摘要/Abstract
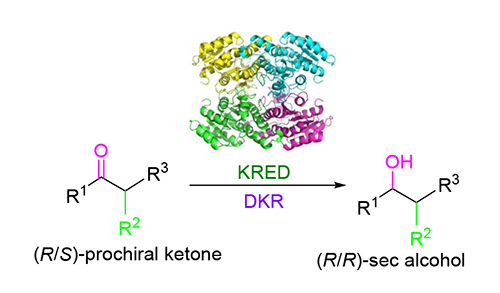
生物催化是不对称催化中制备手性药物的重要方法之一,具有化学、区域与高立体选择性的特点.随着DNA测序与合成技术以及蛋白工程技术的突破,研究者可以快速获得基础与应用研究所需要的酶.近年来,生物催化在不对称催化中的研究较为活跃.在广泛应用的生物催化剂中,羰基还原酶能够高立体选择性地还原羰基为单一手性中心的仲醇.当将羰基还原酶应用于动态动力学拆分时,可经一步还原,高立体选择性地制备含两个手性中心的仲醇.综述了其原理并梳理近十年的研究案例,最后尝试提供一种研究思路:筛酶-消旋-平衡,以期为基础与应用研究提供思路.
关键词: 不对称催化, 生物催化, 羰基还原酶, 动态动力学拆分
Biocatalysis is a basic method of asymmetric catalysis for preparing chiral Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, which owns several "green merits":chemo-, regio-and high enantioselectivity. As the development of DNA seqencing, DNA synthesis and protein engineering, suitable enzymes can be efficiently developed for basic researches and industrial applications. Biocatalysis has been keeping as a hot spot in asymmetric synthesis recently. Carbonyl reductases have been widely used for stereoselectively transforming ketones to chiral second alcohols with only one stereocenter. When combining with Dynamic Kinetic Resolution (DKR), the bioreaction with carbonyl reductases can efficiently construct chiral alcohols with two stereocenters in one step. This review highlights the method of its mechanism and nearly twenty examples from research papers and patents for one decade. We attempt to analyze and conclude the characteristics of this method based on chemical structures and enzymes. At last, a practical and developing research method is recommended in three steps:screening-racemization-balance in sequence. It is hoped to be useful for future basic researches and industrial applications.
Key words: asymmetric catalysis, biocatalysis, carbonyl reductases, dynamic kinetic resolution
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
