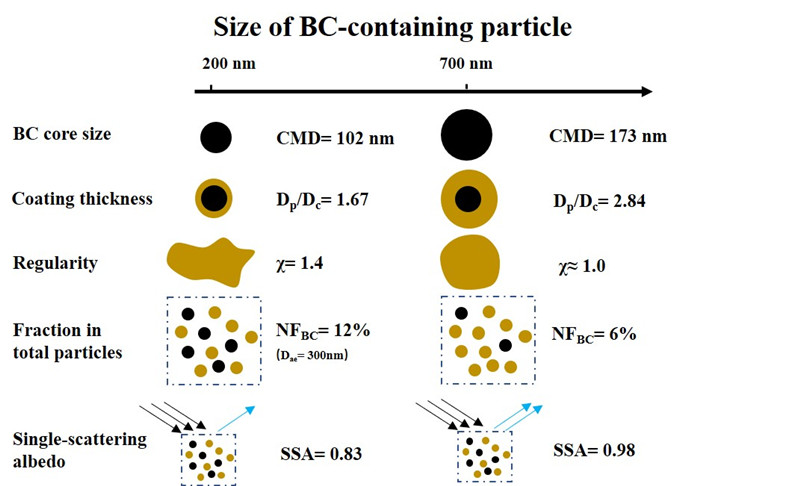
图1. 黑碳气溶胶微物理特性随粒径演变示意图。
黑碳的包裹物厚度还会影响黑碳密度 (Liu et al., 2019),包裹物更厚的黑碳气溶胶结构更为紧密,密度更大。而当包裹物厚度(MR,包裹物质量与黑碳核质量之比)达到6-8以后,此时黑碳气溶胶结构紧密,颗粒物密度主要取决于颗粒物包裹物的特性,黑碳气溶胶核的影响较小(图2)。黑碳气溶胶的结构又会对其光学特性产生明显影响,模拟表明,在黑碳气溶胶结构松散(密度较低)时,采用常规的米散射模型会对黑碳气溶胶的吸收造成高估(图3)。在北京这样有大量机动车排放新鲜黑碳(包裹物比较薄)的地方,必须考虑采用米散射模型进行光学模拟所带来的误差或采用更精细化(如T-matrix)方法来进行模拟评估。
上述研究成果发表在Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 和 Science of The Total Environment期刊,研究得到国家自然科学基金(41605104)资助。
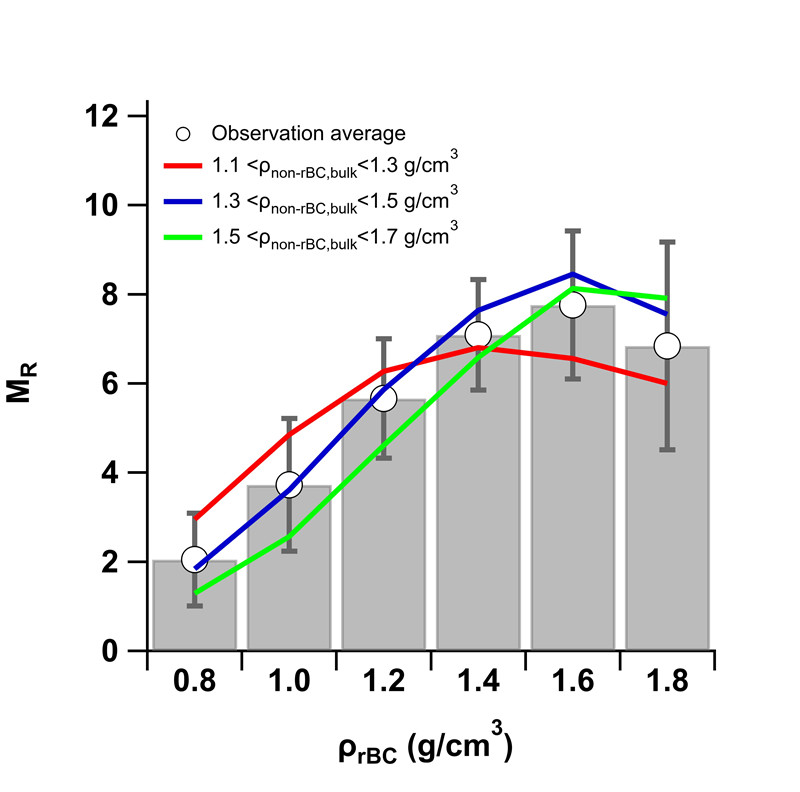
图2. 黑碳气溶胶密度与包裹物厚度(MR)之间的关系。
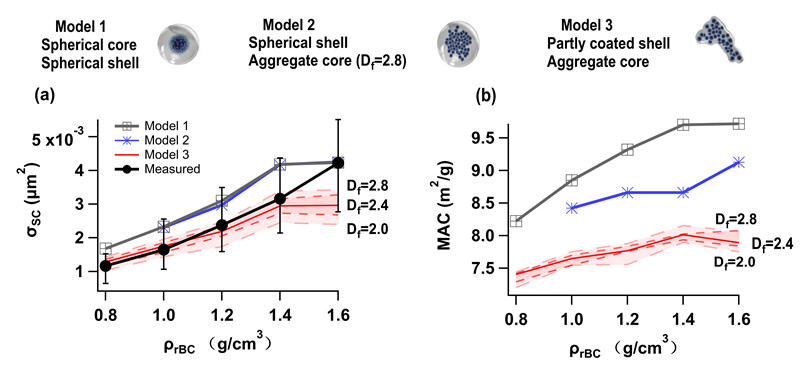
图3. 采用不同光学模型对不同密度黑碳气溶胶光学特性模拟示意图。
Liu H, Pan XL*, Wu Y, Wang DW, Tian Y, Liu XY, et al. Effective densities of soot particles and their relationships with the mixing state at an urban site in the Beijing megacity in the winter of 2018. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 2019; 19: 14791-14804.
文章链接:https://acp.copernicus.org/articles/19/14791/2019/
Liu H, Pan XL*, Wu YF, Ji DS, Tian Y, Chen XS, Wang ZF.: Size-resolved mixing state and optical properties of black carbon at an urban site in Beijing, Science of The Total Environment, 2020; 749: 141523.
文章链接: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004896972035052X
Liu H, Pan XL*, Liu DT, Liu XY, Chen XS, Tian Y, et al. Mixing characteristics of refractory black carbon aerosols at an urban site in Beijing. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 2020; 20: 5771-5785.
文章链接:https://acp.copernicus.org/articles/20/5771/2020/
附件下载:
