 ,, 董学瑞, 唐会会, 闫鹏, 卢霖, 王庆燕, 房孟颖, 王琦, 董志强
,, 董学瑞, 唐会会, 闫鹏, 卢霖, 王庆燕, 房孟颖, 王琦, 董志强 ,*中国农业科学院作物科学研究所 / 农业农村部作物生态与栽培重点开发实验室, 北京 100081
,*中国农业科学院作物科学研究所 / 农业农村部作物生态与栽培重点开发实验室, 北京 100081Effect of tetramethyl glutaric acid on summer maize photosynthesis characteristics
MA Zheng-Bo ,, DONG Xue-Rui, TANG Hui-Hui, YAN Peng, LU Lin, WANG Qing-Yan, FANG Meng-Ying, WANG Qi, DONG Zhi-Qiang
,, DONG Xue-Rui, TANG Hui-Hui, YAN Peng, LU Lin, WANG Qing-Yan, FANG Meng-Ying, WANG Qi, DONG Zhi-Qiang ,*Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology and Ecology, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing 100081, China
,*Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology and Ecology, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing 100081, China通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-01-16接受日期:2020-06-5网络出版日期:2020-06-22
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-01-16Accepted:2020-06-5Online:2020-06-22
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (554KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
马正波, 董学瑞, 唐会会, 闫鹏, 卢霖, 王庆燕, 房孟颖, 王琦, 董志强. 四甲基戊二酸对夏玉米光合生产特征的调控效应[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(10): 1617-1627. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.03002
MA Zheng-Bo, DONG Xue-Rui, TANG Hui-Hui, YAN Peng, LU Lin, WANG Qing-Yan, FANG Meng-Ying, WANG Qi, DONG Zhi-Qiang.
作物生物产量约有95%来自光合作用, 光合产物量即干物质积累是作物生长发育的重要指标[1,2], 也是形成经济产量的物质基础。提高生育期内光能利用效率是发挥玉米高产潜力的重要途径。有****认为, 花后玉米净光合速率与生物产量和籽粒产量呈显著正相关, 群体光合同化量直接决定玉米产量[3]。然而花后玉米叶片开始衰老, 导致光合能力下降, 严重制约着同化物的积累[4,5]。合理密植能够有效提高玉米单位面积生物量和经济产量, 但是种植密度的提高会加剧植株间的遮阴作用, 导致光合速率降低, 中后期甚至引起叶片早衰[6,7]。因此, 在玉米灌浆期, 通过延缓叶片衰老、延长光合速率高值持续期, 是提高灌浆期光能利用率、发挥玉米高产潜力的有效措施[8]。
应用作物化学调控技术可以调节作物自身的内源激素平衡, 调控作物对水分、养分的吸收、同化、运转, 改善作物自身对环境的适应能力, 最终影响作物的产量形成[9,10,11]。通过叶面喷施5-氨基乙酰丙酸(5-ALA)、胺鲜酯(DA-6)、6-苄基腺嘌呤(6-BA)等植物生长调节剂能够有效提高作物叶片光合羧化酶活性以及保护酶活性, 最终提高叶片光合速率[12,13,14], 但是, 这些调节剂针对大田作物的调控效果并不理想, 如5-ALA存在见光易分解的问题, DA-6对喷施时期和剂量均有严格要求, 在生产上进行推广有较大难度。近年来, 通过将植物生长调节剂与种子包衣剂或肥料相结合的化控技术逐渐成为研究热点。四甲基戊二酸(tetramethyl glutaric acid, TGA)普遍存在于植物体内, 具有调控蛋白质代谢的作用; 外源TGA能够被植物快速吸收, 并促进植物生长发育, 提高保护酶活性, 增强植物抗逆性[15]。目前, TGA在园艺作物上应用广泛, 主要用于打破种子休眠、减少落花落果等, 而针对大田作物, 以拌肥方式围绕TGA延缓叶片衰老、提高功能叶光合性能等方面的研究尚未见报道。因此, 本研究通过设置TGA施用梯度(与等量肥料混合基施)处理, 以中单909和京农科728为材料, 研究TGA对夏玉米光合特性和产量的影响, 以期为建立华北地区夏玉米高产高效栽培技术提供一定的理论依据和技术支撑。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验于2018—2019年在中国农业科学院作物科学研究所新乡试验站(35°18′N, 113°54′E)进行, 试验地土壤为黏壤两合土, 土壤有机质含量12.5 g kg-1, 全氮含量1.1 g kg-1, 速效磷含量16.1 mg kg-1, 速效钾含量109.9 mg kg-1, pH 8.1。2年玉米生长季降雨量和温度见图1。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图12018-2019年玉米生长季内日降雨量、日平均温度
Fig. 1Daily precipitation and mean temperature (line) during maize growing season from 2018 to 2019
1.2 试验材料与设计
试验以玉米(Zea mays L.)杂交种京农科728 (JNK728)和中单909 (ZD909)为材料, 试验采用随机区组设计, 4次重复, 小区长7.2 m, 宽10 m, 株距24.5 cm, 60 cm等行距播种, 种植密度为67,500株 hm-2。全生育期施肥量N、P2O5、K2O按125︰75︰35 (kg hm-2)的比例基施, 设置TGA处理0、75、150、225和300 g hm-2 (分别表示为CK、TGA1、TGA2、TGA3和TGA4) 5个TGA施用量, TGA用50 mL蒸馏水溶解后与肥料搅拌均匀后自然晾干, 在玉米播种前一次性基施。田间除草、植保等管理同当地大田生产。2018年试验于6月18日播种, 10月11日收获; 2019年试验于6月18日播种, 10月18日收获。1.3 测定项目与方法
1.3.1 叶绿素和可溶性蛋白含量 在玉米拔节期(V7)、大口期(V13)、开花吐丝期(VT)、乳熟期(R2)、蜡熟期(R4)和收获期(R6), 随机选取4~5株长势均匀一致的植株穗位叶(吐丝期之前的取最新的展开叶), 去除叶尖、叶基部、叶脉。参照Lichtenthaler等[16]的方法测定叶绿素含量(叶绿素a, 叶绿素b), 称取叶片0.15 g,用10 mL 95%乙醇避光浸提48 h, 中间震荡摇匀6次, 保证充分提取, 用双通道紫外-可见分光光度计测量665 nm、649 nm的吸光值。参照邹琦[17]的方法测定可溶性蛋白含量: 将相同位置的玉米穗位叶或新展开叶剪碎, 称取0.15 g样品, 加入1.5 mL Tris-HCl提取缓冲液(内含2 mmol L-1 MgCl2, 2 mmol L-1 DTT, 0.4 mol L-1蔗糖)在4℃冰浴下研磨至匀浆, 匀浆液于4℃ 15,000×g离心20 min, 取12 μL粗酶液, 加1.8 mL考马斯亮蓝充分反应2 min后在595 nm波长下测定吸光值。可溶性蛋白含量(mg g-1 FW) = (C×V/Va)/m, 式中C为查标准曲线所得每管蛋白质含量(mg), V为提取液总体积(mL), Va为测定所取提取液体积(mL), m为取样量(g)。1.3.2 净同化速率、光合势和叶片衰老速率 分别在玉米拔节期(V7)、大口期(V13)、开花吐丝期(VT)、乳熟期(R2)、蜡熟期(R4)和收获期(R6), 选取有代表性植株3株, 测量每株叶片长度和宽度, 叶面积(LA) = L×W×0.75 (0.5), 式中L表示叶片最大长度, W表示叶片最大宽度, 展开叶和未展开叶校正系数分别为0.75和0.5。叶面积测量完毕后, 于105℃杀青30 min后85℃烘干称重。玉米净同化速率(NAR)、光合势(LAD)测定及计算参照王方瑞[18]的方法, 叶片衰老速率计算方法参照Gao等[19]的方法, NAR、LAD和叶片衰老速率分别按照公式(1)、公式(2)和公式(3)计算:
式中, Wa、Wb分别表示前后2个测定时期的植株总干重, LAa、LAb分别表示前后2个测定时期的叶面积, Ta、Tb分别表示前后2次测定时期的时间。净同化速率和光合势从V13~R6期进行计算, 叶片衰老速率从R2~R6期进行计算。
1.3.3 光合速率的测定 使用Li-6400型便携式光合系统测定仪, 在吐丝期和蜡熟期测定2次, 选择晴朗无风的天气于上午9:00—11:30在各处理小区中间位置随机选取5株玉米, 测定玉米穗位叶净光合速率, 测定时避开叶脉位置。
1.3.4 籽粒灌浆特性 在玉米吐丝开始后的第7天开始取样, 取样时从上述标记的玉米植株中取3个玉米雌穗, 取样频率为每周1次至玉米籽粒黑层出现。田间取样后, 将雌穗放入冰盒取回实验室测定, 测定时每穗取中部籽粒100粒放入纸袋, 并在60℃的烘箱中烘干至恒重, 用精确度为0.0001 g天平称重记录。灌浆特征参数通过Richards方程进行模拟计算: y = a/(1+e(b-cx))1/d, 得到Richards方程参数a、b、c (其中a为终极生长量, b为初值参数, c为生长速率参数, 灌浆速率最大时的生长量Wmax = a/2, 达到最大灌浆速率的天数Tmax = (ln b)/c, 最大灌浆速率Gmax = (c×Wmax)/2, 活跃灌浆天数P = 6/c) [20]。
1.3.5 产量与产量构成因素 玉米成熟后, 在小区中部选取3行10 m2测产称重, 并记录有效株数、收获有效穗数(单穗籽粒≥30粒), 用称重法在每个小区选取10个平均穗, 用于调查雌穗穗部性状(穗长、秃尖长、穗粗、穗粒数和千粒重), 并测定出籽率和含水率, 折算产量(按14%含水量计)。
1.4 试验数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel 2013进行数据整理计算及作图, 用SPSS 19.0进行统计分析, 以LSD法(P<0.05)检验处理间差异显著性。2 结果与分析
2.1 TGA对玉米产量及产量构成因素的影响
表1所示, 四甲基戊二酸(TGA)处理均提高了2个品种玉米产量。2018年, JNK728和ZD909相对CK分别增产0.1%~8.1%和2.6%~8.2%, 其中, TGA2 (150 g hm-2)增产效果最优, JNK728和ZD909产量相比CK分别增产8.1%和8.2%; 2019年, JNK728和ZD909相对CK分别增产7.0%~15.3%和6.1%~9.2%, 其中, TGA2 (150 g hm-2)增产效果最优, JNK728和ZD909产量相比CK分别增产15.3%和9.2%。Table 1
表1
表12018-2019年TGA对2个品种玉米产量构成因素的影响
Table 1
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 穗长 Ear length (cm) | 秃尖长 Blade length (cm) | 穗数 Ear number (m-2) | 穗粒数 Kernel number (ear-1) | 千粒重 Kernel weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | |||||||
| 京农科728 | CK | 15.5±0.7 a | 2.3±0.4 a | 68889 b | 340.9±37.5 a | 335.1±7.4 b | 9159±264 b |
| JNK728 | TGA1 | 15.6±0.9 a | 2.2±0.4 ab | 68518 b | 345.6±29.8 a | 326.4±5.3 b | 9173±326 b |
| TGA2 | 15.9±0.7 a | 1.8±0.8 c | 71481 a | 352.5±40.9 a | 332.7±0.8 b | 9899±171 a | |
| TGA3 | 16.0±1.1 a | 2.4±0.6 a | 68889 b | 338.8±36.5 a | 346.3±4.6 a | 9609±354 ab | |
| TGA4 | 15.8±0.8 a | 2.0±0.6 bc | 71111 ab | 358.6±26.8 a | 333.7±1.9 b | 9698±168 ab | |
| 中单909 | CK | 17.2±0.9 ab | 0.8±0.7 a | 69629 a | 443.6±38.6 b | 278.2±8.1 a | 9715±172 b |
| ZD909 | TGA1 | 17.5±1.1 ab | 0.5±0.5 a | 69629 a | 469.0±52.8 a | 283.0±11.1 a | 10,268±65 ab |
| TGA2 | 17.8±1.0 a | 0.5±0.5 a | 69259 a | 468.5±24.9 a | 287.7±3.7 a | 10,508±541 a | |
| TGA3 | 17.2±0.8 ab | 0.8±0.8 a | 68148 a | 439.2±37.3 b | 290.6±8.0 a | 9969±345 ab | |
| TGA4 | 17.1±0.8 b | 0.8±0.5 a | 68889 a | 428.3±37.4 b | 291.7±3.7 a | 9691±133 b | |
| 2019 | |||||||
| 京农科728 | CK | 17.8±1.3 b | 2.6±0.7 a | 67340 a | 446.4±51.2 b | 318.2±11.7 b | 11,145±1493 b |
| JNK728 | TGA1 | 17.7±1.3 b | 2.4±0.8 a | 68080 a | 448.8±51.3 b | 340.9±7.0 a | 11,921±336 ab |
| TGA2 | 18.7±0.8 a | 1.7±0.7 b | 68450 a | 481.1±46.2 a | 337.5±4.8 a | 12,852±193 a | |
| TGA3 | 18.3±1.1 ab | 2.3±0.9 a | 69190 a | 465.8±50.0 ab | 334.4±13.4 ab | 12,274±318 ab | |
| TGA4 | 17.9±0.9 b | 2.4±0.8 a | 69930 a | 445.6±46.2 b | 338.5±9.2 a | 11,968±404 ab | |
| 中单909 | CK | 18.8±0.8 ab | 2.0±0.5 a | 68080 a | 496.9±38.3 b | 314.0±0.5 c | 11,434±200 b |
| ZD909 | TGA1 | 18.6±1.0 b | 1.7±0.6 a | 65860 a | 503.5±38.2 a | 330.1±1.3 a | 12,330±345 a |
| TGA2 | 19.2±0.7 a | 1.9±0.4 a | 67340 a | 526.2±31.4 a | 324.4±3.0 ab | 12,488±187 a | |
| TGA3 | 18.6±1.0 b | 1.8±0.7 a | 67710 a | 510.5±56.1 a | 320.4±9.9 bc | 12,134±446 a | |
| TGA4 | 19.0±0.7 ab | 1.9±0.5 a | 67340 a | 502.5±43.2 a | 318.0±2.7 bc | 12,284±538 a |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
TGA处理下, 2个品种玉米平均穗长、千粒重、穗粒数均高于CK, 而秃尖长低于CK。2年试验中, TGA处理提高了JNK728穗长、穗粒数和千粒重, 尤其是2019年在TGA2处理下, JNK728穗长比CK显著增长5.2%, 穗粒数显著增加6.0%, 千粒重显著提高7.8%; 与之相似, TGA2处理下, ZD909穗粒数和千粒重显著大于CK, 较CK增加5.9%和3.3%; 2018年, ZD909在TGA2处理下穗粒数显著高于CK, 较CK提高5.5%, 千粒重无显著差异, JNK728在TGA2处理下穗长和穗粒数较CK增加2.6%和3.4%。2年试验中, 在TGA2处理下, JNK728秃尖长分别比CK减小21.9%和34.1%, 且差异达显著水平; 与之不同的是, TGA处理对ZD909秃尖长均无显著性差异。
2.2 TGA对玉米光合生产特性的影响
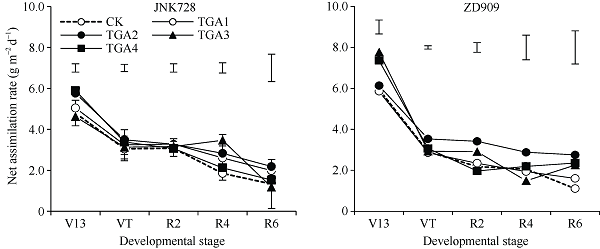
2.2.1 净同化速率(NAR) 图2所示, TGA处理提高了玉米的净同化速率(NAR)。JNK728在TGA处理下, 整个生育期的平均NAR较CK提高了12.5%~31.6%, 其中, TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK提高31.6%, 在V13和R4期, TGA2处理显著大于CK; ZD909在TGA处理下, 整个生育期的平均NAR较CK提高了8.7%~54.1%, 在TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK提高54.1%, 在V13、VT、R2期, TGA2处理显著大于CK。2个品种玉米NAR均在TGA2处理下平均增幅最大, 整个生育期中R6期增幅最大, 较CK增加了64.0%和149.2%。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图22019年TGA对2个品种玉米净同化速率的影响
CK: 对照; TGA1、TGA2、TGA3、TGA4分别代表TGA施用量为75、150、225和300 g hm-2, 图中竖线表示处理间LSD0.05值; V13、VT、R2、R4和R6分别表示玉米的大口期、开花吐丝期、乳熟期、蜡熟期和收获期。
Fig. 2Effects of different TGA treatment on NAR of two varieties of maize in 2019
CK: control; TGA1, TGA2, TGA3, TGA4 denote the TGA application rate of 75, 150, 225, and 300 g hm-2, respectively. Vertical bars represent the LSD0.05 value; V13, VT, R2, R4, and R6 denote the maize of trumpeting, silking stage, milk stage, dough stage, and maturity stage, respectively.
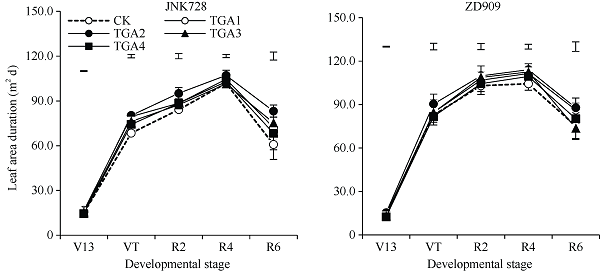
2.2.2 光合势(LAD) 图3所示, TGA处理提高了玉米光合势(LAD)。在VT~R6期, JNK728和ZD909在TGA处理下, LAD较CK分别平均增加了5.8%~16.9%和0.6%~10.9%, 其中, TGA2下增幅最大, JNK728和ZD909相比CK分别增加16.9%和10.9%。2个品种玉米均在R6期光合势增幅最大, 显著大于CK, 较CK增加36.7%和16.6%。
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图32019年TGA对2个品种玉米群体光合势的影响
缩写和处理同
Fig. 3Effects of different TGA treatment on LAD of two varieties of maize in 2019
Abbreviations and treatments are the same as those given in
2.2.3 穗位叶净光合速率(Pn) 表2所示, 在TGA处理下, 2个品种玉米在花期和蜡熟期的净光合速率(Pn)均大于CK。花粒期, JNK728在TGA处理下较CK增加15.4%~32.4%, 其中, TGA2处理下增幅最大, 相比CK增加32.4%; ZD909在TGA1、TGA2、TGA3处理下较CK增加19.1%~30.5%, 在TGA4处理下降低6.2%, TGA2处理下较CK增加30.5%, 增幅最大; 蜡熟期, JNK728在TGA1~ TGA4处理下较CK增加29.6%~77.8%, 在TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK增加77.8%; ZD909在TGA1~TGA3处理下较CK增加8.0%~57.5%, 在TGA4处理下却降低8.5%, TGA2处理下较CK增加57.5%, 增幅达最大。
Table 2
表2
表22019年TGA对2个品种玉米穗位叶净光合速率的影响
Table 2
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 花粒期 Silking stage | 增幅 Growing rate (%) | 蜡熟期 Dough stage | 增幅 Growing rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 京农科728 | CK | 24.9±4.7 b | — | 12.9±2.7 b | — |
| JNK728 | TGA1 | 28.7±5.0 ab | 15.3 | 16.7±2.0 ab | 29.5 |
| TGA2 | 33.0±0.3 a | 32.5 | 23.0±1.3 a | 78.3 | |
| TGA3 | 31.7±0.3 ab | 27.3 | 18.7±0.3 ab | 45.0 | |
| TGA4 | 28.8±4.4 ab | 15.6 | 16.8±1.4 ab | 30.2 | |
| 中单909 | CK | 23.6±5.8 b | — | 18.6±4.3 b | — |
| ZD909 | TGA1 | 28.6±3.4 ab | 21.2 | 20.1±8.1 b | 8.1 |
| TGA2 | 30.8±4.2 a | 30.5 | 29.3±4.0 a | 57.5 | |
| TGA3 | 28.2±0.8 ab | 19.5 | 22.7±3.6 ab | 22.0 | |
| TGA4 | 22.2±1.7 b | -5.9 | 17.0±4.0 b | -8.6 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 TGA对玉米叶片叶绿素和可溶性蛋白含量的影响
2.3.1 叶绿素含量 图4所示, 2个品种玉米在TGA处理后, 叶片叶绿素含量均高于CK。整个生育期, JNK728在TGA处理下较CK平均增加8.5%~19.7%, 其中, TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK增加19.7%, 在V7~R6期叶绿素含量均显著大于CK; ZD909在各TGA处理下分别平均增加7.1%~14.3%, TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK增加14.3%, TGA2处理下, ZD909在各个时期均显著大于CK。图4
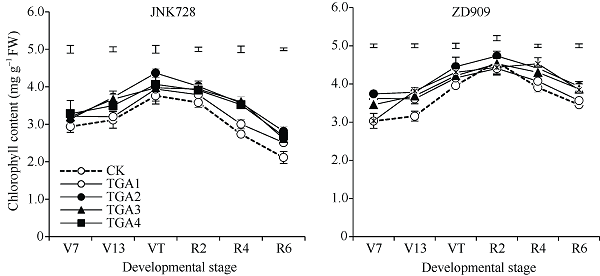 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图42019年TGA处理对2个品种玉米叶片叶绿素含量的影响
V7: 拔节期。缩写和处理同
Fig. 4Effects of different TGA treatment on the concentration of chlorophyll of two varieties of maize leaves in 2019
V7: jointing stage. Abbreviations and treatments are the same as those given in
2.3.2 可溶性蛋白含量 图5所示, 整个生育期, JNK728在TGA处理下较CK平均增加11.8%~22.7%, 其中TGA2处理下增幅最大, 相比CK增加22.7%, 在V7、V13、VT、R4和R6期, TGA2处理可溶性蛋白含量显著大于CK; ZD909在TGA处理下较CK平均增加8.8%~18.7%, TGA2下增幅最大, 相比CK增加18.7%, 在V7、V13、R2、R6期, TGA2处理显著大于CK。
图5
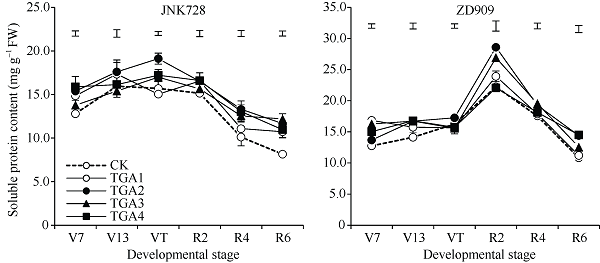 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图52019年TGA处理对2个品种玉米叶片可溶性蛋白含量的影响
V7: 拔节期。缩写和处理同
Fig. 5Effects of different TGA treatment on the concentration of soluble protein of two varieties of maize leaves in 2019
V7: jointing stage. Abbreviations and treatments are the same as those given in
2.3.3 叶片衰老速率 图6所示, TGA处理下, 2个品种玉米叶片衰老速率显著降低, 在R2~R6期, JNK728和ZD909较CK分别平均降低了0.01%~56.5%和31.7%~55.9%, 2个品种玉米均在TGA2下叶片衰老速率最低, 较CK平均降低56.5%和55.9%, 在R6期, JNK728在TGA2处理下显著低于CK, 而ZD909则在R4和R6期, TGA2处理下均显著低于CK。
图6
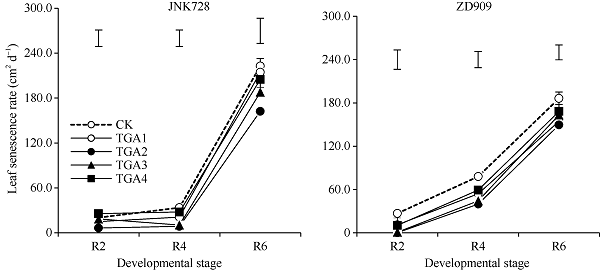 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图62019年TGA处理对2个品种玉米叶片衰老速率的影响
缩写和处理同
Fig. 6Effects of different TGA treatment on the leaf senescence rate of two varieties of maize in 2019
Abbreviations and treatments are the same as those given in
2.4 TGA对玉米籽粒灌浆特性的影响
表3所示, 相比CK, TGA处理提高了籽粒最大灌浆速率(Vmax)和最大灌浆率下的籽粒干重(Wmax), 其中JNK728的Vmax和Wmax较CK平均分别增加4.0%~5.2%和4.5%~16.4%; 相比之下, ZD909的Vmax较CK平均增加2.6%~10.0%, Wmax在TGA1和TGA2处理下较CK增加2.8%~6.8%, 而在TGA3和TGA4处理下低于CK。在TGA处理下, 2个品种玉米达到最大灌浆速率需要的天数(Tmax)均高于CK, 但JNK728的有效灌浆天数(D)低于CK处理, 而ZD909 D值除TGA1处理外均高于CK处理。Table 3
表3
表32019年TGA处理对2个品种玉米籽粒灌浆特征参数的影响
Table 3
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 灌浆速率最大时 籽粒干重 Wmax (mg) | 达到最大灌浆速率 需要的天数 Tmax (d) | 最大灌浆速率 Vmax (mg kernel-1 d-1) | 有效灌浆天数 D (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 京农科728 | CK | 167.5 | 22.1 | 11.0 | 46.8 |
| JNK728 | TGA1 | 174.4 | 24.1 | 11.5 | 45.3 |
| TGA2 | 176.1 | 24.0 | 12.1 | 43.6 | |
| TGA3 | 175.1 | 23.3 | 12.6 | 41.7 | |
| TGA4 | 174.2 | 22.8 | 12.8 | 40.7 | |
| 中单909 | CK | 145.4 | 24.0 | 10.3 | 43.5 |
| ZD909 | TGA1 | 149.2 | 24.1 | 11.0 | 40.8 |
| TGA2 | 154.8 | 25.1 | 10.6 | 43.7 | |
| TGA3 | 160.0 | 26.0 | 9.8 | 48.8 | |
| TGA4 | 157.3 | 26.3 | 9.4 | 50.0 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.5 TGA处理下玉米主要指标间的相关性分析
表4所示, 在TGA处理下, 玉米产量与净同化速率(0.73*)呈显著正相关, 与净光合速率(0.79**)呈极显著正相关, 与叶片衰老速率呈极显著负相关(-0.91**), 表明TGA通过调控玉米生育期内光合生产特性指标来影响产量, 净光合速率提高, 而叶片衰老速率明显降低, 促进光合产物的合成, 为后期光合产物向籽粒中转移及粒重的增加奠定基础。由于叶绿素含量与可溶性蛋白含量(0.98**)呈极显著正相关, 表明叶绿素的合成与可溶性蛋白含量密切相关, 同时叶片衰老速率与叶绿素含量(-0.63*)呈显著负相关, 表明叶绿素含量和可溶性蛋白含量的提高抑制了叶片的衰老, 而叶片衰老速率与净光合速率(-0.91**)呈极显著负相关, 与净同化速率(-0.76*)呈显著负相关。Table 4
表4
表4TGA处理下产量和其他参数的相关性分析
Table 4
| 指标 Item | 产量 Yield | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 净同化速率 Net assimilation rate | 光合势 Leaf area duration | 叶片衰老速率 Leaf senescence rate | 净光合 速率 Pn | 灌浆速率 Grain filling rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield | 1.00 | |||||||
| 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 0.58 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 0.56 | 0.98** | 1.00 | |||||
| 净同化速率 NAR | 0.73* | 0.58 | 0.63* | 1.00 | ||||
| 光合势 LAD | 0.62 | 0.93** | 0.93** | 0.56 | 1.00 | |||
| 叶片衰老速率 Leaf senescence rate | 0.91** | -0.63* | -0.55 | -0.76* | -0.59 | 1.00 | ||
| 净光合速率 Pn | 0.79** | 0.64* | 0.49 | 0.73* | 0.64 | -0.91** | 1.00 | |
| 灌浆速率 Grain filling rate | 0.15 | -0.55 | -0.58 | -0.12 | -0.51 | -0.087 | 0.27 | 1.00 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
3.1 TGA对玉米产量的调控效应
植物生长调节剂作为植物外源生长物质的一种, 通过调控植物内源激素含量影响植物整体生长发育的各种生理代谢指标, 从而提高植株抗逆性及产量[21]。植物生长调节剂能够明显提高玉米功能叶叶绿素含量和光合速率, 延长叶片功能期, 促进功能叶光合产物的合成与积累, 从而利于玉米籽粒产量和品种的提高[22,23,24,25,26,27,28]。高浓度的冠菌素、脱落酸等植物生长调节剂对作物的生长有抑制作用, 而低浓度则表现为促进效应[20,29-30]。本研究发现, TGA处理对2个品种玉米产量的影响具有与其他植物生长调节剂相同的剂量效应, 随TGA施用量的增加, 产量呈先增加后减小的趋势, 表明适宜施用量的TGA处理显著降低玉米果穗秃尖长度, 增加穗粒数和千粒重, 从而提高产量。玉米籽粒灌浆速率与灌浆持续期长短决定了最终籽粒产量, 在玉米灌浆的中后期, 调控籽粒灌浆特性是实现玉米高产的重要途径。灌浆速率和灌浆过程持续天数均与粒重显著相关[31,32]。在本研究中, 由于灌浆中期是籽粒建成的关键时期, TGA处理提高了2个品种玉米在灌浆中期的灌浆速率, 虽然ZD909有效灌浆天数低于CK, 但2个品种玉米的最大灌浆速率和最大灌浆速率持续时间均大于CK, 从而提高了后期籽粒干重。同一品种产量在2年试验中差异较大, 但各处理间产量变化趋势一致, 综合气象数据分析发现, 可能是因为2018年花粒期(VT期)到灌浆初期(R2期)的高温少雨天气, 2018年播种后45 d到播种后60 d期间日平均温度均高于2019年, 影响部分雌穗小花分化和授粉情况, 从而影响穗粒数、千粒重和产量, 总体产量明显较2019年降低。
3.2 TGA对玉米光合生产特性的调控效应
玉米生长后期是玉米产量形成的关键时期, 叶片作为光合产物的主要合成器官, 为籽粒源源不断的输送同化物, 叶片衰老导致光合能力下降, 严重制约玉米有机物的积累, 对玉米产量影响很大[18]。叶片叶绿素含量是衡量叶片衰老和光合功能的重要指标, 叶绿素含量的高低决定了叶片光合速率的大小[33]。本研究中TGA处理下2个品种玉米叶片叶绿素含量明显大于对照处理(CK), 尤其是在玉米灌浆后期, 功能叶叶绿素含量的下降幅度远低于CK。植物细胞中大部分蛋白质都位于叶绿体中, 叶绿体中的Rubsico有30%都是可溶性蛋白, 同时也是光合作用中的关键酶, 与蛋白质降解和叶绿素含量降低有着直接联系[34,35]。叶衰老过程中Rubisco含量的下降是叶片衰老的主要特征[36], TGA处理下, 玉米叶片可溶性蛋白含量较CK上升, 叶片可溶性蛋白含量和叶绿素含量的降解速率较CK减缓, 从而防止玉米叶片后期的衰老。相关性分析表明, 可溶性蛋白含量和叶绿素含量均与叶片衰老速率呈显著负相关, TGA提高了叶片叶绿素含量和可溶性蛋白含量, 抑制单株玉米叶片的衰老, 使玉米在花期之后, 黄叶面积减少, 衰老速率降低。叶片是玉米的主要光合器官, 灌浆期内保持较高的光合速率是获得高产的必备条件[37,38]。在TGA处理下, 2个品种玉米穗位叶净光合速率在花期和蜡熟期均大于CK, 只有ZD909在TGA4施用量下略低于CK, 表明较高施用量下会降低叶片净光合速率, 而在TGA2施用量下均显著高于其他TGA处理, JNK728和ZD909平均分别较CK增加28.0%和29.8%。光合势(LAD)是量化作物群体光合特性的重要指标, 在一定范围内, LAD越大, 群体光能利用率越高, 积累干物质也越多[39]; 而净同化速率(NAR)是植物在一定时期内通过光合作用所积累的干物质量, 是衡量光合能力的重要指标之一[40]。相关性分析表明, 玉米净光合速率与LAD、NAR呈显著正相关, LAD和NAR与生物产量有显著正相关关系, 这与王方瑞的研究结果一致[18]。同时, 玉米产量又与叶片衰老速率呈极显著负相关, 与NAR呈显著正相关, 与净光合速率呈极显著正相关, 说明TGA通过调控玉米生育期内光合生产特性指标来影响产量, 可能是因为TGA处理提高了叶片叶绿素含量和可溶性蛋白含量, 叶片衰老速率降低, 相比CK促进了光合作用, 单株叶片净光合速率提高, 有效光合时间延长, LAD提高, 促进光合产物的合成, 净同化速率显著增大, 为后期光合产物向籽粒中转移及粒重的增加奠定基础。
4 结论
四甲基戊二酸(TGA)对玉米产量及光合生产特征的调控具有明显的剂量效应, 适宜TGA施用量(150 g hm-2)提高玉米群体光合势和净光合速率, 显著增加穗粒数、千粒重和玉米单产。其主要的作用机制是适宜剂量的TGA提高了玉米生育期叶绿素含量和可溶性蛋白含量, 抑制生育后期叶片衰老, 使生育后期光合生产能力增强, 促进了灌浆期光合同化物的积累, 保证了叶片源器官光合产物的供应。因此, TGA适宜作为华北地区夏玉米提质增效的化控技术进行推广应用。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2008.06.011URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.4141/cjps78-126URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2134/agronj1988.00021962008000060004xURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.05.008URLPMID:26057699 [本文引用: 1]

The photosynthetic characteristics of developing leaves of plants grown under artificial conditions are, to some extent, regulated systemically by mature leaves; however, whether systemic regulation of photosynthesis occurs in field-grown crops is unclear. To explore this question, we investigated the effects of planting density on growth characteristics, gas exchange, leaf nitrogen concentration and chlorophyll a fluorescence in field-grown sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Our results showed that close planting resulted in a marked decline in light intensity in lower canopy. Sorghum plants grown at a high planting density had lower net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), and transpiration rate (E) than plants grown at a low planting density. Moreover, in the absence of mineral deficiency, close planting induced a slight increase in leaf nitrogen concentration. The decreased photosynthesis in leaves of the lower canopy at high planting density was caused mainly by the low light. However, newly developed leaves exposed to high light in the upper canopy of plants grown at high planting density also exhibited a distinct decline in photosynthesis relative to plants grown at low planting density. Based on these results, the photosynthetic function of the newly developed leaves in the upper canopy was not determined fully by their own high light environment. Accordingly, we suggest that the photosynthetic function of newly developed leaves in the upper canopy of field-grown sorghum plants is regulated systemically by the lower canopy leaves. The differences in systemic regulation of photosynthesis were also discussed between field conditions and artificial conditions.
DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.19.006URL [本文引用: 1]

2014—2015年,在大田条件下,采用裂-裂区试验设计,以不同株型玉米品种为主区,氮素(N1:0,N2:90 kg N·hm-2和N3:180 kg N·hm-2)为裂区、密度(D1:45 000 株/hm2,D2:60 000 株/hm2和D3:75 000 株/hm2)为裂裂区,测定了植株形态、叶片光合性能和产量等指标。【结果】施氮对节间长度、叶倾角、叶色值、粒重和产量的影响程度均高于密度调控,茎粗、光合速率和穗粒数对增密响应程度较高。与平展型玉米相比,紧凑型玉米茎粗随密度提高降幅较小,第1—3节间长度对增密响应迟钝,随施氮量增加显著缩短(PN2→N3=0.004—0.028),第4—5节间长度对增密的负响应幅度(10.9%)均高于平展型玉米同节间长度对其的正响应幅度(3.3%)。施氮可降低紧凑型玉米棒三叶叶倾角2.9°±1.1°,增密后,其穗下叶叶倾角降幅较高。紧凑型玉米叶色值对施氮量的响应峰值(N3)高于平展型玉米(N2),增密对其光合速率的负效应相对较小,在N3和D3处理下,其叶色值和光合速率均高于平展型玉米。紧凑型玉米穗粒数与粒重受氮密调控影响比平展型玉米小,其收获指数较高,且在氮/密处理间差异均不显著(PN1→N3 =0.16,PD1→D3 =0.12),而平展型玉米在氮/密处理间差异均达显著或极显著水平(PN1→N3 =0.03,PD1-D3<0.01)。紧凑型玉米和平展型玉米分别在N3D3和N3D1处理下获得较高产量,增密和施氮对其籽粒产量的贡献比分别是1﹕2.3和1﹕4.0。【结论】与平展型玉米相比,紧凑型玉米茎基部横/纵向生长对氮密协同提高具有较强的适应能力,施氮可降低紧凑型玉米棒三叶叶倾角,提高穗位叶光合性能。紧凑型玉米在高密高氮处理下较好的形态生理协调性保证了生育后期相对较高的物质转化效率,最终获得较高群体产量。]]>
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/nature08122URLPMID:19553990 [本文引用: 1]

Plant growth and development is regulated by a structurally unrelated collection of small molecules called plant hormones. During the last 15 years the number of known plant hormones has grown from five to at least ten. Furthermore, many of the proteins involved in plant hormone signalling pathways have been identified, including receptors for many of the major hormones. Strikingly, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway plays a central part in most hormone-signalling pathways. In addition, recent studies confirm that hormone signalling is integrated at several levels during plant growth and development.
DOI:10.5846/stxb201212101773URL [本文引用: 1]

试验于2010-2011年在黑龙江省3个积温带哈尔滨市(Ⅰ)、绥化市(Ⅱ)、依安县(Ⅲ)的试验站进行,以郑单958和丰单3号为材料,研究大田条件下温度差异对花后玉米穗位叶氮同化及产量的影响与化学调控剂——聚糠萘水剂(PASP-KT-NAA, PKN)的调控效应。结果表明:(1)硝酸还原酶活性(Nitrate Reductase Activity, NRA)、硝态氮、叶绿素、叶片氮含量表现为Ⅰ > Ⅱ > Ⅲ;可溶性蛋白与游离氨基酸含量花后0-10 d表现为Ⅲ高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ;在花后30-40 d 游离氨基酸Ⅰ高于Ⅱ、Ⅲ;PKN处理提高NRA、硝态氮、叶绿素、叶片氮含量、可溶性蛋白和游离氨基酸含量。(2) 玉米产量均表现为Ⅰ > Ⅱ > Ⅲ,郑单958产量均高于丰单3号;PKN处理后,玉米产量均高于清水对照,其中郑单958化控处理(Zhengdan treatment, ZDTR)在Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ的增产幅度分别为为3.09%-8.81%,4.61%-10.91%,5.91%-13.51%;丰单3号化控处理(Fengdan treatment, FDTR)在Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ的增产幅度为2.43%-5.19%,3.03%-6.01%,2.57%-4.62%。PKN处理提高了3个积温带玉米穗位叶片氮同化关键酶活及其产物含量,促进低温条件下氮同化正常进行,最终提高产量。
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

选用高蛋白品种KB008(KB008)、高脂肪品种花17(H17)和高油酸/亚油酸(O/L)品种农大818(818),在大田栽培条件下,研究了盛花后期叶面喷施多效唑(PBZ)对不同品质类型花生产量、品质及相关碳、氮代谢酶活性的影响.结果表明:喷施PBZ显著增加了3种品质类型花生荚果产量,原因是增加了单株结果数,降低了千克果数而提高了双仁果率.喷施PBZ不同程度地提高了3种类型花生籽仁脂肪和可溶性糖含量,降低了蛋白质含量,显著增加了高脂肪品种H17的O/L值.PBZ使高O/L值品种818的脂肪含量增加显著,同时其蛋白质含量显著降低,而对其他两品种的蛋白质和脂肪含量影响较小.喷施PBZ均降低了3种类型花生结荚期叶片硝酸还原酶(NR)活性及结荚期和饱果期叶片谷氨酰胺合成酶和谷氨酸脱氢酶活性,818的3种酶活性降低幅度最大,KB008和H17的酶活性降幅较小;喷施PBZ均降低了3种类型花生结荚期和饱果期叶片谷草转氨酶和谷丙转氨酶活性.说明氮代谢酶活性的降低是喷施PBZ降低3种类型花生籽仁蛋白质含量的主要原因.喷施PBZ均提高了3品种结荚期和饱果期叶片蔗糖合成酶和磷酸蔗糖合成酶活性,其中显著提高了818的2种酶活性,而对KB008和H17的活性提高不显著;喷施PBZ提高了3品种结荚期和饱果期的磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶和1,5-二磷酸核酮糖羧化酶活性,其中对818在结荚期的活性提高最显著,对H17活性提高较小.碳代谢酶活性的增强是喷施PBZ提高花生籽仁脂肪含量的生理基础.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
MS Thesis of Northwest A&F University,
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
北京: 中国农业出版社,
[本文引用: 1]
Beijing: China Agriculture Press,
[本文引用: 1]
南京农业大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 3]
MS Thesis of Nanjing Agricultural University,
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2017.05.027URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.93007URL [本文引用: 2]

-1)处理显著降低玉米果穗秃尖长度, 增加穗粒数和千粒重, 提高籽粒灌浆速率, 延长灌浆持续期, 提高产量。此外, 适宜浓度COR处理显著提高玉米籽粒灌浆过程中淀粉合成相关酶AGPase、SSS、GBSS和SBE的活性, 上调淀粉合成关键酶基因ZmSH1、ZmSH2、ZmWX1和ZmAE1的表达量, 促进籽粒支链淀粉、直链淀粉和总淀粉的积累, 提高了籽粒淀粉含量。研究结果明确了COR对玉米籽粒形态建成与物质积累的调控效应, 为玉米增产增效栽培提供了新的技术手段。]]>
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
湖南农业大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
MS Thesis of Hunan Agricultural University,
[本文引用: 1]
湖南农业大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
MS Thesis of Hunan Agricultural University,
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
黑龙江八一农垦大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
MS Thesis of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,
[本文引用: 1]
西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
MS Thesis of Northwest A&F University,
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/jac.2008.194.issue-5URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00145-9URL [本文引用: 1]
南京农业大学博士学位论文,
[本文引用: 1]
PhD Dissertation of Nanjing Agricultural University,
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/ppl.1997.101.issue-4URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2003.12.006URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/jxb/err061URL [本文引用: 1]

The genetic variability of the duration of leaf senescence during grain filling has been shown to affect both carbon and nitrogen acquisition. In particular, maintaining green leaves during grain filling possibly leads to increased grain yield, but its associated effect on grain protein concentration has not been studied. The aim of this study was to dissect the genetic factors contributing to correlations observed at the phenotypic level between leaf senescence during grain filling, grain protein concentration, and grain yield in winter wheat. With this aim in view, an analysis of quantitative trait locus (QTL) co-locations for these traits was carried out on a doubled haploid mapping population grown in a large multienvironment trial network. Pleiotropic QTLs affecting leaf senescence and grain yield and/or grain protein concentration were identified on chromosomes 2D, 2A, and 7D. These were associated with QTLs for anthesis date, showing that the phenotypic correlations with leaf senescence were mainly explained by flowering time in this wheat population. Study of the allelic effects of these pleiotropic QTLs showed that delaying leaf senescence was associated with increased grain yield or grain protein concentration depending on the environments considered. It is proposed that this differential effect of delaying leaf senescence on grain yield and grain protein concentration might be related to the nitrogen availability during the post-anthesis period. It is concluded that the benefit of using leaf senescence as a selection criterion to improve grain protein concentration in wheat cultivars may be limited and would largely depend on the targeted environments, particularly on their nitrogen availability during the post-anthesis period.
URL [本文引用: 1]

研究通过3年试验,证明了玉米群体冠层特征及群体内光分布和光合效率随种植密度和施N量而有明显变化。叶面积大小是导致冠层特征变化的主导因子。平展型单交种丹玉13的籽粒产量高限出现在最大LAI变化于4.10-4.7之间,其冠层垂直方向上最大叶面积密度趋于由中部向中上部推移。叶片倾角和消光系数调节幅-于明显增加,光合速率、
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
