

东北大学 理学院, 辽宁 沈阳 110819
收稿日期:2020-07-13
基金项目:中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(N170504014)。
作者简介:于延华(1978-), 女, 湖北荆门人, 东北大学副教授, 博士。
摘要:利用曲面位置向量的正交分解式研究四维欧氏空间中的一类广义常斜坡曲面(即曲面的单位位置向量和单位平均曲率向量的內积为常数的曲面). 首先将曲面的位置向量分解为切部分和法部分, 然后对具有法平行和法部分是平均曲率向量特性的广义常斜坡曲面分别进行研究, 得到了在这两类特殊情况下广义常斜坡曲面的存在性及其分类.讨论了当分解式的法部分完全位于曲面的平均曲率向量方向时, 广义常斜坡曲面满足的表达式及相关性质, 并证明了在这种情况下曲面可以选取曲率网作为参数, 并且此时广义常斜坡面为一类特殊的曲面——陈氏面. 最后给出了这些曲面的一些例子, 并画出了在三维空间上的投影.
关键词:广义常斜坡曲面法平行陈氏面四维欧氏空间內积
Generalized Constant Slope Surfaces in E4
YU Yan-hua, JIA Kun


School of Sciences, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China
Corresponding author: JIA Kun, E-mail: 1458326297@qq.com.
Abstract: Generalized constant slope surfaces(GCSSs), whose inner product of the unit position vector and the unit mean curvature vector is constant, are studied in four dimension Euclidean space.Firstly, the position vector is divided into the tangent and normal parts. Then, two special GCSSs, one is that the parallel normal vector field has the mean curvature vector characteristics and the other is that the normal parts has the mean curvature vector characteristics, are studied, respectively, with the existence and classification of the two special GCSSs obtained. The expression and performance of a GCSS of which the normal plane is parallel to the mean curvature vector are discussed, proving that the GCSS can be parameterized with the principal lines and defined as a Chen surface.Finally, some examples of these surfaces and 3-D projection of the surfaces are given by MATLAB.
Key words: generalized constant slope surfaceparallel normal vector fieldChen surfaceE4inner product
一般螺线在生活中应用很广泛, 将一般螺线的性质推广到曲面上, 可得到常角曲面、常比值曲面和斜坡曲面. 常角曲面是单位法向量和固定方向成固定角的曲面[1-9]. 文献[4]研究了常角曲面在S2×R空间的分类. 文献[10]研究了常比值超曲面.文献[11]研究了广义常比值曲面. 斜坡曲面的位置向量和单位法向量成固定角, 几何意义更加突出. 文献[1]和文献[12]研究了欧氏空间和闵可夫斯基空间中斜坡曲面的分类.
本文主要在四维欧氏空间(E4)中讨论广义斜坡曲面: 单位平均曲率向量和单位位置向量的內积是定值的曲面.并对四维广义斜坡曲面进行了分类. 因为四维空间的不可视化, 本文利用MATLAB画出了四维空间曲面在三维空间中的投影.
1 预备知识令r(s, t): M2→E4是四维欧氏空间中的一个曲面, 且曲面M2的切平面为TM2, 则E4=TM2⊕T⊥M2, T⊥M2是切平面的正交补, 曲面的高斯和Weingarten公式[13]为
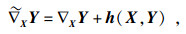 | (1) |
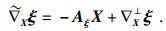 | (2) |
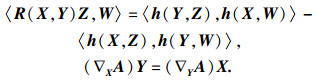 |
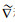
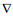
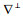
设{e1, e2, N1, N2}为E4中的标准正交基, 则曲面的高斯曲率和平均曲率向量为
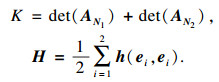 |
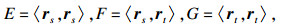 |
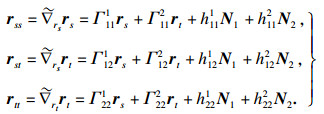 | (3) |
第二基本量为
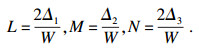 |
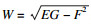
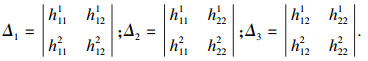 |
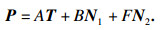 | (4) |
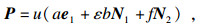 | (5) |
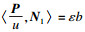
对于任意X∈TM2, 有
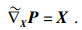 | (6) |
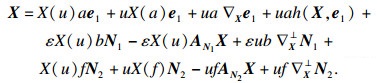 | (7) |
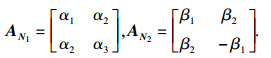 |
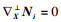
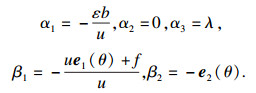 |
命题1 ??法平行条件下广义常斜坡曲面的Levi-Civita联络为
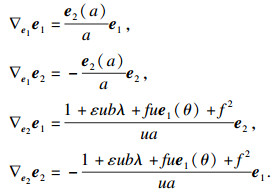 |
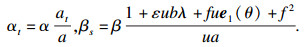 |
证明??由法平行的条件可知曲面应满足命题1和?t?sNi=?s?tNi, (i=1, 2), 直接计算可知, 只有当b=0的时候成立. 所以该曲面不存在.
4 f=0时的广义常斜坡曲面当f=0时, 曲面的法部分完全位于平均曲率向量方向, 此时位置向量可简化为
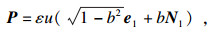 | (8) |
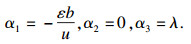 |
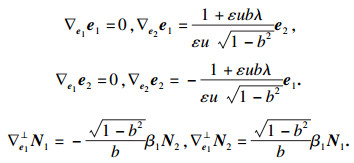 |
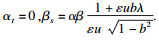
不失一般性, 选取α=1, 可得
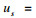
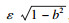
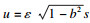
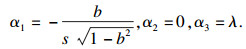 |
证明??由形状算子与ε无关, 可得高斯曲率和平均曲率向量也与ε无关.
定理2 ??当广义常斜坡曲面具有分解式(8)时, 曲面方程满足:
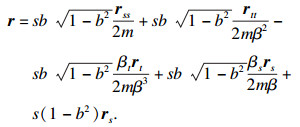 | (9) |
证明??必要性: 由式(7)可得如下的高斯方程(10):
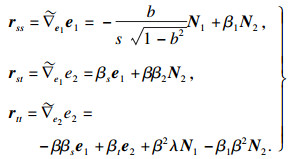 | (10) |
充分性: 由
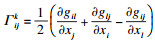
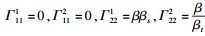
由式(3)和平均曲率向量定义, 可得
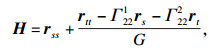 |
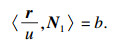 |
情况1:β1=β2=0, 直接计算得L=M=N=0, 则曲面上的点都是平点.此时曲面的法平面退化为共线的两个向量, 四维空间退化为三维空间[2].所以四维空间下的广义常斜坡曲面不存在.
情况2:β1=0, β2≠0, 可得M≠0, L=N=0, 这时广义常斜坡曲面是法平坦的. 由此可得:
命题4 ??具有分解式(8)的法平坦的广义常斜坡曲面是不存在的.
证明??由式(10), rst=βse1.曲面还应该满足Codazzi方程, 所以曲面不存在.
情况3:β1≠0, β2=0, 此时M=0, L≠0, N≠0, 又F=0, 这时曲面可以选择曲率网作为参数, 则有如下结论:
定理3 ??当具有分解式(8)的广义常斜坡曲面选择曲率网作为参数时, 该曲面为陈曲面.
证明??由陈曲面的定义[15]——曲面上的平均曲率向量场满足如下条件:
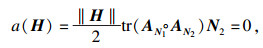 |
定理4 ??当具有分解式(8)的广义常斜坡曲面选择曲率网作为参数时, 曲面表达式为
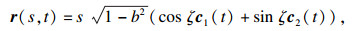 |
证明??必要性: 由式(10)得到r=s(1-b2)rs-s2(1-b2)rss, 解得
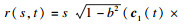
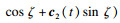
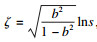
充分性: 由式(10), 且F=0, M=0, 可以算出
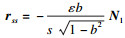
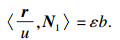 |
定理5 ??b=0时曲面为广义常斜坡曲面的充分必要条件为曲面表达式为r=sc1(t), 其中c1(t)是三维球曲线.
证明??充分性: 曲面F=0, M=0, 可得rtt=Γ221rs+Γ222rt+h221N1, 所以
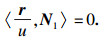 |
当b=1时, 式(7)表示的广义常斜坡曲面的方程为P=εuN1.
定理6 ??当b=1时, 广义常斜坡曲面是球面的一部分, 并且其平均曲率为-1/u.
证明??由P=εuN1可得〈rs, r〉=〈rt, r〉=0, 所以〈r, r〉=u是常数, 则曲面是三维球的一部分, 并且曲面的平均曲率为-1/u.
5 广义常斜坡曲面示例本节对一组K=0的广义常斜坡曲面进行画图讨论, 曲面方程为
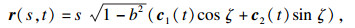 |
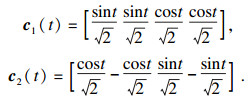 |
图 1(Fig. 1)
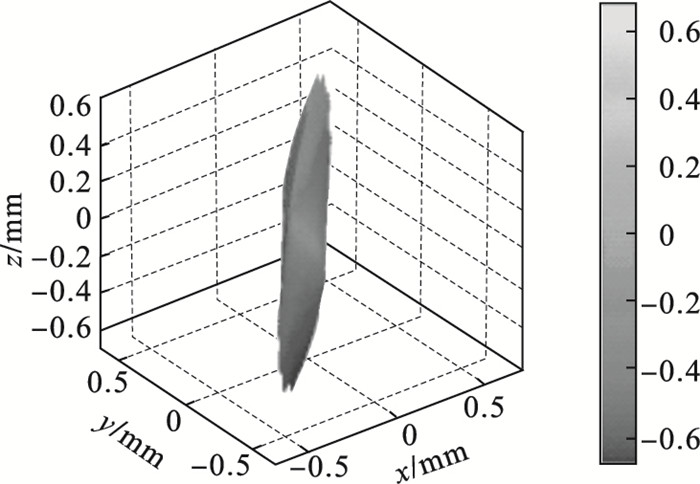 | 图 1 曲面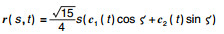 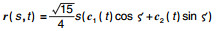 |
图 2(Fig. 2)
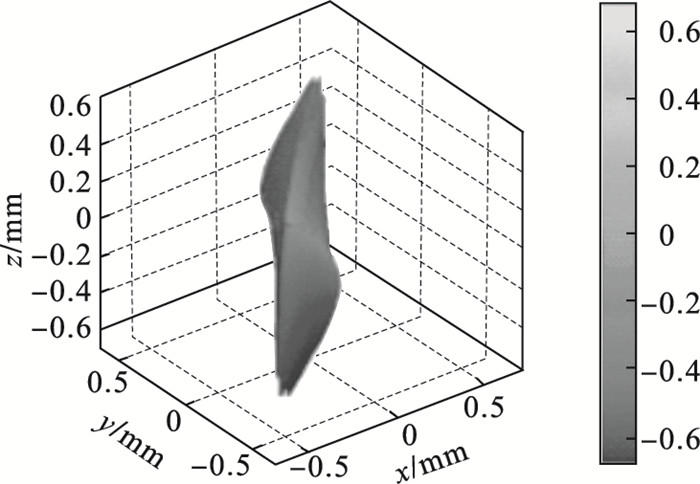 | 图 2 曲面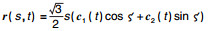 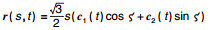 |
图 3(Fig. 3)
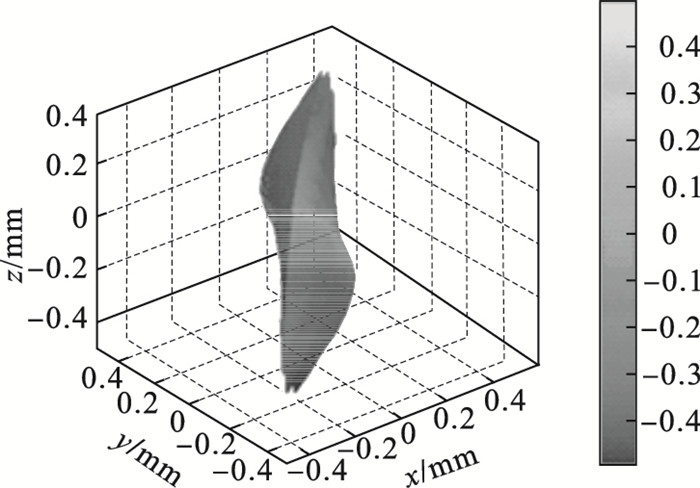 | 图 3 曲面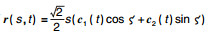 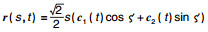 |
图 4为曲面
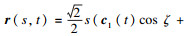
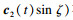
图 4(Fig. 4)
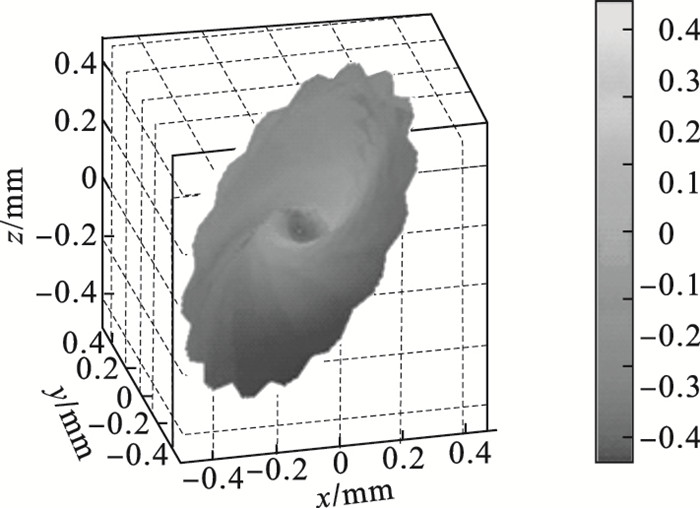 | 图 4 曲面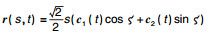 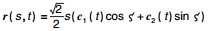 |
图 5是曲面的平均曲率在曲面上的分布情况.
图 5(Fig. 5)
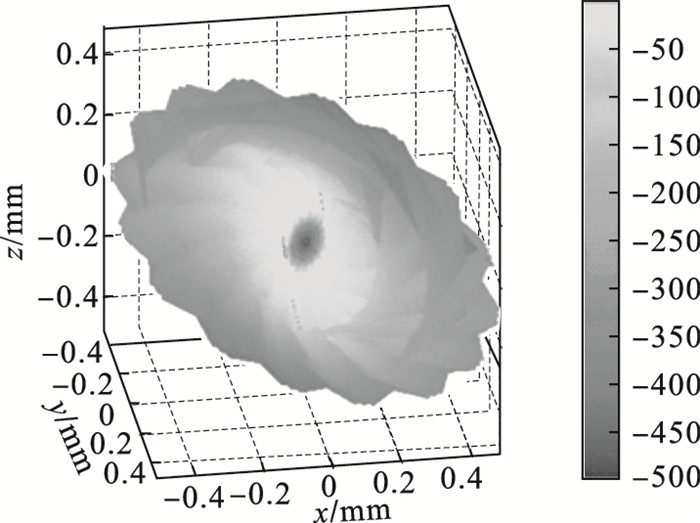 | 图 5 曲面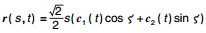 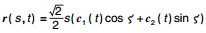 |
6 结论本文在四维欧氏空间中研究了平均曲率向量作为法标架的广义斜坡曲面, 对法平行和法部分完全落在平均曲率向量方向上的两种广义斜坡曲面进行讨论, 并得到以下主要结论:
1) 法平行下的广义斜坡曲面不存在.
2) 当曲面的法向量和平均曲率向量共线且选择曲率网作为参数时, 广义斜坡曲面存在, 且曲面是由两条球曲线构成.最后画出三维投影图像.
参考文献
| [1] | Munteanu M I. From golden spirals to constant slope surfaces[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 2010, 51(7): 073507. DOI:10.1063/1.3459064 |
| [2] | Dillen F, Munteanu M I. Constant angle surfaces in H2×R[J]. Bulletin Brazilian Mathematical Society, 2009, 40(1): 85-97. DOI:10.1007/s00574-009-0004-1 |
| [3] | Lopez R, Munteanu M I. Constant angle surfaces in Minkowski space[J]. Bulletin of the Belgian Mathematical Society-Simon Stevin, 2009, 18(2): 271-286. |
| [4] | Dillen F, Fastenakels J, Van der Veken J, et al. Constant angle surfaces in S2×R[J]. Monatshefte für Mathematik, 2007, 152(2): 89-96. DOI:10.1007/s00605-007-0461-9 |
| [5] | Dillen F, Munteanu M I, Van der Veken J, et al. Classification of constant angle surfaces in a warped product[J]. Balkan Journal of Geometry and Its Applications, 2011, 16(2): 35-47. |
| [6] | Fastenakels J, Munteanu M I, Van der Veken J. Constant angle surfaces in the Heisenberg group[J]. Acta Mathematica Sinica: English Series, 2011, 27(4): 747-756. DOI:10.1007/s10114-011-8428-0 |
| [7] | Fu Y, Nistor A I. Constant angle property and canonical principal directions for surfaces in M2(c)×R1[J]. Mediterranean Journal of Mathematics, 2013, 10(2): 1035-1049. DOI:10.1007/s00009-012-0219-z |
| [8] | Lpez R, Munteanu M I. On the geometry of constant angle surfaces in Sol3[J]. Kyushu Journal of Mathematics, 2011, 65(2): 237-249. DOI:10.2206/kyushujm.65.237 |
| [9] | Dillen F, Munteanu M I, Nistor A I. Canonical coordinates and principal directions for surfaces in H2×R[J]. Taiwanese Journal of Mathematics, 2011, 15(5): 2265-2289. DOI:10.11650/twjm/1500406434 |
| [10] | Chen B Y. Constant-ratio hypersurfaces[J]. Soochow Journal of Mathematics, 2001, 27(4): 353-362. |
| [11] | Fu Y, Munteanu M I. Generalized constant ratio surfaces in E3[J]. Bulletin of the Brazilian Mathematical Society: New Series, 2014, 45(1): 73-90. DOI:10.1007/s00574-014-0041-2 |
| [12] | Fu Y, Wang X. Classification of time like constant slope surfaces in 3-dimensional Minkowski space[J]. Results in Mathematics, 2013, 63(3/4): 1095-1108. |
| [13] | 陈维桓. 黎曼几何引论[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2004. (Chen Wei-huan. Introduction to Riemann geometry[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2004.) |
| [14] | Ganchev G, Milousheva V. On the theory of surfaces in the four-dimensional Euclidean space[J]. Kodai Mathematical Journal, 2008, 31(2): 183-198. DOI:10.2996/kmj/1214442794 |
| [15] | Gheysens L, Verheyen P, Verstraelen L. Characterization and examples of Chen submanifolds[J]. Journal of Geometry, 1983, 20(1): 47-62. DOI:10.1007/BF01917994 |
