摘要/Abstract
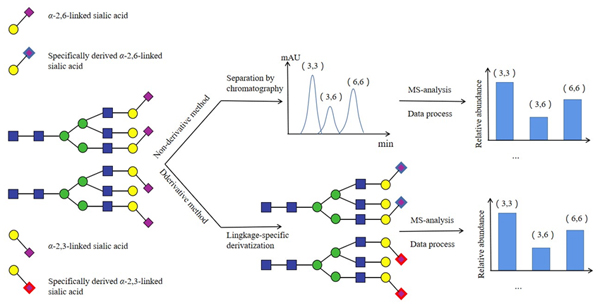
蛋白质在翻译过程中、翻译过程后会发生糖基化. 糖基化会以直接或间接的方式影响蛋白质的功能及其相互作用, 并与多种人类疾病有关, 其中, 唾液酸化N-糖链在一些重要的生理和病理过程中发挥关键作用. 已知的唾液酸与相邻单糖之间的连接方式包括α-2,3-、α-2,6-、α-2,8-、α-2,9-连接, 连接方式不同的唾液酸化N-糖链在细胞活动、生命体的生理和病理过程中的功能往往不同. 质谱技术是分析N-糖链的重要工具, 它能够快速和灵敏地检测N-糖链, 通过将色谱技术以及衍生化方法等与质谱联用可以实现对唾液酸化N-糖链及其连接异构体的分离和检测. 本文主要围绕α-2,3-和α-2,6-连接的唾液酸化N-糖链进行综述, 介绍它们的结构和在细胞活动及疾病中不同的功能, 并综述近年来基于质谱的唾液酸化N-糖链的连接异构体分析方法以及这些方法在生物医学领域的应用, 并对未来的生物医学研究提供新的思路和途径.
关键词: N-糖链, 唾液酸, 质谱, 衍生化, 异构体分离
Protein glycosylation occurs during and after the translation process, and glycosylation will diversify the function of the protein. Glycosylation directly or indirectly affects the function of proteins and their interactions, and is related to a variety of human diseases. Among them, sialylated N-glycans play a key role in many important physiological and pathological processes. Sialic acid usually bonds with adjacent monosaccharides via α-2,3-, α-2,6-, α-2,8- or α-2,9- linkage. Sialylated N-glycans with different linkage always have different functions in cell activities, physiological and pathological processes of living organisms. Mass spectrometry is an important tool for the analysis of N-glycans. It can quickly and sensitively detect N-glycans. The separation and detection of sialylated N-glycans and their linked isomers can be achieved by combining chromatographic techniques and derivatization methods with mass spectrometry. In this review, we mainly focuses on α-2,3- and α-2,6-linked sialylated N-glycans, introduces their structure and different functions in cell activities and various diseases, and summarizes the analysis methods of linked isomers of sialylated N-glycans based on mass spectrometry and the application of these methods in the field of biomedicine in recent years. This review can provide new ideas and approaches for future biomedical research.
Key words: N-glycan, sialic acid, mass spectrometry, derivatization, isomeric separation
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
