全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,在城市污染企业搬迁后遗留、遗弃的工业污染场地中,苯系物、石油烃、多环芳烃等典型有机污染物被高频率检出,这些有机污染物极易扩散到环境中危害居民健康和环境安全[1]。随着《土壤污染防治行动计划》和《土壤污染防治法》的颁布,我国的土壤污染治理修复工作亟待进一步加强[2-4]。目前,已有多种修复技术应用于有机污染场地的修复实践中[5-7]。其中异位热脱附技术具有污染物去除率高、修复周期短、适用性强等显著优势,因而在有机污染场地土壤修复工程中得到普遍应用[8-10]。该技术的基本原理是通过直接或者间接加热,使土壤达到一定温度,其中的有机污染物向气相转换并挥发、分离,进而通过尾气处理系统彻底去除,实现尾气达标排放[11-12]。欧美等发达国家对于异位热脱附技术的探索研发已经开展了30余年,也已广泛应用于工程实践当中[13]。在1985年,该技术就已经入选美国环境保护署推荐技术[14],在1982—2014年开展的571个异位土壤修复项目中,77个采用异位热脱附技术,占项目总数的13.5%[15]。同时,自20世纪80年代以来,美国、法国、加拿大、阿根廷、韩国等多个国家的****针对苯系物、PCBs、PAHs、石油烃类等多种有机污染土壤进行了热脱附修复研究[16]。相关研究涵盖了污染土壤预处理技术[17]、热脱附原理[18]、尾气处理技术[19]、脱附效率影响因素[20]等许多方面,也有部分****开展了流化床式热脱附技术[21]、真空强化远红外线热脱附技术[22]等新型热脱附技术的探索。
我国对于异位热脱附技术设备的自主研发及应用起步较晚。首个关于有机污染土壤热脱附修复技术的中文专利授权于2009年,首篇相关中文文章发布于2011年。自2009年首次引进异位热脱附设备之后,我国的相关企业及科研机构纷纷进行探索研发及工程应用。截至2017年,共开展了23例污染场地异位热脱附修复项目[23],热脱附技术在我国的应用已初具规模。由于当前实际应用需求的增加,国内对于热脱附技术的研究开始进入快速发展阶段[24],相关****针对多种有机污染物,如六六六[25]、有机磷农药[26-27]、滴滴涕[28-29]、多氯联苯[30-31]等,以及汞污染土壤[32-34]开展了实验研究。相关研究主要集中于热脱附设备系统参数(温度、停留时间等)[35]、土壤特性(土壤粒径、含水率等)[36-37]和污染物特性[38-39]等热脱附效率的关键影响因素以及脉冲放电等离子体技术[40]、水泥窑协同处理技术[41]、低温等离子体技术[42]等热脱附尾气处理技术。
除上述理论研究外,少数****还针对热脱附技术设备工程应用开展了实验研究[43-44],为该技术的推广奠定了基础。但是,国内外于对热脱附技术的探索大都开展于小试或中试设备规模,对于大型技术设备的工程应用及工艺路线的分析总结则鲜见报道,现有的热脱附设备也仍然存在基础理论研究薄弱、装备能耗高、故障率高、二次污染控制水平低等问题,亟待进一步开展热脱附工艺优化及工程应用研究[45-47]。
本研究在系统梳理异位热脱附技术与设备在我国应用历程的基础上,结合国内已开展的异位热脱附修复项目,对比分析了典型直接和间接热脱附设备的工艺技术路线以及各自的优缺点,给出修复项目选择热脱附设备时的参考意见,同时提出了下一阶段的研发建议,以期进一步推动我国异位热脱附技术设备的自主研发及工程应用[48-49]。
2013年,中科鼎实环境工程有限公司(简称“中科鼎实”)自主研发了1套大型高温热脱附设备,并应用于北京某焦化污染场地,设计处理量为20~30 t·h?1[51]。2015年,在广州某钢铁厂多环芳烃污染场地修复项目中,建工修复除使用美国引进的设备外,同时也引进了1套芬兰的直接热脱附设备,处理量最高达50 t·h?1,应用效果良好[50]。2016年,为完成首钢原厂区多环芳烃、石油烃类等污染土壤修复工作,首钢环境产业有限公司(简称“首钢环境”)自主研发组装了1套直接热脱附设备,处理量可达25 t·h?1[52]。2018年,江苏盖亚环境工程有限公司自主研发了1套两段窑式直接热脱附设备,设计处理量为20 t·h?1[53]。
2012年,原环境保护部南京环境科学研究所同加拿大某公司合作,依托中加合作示范项目“土壤热相分离技术(TPS)工程化应用”,经过引进、消化和生产,研制出1整套的土壤热相分离系统,并在江苏省吴江市某石油烃类和苯系物污染场地中应用[54]。同年,依托国家“863”计划课题“多氯联苯类污染场地修复技术设备研发与示范”,杭州大地环保有限公司与浙江大学等合作研发了1套间接热脱附技术装备,并在杭州某农药污染场地开展了示范应用,设备处理量为1.2 t·h?1[55]。2013年,依托国家“863”计划课题“化工园区重大环境事故场地污染快速处理技术与装备”,建工修复与清华大学等合作成功研发1套特别针对爆炸型或事故型污染场地产生的高浓度污泥和土壤的热分离技术与装备(见图3),并在广州某项目完成了中试,设计处理量为1 t·h?1[50]。
2015年,建工修复引进了1台加拿大某厂商生产的间接热脱附设备,并应用于宁波某项目一期。同年,南京中船绿洲环保有限公司生产的1套螺旋推进式间接热脱附设备,在宁波某项目上应用实施,该设备由3套热脱附单元并联组成,单套热脱附单元的设计处理量为5 t·h?1[56]。2017年,浙江宜可欧环保科技有限公司自主研发组装了1套螺旋推进式间接热脱附设备,应用于上海宝山某苯系物和TPH污染场地,设备额定处理量为4 t·h?1[57]。同年,建工修复从美国引进了1套回转窑式间接热脱附设备,单套设计处理量为5 t·h?1,并应用于云南某汞污染场地修复工程[50]。
4.1. 直接热脱附技术设备工程应用案例
4.1.1. 江苏某化工污染场地修复项目
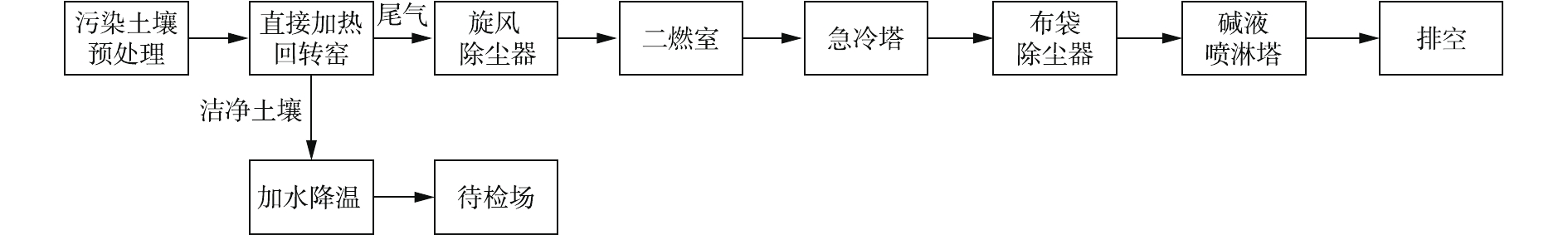
1) 项目概况。该场地在1958—2009年为农药化工厂,主要生产敌敌畏、液氯等,根据相关规划,于2010年正式停产搬迁。场地修复的总土方量约2×105 m3,主要土壤类型包括素填土、粉土夹粉质黏土、淤泥质粉质黏土,主要污染物为苯、甲苯、氯乙烯、1,1,2-三氯乙烷、氯仿等苯系物和氯代烃。综合考虑污染物特性、场地条件及业主要求等因素,选择采用直接热脱附工艺对场地中VOCs和SVOCs污染土壤及底泥进行修复。2) 热脱附设备情况。该场地修复所使用的是美国进口的直接热脱附设备。该套设备占地面积约500 m2,可24 h连续运行,平均处理量达20 t·h?1以上。
设备技术工艺流程为:经过破碎、筛分、调节含水率(20%以下)和除铁等预处理后的污染土壤首先进入顺烧式回转窑,脱附出的烟气进入到旋风除尘器进行除尘,除尘后的尾气进入到二燃室实现高温焚烧过程。随后烟气相继通过急冷塔、布袋除尘、碱液淋洗塔,处理达标后的尾气经过烟囱排空。总体工艺路线如图4所示。
经热脱附设备处理后,污染土壤中苯、甲苯、氯乙烯、1,1,2-三氯乙烷、氯仿等污染物去除率均达到99%以上,且尾气达标排放。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优点。在污染土壤预处理充分的情况下,设备处理量较大,可达到25 t·h?1,并且设备稳定性好,可实现24 h连续稳定运行;设备各处理单元模块化、集成化程度高,易于拆卸组装;设备整体布置紧凑,占地面积小(仅为500 m2左右);该套设备的中控系统较为完善,可实现对包括窑体温度、出料温度、尾气中主要污染物浓度等关键参数的实时监测和控制。②设备缺点。进料口易堵塞,预处理中土壤含水率未降到20%时,易造成设备进料口堵塞,降低产量;回转窑窑体外部保温措施不充分,使得热量散失较多,增加运行的成本;设备未设置余热回用单元,无法对二燃室高温烟气等进行热量回收,实现热能的充分利用。
4.1.2. 广东某钢铁厂污染场地修复项目
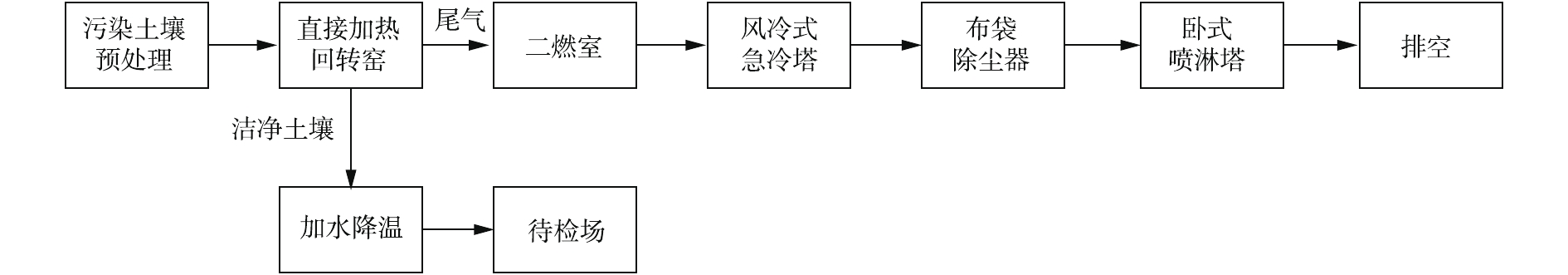
1) 项目概况。原厂为一家涉及黑色冶金及压延加工、物流等多个领域的地方钢铁联合企业,于2011年关停并搬出市区。该场地污染土方量517 591 m3。其中单一多环芳烃污染土壤1 730 m3,重金属和多环芳烃复合污染土壤515 861 m3。重金属污染物包括Pb、As、Cu、Zn和Ni;多环芳烃类污染物包括苯并(a)蒽、苯并(b)荧蒽、苯并(k)荧蒽等。经多方比对研究,确定对污染土壤先进行淋洗实现减量化,后再进行直接热脱附处理。对于重金属和多环芳烃复合污染土壤,在经热脱附处理后,再进行固化/稳定化。2) 热脱附设备情况。该场地上应用的是一套芬兰某厂商生产的直接热脱附设备,占地面积约为2 500 m2,可24 h连续运行,最大处理量达50 t·h?1。
设备主要工艺技术流程为:经破碎筛分机预处理后的土壤,进入大型土壤淋洗设备进行分级筛分处理,最终将筛分下的土壤及淋滤浓缩后的泥饼投入热脱附设备。在回转窑中,采用逆烧的方式对预处理后的污染土壤进行直接加热。脱附尾气相继通过二燃室、风冷式急冷塔、布袋除尘器和卧式碱液喷淋罐,最后达标排放。工艺路线如图5所示。
由于该设备处理的物料主要包括筛分后的土壤及淋洗压滤后的泥饼,预处理措施较好,热脱附设备运行良好,故障率低。处理后土壤中的的多环芳烃类污染物和总石油烃都达到了验收标准,且尾气达标排放,该项目已成功验收。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优势。设备处理量大,实际运行中最大处理量达50 t·h?1,且可实现连续稳定运行;相对于国产设备而言,其故障率更低,稳定性更好;作为该套设备的亮点之一,设备模块化程度较高,可移动性强,各处理单元都是拖车形式或集装箱形式,便于搬运和拆卸组装;该套设备采用了卧式喷淋的布置方式,可增加尾气同喷淋液接触面积,提高除酸效率,值得国产设备在研发过程中借鉴参考。②设备缺点。设备集成度相对而言较低,占地面积大(超过2 500 m2),而且对于基建施工要求较高,会增加项目总体成本;该套设备采用了风冷式急冷塔,运行过程中产生的噪声较大,而且进一步增加了设备的占地面积;整套设备未设置旋风除尘器,回转窑脱附烟气直接进入二燃室,降低了二燃室的处理效率,且易造成二燃室出气口堵塞等问题。
4.1.3. 北京某钢厂土壤修复项目
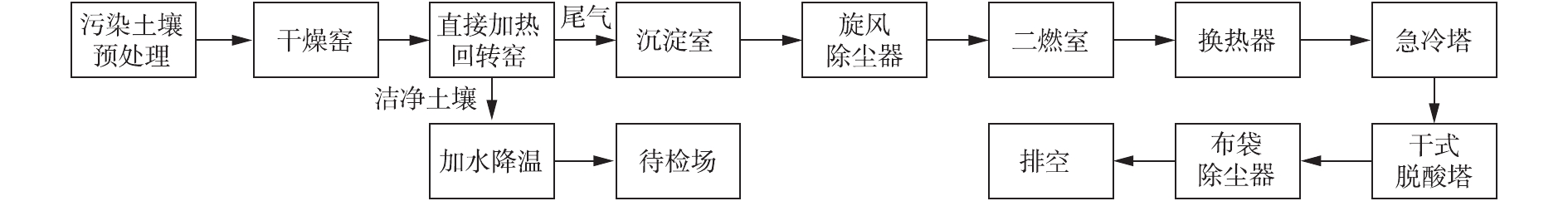
1) 项目概况。2016年,依据国家发改委相关要求,对北京某钢厂厂区已部分污染地块进行治理。项目修复对象为超过1×104 m3的多环芳烃、石油烃类有机污染土壤。结合前期调查结果,并基于技术可行性、经济性等多方考虑,决定采取直接热脱附技术开展治理修复。2) 热脱附设备概况。该项目中应用自主研发的两段窑式直接热脱附设备,处理能力可达25 t·h?1。设备的主要技术工艺流程为:污染土壤经过筛分、除铁、调节含水率(<15%)等预处理后,由螺旋给料机送入热脱附系统。利用预干燥窑、逆烧式回转窑对污染土进行加热(出土温度500 ℃,停留时间15 min),洁净土壤由水冷螺旋出料待检。脱附出的烟气则经沉降室沉降、旋风除尘器除尘、二燃室高温燃烧(温度≥850 ℃,停留时间≥2 s)、烟气余热回收、急冷塔冷却、石灰粉干式脱酸、布袋除尘器过滤后达标排放[43]。工艺路线如图6所示。
经现场检验,场地污染土壤中的多环芳烃、总石油烃去除率均大于98.17%。排放的尾气中各项指标浓度均满足《大气污染物综合排放标准》(DB 11/501-2007)要求。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优点。本套设备采用了串联式预干燥筒设计,同时选用逆烧加热的方式,利用高温烟气对污染土壤进行预干燥,提高了热能利用率;设备的工艺系统中设计添加了热交换器模块,对二燃室排出的高温烟气进行余热回用,并将回用热量用于加热回转窑中污染土壤和预热二燃室助燃空气,提高了热能利用效率,降低了设备的整体能耗。②设备缺点。在设备的尾气处理系统中,添加了沉降室模块,但是在整体设备以负压状态运行、烟气高速流动的情况下,该模块对于粉尘的沉降作用大小有待考证;旋风除尘器设置于进料皮带上方,除尘器沉淀下的飞灰直接输送至回转窑中,造成细颗粒在回转窑内的循环,降低了设备处理效率,并相对增加了设备的整体能耗;整套设备占地面积大,同时集成度较低,可移动性差。设备拆卸、组装、运输不便,不能够满足国内快速开展施工的要求。
4.2. 间接热脱附技术设备应用案例
4.2.1. 云南某含汞盐泥处理工程
1) 项目概况。根据政府相关规划,原厂于2011年4月停产关闭,该修复项目总污染治理方量约7.2×104 m3,其中含汞盐泥约3.1×104 m3,重度污染土壤约2.5×104 m3,中轻度污染土壤约1.6×104 m3。主要污染物包括Hg、As和Cd。对于重度污染土壤和含汞盐泥采用间接热脱附处理工艺,中轻度污染土壤采取固化稳定化工艺处理,验收合格后进行安全填埋。2) 热脱附设备概况。该套设备为美国进口,由2条平行的处理线组成,单条处理线的设计处置能力为5 t·h?1。含汞盐泥或重度污染土经调节含水率等预处理后,进入间接热脱附设备回转窑内进行加热处理,洁净物料经喷加水降温后进入出料斗。脱附烟气首先经陶瓷过滤器过滤,滤下的粉尘同处理后的物料一起完成出料。后续烟气相继进入急冷塔、填料洗涤塔、冷凝盘管和活性炭罐,最终同天然气燃烧后的尾气一起排空。汞污染物则转移富集到水和污泥中,通过净化处理设备进一步处理。工艺路线如图7所示。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优势。整套设备的处理能力较高,单套设备设计处理量达5 t·h?1,且整套设备包含两条平行的处理线,可同时运行,设备的工艺设计较为合理;模块化程度较高,可移动性强,加热单元、尾气处理单元等都设计为单独的集装箱式模块,且箱底配有多组车轮,可实现设备的快速拆卸、组装和运输;设备的集成度高,各处理模块布置紧凑,占地面积小,整套设备的布置安装方式对于国产设备的研发制造具有很好的借鉴、参考价值。②设备缺点。未设置热能回收利用系统,不能充分利用高温烟气等产生的余热;陶瓷过滤器滤下的粉尘直接进入出料系统,可能存在粉尘不达标问题;出料皮带搭建得较高且未封闭,若加水降尘措施不到位,可能会产生扬尘问题。
4.2.2. 上海宝山某化工污染场地修复项目
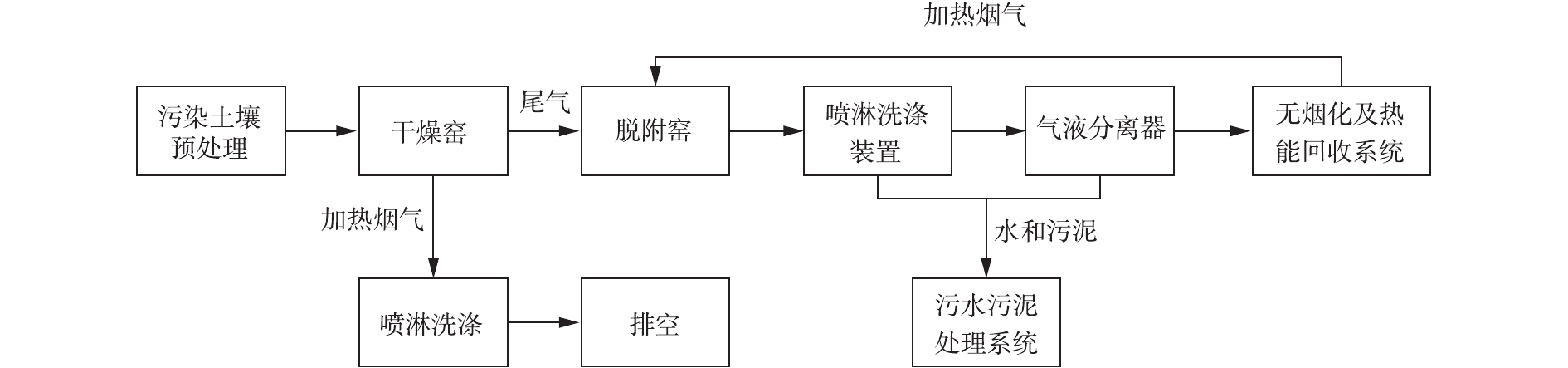
1) 项目概况。原厂创建于1958年,主要生产苯甲腈、苯代三聚氰胺、松香树脂等物质。场地污染土方量为9 612.5 m3,土壤主要为黏土,土质松散湿润。主要污染物包括:乙苯、萘等VOCs;苯并(a)蒽、苯并(a)芘、总石油烃类等SVOCs。对于SVOCs、SVOCs+VOCs高风险污染土壤均采用异位间接热脱附工艺,污染土壤修复后合格进行原位回填处置。2) 热脱附设备概况。本套间接热脱附设备利用生物质作燃料,设备额定处理量为4 t·h?1。主要技术工艺路线为:经过破碎、筛分、调节含水率(≤20%)等预处理后的污染土,由进料设备投入至热脱附回转窑内完成热解脱附过程,清洁土壤经冷却输出装置排出。热解脱附尾气首先进入三相分离系统中,通过喷淋洗涤的方式,对粉尘及有机污染成分进行洗脱,不凝气则通过气液分离器进一步脱水后,进入热解气无害化区。用于加热的烟气经回转窑换热后温度降至200~300 ℃,接下来通过喷淋洗涤塔净化,最终达标排放。喷淋下的污水则排放到循环水处理系统中进行处理。工艺路线如图8所示。经检测,本套间接热脱附设备处理后的有机污染土壤,均达到了修复目标值,且尾气达标排放。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优势。热能利用效率高,设计安装了无烟化及热能回收利用系统,可充分利用余热,降低了设备整体能耗和运行成本。同时,两段炉的设计可降低燃烧炉热损失,有效提高了热能利用率;设备的中控系统较为完善,自动化程度较高,设置了预警、报警、数据采集等控制系统,可及时了解掌握设备运行状态;采用生物质作燃料,供给系统所需热能的方式比较新颖,符合可持续发展的要求,也给国产设备的研发提供了新的发展思路,可考虑设置多能源的热能供给系统。②设备缺点。设备集约化程度较低,各模板布置较为分散,占地面积大,不利于快速安装、运输;作为国产化设备,连续运行稳定性不足的特点较为突出;生物质燃料燃烧后的尾气是否需要进一处理,例如添加除尘模块等,再经活性炭吸附排放,仍然有待商榷。
4.2.3. 宁波市江东某污染场地修复项目
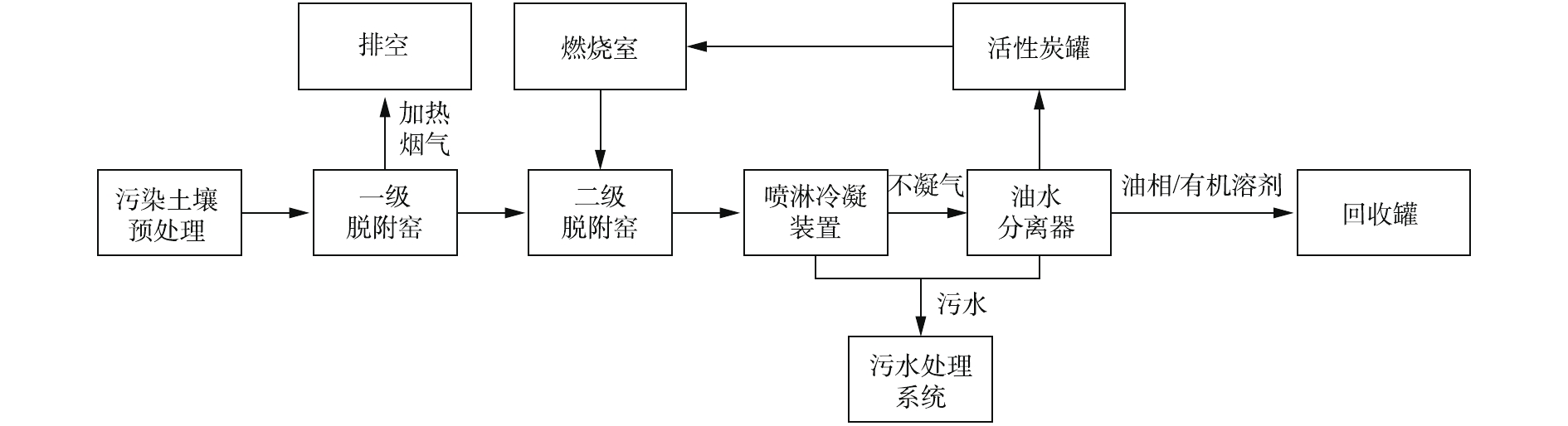
1) 项目概况。场地原址为宁波某农药厂,成立于1958年,主要产品有马拉松、杀螟松等有机农药,根据相关规划,于2004年8月全部停产。本项目土壤修复土方量为56 897 m3,间接热脱附处置污染土壤总方量为24 808 m3。场地土壤主要为回填杂土和粉质黏土,主要污染物包括:苯并(a)蒽、苯并(a)芘、苯并(b)荧蒽、联苯胺、六氯苯等。2) 热脱附设备概况。本项目采用的间接热脱附设备为国内厂商生产制造,由3套热脱附单元并联组成,单套设备设计处理量为5 t·h?1。整套设备组成包括进料单元、出料单元、热脱附单元、冷凝单元、尾气处理排放单元、污水处理单元以及电气控制单元等。
预处理后的污染土壤先后经一级脱附室、二级脱附室进行间接加热,清洁土壤则经加水降温后出料。高温热脱附气通过喷淋冷却降温,冷凝后的含泥、油及其他沉淀物进行油/水分离,污水经处理洁净后被回用至喷淋冷却装置。不凝气经活性炭过滤后再送燃烧室高温分解,确保排放达标。主要工艺路线如图9所示。
经现场检测,本套间接热脱附设备处理后的有机污染土壤均达到了修复目标值,且尾气达标排放。
3) 设备优缺点分析。①设备优势。模块化、集成化程度较高,所有主体单元都集成在相应的框架内,同时设备可拆分成几个集装箱组装运输到特定场地,再组装成一个整体,10 d左右即可完成组装,进行现场调试;热能利用效率较高,采用两级脱附室的设计,加热烟气与污染土壤采用逆向运行的换热方式,都可有效提高热能利用率;设计处理量大,单套热脱附单元处理量为5 t·h?1,3套并联的热脱附单元并联使用,总处理量达15 t·h?1。该套设备也是目前国内应用并联设置套数最多的热脱附设备之一。②设备缺点。作为自主研发设备,连续运行稳定性有待提高;整套设备未设置热能回收利用系统,不能最大程度地利用余热;污水处理模块集约化程度较低,占地积较大;用于加热窑体的烟气未经任何处理直接排放,可能存在不达标问题。
尽管如此,热脱附技术对有机类污染土壤的修复效率、安全性、修复成本及工期方面仍具备一定的优势,在未来一段时间内,其应用前景依旧广阔。表3为直接热脱附和间接热脱附的优缺点对比结果,在实际修复施工时,须综合考虑修复项目的施工工期、目标污染物和土壤理化性质以及工艺成熟度等因素选取相应处理方式。
针对目前我国在用热脱附技术与装备普遍存在的修复能力不足、能效水平低、二 次污染物生成机制认识不清等问题,结合国内场地修复项目周期短、污染情况复杂、修复土方量大、资金有限等情况,对异位热脱附技术与设备研究发展方向提出以下建议。
6.1. 基础理论研究建议
1) 深入开展热脱附技术基础性理论研究,如高温条件下土壤有机污染物固-液-气界面行为及关键影响参数研究、典型污染物的迁移转化规律及控制条件研究、黏性土壤调理及其对典型有机污染物热脱附的作用机制研究等,为该技术应用发展夯实理论支撑。2) 开展直接/间接加热单元中土壤传热传质特性研究,揭示热脱附过程的传热传质机理,得到不同含水量和污染程度的土壤导热系数、水分析出速率及热脱附速率等传热传质参数和关键位置的温度值。同时,针对不同有机污染土壤,通过实验研究和数值模拟等手段研究加热单元关键结构(加热单元直径、长度和布置倾角)设计和运行参数(转速及进出料速度等)与容积利用率的关系,探究加热单元内扬料板等关键部件的结构和布置对土壤传热和污染物脱附效率的影响。
3) 探索热脱附过程二次污染控制机理,获得直接热脱附关键环节(加热单元、急冷和除尘)有机污染物沿程气-固相分布,研究土壤间接热脱附尾气经喷淋冷却后有机污染物的迁移规律,探明喷淋冷却对不同有机污染物捕集的适用条件,分析喷淋水温、循环水量等因素对尾气中污染物在固-液-气三相间的迁移行为影响,获得有机污染物在直接/间接热脱附尾气净化单元沿程分布特性。同时,对比分析螺旋出料和回转窑出料方式对粉尘的抑制效果,降低出料过程中扬尘的产生量。
4) 探索多种修复技术组合的方式,开展多途径耦合联用。例如热脱附耦合化学氧化技术,先通过异位热脱附把污染物由高浓度,降低到低浓度(还没达到修复目标值),再在螺旋出料装置中加入氧化药剂,利用化学氧化技术将污染物彻底降解[60]。
6.2. 设备发展建议
1) 提高设备的模块化程度。每个处理单元进行模块化设计,便于拆卸组装,并可根据项目实际需求添加或减少某一处理模块,扩大设备实际适用范围。2) 提高设备的集成化程度和可移动性。采取紧凑型集成设计,减小设备占地面积,降低基建成本,同时,增加各处理模块的可移动性,缩短建设及运输时间,满足国内快速施工的需求。
3) 提高设备的智能化程度。完善发展自动控制、监测等智能系统,便于对设备运行情况进行实时监测、控制,提高工作效率,降低人工成本。
4) 提高设备处理能力和运行稳定性。可采取多套热脱附处理单位并联的设置方式,提高单位时间的处理能力;同时,需在参考借鉴的基础上,研发生产更为专业化的设备、部件,降低故障率,增强运行稳定性。
5) 发展余热回用技术,提高热能利用率。通过添加热能回收利用模块,对直接热脱附设备的二燃室高温烟气、间接热脱附设备加热烟气等进行余热回用,提高热效率;可发展优化两段窑式设置方式,充分利用热能,降低设备运行成本。
6) 探索研发多能源供给式设备。探索研发天然气、电、燃油、生物质等多能源供给型热脱附设备,扩大设备对不同场地条件、施工要求的适用性。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图