全文HTML
--> --> --> 我国水资源短缺的形势十分严峻,400多个城市常年供水不足,114个城市水资源严重匮乏,水资源短缺已经严重阻碍社会经济的发展。鉴于我国水资源匮乏的现实,《水污染防治行动计划》等明确要求,2020年严重缺水城市再生水利用率应达到20%以上,京津冀区域达到30%以上。城市污水再生利用成为缓解城市水资源供需矛盾和实现水资源可持续利用的重要途径。近年来,越来越多的城市将达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准和《城市污水再生利用 景观环境用水水质》(GB/T 18921-2002)的污水处理厂尾水作为再生水给湖泊或湿地等地表水体补水[1-4]。一级A标准尾水氮、磷污染物含量(TN 15 mg·L?1、TP 0.5 mg·L?1)较高,没有达到《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)V类水质(TN 2 mg·L?1、TP 0.4 mg·L?1),更没有达到国际公认的水体发生富营养化的临界值(TN 0.2 mg·L?1、TP 0.2 mg·L?1)[5]。因此,地表景观水体富营养化控制是再生水回用必须考虑的重要技术问题[6-7]。
本研究以径流雨水和再生水作为主要补水水源的某城市湿地不同区域景观水体为研究对象,有针对性地分析水体TN、TP等6项水质指标3年来的时间、空间变化规律及各项水质指标的相关性,进而全面评价水体富营养化程度,剖析富营养化机理,并探讨富营养化治理对策,以期为我国再生水回用的相关规划设计提供技术参考。
1.1. 研究对象
某城市湿地景观水体包括I、Ⅱ 2个水系分区(见图1),总面积约为9.65×105 m2,水深为0.8~3 m,平均水深约为1.4 m,总容积约为2.09×106 m3。水系Ⅰ区较Ⅱ区地势低,水流通常由水系Ⅱ区流向Ⅰ区,当Ⅱ区水位下降明显时,开启水泵,从Ⅰ区抽水给Ⅱ区补水。水系Ⅰ区补水水源主要为再生水厂尾水和径流雨水,再生水厂尾水水质达到一级A标准,平均尾水量约4×104 t·d?1,尾水量约占总补水量的80%。径流雨水来自水系周边11个雨水排口,雨水汇水面积约2.78×106 m2,其中汇水面积2.34×106 m2的7个雨水排口建有雨水收集池(面积约1.71×104 m2、容积约2.55×104 m3),径流雨水经收集池净化处理后汇入水系Ⅰ区。
水系Ⅱ区补水水源主要为径流雨水,径流雨水来自水系周边12个雨水排口,雨水汇水面积约1.46×106 m2,其中汇水面积1.93×105 m2的3个雨水排口建有雨水收集池(面积约9.5×103 m2、容积约1.4×104 m3)和汇水面积1.9×105 m2的1个雨水排口建有人工快渗处理系统(constructed rapid infiltration, CRI),径流雨水经收集池和CRI净化处理后汇入水系Ⅱ区。
1.2. 研究方法
根据《地表水和污水监测技术规范》(HJ/T 91-2002)[8]进行实验水体水样布点和采集,结合水系功能区划和水流走向,水样点布设见图1。水系Ⅰ区设采样点6个,沿水流走向分别为1号~6号采样点,1号采样点是再生水厂尾水汇入点,6号采样点是水体排放泵站附近水样点。水系Ⅱ区设采样点3个,沿水流走向分别为7号~9号采样点。2015—2017年,每月在各采样点取水样4次,计算水质指标年均浓度作为水体富营养化分析评价的依据。水样的采集和保存参照文献中的方法[9]。水样水质监测项目包括总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、化学需氧量(COD)、悬浮物(SS)、叶绿素a (Chla)、溶解氧(DO)和透明度(SD)。TN的测定采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法(HJ 636-2012)[10]、TP的测定采用钼酸铵分光光度法(HJ 670-2013)[11],COD的测定采用重铬酸钾法(GB 11914-1989)[12],SS的测定采用重量法(GB 11901-1989)[13],Chla的测定采用分光光度法(SL 88-2012)[14],DO采用便携式DO仪(HACH HQ 30 d)测量,SD的测定采用塞氏盘法。
1.3. 分析方法
富营养化评价采用《湖泊(水库)富营养化评价方法及分级技术规定》(中国环境监测总站,总站生字[2001]090号)中的综合营养状态指数法[8-9]进行评价。选取Chla、TP、TN和COD 4个指标的浓度值和SD指标值计算各单项指标的营养状态指数FTLI(j)[15-16]和综合营养状态指数FTLI(∑)[8-9],计算方法见式(1)~式(6)。式中:FTLI(Chla)为Chla的营养状态指数;CChla为Chla的浓度,mg·m?3;FTLI(TP)为TP的营养状态指数;CTP为TP的浓度,mg·L?1;FTLI(TN)为TN的营养状态指数;CTN为TN的浓度,mg·L?1;FTLI(COD)为COD的营养状态指数;CCOD为COD的浓度,mg·L?1;FTLI(SD)为SD的营养状态指数;hSD为透明度,m;FTLI(∑)为综合营养状态指数;Wj为第j种参数的营养状态指数的相关权重;FTLI(j)为第j种参数的营养状态指数。
以Chla作为基准参数,则第j种参数的归一化的相关权重Wj的计算方法见式(7)。
式中:rij的取值参考相关文献中的方法[17-19];Wj为相关权重。
以计算得到的FTLI(∑)为依据,采用?0~100?的一系列连续数值对水体营养程度进行分级评价。FTLI(∑)<30为贫营养(oligotropher),30≤FTLI(∑)≤50为中营养(mesotropher),50< FTLI(∑)≤60为轻度富营养(light eutropher),60< FTLI(∑)≤70为中度富营养(middle eutropher),FTLI(∑)>70为重度富营养(hyper eutropher)。在同一营养状态下,FTLI(∑)越高,水体营养程度越严重。
采用SPSS(19.0)软件进行数据处理与分析,使用Excel软件作图并对数据进行分析。
2.1. TN和TP浓度沿流程的变化
2015—2017年,湿地水系TN、TP年平均浓度变化见图2。近3年来,水系各采样点TN、TP浓度逐年呈现下降趋势,水体水质逐年略有提升。水系Ⅰ区沿水流方向,各年度TN、TP浓度均呈现下降趋势,TN、TP浓度沿流程从1号采样点6.5~9.0 mg·L?1、0.35~0.46 mg·L?1下降到6号采样点4~5 mg·L?1、0.1~0.15 mg·L?1,这表明再生水作为主要补水水源输入了高浓度N、P污染物,目前在降雨、径流雨水稀释作用和植物(水体周边挺水植物较多、沉水植物较少)、微生物、动物等组成的湿地生态系统净化作用下,TN、TP污染物浓度逐步下降,但净化效率整体还不高,水系末端6号采样点TN、TP浓度离地表水IV类标准(TN 1.5 mg·L?1、TP 0.1 mg·L?1)还有一定的差距。水系Ⅱ区沿水流方向,各年度TN、TP浓度呈现先下降再上升的趋势,除9号采样点TN外,其余各点TN、TP浓度基本在0.3~1.5 mg·L?1、0.02~0.05 mg·L?1波动,均达到了地表水Ⅳ类标准,水体水质整体较好,这主要是径流雨水作为主要补水水源输入的N、P污染物浓度较低和生态系统自净作用的结果。2.2. COD和SS浓度沿流程的变化
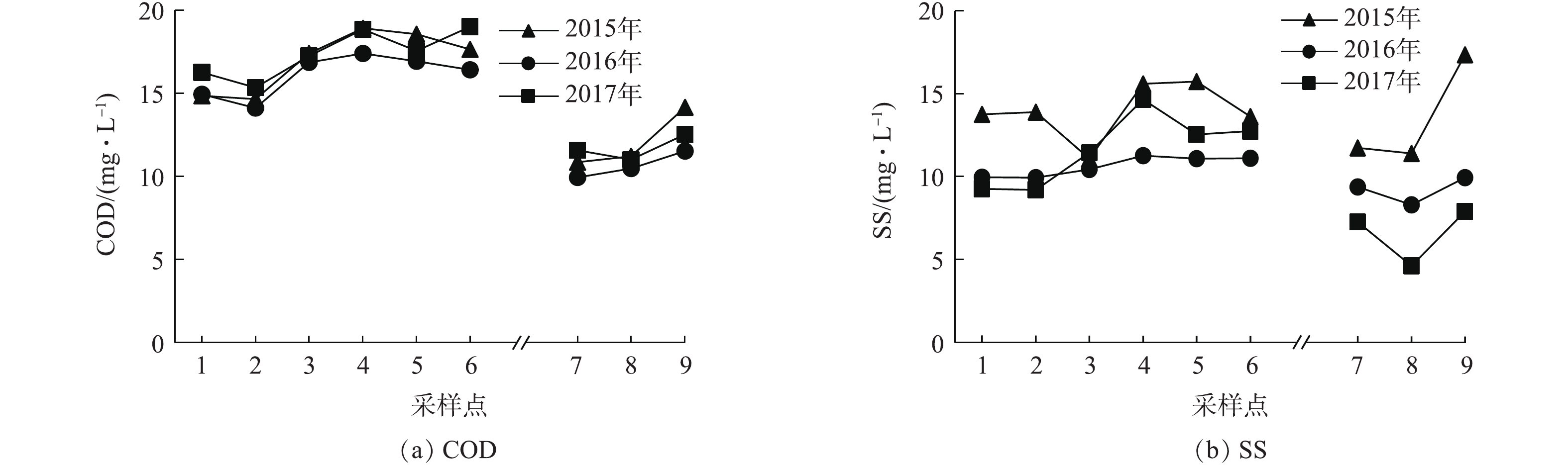
2015—2017年,湿地水系COD、SS年平均浓度的变化见图3。近3年来,沿水流方向,水系Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区COD年均浓度均呈现上升趋势,这可能是由于内源性底泥释放、未收割水生植物季节性凋落降解和地表径流等外源性输入所致。水系Ⅰ区COD年均为12~20 mg·L?1,除个别点的单次监测值外,各点COD均达到地表水Ⅳ类标准。水系Ⅱ区COD年均在10~15 mg·L?1,达到地表水Ⅳ类标准,个别点甚至达到地表水Ⅲ类标准。水系Ⅰ区各水样点COD显著高于Ⅱ区,主要是由于补水水源不同所致。水系中SS年均浓度变化规律性不强、波动较大,且Ⅰ区所有点SS年均浓度均高于再生水厂尾水SS浓度限值10 mg·L?1,主要是由于SS受降雨、沉水植物种植情况、鱼类和人类活动干扰等影响较大所致。2.3. Chla和DO浓度沿流程的变化
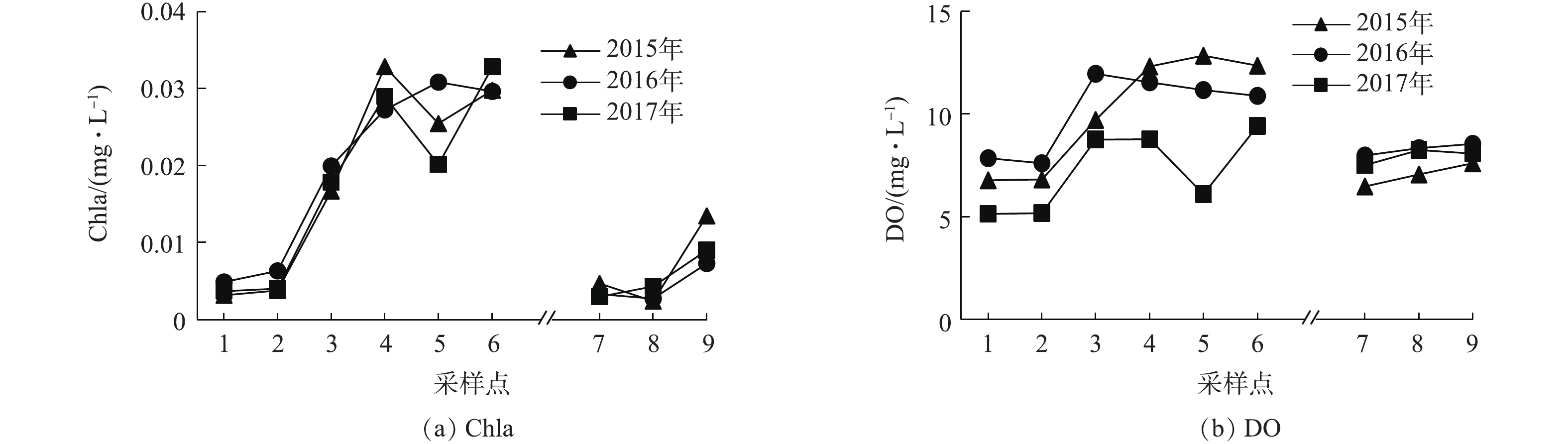
2015—2017年,湿地水系Chla、DO年平均浓度变化见图4。近3年来,水系Ⅰ区Chla浓度沿水流方向均增加了4~7倍,整体呈现显著上升趋势,最大值接近0.035 mg·L?1,这与东莞燕岭湿地水体Chla变化规律[20]一致。同时,水系Ⅰ区DO整体呈现稳定的上升趋势,各点DO浓度均达到地表水Ⅲ类标准规定的5 mg·L?1,3号~6号采样点DO浓度(2017年5号点除外)甚至远大于地表水Ⅰ类标准规定的7.5 mg·L?1(饱和率超过90%)。在现场湿地水体流动性较差和透明度小于1 m的情况下,Chla和DO均呈现显著上升趋势且处于较高浓度水平,主要是由于水体中藻类等浮游植物大量生长繁殖及泌氧所致。水系Ⅱ区Chla、DO浓度也呈现上升趋势,但明显低于水系Ⅰ区浓度值。2.4. 主要污染物指标的季节和空间变化
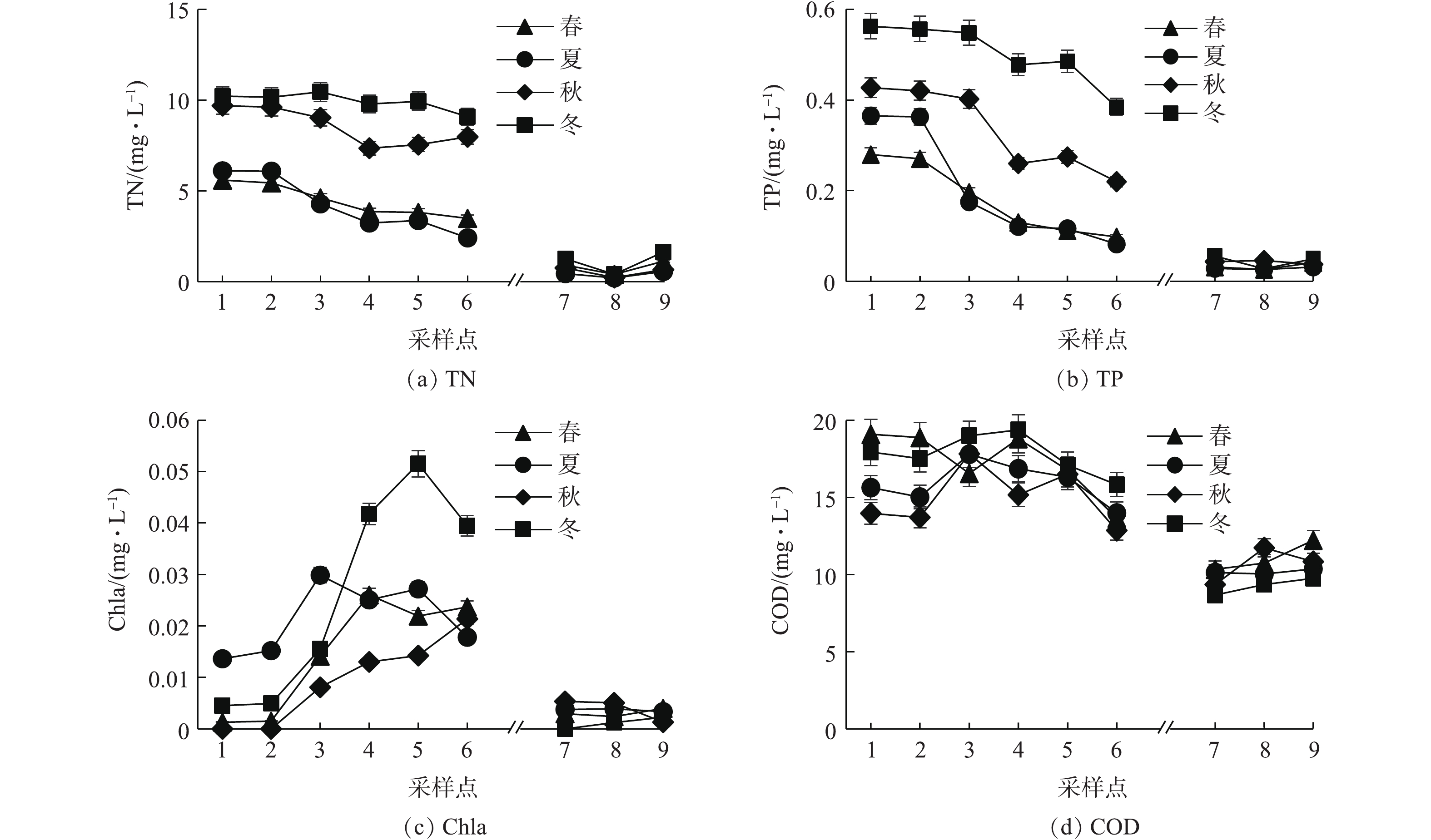
2016年3月—2017年2月,湿地水系TN、TP、Chla和COD 4个指标的季节变化和空间变化规律见图5。从图5(a)和图5(b)看出,水系Ⅰ区各点N、P污染物浓度均为冬季最高,秋季次之,春夏季节相对较低,同时在夏季,N、P污染物浓度沿水流方向下降的趋势最为明显,春季和秋季次之,冬季最不显著。这一方面与再生水厂尾水水质的季节变化规律相同,另一方面也表明,植物、微生物、动物等组成的湿地生态系统对N、P污染物的协同净化效率受季节气候的影响显著,净化效率从高到低依次是夏季、春季、秋季、冬季。水系Ⅱ区N、P污染物浓度随季节变化呈现与Ⅰ区相同的规律,但由于径流雨水N、P污染负荷较低,N、P污染物浓度随空间变化的规律不明显。从图5(c)看出,水系Ⅰ区各点Chla含量在冬季、夏季、春季相对偏高,在秋季相对最低。与此同时,水系Ⅰ区Chla含量沿水流方向除秋季呈稳定上升趋势外,在春季、夏季和冬季都呈现先上升后下降的趋势,分别在4号、3号和5号采样点达到季节最高,且冬季Chla含量在4号、5号和6号采样点均显著高于其他季节各点,并在5号采样点上达到全年最高。这主要是由于湿地水体核心区域3号、4号和5号采样点挺水植物较多和沉水植物相对较多,在春、夏、秋生长季节,植物和微生物协同去除氮磷作用较为显著,而且高等水生植物与微生物互作的化感作用还在一定程度上抑制藻类生长[21]。冬季再生水厂尾水营养负荷较高,而湿地生态系统净化效率最低,大量挺水植物未收割,植物残体在水中分解,造成二次污染,从而造成冬季可见的大量冷水性藻类增殖和Chla含量显著增加。水系Ⅱ区各点Chla浓度变化趋势为秋季、夏季高于春季、冬季,但并没有在冬季达到全年最高,整体处于较低水平。从图5(d)看出,水系Ⅰ区COD春季、冬季相对较高,夏季、秋季相对较低,不同季节沿水流方向变化规律不强。水系Ⅱ区COD由高到低为春季、夏季、秋季、冬季,沿水流方向略有上升趋势。由于补水水源COD负荷不同,水系Ⅱ区COD明显低于Ⅰ区,且COD波动范围较小,均可达地表水Ⅲ类标准。
2.5. 富营养化程度评价
2017年,湿地水体富营养化程度评价见表1。从表1看出,水系Ⅰ区6个点综合营养状态指数FTLI(∑)均为60~70,Ⅱ区3个点为30~60,Ⅰ区整体处于中度富营养状态,Ⅱ区整体处于中营养状态。水系Ⅰ区富营养程度较Ⅱ区明显严重,这主要是由于Ⅰ区再生水厂尾水(TN 15 mg·L?1、TP 0.5 mg·L?1) N、P营养盐输入量较大,而水系Ⅱ区径流雨水(TN 1.5 mg·L?1、TP 0.1 mg·L?1) N、P营养盐输入量较小。显然水系Ⅱ区也整体呈现一定的恶化趋势,9号采样点附近水体处于轻度富营养状态,这是由于目前湿地水系存在水体流动性较差、以沉水植物为主的生态系统构建不完善和大量未收割挺水植物的二次污染等现象。水系Ⅰ区水体由于N、P营养盐常年处于较高浓度水平,已引起Ⅰ区水体藻类等浮游植物大量生长繁殖,进而导致Ⅰ区水体富营养化和Chla、DO维持在较高浓度水平。2.6. 富营养化机理剖析
水体富营养化是由于水体中TN、TP等污染物浓度满足藻类生长条件,引起藻类数量、密度呈几何倍数增长和Chla浓度显著上升的现象,同时藻类的代谢可引起水体DO、SS的动态变化。利用SPSS(19.0)软件对湿地水体主要水质指标进行了K-S正态分布检验,各指标样本Sig.=0.2>0.05,服从正态分布,分析结果见表2。可以看出,Chla与TP、TN在0.01水平下呈显著相关(P<0.01),相关系数为?0.993、?0.973;与SS在0.05水平下呈显著相关(P<0.05),且相关系数为?0.761,与COD、DO在0.01水平下呈显著相关(P<0.01),相关系数为0.944、0.918,这与已有研究结论[19-20]一致。Chla与污染物指标的相关分析表明,当Chla浓度显著上升时,藻类季节性生长繁殖会引起水体TN、TP、SS浓度显著降低,水体COD、DO浓度增加,水体透明度降低。同时,DO与TP、TN在0.05水平下呈显著相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为?0.891、?0.861,表明在好氧条件下,水体生态系统有一定的净化能力,TN、TP浓度降低;相反在厌氧情况下,湿地净化能力丧失,TP、TN浓度上升。这是因为,藻类生长繁殖的过程是吸收消耗污染物和泌氧的过程,可使TP、TN浓度降低,DO浓度增加;然而藻类生命周期较短,当大面积藻类覆于水面,藻类新陈代谢结束后,其残体腐烂会消耗大量DO,吸收的营养物质会再次释放到水中,造成二次污染,引起TP、TN浓度再次上升。水体局部区域浮萍、满江红、水葫芦等一年生浮水植物的季节性繁殖导致的水质波动也是同理。在水体流动性欠佳、活性污泥生物脱氮除磷效果受限的情况下,湿地植物的季节性生长对氮、磷营养物浓度变化有显著影响。近3年来,湿地水体水质数据相对稳定,水系Ⅰ区呈现中度富营养化趋势,没有出现Chla、DO浓度显著下降和TN、TP浓度显著升高的情况,正如现场可见的湿地水体尚未发生大面积藻类腐烂,进而消耗大量DO,造成水体厌氧和出现重度富营养化的情况。2.7. 富营养化治理对策探讨
目前,我国再生水回用有关水质标准与地表水环境质量标准相差甚远,对于水流较缓、水环境容量较小和自净能力有限的地表水体,一级A标准尾水长期补水必然导致氮、磷营养盐积累增加,并逐步出现富营养化趋势,因此,有必要系统探讨再生水作为补水水源的城市湿地景观水体富营养化的治理对策。众所周知,湿地景观水体净化能力受补水污染负荷、气候、水文、二次污染等多方面因素的影响。首先,应确保再生水给湿地景观水体输入的氮、磷污染负荷应控制在水环境容量允许水平内,可通过采用污水深度脱氮除磷技术提高再生水的水质[22-26],如日本滋贺县湖南中部净化中心采用深度脱氮除磷处理工艺并执行极其严格的排放标准(TN 5.5 mg·L?1、TP 0.06 mg·L?1),有效保护了琵琶湖生态环境质量[26],还可采用河流等地表水作为补水水源,将再生水补水量控制在合理范围内,或同时控制再生水补水的水质和水量[1]。其次,应结合受纳湿地景观水体的地形、地貌、气候、水文条件,有针对性地采用一些清淤、水系连通、水系循环、生态浮床或多元组合系统[27-31],构建流动性好和以沉水植物为主的健康生态系统,以大幅提高湿地净化能力。最后,应加强城市湿地景观水体的长期维护管理,从而有效控制水体不遭受二次污染,特别是水生植物的季节性收割和藻类、漂浮植物和漂浮垃圾等的及时打捞,这对保持景观水体水质极为重要。2)以再生水、径流雨水作为补水水源的2个水系区域分别处于中度富营养、整体中营养,主要是由于再生水补水的氮、磷营养盐输入量远高于径流雨水补水。藻类季节性生长繁殖和Chla浓度显著上升表现为水体中度富营养化,同时引起水体TN、TP和SS浓度显著降低,COD、DO浓度增加和透明度降低。
3)在系统考虑再生水回用的受纳湿地景观水体的富营养化治理技术对策的基础上,可从再生水补水的水质和水量控制、因地制宜的受纳湿地水体健康生态系统的构建和水体的长期维护管理3个方面进行湿地景观水体富营养化的综合治理。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 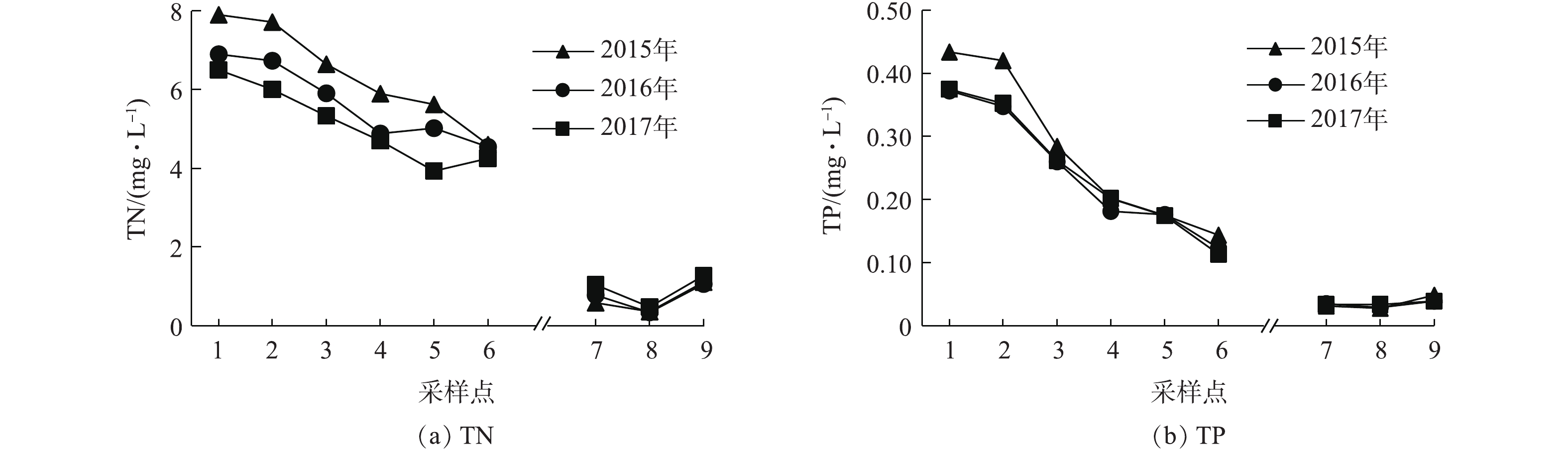
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图