命题和政策困惑.而越来越多的证据表明社会资本对增长、公平、贫困和环境可持续发展等有重要影响,本文以中国日趋加剧和受关注的环境问题为研究对象,提出了社会资本、制度环境与环境治理绩效之间关系的三个基本假说。采用结构方程中的MIMIC方法测算了2004-2011年186个地级及以上城市宏观层面的社会资本水平,实证考察了社会资本对环境治理绩效的影响程度和两者间的非线性关系以及制度异质效应。稳健性检验也进一步证明了结论的可靠性。研究发现:全国层面的社会资本呈现出较稳定的上升趋势。在地区分布上。东部地区的社会资本最高.西部地区其次.中部地区最后;社会资本总体上有利于环境治理。尤以社会信任和社会沟通的效应最为明显;社会资本与环境治理之间确实呈现倒U型的非线性关系,社会资本存在着一个适度水平;政府质量和市场化程度越高.社会资本的环境治理效应越大,改善政府质量所带来的社会资本边际环境治理效应更高.目前中国环境治理困局是多方面原因造成的,绝大部分城市面临着社会资本不足所导致的社会机制不全的困境;社会资本水平并不是越大越好。特别是当所处的制度环境尤其是政府部门难以满足社会资本的“需求”时,社会资本反而会引致环境治理的低效;但是如果政府部门努力提升公共服务水平和自身的运行效率,引导和沟通机制顺畅,实现与社会资本的匹配.会更有利于提升环境治理绩效。本文建议,重视社会机制尤其是社会资本在环境治理过程中的作用.发挥政府质量和市场机制在形塑和提升社会资本环境治理效应中的作用,促进社会资本与制度环境的匹配与衔接。对社会资本不同类型地区而17
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0455-2059.2013.03.002URL [本文引用: 2]

利用1998-2008年56个气象台站降水资料,结合TRMM月降水产品,通过对TRMM3B43降水数据在不同气候区、不同时空尺度的精度对比分析,探讨了卫星遥感反演降水产品在中国西北内陆河流域的适应性.结果表明:TRMM探测的月降水数据与实测月降水数据在整体上具有较好的一致性和线性相关性,相关系数为0.76,效率系数为0.58,其探测的降水量比观测值略大;TRMM在高原气候区月降水量的探测效果要优于在西风带区的;TRMM数据所反映的降水量的年内变化过程和实测降水量结果基本一致,但在具体的量上有一定的差异,表现为对降水相对集中的5-9月低估实测降水量,而在降水较少的10月-次年4月高估实测降水量,反映了TRMM对较大强度降水量的探测能力不足.流域多年平均降水量呈现南、北部大,中部小的格局,降水量的高值中心主要出现在高山地区,高达300 mm;而受西风环流影响的塔里木盆地东南面的且末-若羌一带、吐鲁番盆地和受高原区影响的柴达木盆地为极端干旱少雨区,降水量均不足100 mm.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0455-2059.2013.03.002URL [本文引用: 2]

利用1998-2008年56个气象台站降水资料,结合TRMM月降水产品,通过对TRMM3B43降水数据在不同气候区、不同时空尺度的精度对比分析,探讨了卫星遥感反演降水产品在中国西北内陆河流域的适应性.结果表明:TRMM探测的月降水数据与实测月降水数据在整体上具有较好的一致性和线性相关性,相关系数为0.76,效率系数为0.58,其探测的降水量比观测值略大;TRMM在高原气候区月降水量的探测效果要优于在西风带区的;TRMM数据所反映的降水量的年内变化过程和实测降水量结果基本一致,但在具体的量上有一定的差异,表现为对降水相对集中的5-9月低估实测降水量,而在降水较少的10月-次年4月高估实测降水量,反映了TRMM对较大强度降水量的探测能力不足.流域多年平均降水量呈现南、北部大,中部小的格局,降水量的高值中心主要出现在高山地区,高达300 mm;而受西风环流影响的塔里木盆地东南面的且末-若羌一带、吐鲁番盆地和受高原区影响的柴达木盆地为极端干旱少雨区,降水量均不足100 mm.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2004.04.001URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

水资源是人类生存和社会发展中最重要的成分, 中国内陆河的可持续发展所面临的生态问题源自有限的水资源和高的人口压力这两个方面的不协调。通过总结"黑河流域水生态经济系统试验示范研究"项目近几年在涵养水源、绿洲尺度的水利用率提高和流域水生态经济系统中的水资源配置的部分试验成果和研究进展, 以实际事例展示了在流域尺度上提高水资源利用率的可行性和潜力。加强基础研究、引入"虚拟水"等创新意识、通过专家和管理层的结合可进一步提高流域水资源利用率。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2004.04.001URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

水资源是人类生存和社会发展中最重要的成分, 中国内陆河的可持续发展所面临的生态问题源自有限的水资源和高的人口压力这两个方面的不协调。通过总结"黑河流域水生态经济系统试验示范研究"项目近几年在涵养水源、绿洲尺度的水利用率提高和流域水生态经济系统中的水资源配置的部分试验成果和研究进展, 以实际事例展示了在流域尺度上提高水资源利用率的可行性和潜力。加强基础研究、引入"虚拟水"等创新意识、通过专家和管理层的结合可进一步提高流域水资源利用率。
URL [本文引用: 1]

水资源已从自然资源跃升为国家关键性、基础性战略资源,我国被联合国列为13个贫水国之一,占国土面积1/3的内陆河流域先天性的资源缺陷叠加不合理的利用使得水问题成为内陆河流域经济发展和环境保护的关键性问题。中国西北内陆河流域独特的山区降水集流、绿洲集约转化、荒漠耗散消失的水文循环和水资源分配机理,形成了山区以森林、草甸为主体的山地生态系统和平原以绿洲、过渡带、荒漠渐次交错为圈层的平原生态系统;反过来,生态系统又维系着与其息息相关的水循环系统,两者相互依存、相互作用和相互发展,形成了西北内陆河流域独特的水循环-生态复合系统;并以塔里木河、黑河、石羊河流域为例,论述了流域尺度的水资源开发利用现状、存在问题及生态环境变迁机制,并提出水-生态-经济和谐可持续发展的对策。
URL [本文引用: 1]

水资源已从自然资源跃升为国家关键性、基础性战略资源,我国被联合国列为13个贫水国之一,占国土面积1/3的内陆河流域先天性的资源缺陷叠加不合理的利用使得水问题成为内陆河流域经济发展和环境保护的关键性问题。中国西北内陆河流域独特的山区降水集流、绿洲集约转化、荒漠耗散消失的水文循环和水资源分配机理,形成了山区以森林、草甸为主体的山地生态系统和平原以绿洲、过渡带、荒漠渐次交错为圈层的平原生态系统;反过来,生态系统又维系着与其息息相关的水循环系统,两者相互依存、相互作用和相互发展,形成了西北内陆河流域独特的水循环-生态复合系统;并以塔里木河、黑河、石羊河流域为例,论述了流域尺度的水资源开发利用现状、存在问题及生态环境变迁机制,并提出水-生态-经济和谐可持续发展的对策。
DOI:10.1111/j.0950-0804.2005.00249.xURL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract. Pedagogically, literature reviews are instrumental. They summarize the large literature written on a particular topic, give coherence to the complex, often disparate, views expressed about an issue, and serve as a springboard for new ideas. However, literature surveys rarely establish anything approximating unanimous consensus. Ironically, this is just as true for the empirical economic literature. To harmonize this dissonance, we offer a quantitative methodology for reviewing the empirical economic literature. Meta egression analysis (MRA) is the regression analysis of regression analyses. MRA tends to objectify the review process. It studies the processes that produce empirical economic results as though they were any other social scientific phenomenon. MRA provides a framework for replication and offers a sensitivity analysis for model specification. In this brief essay, we propose a new method of reviewing economic literature, MRA, and discuss its potential.
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-6419.2009.00592.xURL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract. Benefit transfer uses research results from pre-existing primary research to predict welfare estimates for other sites of policy significance for which primary valuation estimates are unavailable. Despite the sizable literature and the ubiquity of benefit transfer in policy analysis, the method remains subject to controversy. There is also a divergence between transfer practices recommended by the scholarly literature and those commonly applied within policy analysis. The size, complexity and relative disorganization of the literature may represent an obstacle to the use of updated methods by practitioners. Recognizing the importance of benefit transfer for policymaking and the breadth of associated scholarly work, this paper reviews and synthesizes the benefit transfer literature. It highlights methods, trends and controversies in contemporary research, identifies issues and challenges facing benefit transfer practitioners and summarizes research contributions. Several areas of future research on benefit transfers naturally emerge.
DOI:10.1016/j.eneco.2015.06.005URL [本文引用: 6]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00070-1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1023/A:1023658501572URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3390/w7052472URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.30955/gnj.000903URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

生态系统服务价值的计算是生态补偿的关键问题, 是生态经济学研究的热点。本文以塔里木河流域九大水系之一的渭干河流域为靶区, 采用条件价值评估方法(contingent valuation method, CVM), 通过调查流域居民的支付意愿来反映该区域的生态系统服务价值, 并运用皮尔逊相关系数和多元线性回归方法对支付意愿与社会经济变量之间关系进行分析。结果表明: 1)渭干河流域居民每户每年的平均支付意愿为96.22元, 该结果与国外及国内东部地区流域的研究成果相比偏低, 与国内西北地区流域的研究结果接近。渭干河流域生态系统服务价值为2 443.46万元。2)渭干河流域居民的支付意愿与收入水平、受教育程度、对生态环境重要性的认知水平及户籍等因素显著正相关, 与支付方式负相关, 与性别和年龄的相关性不显著, 各因素在流域上下游间表现出差异性。3)社会经济因素中, 收入水平对支付意愿的影响程度最大, 标准化系数达到0.604, 其次是对生态环境重要性认知及支付方式, 受教育程度对居民支付意愿的影响相对较小。4)CVM方法在相近区域的研究结果接近, 与运用遥感手段及相应方法计算结果一致; 不同方法计算的生态系统服务价值差距甚大, 同时就多元回归方法存在的共线性问题及解决方法进行了分析讨论。研究丰富了条件价值评估方法在干旱区内陆河流域少数民族地区的应用, 为流域生态补偿标准的制订提供科学依据。
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

生态系统服务价值的计算是生态补偿的关键问题, 是生态经济学研究的热点。本文以塔里木河流域九大水系之一的渭干河流域为靶区, 采用条件价值评估方法(contingent valuation method, CVM), 通过调查流域居民的支付意愿来反映该区域的生态系统服务价值, 并运用皮尔逊相关系数和多元线性回归方法对支付意愿与社会经济变量之间关系进行分析。结果表明: 1)渭干河流域居民每户每年的平均支付意愿为96.22元, 该结果与国外及国内东部地区流域的研究成果相比偏低, 与国内西北地区流域的研究结果接近。渭干河流域生态系统服务价值为2 443.46万元。2)渭干河流域居民的支付意愿与收入水平、受教育程度、对生态环境重要性的认知水平及户籍等因素显著正相关, 与支付方式负相关, 与性别和年龄的相关性不显著, 各因素在流域上下游间表现出差异性。3)社会经济因素中, 收入水平对支付意愿的影响程度最大, 标准化系数达到0.604, 其次是对生态环境重要性认知及支付方式, 受教育程度对居民支付意愿的影响相对较小。4)CVM方法在相近区域的研究结果接近, 与运用遥感手段及相应方法计算结果一致; 不同方法计算的生态系统服务价值差距甚大, 同时就多元回归方法存在的共线性问题及解决方法进行了分析讨论。研究丰富了条件价值评估方法在干旱区内陆河流域少数民族地区的应用, 为流域生态补偿标准的制订提供科学依据。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
//
[本文引用: 1]
//
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

条件估值方法是当前国际上流行的衡量环境物品非利用经济价值的方法,通过调查居民针对不同环境状况变化的支付意愿,从而定量确定环境状况变化带来的经济效益和损失.针对黑河流域额济纳旗生态系统恶化的现状,以投标支付卡的方法设计了700份调查问卷,调查了黑河流域居民恢复额济纳旗生态系统的支付意愿,并采用非参数分析方法对结果进行分析.结果表明,用20a的时间将额济纳旗的生态系统恢复到20世纪80年代初的水平,黑河流域总共有92.3%的居民家庭存在支付意愿,有支付意愿家庭的平均支付意愿为每年每户43.39元,同时采用列联表检验的方法辨明了被调查者的年龄、学历、收入、户籍和居住的地理区域等因素对支付意愿的影响.最后在综合不同区域居民支付意愿差异的基础上,采用当前的市场利率将计算结果在时空尺度上加总,得到恢复黑河下游额济纳生态系统的总经济价值的现值为2.94×10<sup>8</sup>元.
Magsci [本文引用: 1]

条件估值方法是当前国际上流行的衡量环境物品非利用经济价值的方法,通过调查居民针对不同环境状况变化的支付意愿,从而定量确定环境状况变化带来的经济效益和损失.针对黑河流域额济纳旗生态系统恶化的现状,以投标支付卡的方法设计了700份调查问卷,调查了黑河流域居民恢复额济纳旗生态系统的支付意愿,并采用非参数分析方法对结果进行分析.结果表明,用20a的时间将额济纳旗的生态系统恢复到20世纪80年代初的水平,黑河流域总共有92.3%的居民家庭存在支付意愿,有支付意愿家庭的平均支付意愿为每年每户43.39元,同时采用列联表检验的方法辨明了被调查者的年龄、学历、收入、户籍和居住的地理区域等因素对支付意愿的影响.最后在综合不同区域居民支付意愿差异的基础上,采用当前的市场利率将计算结果在时空尺度上加总,得到恢复黑河下游额济纳生态系统的总经济价值的现值为2.94×10<sup>8</sup>元.
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2004.02.014Magsci [本文引用: 1]

条件价值评估法的调查问卷格式主要有连续型(包括开放式、支付卡式)和离散型(即封闭式)两种类型。针对黑河流域张掖市生态系统退化的现状,在连续型的支付卡问卷格式调查的基础上,以离散型单边界两分式和双边界两分式的封闭式问卷格式各设计了400份调查问卷,调查了黑河流域居民对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的支付意愿。封闭式两分式问卷调查结果的分析表明,黑河流域90.2%的居民家庭对恢复张掖市生态系统服务存在支付意愿。单边界两分式和双边界两分式问卷分析的黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年分别为162.82元和182.38元。按黑河流域有支付意愿的家庭数量计算,用单边界两分式和双边界两分式问卷分析,恢复张掖市生态系统服务的经济效益每年分别为7094.36×104元和7946.66×104元。由于双边界两分式问卷更能逼近市场行为,以双边界两分式问卷的结果作为条件价值评估的结果相对比较恰当,因此,未来5年时间恢复张掖市生态系统服务总经济价值的现值为3.7478×108元。由于恢复张掖市生态系统服务具有巨大的正外部效应,因此,仅就黑河流域居民家庭数量估计的经济价值是对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的经济价值的最低估价。
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2004.02.014Magsci [本文引用: 1]

条件价值评估法的调查问卷格式主要有连续型(包括开放式、支付卡式)和离散型(即封闭式)两种类型。针对黑河流域张掖市生态系统退化的现状,在连续型的支付卡问卷格式调查的基础上,以离散型单边界两分式和双边界两分式的封闭式问卷格式各设计了400份调查问卷,调查了黑河流域居民对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的支付意愿。封闭式两分式问卷调查结果的分析表明,黑河流域90.2%的居民家庭对恢复张掖市生态系统服务存在支付意愿。单边界两分式和双边界两分式问卷分析的黑河流域居民家庭对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的平均最大支付意愿每户每年分别为162.82元和182.38元。按黑河流域有支付意愿的家庭数量计算,用单边界两分式和双边界两分式问卷分析,恢复张掖市生态系统服务的经济效益每年分别为7094.36×104元和7946.66×104元。由于双边界两分式问卷更能逼近市场行为,以双边界两分式问卷的结果作为条件价值评估的结果相对比较恰当,因此,未来5年时间恢复张掖市生态系统服务总经济价值的现值为3.7478×108元。由于恢复张掖市生态系统服务具有巨大的正外部效应,因此,仅就黑河流域居民家庭数量估计的经济价值是对恢复张掖市生态系统服务的经济价值的最低估价。
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.01.002URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.biocon.2007.07.015URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
Magsci [本文引用: 2]

<p>运用条件价值评估法中支付卡式(PC)和二分式(DC)两种问卷,对九华山风景区游客保护古树名木的支付意愿进行研究,并分析了其影响因素。结果表明:838%的游客认为应该对古树名木进行保护,仅有302%对保护现状满意。支付卡式问卷调查结果为808元/(人·月),二分式问卷调查结果为954元/(人·月);按2010年游客接待量401万人次计算,2010年游客对九华山风景区古树名木保护的总支付意愿分别为1500×108元和4589×108元。影响支付卡式问卷支付意愿值的主要指标是年龄、个人年收入、文化程度和职业的相关性;影响二分式问卷支付意愿的主要指标是个人年收入。支付卡式问卷和二分式问卷支付意愿均与第一次调查结果无显著差异,PC1和PC2、DC1和DC2支付意愿值相差分别为062和173元,两次结果重现性良好,对本次研究结果的可靠性给予了保证</p>
Magsci [本文引用: 2]

<p>运用条件价值评估法中支付卡式(PC)和二分式(DC)两种问卷,对九华山风景区游客保护古树名木的支付意愿进行研究,并分析了其影响因素。结果表明:838%的游客认为应该对古树名木进行保护,仅有302%对保护现状满意。支付卡式问卷调查结果为808元/(人·月),二分式问卷调查结果为954元/(人·月);按2010年游客接待量401万人次计算,2010年游客对九华山风景区古树名木保护的总支付意愿分别为1500×108元和4589×108元。影响支付卡式问卷支付意愿值的主要指标是年龄、个人年收入、文化程度和职业的相关性;影响二分式问卷支付意愿的主要指标是个人年收入。支付卡式问卷和二分式问卷支付意愿均与第一次调查结果无显著差异,PC1和PC2、DC1和DC2支付意愿值相差分别为062和173元,两次结果重现性良好,对本次研究结果的可靠性给予了保证</p>
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.3368/le.86.3.552URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.08.030URL
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
//Bateman I, Willis K.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3368/le.85.3.410URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.11.002URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
