 ,1,2, 胡志丁
,1,2, 胡志丁 ,3,4, 葛岳静1,2,5, 黄宇6,7, 胡伟8
,3,4, 葛岳静1,2,5, 黄宇6,7, 胡伟8Analysis on the national geo-setting of geo-strategic intersection area: Take Ukraine as an example
YE Shuai ,1,2, HU Zhiding
,1,2, HU Zhiding ,3,4, GE Yuejing1,2,5, HUANG Yu6,7, HU Wei8
,3,4, GE Yuejing1,2,5, HUANG Yu6,7, HU Wei8通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-10-27接受日期:2021-01-15
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-10-27Accepted:2021-01-15
作者简介 About authors
叶帅(1987-),男,安徽亳州人,博士研究生,主要研究方向为全球化与地缘环境。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (3004KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
叶帅, 胡志丁, 葛岳静, 黄宇, 胡伟. 地缘战略交汇区类属的国别地缘环境解析——以乌克兰为例[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(9): 2591-2605 doi:10.11821/dlyj020201033
YE Shuai, HU Zhiding, GE Yuejing, HUANG Yu, HU Wei.
1 引言
政治地理学是一门关注国际政治与地理环境之间关系的学科[1]。地缘环境是当前政治地理学研究的热点领域,它是“一带一路”倡议背景下加强世界地理研究的现实需求及国内地缘政治学复兴的创新转型[2,3]。一方面,对其研究规避了古典地缘政治的地理决定论、种族主义和殖民主义倾向以及为霸权行径提供理论支持等畸形发展的风险[4]。另一方面,它也有效避免了现代地缘政治学因学科维度多元化或研究范式过于固化所导致的解决现实问题不足所面临的窘境[5]。已有的地缘环境研究在概念界定[6]、要素解析[7]、定性定量评估[8,9]、系统模拟[10]、GEAM图形化建模[11]等领域开展的比较多。整体来看,当前地缘环境仍然以经验性研究为主,较少基于实证研究论证相关判断[12]。同时,自2000年以来,国内国别地理研究也几乎处于停滞的状态[13]。地缘环境和国别地理研究的这种现状显然与全球化背景下中国融入世界的现实需求之间不相匹配[13]。近期,有****基于跨学科融合的思路,很好地阐释了国别地缘环境分析的路径和方法,但他们更多的思考是国别地缘环境普遍属性分析的规范化指导,并没有对国别地缘环境的分类解析进行深入探讨[14]。因此,很难提出针对特殊国别地缘环境演变的预判方案。地理环境具有空间异质性[15],地理环境是地缘环境的本底要素[16],地缘环境也应具有差异性。分类进行国别地缘环境的解析是正视地缘环境差异性的必然要求。从地缘战略实践的空间视角看,全球可以划分为三种类型的国别地缘政治空间单元,即承受一种地缘战略的国家、完全不受地缘战略影响的国家以及地缘战略交汇区的国家。其中,地处地缘战略交汇区的国家是地缘行为体地缘战略实践的空间交集,是大国攘权夺利的焦点地区,地缘环境演变最为剧烈,有时甚至成为地区乃至全球政治经济格局变动的诱发因子。近一段时期内,特别是在全球化进程深入推进和以中国为代表的新兴国家崛起的双重背景下,全球财富和战略资源正在加速东移,导致亚太地区的地缘环境愈发复杂[17]。与此同时,霸权行径、领土争端、民族纠纷、宗教冲突等非传统安全因素也交织叠加在中国周边地区,这些都已经严重威胁到中国的国家安全[18]。因此,科学地解析、评估和预判地缘战略交汇区的地缘环境演变规律具有一定的现实意义。
乌克兰以其特殊的地缘战略区位成为后冷战时期俄罗斯和欧美的共同觊觎点,历次危机更是外部势力引燃其显著分异的国内环境导火索进行地缘政治博弈的结果。在西方鼓动和支持下,乌克兰持续推动“脱俄入欧”进程。同时,俄罗斯也积极拉拢其加入前苏联地缘政治空间范围。乌克兰在东西取向问题上俨然陷入了一场多边地缘政治博弈的“拉锯战”中,其地缘环境是地缘战略交汇区国别地缘环境的天然标本。围绕乌克兰问题,国外****分别从乌克兰国家认同[19]、俄罗斯与欧美战略互动[20,21,22]、危机对欧盟外交政策的影响 [23,24]等视角展开讨论。国内研究更多关切斯拉夫历史渊源及多元民族宗教文化分歧[25,26]、民主政治制度改革与社会转型[27]、俄罗斯与欧美国家地缘政治博弈[28]等方面。既有研究为本文提供了有益的借鉴和丰富的基础资料,但是这些研究大多是从国际关系学、历史学、政治学等学科视角针对单一要素分析乌克兰问题,未能有效地把乌克兰地缘环境各组成要素进行有机串联,由此导致对乌克兰问题的解释力差强人意。为弥补上述缺憾,特别是开启国别地缘环境分析的类属化和精准发力,本文在前人对地缘环境解析思路、跨学科融合路径和分析框架研究的基础之上,进一步提出地缘战略交汇区类属的国别地缘环境解析方案。以乌克兰为实证研究的案例国,洞悉其显著分异的地理环境、高度依赖的地缘关系、主体之间的地缘结构,以期破解乌克兰危机的地缘政治谜题,为其他同类属的国别地缘环境分析提供参考。
2 类属划分、属性特征与解析框架
2.1 类属划分与属性特征
地缘战略是把具体国家的安全和发展放到全球宏观背景之下,从地理的角度考察国际政治关系,制定出一个国家当前和未来一段时间内对外的政治、军事、经济、文化战略,该战略同时也为本国的政治、军事、经济、文化发展服务[29]。体现国家意志的地缘战略一旦付诸于实践,最终都将在具体的地理空间中得以施展。地缘战略的实践对象是具有一定地域空间的地缘体,包括国家地缘体以及非国家地缘体。一些国家因其地理位置、资源条件、历史文化和民族宗教等地理要素的特殊组合状态时常成为多个大国权力角逐的交汇区域。按照是否受到地缘行为体地缘战略实践的影响,可以将国家地缘体划分为三种类属,一类是永久中立国,二类是承受单一地缘战略的国家,三类是地缘战略交汇区国家(见表1)。这里要说明的是,虽然一个国家的自然地理环境不会在短时间内有太大变化,但经济社会文化环境的变化却日新月异。加之国际政治格局的风云变幻,地缘战略制定国也会适时对本国的地缘战略进行动态调整,制定更加符合时代背景的国家地缘战略。因此,随着内外部环境的变迁国别地缘环境也可能会发生类属转型。本文对国别地缘环境类属的划分是参考已有的可视化成果,选取的是2000—2019年承受单一地缘战略及处于地缘战略交汇区的部分国别样本[30]。三种类属的国别地缘环境中,地缘战略交汇区国家因其承受两种及其以上的地缘战略的影响,国内政治局势变化多端。同时,由于域外势力的频繁介入,地缘战略交汇区国家往往是国内问题国际化、简单问题复杂化,其地缘环境演变规律最为扑朔迷离[30]。Tab. 1
表1
表1国别地缘环境类属划分
Tab. 1
| 国别地缘环境类属 | 代表国家 | 地缘环境描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 永久中立国 | 瑞士 土库曼斯坦 | ① 不签订承担战争义务的条约,如同盟条约;② 不采取使本国卷入战争的行动及承担相关方面的义务,如承接外国军事设施的布局;③ 不参与对别国的经济制裁和封锁;④ 不接受附有损害中立地位的条件援助 |
| 承受单一地缘战略的国家 | 日本 韩国 以色列 | ① 意识形态高度聚合;② 民族构成较为单一或主体民族占绝大多数人口;③ 与某一大国或集团签署军事同盟条约 |
| 地缘战略交汇区国家 | 乌克兰 缅甸 叙利亚 | ① 战略区位价值较高;② 国内环境显著分异,具有脆弱性和暴露性;③ 经济发展高度依赖周边大国;④ 外部势力对其内政和外交干预明显 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
影响国家生存与发展的地理位置及其所附属的地理要素的时空关联情势构成一个国家或地区的地缘环境,它由地缘体、地理环境、地缘关系及地缘结构组成[16]。地缘战略交汇区国别地缘环境变化背后的实质是地缘行为体利用交汇区国家内部环境进行地缘政治博弈的结果,其指涉对象涵括客观存在的地理本底要素、历史渊源和主观建构的关联要素及国际社会行为体间的互动格局,该类国别地缘环境兼具脆弱性、依赖性及主体间性三大特殊属性[32,33,34]。其中,脆弱性表现在交汇区国家显著分异的地理环境及其为地缘行为体的渗入提供的可能性和可操作性空间较大,此凸显地理本底要素对地缘环境的基础性作用。依赖性指地缘行为体与交汇区国家之间的历史渊源及地缘行为体利用交汇区国家高度裂化的内部环境而人为构建的双边依赖关系,这是地缘环境中关联要素的集中体现。主体间性是地缘行为体对交汇区国家的地理位置和资源条件等区位价值的认知趋同而产生的行为体间的交互争夺行为,这是交汇区国家地缘环境中国际结构模式的表征。可以看出,虽然外部势力在交汇区国家地缘环境演变过程中更多的时候是扮演幕后推手的角色,但它却是地缘环境演变的重要驱动力。外部势力之所以对交汇区国家进行激烈争夺,是源于历史时期大国对交汇区国家地理环境所达成的共同理解,并在未来交往实践中不断遵循和强化这一认知原则的缘故。
2.2 解析思路与框架构建
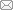
由地缘战略交汇区国别地缘环境的属性特征分析可知,解析这一类属的国别地缘环境首先要查阅有关交汇区国别地理方面的文献资料,旨在尽可能完整的挖掘出其地理位置、资源禀赋等自然地理环境的特殊性,目的是寻找地缘行为体对其争夺的原始动机,为民族成分、语言文化、宗教信仰、政党派别等人文社会环境的现状追根溯源,这也是分析地缘关系和地缘结构的支撑工作;其次,丰富阅读国别(区域)经济史、军事史、制度史、文化史等史籍资料,厘清地缘行为体利用交汇区国内环境的裂隙而建构起来的地缘关系及由历史渊源所产生的因果关联,系统考察交汇区对地缘行为体的依赖领域及其脆弱程度;而后,转向分析由地理位置形成的空间结构、资源禀赋差异形成的物质结构、地缘利益集团基于共同的国家利益而建构的理念结构、各种结构再组合的过程结构及所有结构的地缘效应。最后,综合判断和预测地缘战略交汇区国别危机事件发生的原因和走向。地缘环境具有整体性和差异性等普遍属性。一方面,地缘环境系统各组成要素相互影响相互制约共同构成了地缘环境的整体性,各组成要素对地缘环境具有“牵一发而动全身”的作用。另一方面,由于各国所处的地理环境不同,形成不同的国际关系网络和地缘空间格局,使得国家间的地缘环境也迥然相异。地缘环境的差异性决定分类属构建国别地缘环境解析框架的必要性,而地缘环境的整体性则要求其解析框架必然是一个跨学科、多维度的嵌套系统(见图1)。
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1地缘战略交汇区类属的国别地缘环境解析框架
Fig. 1Analysis framework of national geo-setting of geo-strategic intersection area
地理位置以及与此相联系的各种自然环境、经济和社会文化环境的总和构成一国的地理环境[35]。地缘战略交汇区国家地理位置的特殊性,使其在大国地缘政治博弈中往往充当地缘战略的支轴或战略缓冲地的角色,这是周边地缘行为体对其争夺的原始动机。随着地缘行为体博弈的不断深化,社会经济文化环境中的意识形态、民族构成、宗教信仰、语言文化及政党制度等因素逐步分化,即交汇区国家人文地理环境的分异,进而形成不同层面的国家认同危机。同时,自然地理环境中的地形地貌、河流湖泊、沼泽湿地、沙漠戈壁等制约着机械化兵种的顺利推进和国际商品贸易往来,会影响到外部势力的介入速率及方式的选择。
现代国家尺度的地缘关系,是以位势、距离、流量等地缘要素为基础的国家间的政治、军事、经济及文化关系[16]。刻画地缘战略交汇区国家的国际地缘关系必须梳理清楚大国在博弈过程中基于自我国别利益利用交汇区地理环境而主观建构起来的经贸往来、军事合作等复杂网络关系以及由社会文化的历史渊源所产生的因果关联。同时,还应注意到各种地缘关系的稳定程度,一般因果关联型的地缘关系比较稳定,主观建构的地缘关系波动较大,双边建构的地缘关系维系时间长于单边建构的地缘关系。
地缘结构指国家地缘体间的绝对空间格局以及它们在长期交往实践中所形成的理念共识和认同规则[36]。显性结构上,空间资源的有限性导致国家对生产资料的激烈争夺,国际(地区)资源禀赋差异会产生某种物质链结构。交汇区国家与周边地缘行为体绝对的空间位置关系也会形成某种空间格局[37]。此外,我们还可以通过对事物特征进行合乎逻辑的推理和预设,进而认识“主权”“关系”之类事物的形态[34]。隐性结构上,地缘行为体具有主观能动性,这充分体现在地缘结构系统中的部分子系统是由地缘行为体基于自我主权身份和国家利益在国际交往实践中通过制度建构而来。同时,已经形成的物质、理念结构再组合化的过程结构也属于隐性结构的范畴。
不同层面的国家认同危机致使交汇区国家内部政局分野,成为外部势力干预其国内局势的着力点。与之同时,交汇区国家不均衡的对外依赖关系以及主体间地缘结构所形成的共识效应共同加剧了地缘行为体对其争夺博弈。国内和国际环境共同促使了交汇区国家危机事件的出现。
3 实证研究——乌克兰地缘环境
地处欧亚大陆西缘文明断层线上的乌克兰,是东方和西方相遇之处,许多个世纪以来都是亚洲通往欧洲的门户地带[38]。当战争和冲突到来之际,关闭的欧洲之门成为阻挡东来或西来侵略的屏障,而当欧洲之门开启,乌克兰就成为连接欧洲与亚洲、东方与西方的枢纽[39]。每当周边地缘行为体东向或西向发展受阻时,总会选择不惜一切代价将乌克兰纳入自己的势力范围,这从1783年叶卡捷琳娜大帝发动的俄土战争、1854年英法土联盟与俄罗斯之间的克里米亚战争以及二战期间德国进攻乌克兰都可以得到历史佐证[40,41,42]。美国著名地缘战略家布热津斯基曾指出,地缘战略支轴国家乌克兰因其所处敏感的地理位置及潜在的脆弱状态,成为后冷战时期欧亚大陆地缘政治棋手国际博弈的重要棋子[43]。因此,独立后的乌克兰所发生的历次危机都是其国内环境与国际环境交织作用下的结果[44,45]。3.1 地理环境
乌克兰位于欧洲东部,北方和东方与白俄罗斯、俄罗斯接壤,西邻波兰、斯洛伐克、匈牙利、罗马尼亚与摩尔多瓦,南滨黑海和亚速海与土耳其隔海相望[46]。地处“三洲五海”要冲之地的乌克兰,自古以来就是人类迁徙的十字路口,各种文明冲突交汇于此,致使历史上周边大国彼此征伐、竞相争夺[26]。公元882年,维京人征服基辅及其周边地区,定都基辅,建立了东斯拉人为国民主体的君主制国家,史称基辅罗斯。这是俄罗斯族、乌克兰族和白俄罗斯族共同的斯拉夫文化渊源。公元3世纪,基督教已是一个以主教自治和普世大公会议至上为基本纲领的国际性宗教组织,它承认主教团中每位主教的绝对权威[47,48]。罗马帝国瓦解后,基督教顷刻分化成为以希腊语地区为中心的东派和以拉丁语地区为中心的西派[47]。起初,弗拉基米尔一世带领基辅罗斯皈依的是基督教东支东正教。然而,自奉天主教为圭臬的波兰-立陶宛王国入侵后,就拉开了乌克兰国内宗教信仰千年决裂的大幕。公元13世纪,蒙古金帐汗国入侵基辅罗斯,导致基辅罗斯内部封建势力割据。其中,东北罗斯(今俄罗斯部分)和西北罗斯(今白俄罗斯部分)先后臣服于蒙古,而西南罗斯(今乌克兰部分)则在波兰、立陶宛等基督教国家的支持下保持相对独立[46]。此后,古罗斯部落逐渐分化成俄罗斯人、乌克兰人和白俄罗斯人三大族群,语言也发展成俄语、乌克兰语及其他语系分支。随着宗教、民族、语言等社会要素的历史分化,社会分异的高阶表征,代表一定阶级利益的现代政治党派也出现显著分野。各政党利用国内族群分裂为少数经济寡头的一己之私而争权夺利,国际政治立场和国内执政理念分歧较大(见表2)。Tab. 2
表2
表2乌克兰主要政党及其执政理念
Tab. 2
| 政党名称 | 政治立场&执政理念 |
|---|---|
| 波罗申科联盟(Блок Петра Порошенка «Солідарність») | 全面加强与西方合作,坚决抵制俄罗斯,恢复国内秩序 |
| 人民阵线(Народний фронт) | 倾向西方,主张重建经济、根除腐败及平息东部冲突 |
| 季莫申科集团(Блок Юлии Тимошенко) | 建立民主国家,推行市场经济,增加社会福利,加速私有化进程 |
| 反对派联盟(Опозиційний блок) | 亲美党派,利用美国与俄罗斯的战略分歧获得西方政治支持 |
| 乌克兰争取改革民主同盟(Украинский Демократический Альянсза Реформы) | 亲欧同盟,积极治理腐败,营造良好的经济发展环境 |
| 乌克兰自由运动(Всеукраинское объединение "Свобода") | 右翼党派,民族主义和民粹主义的拥趸 |
| 乌克兰共产党(Комуністична партія України) | 改革和完善国家管理机构,取消总统制和州长制,国家权力交给劳动者,强调地方代表大会的作用 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
在诸多地缘环境的影响变量中,自然地理因素往往是最容易被忽视的一部分。事实上,地形地貌、河流分布、资源禀赋等都或多或少地影响着一个国家的对外关系。乌克兰大部分地区属于东欧平原,西部是海拔较高的喀尔巴阡山脉,南部是克里米亚山脉的一部分,东南部与俄罗斯隔刻赤海峡相望,以海拔较低的沿海平原和低山丘陵为主。刻赤海峡是沟通黑海与亚速海的狭长水道,其东西两岸多为基岩质海岸,岩性坚硬,利于军事工程设施建设。2013年乌克兰危机期间,俄罗斯正是充分利用有利的自然条件迅速封锁了刻赤海峡,并在极短的时间内建造出一座连接克里米亚半岛和克拉斯诺达尔地区的公路和铁路双用桥梁,以此赢得了战略上的主动。乌克兰煤、铁、锰、镍等矿产资源丰富,石油和天然气能源资源较为匮乏,这为俄罗斯使用“能源武器”牵制乌克兰政局提供了可能。除此之外,第聂伯河的穿流而过天然地将乌克兰的政治版图一分为二,河西岸是倾西方的大本营所在地,河东岸则是与俄罗斯联系更为密切的主阵地[49]。
特殊的地理位置和资源条件使得乌克兰历来都是周边地缘行为体竞相争夺的对象,价值观取向不同的外部势力进入乌克兰致使其民族构成、语言文化、宗教信仰、政党派系出现对垒分化,加之河流、地形所形成的自然分异,使得乌克兰出现历史文化、民族宗教、价值观、政治制度、地域等多个层面的认同危机[50]。社会结构离异化的过分膨胀,叠加各种体制没有实现其合理化的建构,动乱充斥着整个乌克兰社会。
3.2 地缘关系
无论民族起源、文化认同还是宗教信仰,乌克兰与俄罗斯都有着厚重的历史渊源[51]。这从上文对国内环境的分析已经可以得到答案。同时,因果作用所产生的地缘关系也是既有研究主要关注的[25,26],此处不再详述。地缘关系不仅是历史渊源所形成的关系,还有地缘行为体利用乌克兰国内环境而主观建构的双边关系。苏联解体后,俄罗斯曾幻想融入西方社会,在处理乌克兰等前苏联加盟共和国的问题上采取“甩包袱”的态度。加之在黑海舰队的归属、前苏联债务分配、克里米亚主权以及核武器处理等问题上双边分歧较大,两国地缘关系处于不温不火的状态。俄罗斯多次尝试加入西方换来的不是欧美国家的信任,却是北约和欧盟东扩的“号角”,俄罗斯人越发意识到加强与文化更为接近的前苏联国家合作的重要性。叶利钦对独联体国家总体战略构想是构建一个以俄罗斯为中心并在国际社会中有一定影响力的政治、经济、军事联盟。独立国家联合体(Commonwealth of Independent States)组织成立后,一系列条约协议的签署、联合军事演习及高层互访标志着俄罗斯开始积极改善与乌克兰的地缘关系。普京当选俄罗斯总统后,采取更为灵活的地缘方针,一并解决了能源供应、独联体自贸区、统一电网等多个搁置多年的问题。2013年乌克兰危机爆发,克里米亚共和国和塞瓦斯托波尔市加入俄罗斯,乌克兰(波罗申科政府)解除与俄罗斯之间的友好关系,并启动退出独联体国家程序。此后,乌克兰和俄罗斯之间的地缘政治和地缘军事关系几乎处于决裂的态势,地缘经济关系相较于其他欧美国家也渐行渐远(见表3)。
Tab. 3
Tab. 3Bilateral trade volume between Ukraine and Russia, Germany, France and the United States (亿美元)
| 乌俄贸易额 | 乌德贸易额 | 乌法贸易额 | 乌美贸易额 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011年 | 489.52 | 102.78 | 20.48 | 37.15 |
| 2012年 | 450.50 | 96.38 | 20.61 | 39.29 |
| 2013年 | 383.21 | 96.37 | 21.13 | 36.60 |
| 2014年 | 224.78 | 72.09 | 17.30 | 26.00 |
| 2015年 | 123.20 | 55.00 | 12.75 | 19.66 |
| 2016年 | 87.42 | 62.76 | 14.31 | 21.20 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
为了摆脱对俄罗斯的高度依赖,几乎每届乌克兰政府都在寻求西方的政治庇护、军事协防和经济支援(见表4)。独立之初的乌克兰完全按照西方的模式进行政治、经济、军事改革,对外政策奉行“一边倒”的亲美政策[52]。出于冷战后继续围堵俄罗斯的地缘战略需求,美国更是持积极迎合的态度。这一时期,双方围绕核武器销毁等多个议题进行多轮磋商。库奇马执政时期,乌克兰放弃了“一边倒”的亲美政策,实施“东西平衡战略”,美国则集中力量支持库奇马开展独联体国家的离心活动。“橙色革命”后,尤先科政府全面加强了与美国的战略伙伴关系。美国运用“巧实力”对乌克兰施加影响,提供一系列经济援助,协助进行民主化改革,支持其加入北约组织。亚努科维奇执政时期,乌克兰奉行独立自主、结伴不结盟的原则,参与欧洲一体化组织,继续保持与北约的军事合作。美国担心乌克兰与俄罗斯建立更为密切的经济关系,转向支持乌克兰加入欧盟,助力其摆脱对俄罗斯的经济依赖。波罗申科执政时期,渴望得到美国的经济援助和军事保护,外交全面转向西方。美国对乌克兰更多的是言语大于行动,实质性援助较少,将精力主要集中在对俄罗斯的制裁方面。泽连斯基上任伊始就宣布对拜登父子展开调查,随后而来的“通话门”事件暴露出其讨好美国政府的目的,如果拜登是在任美国总统,被调查的或许就是共和党人。
Tab. 4
表4
表4历届乌克兰政府对西方的外交政策
Tab. 4
| 时任总统 | 对西方的外交政策 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1991—1994年 | 克拉夫 丘克 | “亲美不成蚀把武器”:任内多次会晤美国总统布什,承诺销毁核武器,乞求美国经济援助。然而,对于俄罗斯的援助美国都勉为其难,再加上乌克兰更力不从心。最终,没有得到西方任何安全保障承诺。看到民不聊生、动荡不安的乌克兰,作为苏联解体的主要发起者晚年后悔不已 |
| 1994—2005年 | 库奇马 | 第一任期“左右逢源的外交”:积极开展与俄罗斯互利合作,同时加强与北约交流,建构欧洲国家身份,主导并参与独联体内部的离心活动 第二任期“识时务使经济升温”:与俄罗斯开展互信对话,双边贸易额回升,构建俄白哈乌经济合作框架。但在天然气合作方面与俄罗斯存在分歧,而后转向与西方更多的经济联系 |
| 2005—2010年 | 尤先科 | “全面亲西方”:在西方支持下发起“橙色革命”,重选中力压亚努科维奇成功当选。任期内始终以加入北约和欧盟为外交目标,但并没有得到“加盟”和“入约”的确切时间表 |
| 2010—2014年 | 亚努科 维奇 | “实用主义”:奉行独立自主、结伴不结盟的原则,积极推进加入欧洲一体化组织,继续保持与北约军事合作。同时,积极发展与俄罗斯关系,并在黑海舰队、边界划定、天然气等问题上达成诸多共识 |
| 2014—2019年 | 波罗申科 | “西靠新高度”:曾资助尤先科完成“橙色革命”的胜利。2013年乌克兰危机,克里米亚共和国、塞瓦斯托波尔市入俄以及乌东部局势的持续动荡,与俄罗斯关系持续降温。外交政策全面转向西方,尤其渴望得到美国为首的北约军事保护,多次力促乌克兰东正教会转归君士坦丁堡牧首区管辖 |
| 2019年— | 泽连斯基 | “政治素人待观察”:没有从政经历的泽连斯基意外当选乌克兰总统。执政伊始,外交政策不甚明了,但“通话门”事件的曝出,其与美国的关系可见一斑。多次造访东部地区,可以看出其解决国内危机的决心,但如若不能很好地处理与俄罗斯的双边关系,即便有美国支持其东部政策也很难落实 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
乌克兰和欧盟(European Union,EU)的地缘关系主要体现在地缘政治层面,其进程大体可以划分为三个阶段。1999—2005年,欧盟经济共同体日趋完善,在外交和安全政策上也达成了诸多共识。面对新成立的独联体国家,欧盟先是采取以俄罗斯为主,其他国家为辅的政策。但随着欧盟睦邻政策的实施,乌克兰等东欧国家不再被欧盟国家看作俄罗斯的附庸国;2005—2010年,“橙色革命”爆发,尤先科提出加入欧盟的要求。然而,让乌克兰失望的是,此时欧盟对于乌克兰的态度是建立共同的价值观而非乌克兰加入欧盟。亚努科维奇政府也渴望加入欧盟,但一直没有从欧盟方面得到具体时间表。2010年至今,这一时期的欧盟与乌克兰地缘关系更加清晰。首先,欧盟愿意给出乌克兰“入盟”远景;其次,欧盟针对乌克兰、白俄罗斯、摩尔多瓦等独联体国家制定了东部伙伴关系峰会机制,以期深化与独联体国家之间的关系,稳固其东部边界[53]。乌克兰和欧盟密切的联系最终引燃了2013年乌克兰危机。尽管波罗申科执政后继续强化与欧盟关系并签下了欧盟联系国协定书,此时的欧盟却因为忌惮俄罗斯在乌克兰危机中的强势介入,并没有进一步发展与乌克兰地缘政治关系的意愿。
北约(North Atlantic Treaty Organization,NATO)是以美国为首的西方军事一体化组织。从第二任总统库奇马开始,乌克兰一直致力于逃脱俄罗斯的地缘辐射空间,加入北约组织是其军事“脱俄”的重要途径[54]。冷战后北约不但没有减弱对欧洲的控制,反而进行了多轮东扩,意在进一步压缩和封锁俄罗斯的地缘战略空间,乌克兰为代表的东欧国家是北约东扩的终极目标。因此,独立后的乌克兰一直与北约保持密切的双边地缘军事关系(见表5)。
Tab. 5
表5
表5乌克兰“入约”进程
Tab. 5
| 乌克兰地缘愿景 | 北约地缘战略 | 地缘军事实践 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994年 | 回归欧洲,实现军事层面的乌欧一体化 | 继续围堵俄罗斯,尝试吸纳前苏联势力 | 参加北约“和平伙伴计划” |
| 1997年 | 为深化合作奠定基础 | 东扩已经开始,保持与乌克兰密切联系 | 签署北约《特殊伙伴合作宪章》 |
| 1999年 | 争取尽早加入北约 | 进一步与乌克兰建立特殊 伙伴关系 | 加入乌克兰-北约行动计划,出席在华盛顿举行的北约成立50周年庆典 |
| 2004年 | 寻求地缘安全保障 | 深入欧亚大陆,直接接触乌克兰 | 签订《关于支持北约行动的备忘录》 |
| 2009年 | 军事协防,节约国防成本 | 配合先前东扩,对俄罗斯实行“双钳”夹挤 | 议会通过特别法案,允许北约军队入境参加联合军事演习 |
| 2018年 | 彻底脱离俄罗斯,积极寻求西方军事援助 | 回应俄罗斯在处理克里米亚和顿巴斯事件时的强硬态度 | 放弃不结盟地位,为加入北约夯实法理基础 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
受因果关联和主观建构的双重作用,乌克兰与俄罗斯多个层面的地缘关系都比较密切。历史渊源的因果关联很难在短期内消解,致使乌克兰与俄罗斯在社会文化领域一直保持较高的依赖状态。主观建构的地缘关系因地缘行为体国家利益的变化而波动较大,加之俄罗斯与乌克兰的地缘关系以俄罗斯单边建构为主。因此,乌克兰与俄罗斯在地缘政治、地缘军事及地缘经济领域出现时而合作时而脱钩的状态。独立后的乌克兰一直在寻求西方的政治庇护、军事协防及经济支援。同时,欧美基于构建一个围堵俄罗斯的地缘封锁圈的现实需求,时常向乌克兰抛出“入约”和“加盟”的橄榄枝,并充分利用其国内环境扶植代理人。在双边互相建构的作用下,乌克兰与欧美地缘关系较为稳定且维系时间较长。
3.3 地缘结构
由于特殊的地理空间位置,俄罗斯一直把乌克兰当作其传统势力范围和突破北约围堵的战略要塞。以美国为首的北约致力于东扩,乌克兰是其东扩的终极目标和围堵俄罗斯的前沿哨所。由此,乌克兰与周边地缘行为体之间上形成了俄罗斯-乌克兰-欧美这种主体间钳形的地理空间格局。俄罗斯拥有丰富的天然气和石油资源,欧洲拥有庞大的消费市场,乌克兰是俄罗斯油气资源输往欧洲的能源大通道,资源禀赋的结构性差异生产出能源供应国-通道国-需求国物质链国际结构模式。近年来,影响乌克兰的地缘行为体主要是俄罗斯、德国、法国、英国和美国等国家[55],其中德国、法国、英国和美国基于欧盟和北约组织共同的身份建构成乌克兰问题上的利益集团[56,57],这是乌克兰所处的地缘结构理念性的一面,即乌克兰始终在欧美与俄罗斯二元利益集团对立博弈的夹缝中生存。随着中国“一带一路”倡议在东欧的不断推进以及欧洲内部的分化(诸如英国脱欧等黑天鹅事件的出现),影响乌克兰地缘环境的周边地缘体身份、利益和现有地缘格局的不断互构,地缘秩序不断进行着重组,乌克兰所处的地缘结构将趋于多边网络状。在主体间地缘结构作用下,俄罗斯和欧美对乌克兰不断进行着交互争夺,乌克兰国家危机事件还会再出现。受多边网络地缘结构影响,乌克兰国家危机事件的激烈程度会有所降低。4 结论与讨论
鉴于乌克兰地缘环境的极其特殊性,依据其地缘环境特征实证地缘战略交汇区类属的国别地缘环境分析框架略显单薄。因此,本文还将简要进行缅甸、叙利亚与乌克兰国别地缘环境的类比分析,以期超越特殊性寻求普遍性,验证解析框架构建的可信度。缅甸位于东南亚与南亚的过渡地带,介于多支地缘力量的战略交汇区域。随着美国重返亚太、中国“一带一路”倡议的提出,其地缘战略区位价值越发凸显。多民族多宗教的社会分离状态、少数民族武装与军政府冲突不断、传统农业为主的经济发展水平致使其国内环境极其脆弱和暴露[58]。近年来,中国正积极通过多样化的制度创新、顺应东道国的社会改革、突破制度和文化的制约,取得与当地政府、企业多赢局面的合作模式[59]。美国(奥巴马政府)为配合其提出的“亚太再平衡”战略,对缅甸增加政治互动、取消经济制裁、鼓励企业投资,积极建构与缅甸地缘关系。处于中东地缘板块中心位置的叙利亚历来都是周边强权争夺的对象[60]。冷战后,俄罗斯为重塑其世界大国形象,开始重返中东,俄罗斯与叙利亚地缘军事合作日益密切[61]。美国则是以“支恐国家”为由对叙利亚进行不遗余力的打压和制裁。此外,土耳其、伊朗也多次向叙利亚伸出宗教地缘战略的触角。各地缘行为体对叙利亚侵入的着力点正是其民族、宗教、政党等百孔千疮的国内环境[62]。缅甸、叙利亚与乌克兰地缘环境略有不同。如,叙利亚的非传统安全(恐怖组织、宗教安全)战略价值凸显,乌克兰的传统安全(军事国防)价值较高,缅甸的地缘战略价值更多的是源于行为体的地缘政治想象。但是,这仅仅是外部势力对其达成认知共识的内容差异,地缘环境中地理环境、地缘关系及地缘结构等要素的相似性依然普遍存在。因此,完全可以提取出它们之间相似度最大的地缘环境类属基因序列,为分析其他地缘战略交汇区国别地缘环境提供比对参照(见图2)。图2
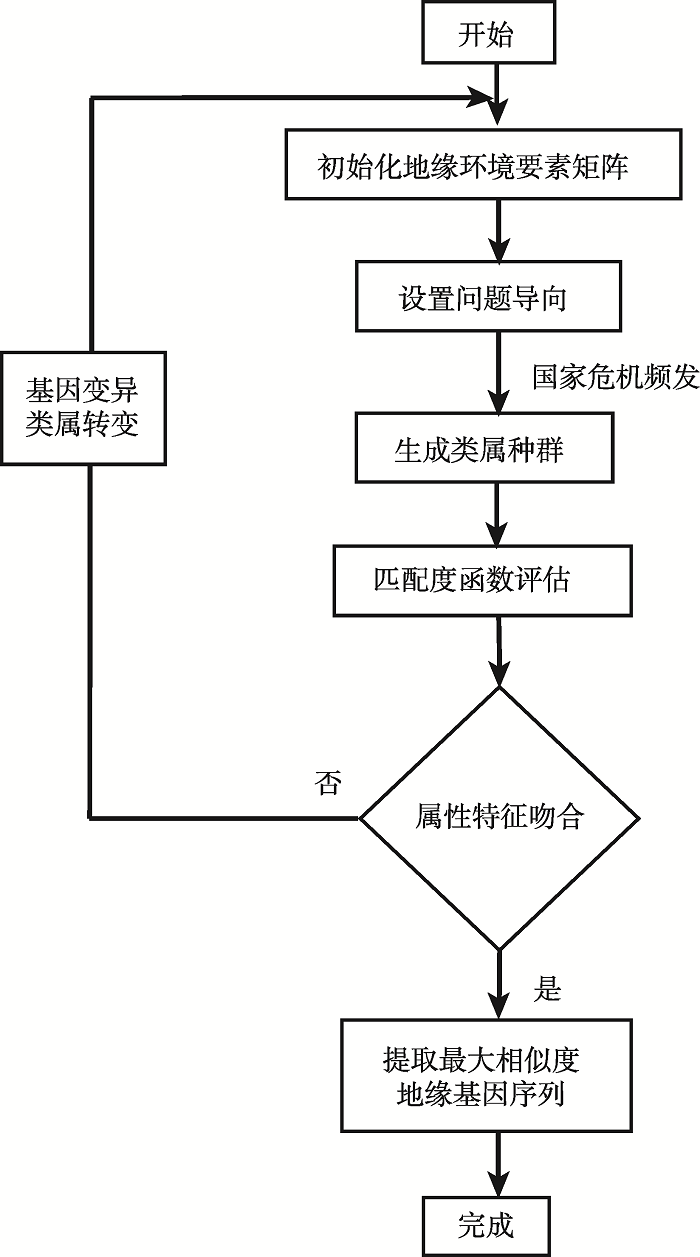 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2国别地缘环境类比分析流程
Fig. 2Analogue analysis process of national geo-setting
本文进一步深化了国别地缘环境研究,基于地缘战略实践的空间视角,划分出单一战略型、战略交汇型及永久中立国型3种类属的国别地缘环境。凝练出地缘战略交汇区类属的国别地缘环境的脆弱性、依赖性和主体间性等属性特征,并构建出该类属国别地缘环境解析框架。在此框架的指导下对乌克兰地缘环境进行了实证研究。主要结论如下:① 无论是自然地理还是社会经济文化,乌克兰都呈现出显著的地域分异。自然地理方面,地形河流的分布影响着周边地缘体对其国内环境的干预方式和速率。社会经济文化方面,乌克兰复杂的东斯拉夫历史渊源、对立的宗教信仰、特殊的民族构成、派系林立的政党制度都为俄罗斯和西方国家的渗入提供了可能性和可操作性。② 因果关联作用下,共同的斯拉夫历史渊源导致乌克兰在社会文化领域对俄罗斯的依赖程度较高。建构作用下,出于对乌克兰特殊的战略位置及优越的资源条件的觊觎,俄罗斯和欧美都在积极构建与乌克兰的地缘关系。同时,这种基于国别利益而主观建构的关系波动较为剧烈,双边互构的乌克兰与欧美的地缘关系维系时间明显长于俄罗斯单边建构的。③ 俄罗斯、欧美和乌克兰之间不仅形成了空间和物质上的显性结构,还有隐性的主观理念结构以及历史演变的过程结构。空间结构上,乌克兰地缘格局呈现出欧美-乌克兰-俄罗斯主体间钳形状。物质结构上,乌克兰是俄罗斯能源输往欧洲市场的过境国。理念结构上,乌克兰在欧美利益集团与俄罗斯二元力量对立的夹缝中生存。过程结构上,乌克兰所处的地缘结构将趋于多边网络状。显著分异的地理环境、高度依赖的地缘关系及主体间的地缘结构综合作用下的乌克兰,国家危机事件频繁出现。未来,乌克兰危机的激烈程度会有所降低。通过对缅甸和叙利亚与乌克兰国别地缘环境的类比分析,再次证明了地缘战略交汇区国别地缘环境解析框架的可行性和可操作性。
空间异质性的客观存在要求我们对地缘环境研究要因国甚至因区域而异,不宜采用统一的框架。只有分门别类地进行国别地缘环境的类属划分,才能确定各类属国别地缘环境解析的侧重点,这样解析国别地缘环境才更逼近客观实际且兼具效率,同时也合理规避了地缘政治学研究的形而上学主义的出现。本文首次尝试对国别地缘环境进行类属划分,并构建出地缘环境演变最为剧烈的战略交汇型的解析思路与框架,以期为同类属地缘环境的研究提供相应的理论支撑。百年未有之大变局中的中国,周边汇聚了来自不同方向的地缘力量,解密周边地缘危机事件背后的权力游戏是化解其地缘安全风险的首要任务。正如前文所述,本文所构建的地缘环境解析框架也只是为乌克兰及其同类属的地缘战略交汇区的国别地缘环境“量身打造”的,对于其他类属的国别地缘环境的解析仍要继续深化研究。同时,地缘环境是一个庞大而复杂的时空系统,它涉及地缘政治、国际关系、历史等众多学科,跨学科研究是其难点所在,如何对如此之多的地缘要素进行系统整合与模拟也需进一步思考。
致谢:
真诚感谢二位匿名评审专家在论文评审中所付出的时间和精力,评审专家对交汇区国别地缘环境属性特征提炼、解析框架构建及类比分析等方面的修改意见,使本文获益匪浅。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190921 [本文引用: 1]

以西方为主的国外政治地理和地缘政治学说为中国政治地理和地缘政治的发展提供了很好的参照和基础。因此,如何理性对待西方的政治地理学和地缘政治学的研究、如何正确处理中国政治地理学和地缘政治学中的本土化与国际化关系是关乎中国政治地理学和地缘政治学学科方向的重要议题。然而,目前中国政治地理学和地缘政治学的发展在这一问题上存在困惑乃至两难。一方面,过度依赖西方研究框架和理论为中国政治地理学和地缘政治学的学科建设带来了一定风险;另一方面,在对西方研究保持谨慎态度的同时不能走向封闭乃至仇外的极端,破除“唯西方论”的同时不能走进“中国特殊论”的陷阱。为此,国内高校和科研院所从事政治地理和地缘政治研究的青年****自发于2019年举办了一次“政治地理与地缘政治理论前沿”青年论坛,集中探讨了对西方政治地理与地缘政治发展的借鉴与反思,取得了初步的共识。具体而言,西方政治地理学和地缘政治学研究议题的多尺度性、研究方法的多样性、研究氛围的批判精神、研究视野的国际化和研究规范的严谨性等方面值得中国借鉴;而历史视角缺失、知识生产不平衡、地图空间表达不足、话语分析过多、解决现实问题不足等方面存在局限,中国政治地理学和地缘政治学未来发展过程中应加以避免。希望本次讨论抛砖引玉,吸引更多****共同推动中国政治地理学和地缘政治学的学科发展。
[本文引用: 1]

The Western-oriented foreign political geography and geopolitics theories provide a good reference and basis for the development of Chinese political geography and geopolitics. In this sense, it is a very vital issue related to the direction-guiding for the disciplines of Chinese political geography and geopolitics, in particular in regards to how to rationally treat the studies of political geography and geopolitics in the West as well as how to correctly handle the relationship between these subjects' localization and internationalization within China. Nevertheless, the current development of China's political geography and geopolitics still has confusion and even dilemma on this issue. On the one hand, the over-reliance on the Western research frameworks and theories has brought certain risks to the discipline construction of Chinese political geography, while on the other hand, we cannot move towards the extreme of closedness or even xenophobia while being cautious about Western research, and most importantly we must break up the trap of "Chinese particularism" while breaking "Westernism". To this end, young scholars engaged in political geography and geopolitical research in domestic Chinese universities and research institutions have voluntarily organized a Youth Forum themed on "The Frontiers of Political Geography and Geopolitical Theories" in 2019, which focused on the references and reflections on the development of Western political geography and geopolitics, and reached preliminary conclusions. Most specifically, the multi-scale nature of Western political geography topics, the diversity of research methods, the critical spirit of the research atmosphere, the internationalization of research horizons, and the integrity and standardization of research paradigms are worthy of reference for Chinese political geography, and meanwhile Chinese political geographers should avoid the lack of historical perspective, imbalanced knowledge production, inadequate map space expression, excessive discourse analysis, and inadequate solutions to real problems that are identified in the forum discussions. We hope that this discussion will attract more scholars to jointly promote the development of the disciplines of Chinese political geography and geopolitics.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.02.129 [本文引用: 1]

通过梳理西方100多a海洋地缘政治的发展脉络,系统总结和归纳其海洋地缘政治发展的4个阶段与特征:自然演进模式下的海洋地缘政治理论形成阶段( 1890s前)、国家空间-权力关系下的理论发展阶段(两次世界大战前后)、海洋地缘政治的现代化阶段(1960s-1990s)、新海洋地缘政治理论阶段(1990s后)。与国外相比,中国的海洋地缘政治研究起步较晚且未得到足够的重视,通过分析新中国成立以来中国地缘政治****在海洋地缘政治领域的探索历程发现:中国海洋地缘政治发展缺乏相关学科理论的支撑和整合,难以形成完整的理论体系,研究手段也较为单一并缺乏建设性的实证研究,这与中国在世界“海洋地缘环境”格局中的现状严重不符。因此,面对批判地缘政治学的“多尺度转向”背景与中国发展的具体国情,提出发展中国“海洋地缘环境”的研究作为响应,并深入探讨“海洋地缘环境”的内涵与研究的空间尺度。最后,对海洋地缘环境近期重点研究方向做出展望:① 深化海洋地缘环境理论基础与研究方法;② 加强不同尺度的海洋地缘环境时空分异格局及其形成机理研究;③ 安全转向背景下的多尺度海洋地缘环境系统脆弱性研究;④ 结合中国实际,加强边境与边界的相关研究。
[本文引用: 1]

The 21st Century is the century of the ocean, which has become an important guarantee for the sustainable social and economic development of coastal States and the national hot space of interests. Based on the macro mode of thinking and sensitive to the reality of international problems, marine geopolitics theory has influenced the whole process of world history greatly. After summarized the research progress during 100 years of western marine geopolitics, found that it has 4 development stages and each stage has its distinctive development characteristics: natural evolution of marine geopolitics pattern formation stage (-1890s), the state space of power relations theory development stage (around World War I and World War II), the stage of modern marine geopolitics (1960s-1990s), and a new marine geopolitics theory (1990s-). Compared with foreign countries, China marine geopolitics research started late and did not got enough attention. Through the analysis of modern exploration process in China of marine Geopolitics, it can be found that China marine geopolitics is lack of theory support and integration, which is difficult to form a complete theoretical system. Moreover, the research methods are empirical study single and lack of construction, which is seriously unfit the pattern —‘the marine geo-setting ’in the world. Therefore, combine critical geopolitics "multi scale to" background and specific national conditions of China development, the paper puts forward the research direction of "marine geo-setting" in China as a response to the spatial scale, then explore the connotation of the marine–geo environment. Finally, prospect the content of the research of marine–geo environment: ①develop the theory and method of marine–geo; ② strengthen the variation pattern and its formation mechanism of different scales of marine–geo environment; ③ vulnerability research on multi-scale marine geo environment system under the background of steering the security; ④strengthen border research combined with the actual situation in China.
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201702002 [本文引用: 1]

作为全球性大国,美国地缘政治战略的制定和实施极大地影响了世界经济与政治格局。系统分析美国所处的地缘区位特征,并归纳美国崛起的地缘政治战略阶段演化及不同阶段的地缘战略特点。远隔重洋为其建国营造了相对独立的优越环境;美国是美洲唯一的强权,控制着美洲大陆的核心;美国本土地势广阔且平坦,具有全球最大的宜居和连续适宜耕种土地。依托于优良的地缘区位,美国自1776年建国以来,历经独立与建国、大陆扩张、海外扩张、世界秩序搭建、全球霸权等地缘政治发展阶段。在其崛起过程中,美国的地缘政治战略表现出不同发展阶段制定相应的地缘政治战略;美国“国家利益”为核心的大陆控制战略;强化海权的战略保障力量;国际秩序体系的制定、维护;价值观的输出与推广等特点。美国崛起对中国的启示在于:崛起阶段,中国决策者有必要积极参与和制定涉及货币、贸易等重要方面的全球治理秩序;提高海权的战略保障力量;通过“一带一路”确保中国在欧亚大陆的核心地位;制定中国全面、长期和完善的地缘战略图谱;提升中国的软实力;加强地缘战略研究智库建设。
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908004 [本文引用: 1]

地缘关系研究作为地理学中一个重要研究领域越来越受到****关注,开展基于大数据的地缘关系的定量研究,是对传统地缘关系研究的重要补充。利用新闻媒体大数据GDELT从全球性的视角将中国及其周边国家间地缘关系综合表达为合作与冲突关系,通过有序聚类方法识别中国及其周边国家合作与冲突的阶段划分,并对不同阶段国家间的合作与冲突关系进行社会网络分析,利用社区探索等工具对合作与冲突网络进一步剖析和解译,最后对不同时段内突出的双边关系进行对应分析,以及以中国为中心的均衡度分析。结果发现:1979-2017年中国及其周边国家间合作与冲突关系在时间上表现出明显的3个阶段,中国逐渐成为网络的中心,形成了以中国为中心,以俄、日、韩为支撑的广泛合作格局;中越、中日、中俄、朝韩等各阶段突出的双边关系表现出各异的发展态势和驱动因素;伴随着中国和平崛起的进程,中国与周边国家的合作越来越均衡,与此同时中国与周边国家的冲突范围不断扩大。
[本文引用: 1]

Geo-relationships, as an important field of research in geography, have attracted much attention from scholars. Quantitative research on geo-relationships based on big data is an important supplement to traditional geo-relationships study. This paper uses GDELT mass media data to express the geo-relationships between China and its neighboring countries as a global relationship of cooperation and conflict, and identifies the stage division of these relationships using ordered cluster analysis. Social network analysis is conducted for each stage of the cooperation and conflict relationship, and community detection is used to further analyze and interpret the networks of cooperation and conflict. Finally, we highlight bilateral relations in various stages and conduct a China-centered equilibrium analysis. Three main results are presented. First, from 1979 to 2017, the cooperation and conflict relationship between China and its neighboring countries demonstrated an obvious three-stage temporal division. China has gradually become the center of the network, and a broad cooperation pattern centered on China and supported by Russia, Japan, and South Korea has formed. Second, the highlighted bilateral relations in each stage, such as China-Vietnam, China-Japan, China-Russia, and DPRK-ROK, show varied development trends and driving factors. Third, with the process of China's peaceful rise, cooperation between the country and its neighbors is becoming more and more balanced, and conflict between them is expanding.
[本文引用: 1]

Geographical circumstances are the fundamental background for all kinds of geopolitical events. The geopolitical environment system (GES) refers to a system that combines both physical and anthropogenic subsystems. Research on the geopolitical environment system simulation is a key to understanding the international geopolitical phenomenon. The theory of GES arose from the integration of the traditional geopolitics and earth system sciences. As an interdisciplinary system composed of many different fields, integrated reviews and a metadata study of GES are urgently needed. This paper presents a comprehensive view into the origination and advance of the GES theory. The conceptual framework of the GES is described in detail. The methodology for simulating and forecasting geopolitical events is also provided. It is proposed that the core topics of the GES science may include, but are not limited to, issues as data acquisition technologies; principles on the interactions between multiple subsystems (or factors) at different scales; evaluating and mitigating the global geopolitical risks, including the political risks, economic risks, the social risks, the environmental risks and the technological risks; and forecasting the geopolitical events with machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.06.002 [本文引用: 1]

援引后人文主义地理学作为批判地缘政治学的一个延续,以《人民日报》纸媒和官方微博为例,采用NVivo分析和对比分析的方法探讨了“美国反恐”这个当代热点地缘政治话题在两个不同媒体空间被呈现的形式。基于后人文主义思潮对物质的关注,讨论了“人”及其地缘环境认知是否受“物质”(在文中具化为网络技术)影响而动摇其在理解“人地关系”过程中的支配地位。研究发现:一方面网络技术多线参与和呈指数型信息传播的特征使得网络空间出现了多元化的声音并最终呈现出多元和复杂的网络地缘政治景观;另一方面,网络技术迫使当代媒体追求“快”和“新”从而摒弃了传统媒体所强调的权威、真实和逻辑性,取而代之的是情绪化的话语表述,呼应了后人文主义地理学对人以外的要素的关注,讨论了网络技术作为一种物质要素对“人地关系”认知的影响。研究证实,受网络技术及其带来的信息革命的影响,它在一定程度上确实能够对具有主体性的人的地缘认识产生影响。
[本文引用: 1]

Highlighting the significance of ‘humanity’ in understanding of ‘human-land relations’, the humanist thinking has a great impact upon the current research in the field of human geography. Taking the sub-field of geopolitics as an example, the current geopolitical research has focused too much on the element of humanity for the production of geopolitical knowledge, which is majorly related to the study of ‘critical geopolitics’. However, the most recent studies in human geography have begun to re-emphasize on the importance of ‘materiality’ under the theoretical framework of posthumanism, discussing how the materiality subverts the subjectivity of the humanity. On this basis, this article draws on the case study of People’s Daily and Sina Weibo and adopts the methods of NVivo and comparative study to explore how topic of the US war on terror is discussed in these two various media spaces, from the lens of posthumanism which, to a great extent, can be read as an extension of critical geopolitics. Specifically, this article explores whether and (if so) to what extent the humanity and their understanding of geopolitics are under the impact of the ‘materiality’ (which is embodied as Internet technology in this article), and whether the dominance of humanity in the understanding of human-land relationship is and will be challenged. The NVivo analysis and the comparative study shows that, the Internet technology to a significant extent impacts Chinese people’s subjectivity and their geo-understandings, for the reason of its revolutionary influence upon political communications. To be exactly, the feature of the multi-intervention and exponential ways of communication in the Internet based communities has finally resulted in the multivariate media landscape in this space. Moreover, the Internet technology has urged the contemporary media to pursue ‘fast’ and ‘new’, and thus abandoned the authority, authencity and logic that are underlined in the traditional media. Such technology-based media behavior to a certain extent leads to the emotional and affectual geopolitical expressions in the Internet space. On this basis, this article has contributed to the renewal of theories, methodologies and philosophies in the recent studies of human geography, paying attention to whether ‘material’ elements have impact upon people’s understandings of human-land relationship. In so doing, this article has contributed to the development of posthumanist geography in geographical studies. From an empirical and practical perspective, this article warns the danger of that, the Internet technology and related equipment are becoming extensions and parts of human bodies and so that are gradually eroding the humanity’s biological characteristics.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202010002 [本文引用: 1]

自“地缘政治”一词创立以来,西方地缘政治学已经历了120年的发展,期间诞生了众多理论流派,然而其影响却在日渐衰落。这在一定程度上源于其发展思路以及由此导致对现实研究不足所致。中国地缘政治研究起步较晚,长期以借鉴西方地缘政治理论为主,直到2010年掀起以“地缘环境”研究为主题的复兴议程。地缘环境研究将地理知识和政治融入地缘政治分析过程中,这一研究方向与思路不仅有助于地缘政治研究的变革与创新,还有助于推进“一带一路”倡议和人类命运共同体建设,具有重要理论与现实意义。本文基于前期对有关地缘环境概念、构成、结构、模拟等内容的研究进展,提出了国别地缘环境研究思路、跨学科融合路径和分析框架,并以德川幕府时期的日本为例,展现了跨学科融合研究视角下日本受国内外多要素、长时间、多尺度综合作用所导致的地缘环境演变,对其中涉及到的日本对内、对外的政策制定与变化也从其面临的地缘环境视角进行了解读。最后为深化对当前国别地缘环境研究提出了三条建议。
[本文引用: 1]

Although many theoretical schools have been developed and thrived in the field of "geopolitics" in Western academia over the past 120 years, the influence of geopolitical research has been declining partly due to the lack of concern for realistic issues, which is embedded in its traditional research agenda. In China, geopolitical studies have mostly followed the Western approach until 2010 when a new "geo-setting" research agenda was launched. This geo-setting research agenda incorporates geographic knowledge and politics into the process of geopolitical analysis, which has demonstrated both theoretical and practical significance because it not only brings reform and innovation to geopolitical studies but also contributes to the promotion of the Belt and Road Initiative and the construction of a community with a shared future for mankind. This paper proposes a research approach and an analytical framework for nationa-state based and integrated interdisciplinary geo-setting studies, according to previous academic findings on geo-setting, including conceptualization, leading elements, structure, and simulation. This framework is illustrated by a case study of Japanese geo-setting during the period of Tokugawa Bakufu. From an integrated interdisciplinary perspective, this paper unveils how the Japanese geo-setting had evolved under the combined effects of both domestic and international factors at multiple scales. It also sheds light on Japan's domestic and external policy formulation and changes during the period of Tokugawa Bakufu. Finally, three suggestions are put forward to strengthen the current nation-state based geo-setting research: (1) to continue to apply the interdisciplinary approach; (2) to highlight an integrated approach featured by multi-factor, multi-scale and long-term analysis; and (3) to pay consistent attention to long-term dynamic simulation.
DOI:10.2307/143141URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201801001 [本文引用: 3]

“一带一路”倡议是人类历史上最伟大的全球治理工程,开辟了政治地理学研究的新纪元,为地缘关系研究提供了大舞台。地理学是从时间、空间和自然—社会系统三个维度理解陆地表层过程的科学,对地缘关系研究具有独特的功能和作用。因此,从地理学视角研究地缘关系具有其他学科无法比拟的优势。“一带一路”是当前最具挑战的科学和政策命题,从地缘关系视角研究“一带一路”,需要加强四个方面的结合:① 在科学思维上,需要还原论与系统论思维相结合;② 在科学数据建设上,需要社会人文与自然环境数据相结合;③ 在科学问题选择上,需要社会过程、人文过程、政治过程和自然过程相结合;④ 在研究方法上,需要经验方法、实证方法、系统方法与大数据研究方法相结合。中国地理****应兼顾政治地理学科建设、地缘关系的学科交叉研究和“一带一路”全球实践开展研究。
[本文引用: 3]

The Belt and Road Initiative is the greatest project aimed to improve global governance in human history ever before. It opens a new era for the research of political geography, and in particular it provides great opportunities for geo-relation research. Geography is a science that explores the surface of earth from three perspectives including the time, space and nature-society system, which equips it to undertake geo-relation research with unique tools and advantages. The Belt and Road Initiative is one of the most challenging scientific and policy issues in the world. To better study the Belt and Road Initiative from the geo-relation perspective, geographers need to make combinations in the following four ways: (1) combining reductionism and system theory in scientific thoughts; (2) combining data of both human-society and nature-environment; (3) combining research questions based on social, human, political and natural processes; (4) combining research methods on empirical, positivism, systematic, and big data. Chinese Geographers need to give considerations to balance the development of political geography, multi-discipline oriented research on geo-relations and the implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative globally.
[本文引用: 1]

大国间的争霸与兴衰更替,无疑不受地缘政治和地缘经济法则的支配。冷战结束以来,随着中国等新兴国家经济的迅速发展,国际权力结构正发生深刻重组,世界正在进入新的地缘政治、地缘经济大时代,中国和平发展亟需地缘政治学、地缘经济学的理论支撑。本文在总结世界地缘政治和地缘经济发展态势的基础上,从思想渊源上论述了地理学在地缘政治学和地缘经济学发展中的基础性作用,剖析了当前中国地理学在地缘政治地缘经济领域研究中的不足,进而提出了地理学界如何加强地缘政治地缘经济研究的几点建议。
[本文引用: 1]

The rise and fall of the great powers undoubtedly is not dominated by geo-political and geo-economic rules. Since the end of the Cold War, with the rapid economic development of China and other emerging countries, the international power structure is undergoing profound restructuring and the world is entering the new geo-political and geo-economic era. At present, China's geopolitical environment has become increasingly complex and its peaceful development urgently needs geopolitical and geo-economic theoretical support. Based on analysis of the current world geopolitical and geo-economic development trend, this paper discusses the ideological origins on the fundamental role of geography in the development of geopolitics and geo-economics; analyzes the deficiencies of the Chinese geographers in the field of geopolitics and geo-economics; and then puts forward some suggestions how to strengthen the geopolitical geo-economic studies.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.03.001 [本文引用: 1]

在对19 世纪末和20 世纪西方代表性地缘政治与地缘经济理论进行重点介绍的基础上,分析了中国周边地缘政治与地缘经济的历史和现状特点,阐述了中国周边地缘政治与地缘经济的基本格局与发展态势,即:北部地缘政治关系紧密,地缘经济发展较快;西部地缘政治关系持续发展,地缘经济合作前景广阔;西南部为地缘政治破碎带,地缘经济极具潜力;南部地缘政治与地缘经济关系总体良好,但南海问题是不稳定因素;东部地缘政治热点问题敏感复杂,地缘经济结构相对稳定。最后提出了改善提升中国周边地缘政治关系与发展地缘经济的“北联、西进、南合、东拓”地缘战略及对策建议。
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the introduction of representative Western geopolitical and geoeconomic theories of the late nineteenth century and the twentieth century, this paper analyzes the characteristics of historical and contemporary geopolitics and geoeconomics in China's surrounding areas. It also discusses the basic patterns and trends of geopolitical and geoeconomic situations in the area. The main patterns and characteristics are as follows. China's geopolitical relationship is close and geoeconomic relationship develops at a relatively rapid pace with northern neighboring countries. Its geopolitical relationship continuously develops and prospect of geoeconomic cooperation is very promising with neighboring countries to the west. On the other hand, China's geopolitical relationship with countries to the southwest is very fragile but the geoeconomic relationship has great potential to develop. In the south, China's geopolitical and geoeconomic relationship with neighboring countries is overall healthy, but the issue of South China Sea can be a potential cause of instability. Last but not the least, the geopolitical situation in the area to the east has sensitive and complex hotspots, whereas the structure of geoeconomics maintains relatively stable. This paper puts forward strategies and countermeasures in order to improve the geopolitical and geoeconomic situations, which can be summarized as "Uniting in the North, Advancing in the West, Cooperating in the South, and Extending in the East". More specifically, "Uniting in the North" focuses on building a stable zone geopolitically based on mutual trust, economic and trade ties, science and technology, culture and other fields of cooperation with countries including Russia and Mongolia. "Advancing in the West" means expanding the economic and trade cooperation and cultural exchanges with five Central Asian countries, Russia and West Asia, Eastern Europe and the European Union countries through the development of the "Silk Road Economic Belt", which vigorously promotes the vast development of geoeconomics and creates a favorable geopolitical environment for Western China. "Cooperating in the South" aims at further strengthening traditional cooperative relations with South Asia and Southeast Asia countries by means of negotiation and dialogue, gradually resolving the Sino-Indian border dispute and territorial disputes in South China Sea. It also means promoting regional cooperation between China and ASEAN countries and countries located in the South Asia subcontinent, deepening the strategic friendship relations. All goals under "Cooperating in the South" cannot be accomplished without the development of the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area, the China-Burma-India-Bangladesh economic corridor and the twenty-first century maritime Silk Road. At last, "Extending in the East" places emphasis on breaking the first and second island chain encircled China set by USA and Japan and makes an ambitious plan that captures the mastery of the seas in 2020.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1163/1871191X-13020050URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.04.002 [本文引用: 1]

中国崛起面临的地缘环境是人类历史上最为复杂的,建立和完善地缘环境分析体系,预判预研地缘环境变化态势是学科发展和国家发展的需要。当前关于中国地缘环境的研究方兴未艾,研究内容多以地缘环境内涵、地缘环境解析、地缘环境驱动机制、地缘环境中的地缘关系和地缘环境研究方法的单项研究为主,而缺乏对地缘环境要素的系统研究,尚未提出一套完整的公认的地缘环境驱动机制,更未搭建完整的地缘环境分析框架。论文认为地缘环境是人文地理学的重要研究议题,地理要素通过地缘环境影响地缘政治和地缘经济,地缘体、地理环境、地缘关系、地缘结构组成地缘环境系统,地缘距离和地缘流量是地缘环境的核心变量。为此,未来的地缘环境研究需更加关注地缘结构影响下的地缘关系,加强多维度、多尺度、长周期的地缘环境驱动机制和地缘环境要素相互作用机制探讨,拓展地缘环境研究方法和技术,深化面向“一带一路”的地缘环境研究。
[本文引用: 1]

China's rise is faced with the most complex geo-setting in human history. Establishing and improving the geo-setting analysis framework and researching and forcasting the changing situation of China's geo-setting are the needs of both the disciplinary development in human geography and national development. Currently, the research on China's geo-setting is progressing. The main researching contents are seperate studies on geo-setting definition, geo-setting analysis, driving mechanism of change in geo-setting, geo-relationships, and research methods of geo-setting. However, there is a lack of systematic research on geo-setting elements, and a complete set of recognized geo-setting change driving mechanisms has not been proposed yet, nor has a completed geo-setting analysis framework been established. Based on the past research and looking into the future, this article holds that geo-setting is an important research issue of human geography. Geographic elements influence geopolitics and geoeconomics through geo-setting. Geo-entities, geographical environment, geo-relationships, and geo-structures constitute the geo-setting system. Geo-distance and geo-flows are the core variables of a geo-setting. Therefore, future geo-setting research needs to pay more attention to the geo-relationships under the influence of geo-structures, strengthen the discussion of multidimensional, multiscale, and long-period geo-setting change driving mechanisms and interactions of geo-setting elements, expand geo-setting research methods and techniques, and deepen the geo-setting research of the Belt and Road region.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.07.002 [本文引用: 1]

借鉴哲学及相关学科、****对结构主义研究的最新进展,特别是社会理论对社会结构、国际关系学对国际社会结构和地理学对空间结构的研究,探讨了地缘结构的理论基础、概念和分析框架。地缘结构的分析框架包括5部分,即作为构成物的结构、作为过程的结构、结构系统、2个层次和2种作用机制;对地缘结构的每部分及不同部分之间的联系以及如何形成单一的整体结构进行阐述;最后对使用地缘结构存在的一些问题和当前的国际形势进行了简单讨论。
[本文引用: 1]

With the diversification of the research paradigm and methods of human geography, the research perspectives and methods of geopolitics, as an important branch of human geography, also become diversified. Especially since the 1960s, the structural turn of geopolitics has led to a number of important research results in geopolitics. However, on the whole, the study of geographical structure is too simple and immature. Drawing on the latest progress of structuralism in philosophy and related disciplines, especially the study of social theory on social structure, international relations on international social structure and geography on spatial structure, this article discusses the theoretical basis, concept and analytical framework of geo-structure. The analytical framework of the geostructure consists of 5 parts: structure as a component, structure as a process, structure system, 2 levels of structure and 2 mechanisms of action. The contents that constitute the geo-structure can be roughly divided into 3 kinds, namely, material structure, conceptual structure and spatial structure. The structure as a process focuses on exploring the relationships and their interdependence within the structure, and the impact of these changes on the identities and interests of geo-bodies, which means that the structure itself is changing. The geo-structural system has not been seriously studied. But with the advent of the geo-economic era, the transformation of Hobbes culture to Lockean culture, especially the interdependence under various relations, makes the international anarchic society move towards a structural system composed of politics, military, economy and culture. The 2 levels of the geopolitical structure and the 2 mechanisms are closely linked, reflecting the relationship between geo-bodies and the geopolitical structure in which the geopolitical body is placed. Each part of the geo-structure should form a whole in order to explore its impact. In the end, some problems in using geo-structure and the current international situations are briefly discussed in this study.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.06.007 [本文引用: 1]

当今国际地缘政治经济格局正处于剧烈变动中,并对缅甸地缘环境的复杂性及地缘脆弱性产生深刻影响。缅甸所在的大湄公河次区域日益成为世界重要地缘政治力量博弈前沿和焦点。系统研究缅甸国家地缘脆弱性,对于中国西部大开发、“一带一路”及周边地缘环境建设具有重要战略意义。本文基于地缘政治及人地关系地域系统等学科理论,规范分析与实证分析相结合,从暴露性、敏感性和适应性等方面构建了国家地缘脆弱性研究框架,系统探索了缅甸典型的国家地缘脆弱性特征。资源环境禀赋、内部地域结构等引致的经济政治体系、社会文化传承等方面是缅甸脆弱性的本底特征,而缅甸与中国的地缘关系及决策则从根本上影响其地缘战略位态。缅甸地缘政治脆弱性及其与中国的相互依赖使之成为西方“U型封堵大陆战略”的薄弱点和今后角逐的着力点,也是中国解围破局重要的地缘战略出口。近期中国应通过“一带一路”孟中印缅经济走廊建设,大力加强中缅之间政治、经济、文化等各方面友好关系。
[本文引用: 1]

At present international geopolitical pattern is drastically changing, which may have a profound influence on the complexity of Myanmar’s geopolitical context and vulnerability. Myanmar and the Greater Mekong Sub-region are becoming the world's major forefront and focus of geopolitical power game. Consequently, research on Myanmar geopolitical vulnerability would have great theoretical and practical significance for the development of western China and the “Belt and Road” initiative, as well as China’s surrounding geopolitical environment. National geopolitical vulnerability is a geopolitical concept, especially related with traditional implication of “small country.” Based on theories and methodologies of geopolitics and human-environment system research, this study defines national geopolitical vulnerability with regard to exposure, sensitivity, and adaptability, combining normative analysis with empirical study, and then systematically explores the structural effects and typical characteristics of national geopolitical vulnerability of Myanmar. With regard to internal vulnerability (sensitivity and adaptability), Myanmar has a vulnerable geopolitical location with the narrow shaped territory surrounded by multi-national powers, traditional agriculture-based economy and widespread poverty conditions, complex regional structure with multi-ethnic and multi-cultural conflicts, and long-term instability of government system. All these geopolitical factors and their succession mechanism determine its national geopolitical vulnerability. Significantly, China-Myanmar geopolitical relations fundamentally affect the geostrategic position of Myanmar. Myanmar’s geopolitical vulnerability and the corresponding dependence on China make it a weak point of the Western U-shaped besieging strategy and future critical point of the power competition, also an important geostrategic opening to China for breaking the geopolitical siege. It would be indispensable to continue to strengthen interdependence between China and Myanmar, and to maintain sound friendly bilateral relations. Myanmar is being faced with parliamentary election changes at present. Its political orientation will determine the future national development process and the corresponding geopolitical landscape of Southeast Asia, South Asia, and even the Asia-Pacific region for decades.
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200357 [本文引用: 1]

“一带一路”倡议的深入推进加速了中国企业对外投资的步伐。而对于这些“走出去”的企业而言,往往面临着东道国社会环境及治理结构变革、制度制约、文化冲突等多重挑战。此前经济地理学提出的“主动嵌入”和“被动嵌入”,并不能完全解释“一带一路”倡议背景下中国企业在“走出去”过程中所呈现的“外资”与东道国治理结构、地方制度文化环境之间的复杂相互作用关系。本研究构建了“全球-国家-地方”多尺度嵌入的分析框架,以缅甸莱比塘铜矿为例,阐释企业如何通过多样化制度创新,顺应东道国的社会变革,突破制度和文化的制约,从而取得政府、企业、当地社区“多赢”局面的合作模式,从而从新的视角理解制度的多尺度性和尺度之间的相互作用。研究发现:尺度要素之间存在耦合关联作用,且作用模式有不同的组合,同时多个尺度要素的嵌入和影响过程也存在时序效应。最后,结合莱比塘案例,为中国企业“走出去”提出了政策建议。
[本文引用: 1]

The in-depth promotion of the Belt and Road Initiative has accelerated the pace of outward foreign direct investment of Chinese enterprises. These “going out” enterprises often face multi-scalar challenges such as the reform of the host country's social and political environment, institutional constraints, and cultural conflicts. The “active embeddedness” and “obligated embeddedness” proposed by the early economic geographers cannot fully explain the correlation between the “foreign capital” and the host country's governance structure and the local institutional culture in the process of “going out” of Chinese enterprises under Belt and Road Initiative. This article argues that the process of outward investment is influenced by “multi-scale” factors from the global, national and local levels, and the key to success is for enterprises to make timely adaptive adjustments in dynamic environmental changes to better embedded locally. By constructing an analysis framework of “global-national-local multi-scalar embeddedness”, it explains how Chinese enterprises are embedded in the social reform of the host country and break through the constraints of institutions and culture through social innovations. A cooperative model of the “win-win” situation of the government, enterprises and local communities had been built, so as to understand the multi-scalar and inter-scalar connections from a new perspective. Taking the Letpadaung Copper Mining Project invested by China in Myanmar as an example, the Chinese firm Wanbao has taken multi-scalar actions to embed into the political, economic and social environment of the host country. On a global scale, Wanbao has considered the international relations with major countries such as the United States and Japan and the influence of western non-governmental organizations on the global production network and local areas. On the national scale, the cooperation model between foreign capital and different political parties, economic benefits and employment of host countries, ethnic and religious issues as well have been considered comprehensively. On the regional scale, attention has been paid to the social impact, religious issues, people's livelihood issues and environmental protection issues brought by the entry of foreign-funded projects. The paper finds that multi-scalar factors are highly coupling with each other and act in different models. Meanwhile, the impact process has timing effects. Research is of great significance for revisiting “institutional and cultural turn” and guiding Chinese enterprises to “going out”.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
