全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,污水处理厂的出水,甚至再生水中,均检测出了未代谢药物、内分泌干扰物等生物难降解有机物[1]。虽然其浓度较低,但在大水量排放的情况,其在环境中会不断积累,存在一定的生态风险[2]。其中,以双酚A(bisphenol A,BPA)为代表的一类内分泌干扰物最为典型[3]。由于塑料制品的广泛应用,BPA已经在野生动物和人体中被大量发现。因此,对于该类污染物的深度处理受到了广泛的关注。大量研究者通过吸附[4]、膜分离[5]等物化方法尝试对BPA进行针对性去除,取得了较好的效果。然而,这些方法通常存在去除效率低、操作复杂等缺点。因此,开发高效的BPA去除技术迫在眉睫。高级氧化技术(advanced oxidation processes, AOPs)是一种通过氧化剂产生强氧化性的活性自由基,将难降解有机物直接矿化或分解成无毒小分子的水处理技术。该技术近年来在水处理领域得到越来越广泛的研究和应用,其中以芬顿工艺最为常见[6-7]。在该工艺体系中双氧水在特定pH环境下,被Fe2+活化从而产生羟基自由基(·OH),通过其极强的氧化性实现水中难降解有机物的降解或矿化。但芬顿技术存在化学污泥产量大、氧化性能相对不足的问题[8]。此外,芬顿氧化通常要求酸性反应环境,这在实际生产应用中极大增加了工艺的复杂程度,限制了其推广应用。为了解决这些问题,基于硫酸根自由基(


相对于均相过渡金属反应体系,采用非均相催化剂活化PMS具有能够抑制金属离子溶出、不易造成二次污染等优点。其中,铁氧体MFe2O4(M = Co, Mn, Cu, Zn等)是最广泛使用的催化剂之一。在不同的过渡金属铁氧体中,钴铁氧体在活化PMS过程中表现出了最佳的催化性能[15]。但由于钴本身具有生物毒性,溶出到污水中易产生二次污染,这使得毒性较低的锰成为了一个良好的替代选择[16]。有研究表明,铁锰氧化物中铁的存在可以显著增强体系对有机物和PMS的吸附作用,从而为锰进一步活化PMS并降解污染物提供先决条件[17]。同时,铁的存在亦可一定程度上抑制锰的溶出,使催化剂具有良好的稳定性。因此,制备锰铁氧体,使其活化过硫酸盐用于有机物的降解的可行性较高。值得注意的是,在过渡金属氧化物活化PMS的过程中,通常认为体系产生的大量自由基与一定量的单线态氧是实现污染物降解的主要途径。然而,有机物与过渡金属氧化物表面吸附态PMS之间是否存在直接电子传递作用,并导致其对污染物降解产生贡献,尚缺乏相关报道。
本研究通过水热法合成了基于Mn/Fe的双金属有机框架材料,通过对其进行适宜的热处理,制备了传质效率良好的锰铁氧体催化剂。通过场发射扫描电镜、X射线衍射分析,X射线光电子能谱等手段对所制备催化剂的基础物化性质进行了详细的表征,并使其耦合PMS构建了非均相的硫酸根自由基高级氧化体系,用于目标污染物BPA的降解。实验中考察了催化剂投加量、氧化剂投加量、pH对降解效果的影响,并通过顺磁共振、自由基淬灭实验、电化学分析等手段,对过程机理进行了深入分析。
1.1. 实验原料
乙酰丙酮铁 ((Fe(acac)3)、对苯二甲酸(C8H6O4)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O),过硫酸氢钾复合盐(Oxone, KHSO5·0.5KHSO5·0.5K2SO4)、双酚A (BPA)、N’N-二甲基甲酰胺 (DMF)、盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)等试剂均购于上海麦克林公司(分析纯)。无水乙醇、甲醇、乙腈等色谱纯有机溶剂均购于赛默飞公司。实验用水均出自Milli-Q超纯水系统。1.2. 实验方法
1)催化剂的制备与表征。本实验采用水热法与煅烧法耦合制备催化剂。具体方法如下:将1 mmol 乙酰丙酮铁、1.67 mmol 对苯二甲酸、0.5 mmol 四水合氯化锰溶于15 mL乙醇和25 mL DMF的混合溶液中,并在室温下不断搅拌直至全部溶解;将混合溶液转移到高压反应釜并放入烘箱,在120 ℃条件下反应12 h;水热反应结束后自然冷却至室温,将产物离心分离并使用甲醇清洗3次,然后在60 ℃烘箱中烘干得到锰铁双金属有机框架材料(Mn/Fe-MOFs);将该材料在马弗炉中以10 ℃每分钟升温速率升至450 ℃并煅烧1 h(空气气氛),结束后冷却至室温即可得到催化剂。2)实验仪器。本研究使用Quanta FEG, 250场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)观察催化剂的微观形貌,使用Rigaku Ultimate IV型X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行催化剂晶相分析,利用Thermo Fisher K-Alpha型X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析催化剂反应前后其组分价态环境变化,V-sorb 2800P型孔径分析仪分析催化剂的比表面积,使用Bruker EMXmicro-6/1电子顺磁共振(EPR)鉴别体系中的活性氧物种的类型,使用Nicolet iS50型傅里叶红外光谱仪分析PMS在催化剂表面的吸附行为 (ATR-FTIR)。催化剂活化PMS过程的电化学行为通过电化学工作站(CHI660E)进行分析,分析过程采用三电极模式。其中饱和甘汞电极作为参比电极,铂电极作为对电极,碳玻电极作为工作电极,电解质采用100 mmol·L?1硫酸钠溶液。
3)BPA降解实验。BPA降解实验在100 mL玻璃烧杯中进行,反应前,首先使用HNO3(0.1 mol·L?1)或NaOH(0.1 mol·L?1)将BPA溶液pH调节至6.5。将不同投加量的催化剂加入到BPA溶液的烧杯中,放入超声清洗器中超声分散10~15 s,使催化剂完全均匀分散于溶液。然后向溶液中加入PMS激发氧化反应,反应过程中采用磁力搅拌器缓慢搅拌,搅拌速率约120 r·min?1。在预设的时间间隔进行取样,每次取样量为1 mL,使用0.22 μm滤膜过滤样品,而后加入1.5 mL高效液相色谱取样瓶中,并立即用0.5 mL甲醇进行淬灭。常规实验中,反应过程均在水浴中完成,反应温度为(25±0.5) ℃,BPA浓度为40 μmol·L?1,PMS浓度为0.4 mmol·L?1,催化剂投加量为0.1 g·L?1,初始pH为6.5±0.1。影响因素分析实验中,仅改动单个反应条件并保持其他条件相同,以分析其对最终结果的影响。
所取水样在2 h内使用超高效液相色谱进行测定,流动相采用水和乙腈混合液(乙腈体积比为40%),流速为0.2 mL·min?1,检测波长为278 nm,柱温控制为35 ℃。表观降解动力学常数由式(1)计算获得。
式中:C0为初始浓度,μmol·L?1;Ct为t时刻浓度,μmol·L?1;t为时间,min;kapp为表观动力学常数。
2.1. 催化剂物化性质分析
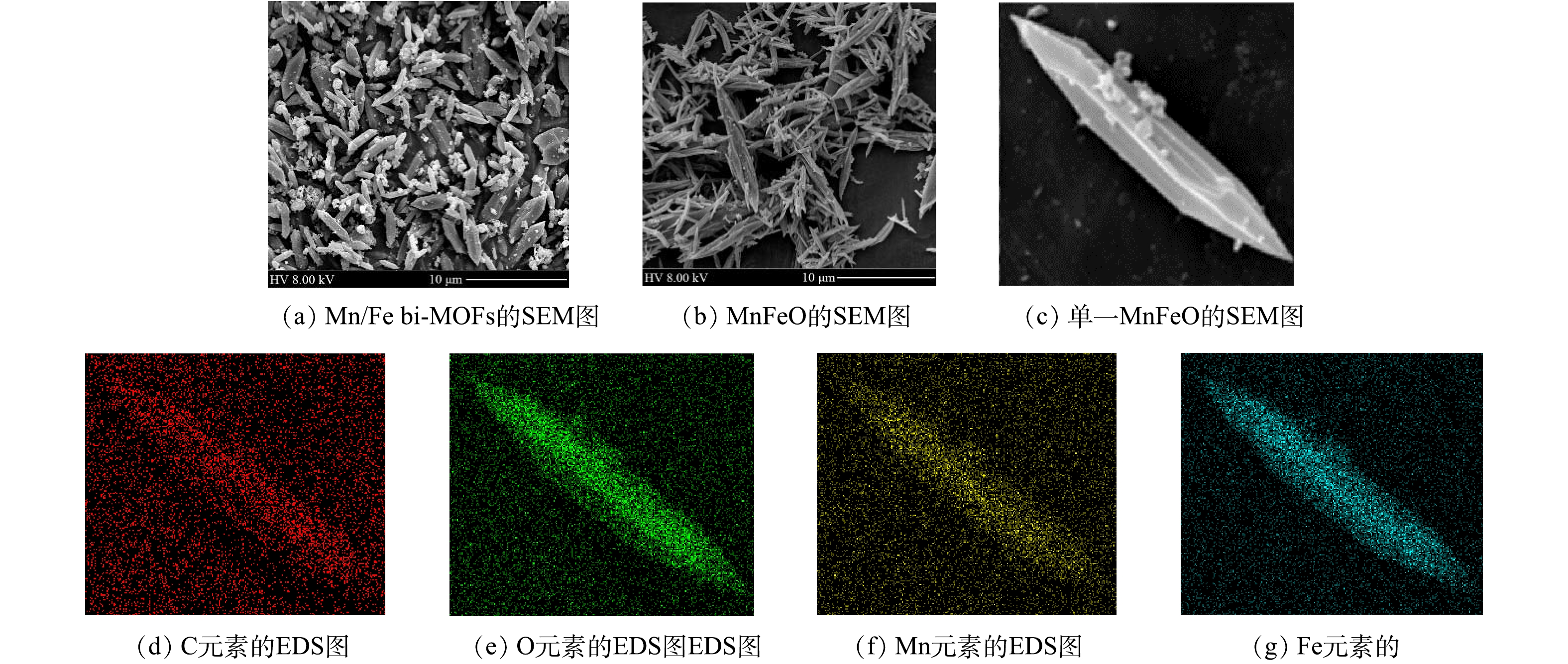
使用FESEM对所制备Mn/Fe-MOFs和煅烧所得催化剂的形貌和基本组分进行分析。由图1(a)可以看出,所制备Mn/Fe-MOFs具有纺锤状微观形貌,尺寸不均一,常见尺寸为2~6 μm。通过热处理得到的催化剂形貌如图1(b)所示,可见通过热处理后,Mn/Fe-MOFs的微观形貌发生了很大的变化,其纺锤结构保留度较低,形成了大量针状催化剂。这表明,在Mn/Fe-MOFs的煅烧过程中,其中的碳组分在空气中氧分子的存在下转化为二氧化碳,使得MOFs中残余的金属离子转化为氧化物。EDX-mapping分析结果表明,催化剂中Mn、Fe元素较为均匀地分布于材料表面,且Mn、Fe元素分布与O元素高度重叠,表明形成了锰铁复合氧化物。此外,EDX-mapping分析结果也表明,催化剂中残余有少量的C元素,说明450 ℃没有使MOFs中的碳元素完全燃烧。使用XRD分析进一步确认了合成催化材料的物相,结果如图2(a)所示。所制备催化剂在2θ为17.99°、30.02°的衍射峰对应MnFe2O4的(111)和(202)晶面,42.52°、56.19°、64.79°的衍射峰分别对应MnFe2O4的(400)、(511)和(531)晶面。此外,基于XRD衍射信号还可分析出Fe2O3的存在。因此,可推断所制备催化剂主要成分为MnFe2O4与Fe2O3(MnFeO)。能谱分析结果进一步确认了MnFeO中各元素的原子浓度,其中氧、碳、锰和铁原子浓度分别为43.05%、10.75%、10.70%和32.51%,表明催化剂中金属元素均已氧化物形式存在,这与XRD分析结果高度一致。N2吸附/脱附分析结果表明,所制备催化剂BET表面积为33.9 m2·g?1,平均孔径为16.2 nm,孔体积为0.092 cm3·g?1。
2.2. PMS活化降解BPA中的影响因素
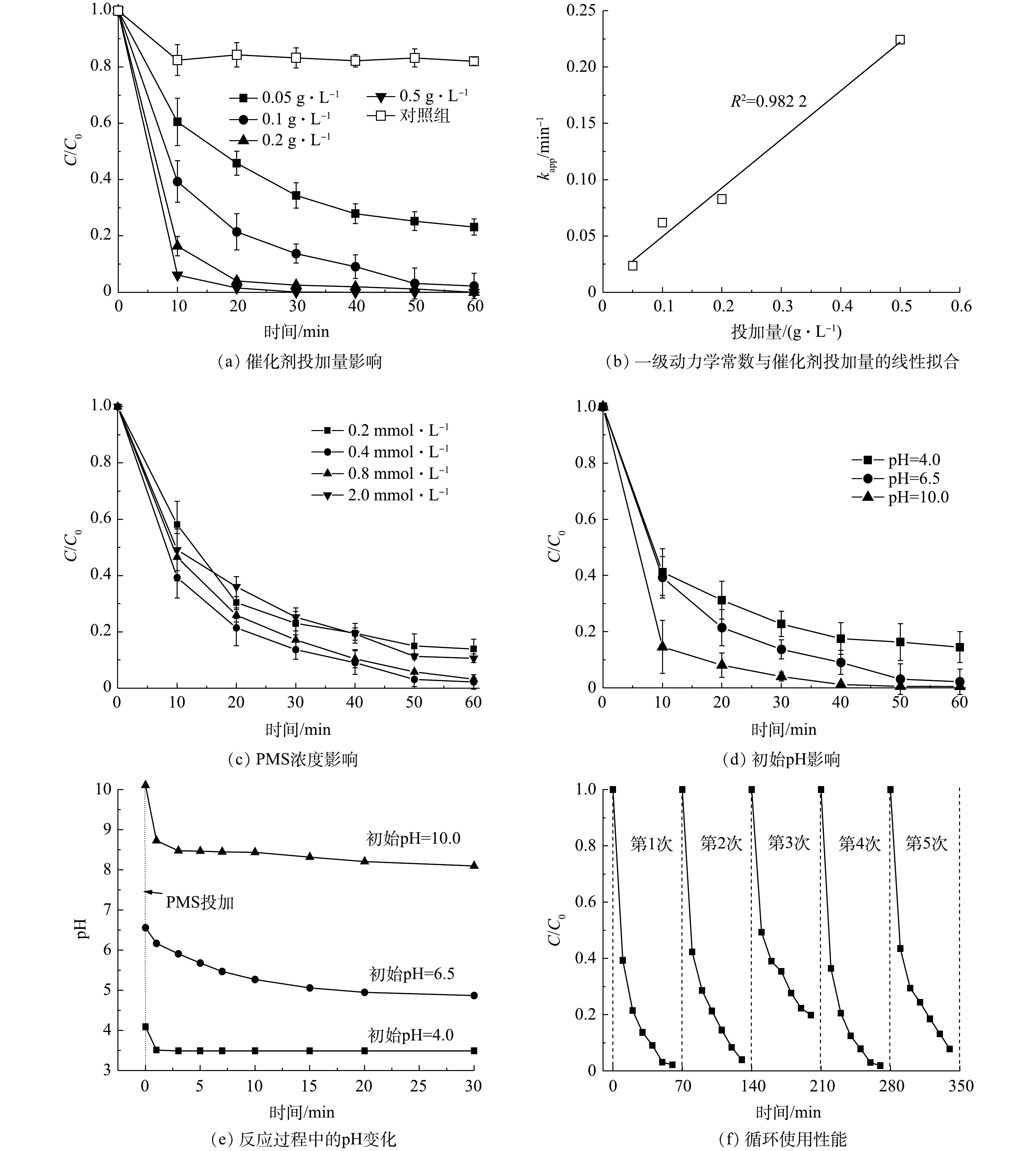
1)催化剂投加量的影响。由图3(a)可知,在无PMS投加情况下(T为(25±0.5) ℃、BPA为40 μmol·L?1、PMS为0.4 mmol·L?1、MnFeO投加量为0.1 g·L?1、pH0为6.5±0.1),约有18.2%的BPA被去除,这表明MnFeO具有一定的BPA吸附性能。在PMS存在情况下,当MnFeO投加量为0.05 g·L?1时,60 min内BPA降解率为75%。而随着MnFeO投加量增加,BPA的催化效果显著增强。该现象是由于催化剂投加量的增加显著提升了反应体系中催化活性位点的丰度,使得催化剂对PMS的吸附性能增强,该过程强化了催化剂与PMS的接触几率,从而使体系产生的氧化性物种数量显著增加[18-19]。而当催化剂的用量增加到0.5 g·L?1, BPA在20 min内达到完全降解。使用一级动力学(式(1))反应分析不同投加量下的表观反应动力学常数,可以发现表观反应速率常数kapp随着催化剂浓度的增加而增加,当催化剂投加量为0.05、0.1、0.2和0.5 g·L?1时(其他条件不变),对应的表观动力学常数kapp分别为0.023 8、0.061 9、0.082 8和0.224 2 min?1。通过反应速率常数与催化剂投加量相关性分析可以发现,反应速率与投加量(d)之间存在kapp=0.431 7d - 0.006 4的关系,且拟合度(R2)达到0.988 1。这表明催化剂投加量与催化反应效率提升之间的直接相关。此外,以0.1 g·L?1为投加量的MnFeO金属离子溶出液为研究对象,通过溶出液直接活化PMS对反应过程的非均相途径贡献进行了分析。结果表明,相同条件下仅9%的BPA被溶出液降解,表明MnFeO/PMS降解BPA的过程为PMS非均相活化过程。由ICP分析结果可见,该条件下MnFeO的锰离子溶出量仅为37.2 μg·L?1。而在MnFeO/PMS体系中,60 min后锰离子溶出量为61.7 μg·L?1,这表明PMS存在下的弱酸性环境会加速锰离子的溶出。2) PMS投加量的影响。通过不同PMS投加浓度,分析相同催化剂投加下的氧化性能表现,对PMS适宜浓度的选择具有较好的参考价值。本研究考察了PMS投加量为0.2~2.0 mmol·L?1对BPA降解效果的影响(T为(25±0.5) ℃、BPA为40 μmol·L?1、MnFeO投加量为0.1g·L?1、pH0为6.5±0.1)。如图3(c)所示,控制PMS浓度对BPA的降解行为具有明显的影响。当PMS浓度由0.2 mmol·L?1增至0.4 mmol·L?1时,一级动力学常数k值由0.032 5 min?1升至0.061 9 min?1,表明PMS浓度的增加强化了传质推动力,使更多的PMS被吸附到催化剂表面并进行了活化,体系的氧化性得到了大幅的提升。通过该结论可以预测,当PMS浓度进一步升高时,其氧化性能会得到更高的提升。然而,进一步研究发现,当PMS浓度提升至0.8 mmol·L?1时,其反应速率并未得到上升,反而有了显著的下降(kapp=0.054 9 min?1)的趋势。相反,当PMS进一步提升至2.0 mmol·L?1时,反应速率反而降至0.036 7 min?1,与PMS为0.2 mmol·L?1时氧化性能的表现基本相同。该结果表明,体系中存在过量PMS时,对反应具有显著的抑制作用[19]。进一步分析发现,过量的PMS会淬灭催化剂表面已经产生的·OH和SO4·? (式(2)和式(3)),生成氧化性较弱的SO5·?,使氧化性物种产生了一定量的消耗,导致了污染物降解性能的显著降低[20]。因此,选择适宜的PMS浓度具有非常重要的实际意义。
3)初始pH影响。pH是化学反应过程中的一个重要参数,本研究考察了初始pH在4.0,6.5和10.0时MnFeO/PMS体系对BPA的降解情况(T=(25±0.5) ℃、BPA为40 μmol·L?1、PMS为0.4 mmol·L?1、MnFeO投加量为0.1 g·L?1)。由于PMS与催化剂的反应会使溶液pH发生显著变化,因此,首先通过对照实验分析了不同初始pH下,反应体系pH随着PMS活化反应的变化。实验结果表明,在不同初始pH下,MnFeO/PMS体系的pH在经历初期的迅速下降以后变得比较平缓(图3(e))。其中,初始pH为4.0和6.5时,体系pH在30 min后稳定在3.5和4.9。而初始pH为10.0时,30 min后pH降为8.1,为弱碱性。BPA降解实验结果表明(图3(d))),催化剂在较宽pH范围内均展现出了的较强降解效果。但通过总结可以发现,体系对污染物的降解性能随着体系初始pH的提高而升高。在初始pH为4.0、6.5、10.0时,去除率依次为85.2% (60 min)、97.8% (60 min)和98.8% (40 min),对应的反应速率常数kapp依次为0.029 3、0.061 9和0.085 7 min?1。MnFeO的零电荷点(pHzpc)为6.8[17]。当体系pH<6.8时,催化剂表面带正电,可强化其对PMS的吸附;相反,当体系pH>6.8时,催化剂表面负电点位逐步增多。而HSO5-离子的解离常数(pKa)为9.4[21]。在极酸条件下存在形式为H2SO5,在碱性条件下其存在形式为





催化剂的循环利用性能,是其能否持续高效降解有机物的关键指标,本研究对所制备MnFeO催化剂的循环利用性能进行了综合分析。每轮反应条件保持相同,其中,温度为(25±0.5) ℃,BPA浓度为40 μmol·L?1,PMS浓度为0.4 mmol·L?1,MnFeO投加量为0.1 g·L?1,初始pH为6.5±0.1;每次反应结束后,使用0.45 μm滤膜分离催化剂并在60 ℃下烘干备用。如图3(f)所示,可以发现在逐轮的使用过程中,催化剂的PMS活化性能有轻微的衰减,在第2轮中污染物的降解效率为96%,在第3轮中下降至80%。这可能是由于催化剂在使用过程中形成的表面羟基吸附了污染物以及中间产物,造成了活性位点的覆盖,导致活性位点无法与PMS接触。因此,对使用后的催化剂在450 ℃条件下进行了再次煅烧。实验结果表明,再次热处理后催化剂的PMS活化性能得到了有效的恢复,BPA降解效率在煅烧后恢复到98.1%,与首轮使用性能基本一致,表明催化剂具有良好的循环利用性能。
2.3. 反应机理分析
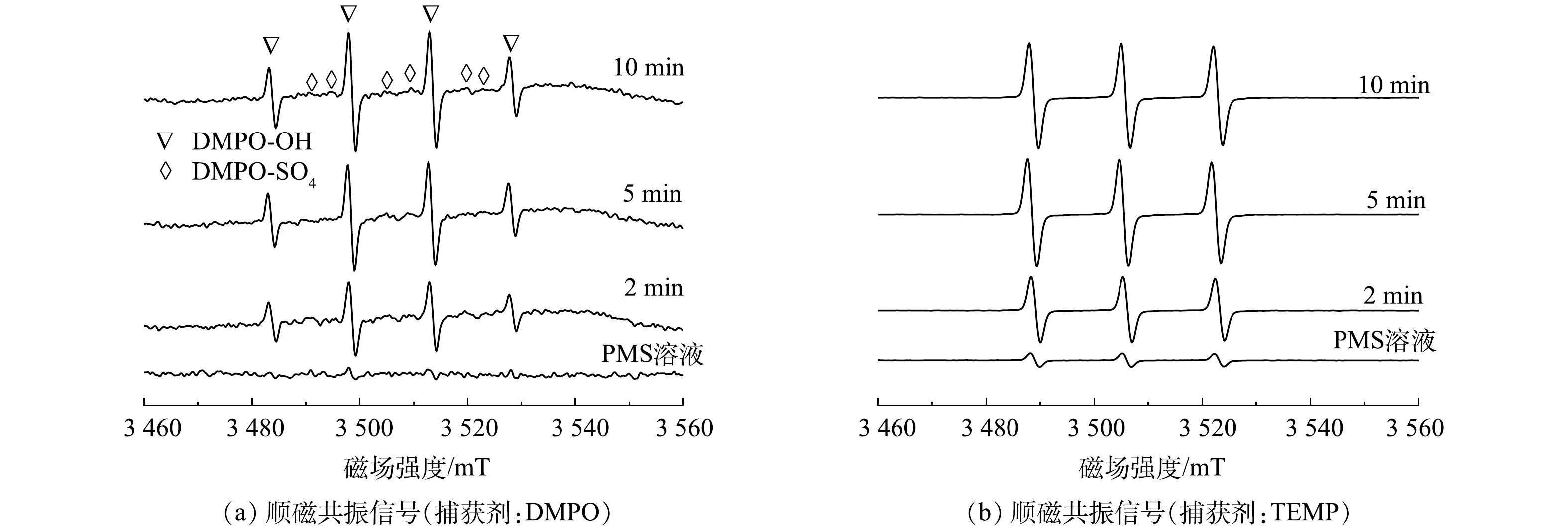
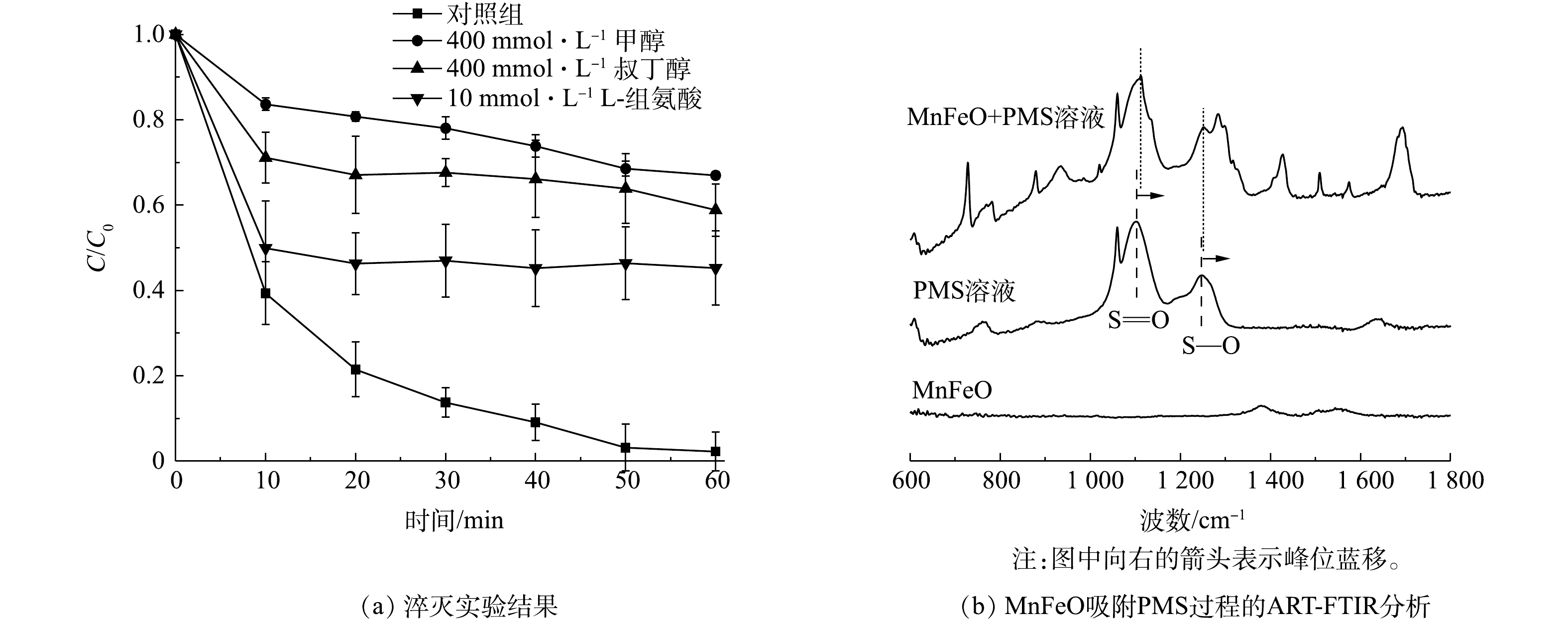
由前述讨论可知,体系中可能存在的氧化性物种有SO4·?、HO·和1O2等[25]。因此,使用顺磁共振对反应体系中的活性物种进行了鉴定。通过5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物(5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide,DMPO)作为自旋捕获剂,可以有效观察到羟基自由基和硫酸根自由基的信号,表明MnFeO活化PMS过程中存在自由基途径(图4(a))。通过2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine, TEMP)作为自旋捕获剂,可直接观察到1O2的特征峰(图4(b))。根据峰强度随反应时间的变化可以看出,自由基信号随着反应时间的增加而增强,而1O2的信号强度在反应过程中也随着反应时间的增加显著增强,表明在PMS活化过程中不断产生自由基与1O2。此外,通过淬灭实验对反应体系过程机制做了进一步分析。叔丁醇(TBA)与SO4·?的反应速率为4~9.1×105 L·mol?1s?1,与HO·的反应速率为3.8~7.6×108 L·(mol·s)?1;由于甲醇包含1个α-H,使其可以快速的与SO4·?和HO·反应,其与SO4·?的反应速率为3.2×106 L·(mol·s)?1,与HO·的反应速率为9.7×108 L·(mol·s)?1[25]。因此,分别使用甲醇和叔丁醇作为淬灭剂并对照污染物降解效果,可初步确定SO4·?与HO·对污染物降解的贡献。结果表明,甲醇表现出了强于叔丁醇的淬灭效应,表明在自由基途径中SO4·?与HO·共同对污染物的降解起到了作用(图5(a)),且
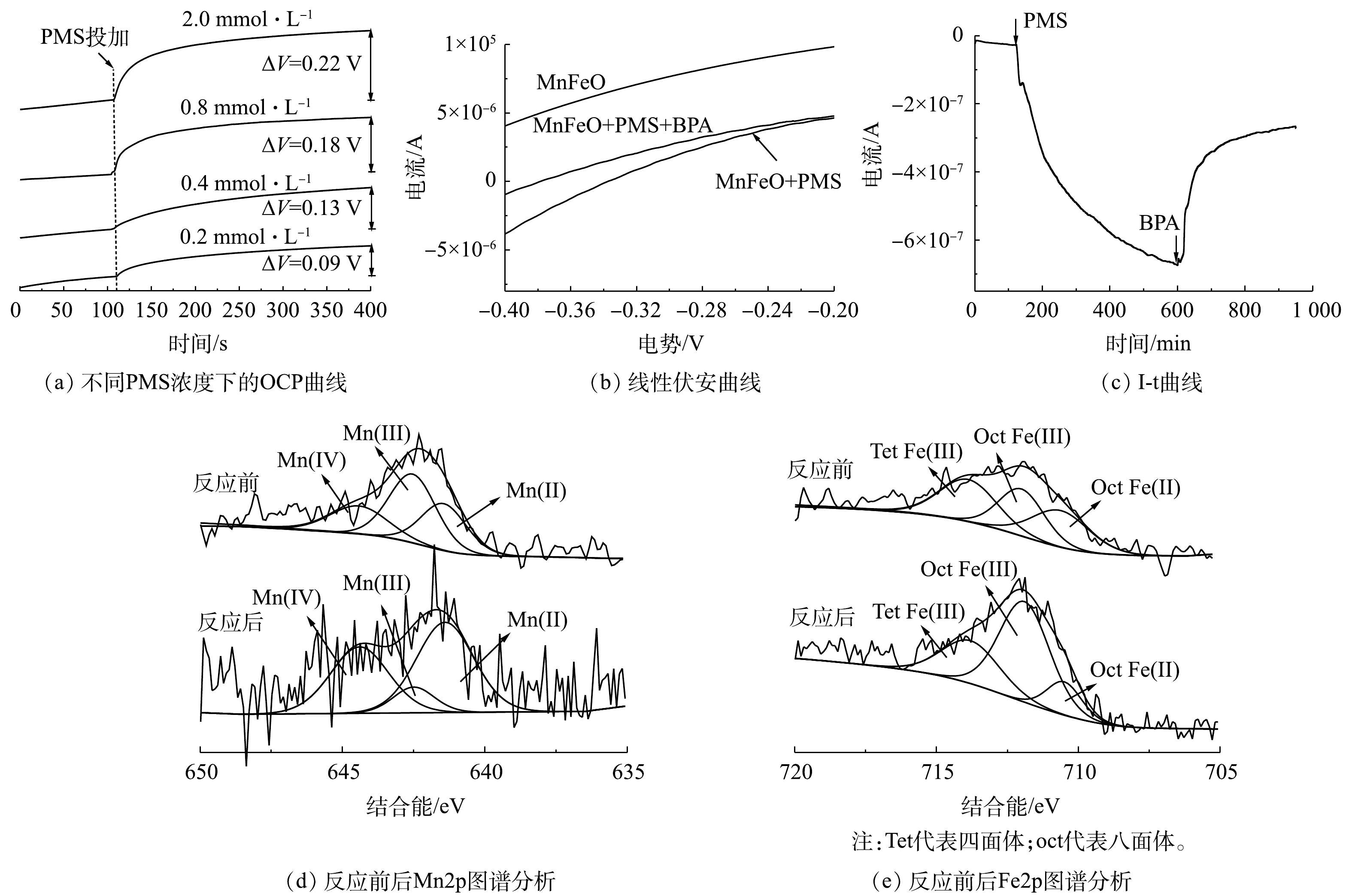
在PMS活化过程中,PMS需要首先吸附到催化剂表面,进而通过PMS的断裂产生对应的氧化性物种。ATR-FTIR分析可明显观察到PMS的S—O及S=O特征键(图5(b))。然而,当PMS与MnFeO接触后,可观察到对应特征键的波数发生了蓝移。其中,S=O从1 101.64 cm?1移动到1 111.76 cm?1,而S—O从1 244.84 cm?1移动到了1 251.57 cm?1。特征波数的蓝移通常是由于PMS被吸附在MnFeO表面,导致其特征键的振动方式发生了变化。对于PMS的活化,自由基的产生通常需要催化剂供出电子,实现PMS中过氧键O—O的断裂[26]。因此,使用电化学工具对体系中催化剂、PMS以及BPA 3个组分之间的作用关系做了了进一步分析。开路电位(OCP)分析结果(图6(a))表明,PMS浓度的增加,使催化剂-PMS复合体的电位有了显著提升,且电位提升效果随着PMS浓度的升高而升高。该结果表明,溶液中的PMS被MnFeO吸附,吸附态PMS为后续的活化提供了先决条件,这与ATR-FTIR分析的结果一致。线型伏安(LSV)分析结果表明,在相同的外电势下,体系中PMS的投加大幅提高了体系的电流密度,表明催化剂与吸附态PMS之间存在电子传递过程,这可能是PMS活化的主要原因(图6(b))。而BPA在MnFeO/PMS体系中的额外引入,使得体系的电流密度有了一定程度的减弱,表明BPA与MnFeO-PMS复合体之间存在直接电子传递过程。该现象可能是由于MnFeO/PMS复合体较高的电位具有更强的电子获得能力,导致吸附态BPA中的电子直接传递到MnFeO-PMS复合体中,实现了BPA的降解。该过程被I-t曲线的分析结果进一步验证。由图6(c)可见,PMS的投加使催化剂界面的电流密度显著降低,而后续BPA的投加有效降低了电流密度,导致电子从BPA向MnFeO-PMS复合体的传递,进而对BPA的降解做出了显著贡献。
基于上述电化学过程分析结果,使用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对反应前后催化剂中的元素价态变化进行了直接分析。结果表明,反应前MnFeO中锰元素的价态形式主要为Mn2+、Mn3+和Mn4+,相对含量约为30.48%、46.19%和23.32%(图6(d));铁元素的价态主要为八面体位Fe2+、八面体位Fe3+与四面体位Fe3+,其相对含量分别为31.34%、32.49%和36.17%(图6(e))。而反应后,金属元素的价态分布发生了显著的变化,其中Mn2+的相对含量显著提升至51.29%,而Mn3+的相对含量显著降低。此外,Fe(II)的总体含量降低至13.32%,这表明MnFeO中少量的Fe(II)也参与了PMS的活化过程;同时,反应后表面羟基的含量显著增加。基于此,可总结出该体系反应机理如下。MnFeO在PMS溶液中首先发生表面羟基化过程(式(6)),而后羟基化位点吸附溶液中的PMS,通过催化剂向PMS的电子传递,形成过氧键的断裂,并生成SO4??(式(7)~式(8))。反应过程中伴随催化剂中低价态锰(Mn2+和Mn3+)向高态锰的转化(Mn3+和Mn4+)。需要注意的是,反应体系中Mn3+/Mn2+的电极电位为1.71 V,




2) PMS的浓度对体系的氧化性能影响较大,高于0.8 mmol·L?1的PMS会触发自淬灭效应,从而导致体系氧化性能降低。
3)体系在不同pH下均表现出良好的PMS活化性能,弱碱性条件有利于体系氧化性能的提高;催化剂在连续使用下催化性能有微弱的衰减,通过简单的煅烧可完全实现催化剂活化性能的恢复。
4)锰元素供出电子生成的SO4·?以及后续形成的HO·是主要的活性组分,同时过程中伴随着1O2的形成;有机物与吸附态PMS之间存在直接电子传递过程并同时实现了有机物的非自由基途径降解,该现象在类似体系中值得深入探索。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 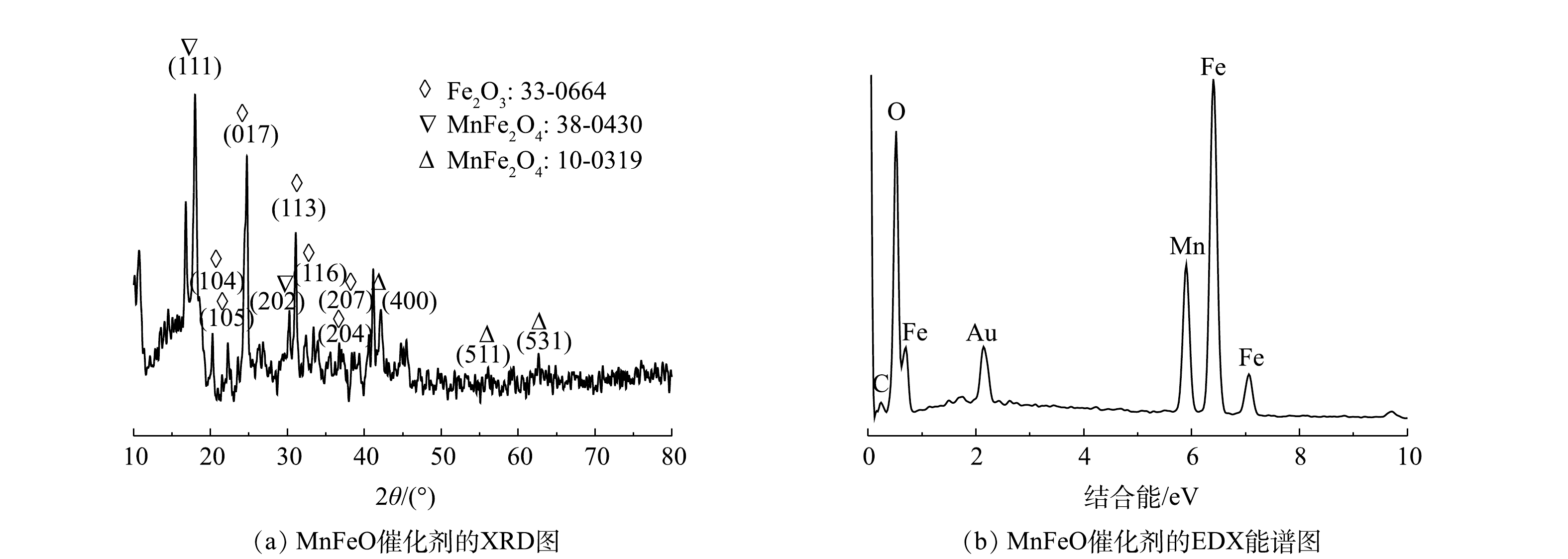
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图