摘要/Abstract
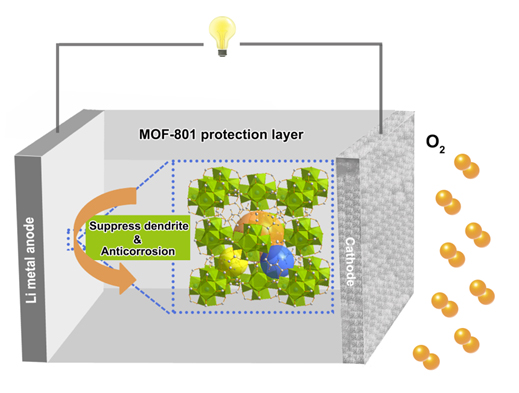
在众多能源储存系统中,锂氧气电池以其高达3500 Wh·kg-1的理论能量密度有望在性能上超越商用锂离子电池.然而,在电池充放电过程中,金属锂不可控的枝晶生长和严重的腐蚀问题极大地阻碍了锂氧气电池的发展.为了解决以上问题,制备了一种具有高比表面积、丰富孔道结构的金属有机框架材料(MOF-801),并将其设计成金属锂负极的保护层应用在锂氧气电池中.在本工作中,成功合成了具有高达762.9 m2·g-1比表面积,边长约为800 nm的立方体状纯净MOF-801材料.并且这种材料表现出对于有机电解液体系(四乙二醇二甲醚1 mol·L-1三氟甲基磺酸锂)和强还原性的金属锂都具有很好的稳定性.得益于该材料丰富的孔道结构以及高比表面积,锂离子得以更均匀地分布在电极表面促进金属锂均匀沉积,有效避免了由于枝晶刺破隔膜而导致的短路甚至火灾事故.此外,MOF-801保护层本身的阻隔作用和材料捕捉水的特性可以帮助减少污染物质(水、氧气、强氧化性物质等)的穿梭效应带来的副反应,缓解锂氧气电池中金属锂负极的腐蚀情况.因此,将经过保护的金属锂组装成的对称电池进行测试,循环寿命长达800 h,同时充/放电过电势仅为0.023 V(未经保护的电池寿命仅为254 h,最终充/放电过电势高达5 V),且循环阻抗大大降低,证明了这种策略有效地稳定了金属锂/电解液界面.将经过MOF材料保护的电极实际应用在锂氧气电池中,在限容量1000 mAh·g-1,限电流500 mA·g-1条件下,可以实现长达170圈的稳定长寿命的循环(是未经保护的电池寿命的2.88倍).使用MOF-801保护层的锂氧气电池还表现出了高达8935 mAh·g-1的高比容量.因此,本工作所报道的保护层策略为未来的碱金属空气电池负极保护领域提供了新颖的视角.
关键词: 锂氧气电池, 金属锂负极, 金属有机框架材料, 枝晶抑制, 金属锂腐蚀
Among the numerous successors of Li-ion batteries, Li-O2 cells become promising candidates because of their higher theoretical energy density (3500 Wh·kg-1). However, the uncontrolled dendrite growth and serious corrosion issues of lithium metal anode are major bottlenecks for practical application of Li-O2 batteries. To solve the above challenges, herein, we prepared metal-organic frameworks materials (MOF-801) with high specific surface area and abundant pores as a protection layer on lithium metal anode in Li-O2 batteries. In this manuscript, pure and cubic-shaped MOF-801 materials are successfully synthesized and the high specific surface area (762.9 m2·g-1) is confirmed. And MOF-801 is verified stable enough as a protection layer towards lithium metal anode and tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether (TEGDME) 1 mol·L-1 LiCF3SO3 electrolyte system. Due to the rich pore structures and high specific surface area, MOF-801 can assist to form uniform Li+ flux and dendrite-free lithium deposition morphology can be confirmed in the scanning electron microscope images, which can avoid the short circuit even fire disaster from the uncontrollable dendrite growth. Besides, the shield effect as well as the water capture function of MOF-801 protection layer can also effectively prevent serious side reactions from the shuttle effect of the contaminants (H2O, O2 and strong oxidizing species). Consequently, this strategy enables stable electrode/electrolyte interface and achieves 800 h plating/stripping cycles under a low overpotential of 0.023 V. In contrast, the batteries without protection can only run for 254 h with the overpotential as high as 5 V at last. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results also verify that the much lower impedance of the lithium metal anode after protection. When applied in practical Li-O2 batteries with a fixed capacity of 1000 mAh·g-1 at a current density of 500 mA·g-1, stable and long-life cycle performance
(170 cycles) has been realized in the Li-O2 batteries with MOF-801 protection layer, which is 2.88 times longer than those without protection. The batteries with MOF-801 protection layer also deliver a high discharge specific capacity of 8935 mAh·g-1. This unique protection layer design strategy illustrates fresh insight towards protection strategy in alkali metal anode batteries.
Key words: Li-O2 battery, lithium metal anode, metal-organic frameworks, dendrite suppression, lithium corrosion
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
