摘要/Abstract
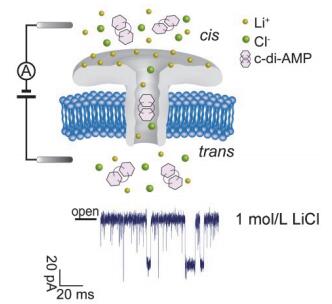
环二腺苷酸(c-di-AMP)是原核细胞中普遍存在的第二信使, 不仅能够有效调控细胞生长、离子转运、细胞壁代谢平衡等多种生理过程, 还能引发I型干扰素应答, 激发机体天然免疫反应. 本实验使用单个气单胞菌溶素(Aerolysin)纳米孔道蛋白构建的单分子界面, 对c-di-AMP进行单分子测量研究. 为提高Aerolysin纳米孔对带负电小分子化合物的测量灵敏度, 本实验利用LiCl为支持电解质, 有效屏蔽Aerolysin孔口表面负电荷, 减小c-di-AMP与Aerolysin纳米孔之间的静电排斥, 从而显著增强了Aerolysin纳米孔道对单个c-di-AMP分子的检测能力. 实验结果显示, 在90 mV电压下, 每分钟在LiCl中获得的有效穿孔事件的数量最高可达同条件KCl支持电解质的30倍, 且有效穿孔事件占总体事件的比例在不同电压下提升了7~11倍. 进一步表明, 使用LiCl支持电解质, 可有效增强Aerolysin孔道对带负电小分子化合物的测量灵敏度. 因此, 本研究实现了Aerolysin纳米孔道对单个环二核苷酸的高灵敏免标记检测, 有望为单分子水平上阐明新型免疫干扰机制提供新的分析方法.
关键词: 环二腺苷酸, 环二核苷酸, 气单胞菌溶素, 单分子界面, 生物纳米孔道
Cyclic di-AMP (c-di-AMP) is a ubiquitous second messenger in prokaryotic cells. c-di-AMP can not only effectively regulate various physiological processes such as cell growth, ion transport and cell wall metabolism balance, but also trigger type I interferon response to inspire the body's immune response. Nanopore-based single molecule detection technology is an emerging single molecule detection method which is currently applied to various fields since it has many advantages such as high speed, label-free, high sensitivity and low cost. Aerolysin is a robust biological nanopore with high temporal resolution and high current resolution, which has achieved single oligonucleotide detection, polysaccharide analysis and the studies of enzymolysis kinetics. Aerolysin nanopore is negatively-charged protein nanopore which has numerous negatively charged amino acid residues around its cis entrances. The electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged c-di-AMP and negatively charged amino acid residues around the cis entrances prevents c-di-AMP entering the nanopore. In this study, 1.0 mol/L LiCl was used as electrolyte solution to facilitate aerolysin analysis of single c-di-AMP molecule. Each event can be characterized by two parameters, the current blockade, I/I0, and the blockade time, τoff. The blockades are classified into two populations as PI and PII. The PI events are assigned to c-di-AMP that bump into the pore and then diffuse away. PII events are assigned to traversing of c-di-AMP through the nanopore. Compared with potassium ions, lithium ion can be more effectively to associate with the negative charges on the aerolysin nanopore surface and reduce the electrostatic repulsion between the c-di-AMP molecule and the Aerolysin. The results showed that number of PI events in per minute was significantly increased in 1.0 mol/L LiCl. The number of PI events in per minute in LiCl is 30 times than that in KCl at 90 mV. Hence, Aerolysin nanopore can be used as an ultrasensitive single molecule sensor for cyclic dinucleotides.
Key words: c-di-AMP, cyclic dinucleotides, aerolysin, single molecule interface, biological nanopores
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
