 ), 耿秋晨1
), 耿秋晨1 1山东师范大学心理学院, 济南 250358
2山东中医药大学中医学院, 济南 250355
收稿日期:2018-04-12出版日期:2019-03-25发布日期:2019-01-22通讯作者:毛伟宾E-mail:wb_mao@163.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金(31571113);山东省自然科学基金资助(ZR2014CM022)The effect of emotion on directed forgetting for continuous events
REN Xiaoyun1, LI Yuting2, MAO Weibin1( ), GENG Qiuchen1
), GENG Qiuchen1 1 School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
2 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, China
Received:2018-04-12Online:2019-03-25Published:2019-01-22Contact:MAO Weibin E-mail:wb_mao@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究采用项目法定向遗忘范式以中性和负性连续事件的视频为实验材料, 通过2个实验考察了情绪对连续事件定向遗忘的影响, 并进一步探讨了情绪对细节记忆和要义记忆的定向遗忘的影响。结果发现, 情绪可以消除细节记忆的定向遗忘效应, 而仅有要义记忆的定向遗忘效应则主要受到事件连续性而非情绪的影响。
图/表 9

图1再认图片示例
 图1再认图片示例
图1再认图片示例
图2学习阶段流程图
 图2学习阶段流程图
图2学习阶段流程图表1不同情绪类型下记住和忘记片段的要义和细节回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 要义回忆 | 0.25 ± 0.10 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 0.31 ± 0.12 | 0.29 ± 0.11 |
| 细节回忆 | 0.12 ± 0.11 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 0.04 |
表1不同情绪类型下记住和忘记片段的要义和细节回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 要义回忆 | 0.25 ± 0.10 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 0.31 ± 0.12 | 0.29 ± 0.11 |
| 细节回忆 | 0.12 ± 0.11 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 0.04 |
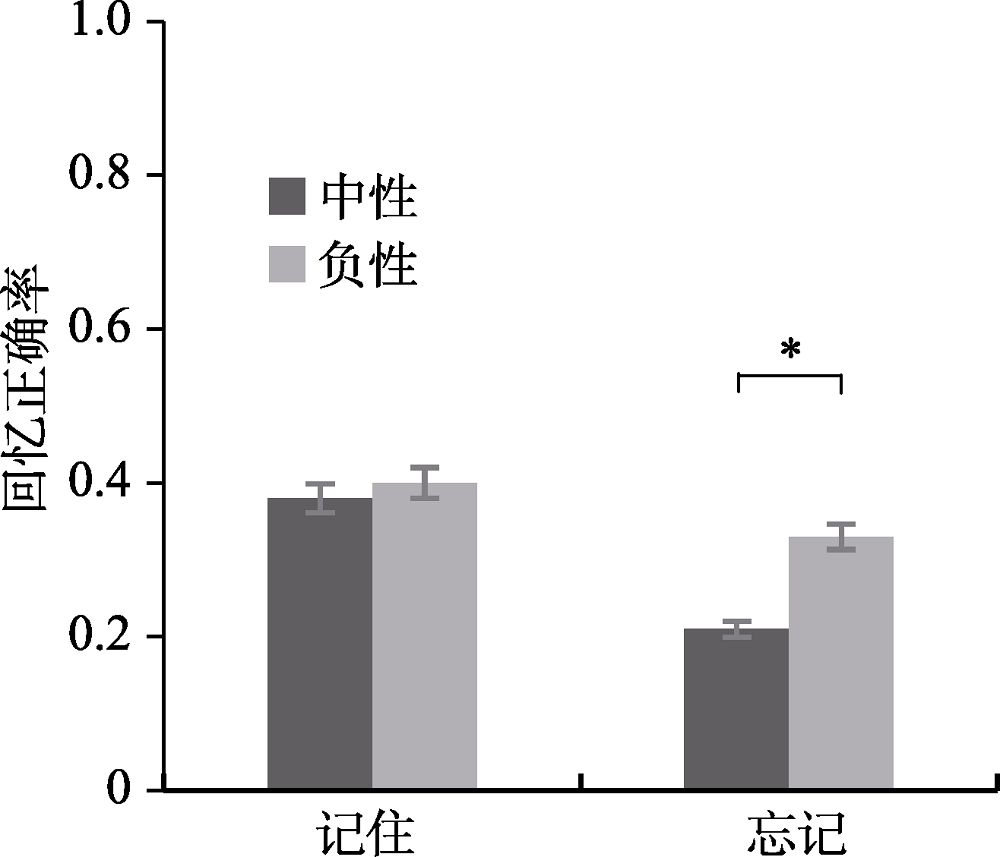
图3不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的回忆正确率
 图3不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的回忆正确率
图3不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的回忆正确率表2不同情绪类型下记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 细节再认 | 0.82 ± 0.13 | 0.70 ± 0.24 | 0.83 ± 0.10 | 0.84 ± 0.13 |
| 仅有要义再认 | 0.53 ± 0.22 | 0.51 ± 0.27 | 0.55 ± 0.22 | 0.48 ± 0.25 |
表2不同情绪类型下记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 细节再认 | 0.82 ± 0.13 | 0.70 ± 0.24 | 0.83 ± 0.10 | 0.84 ± 0.13 |
| 仅有要义再认 | 0.53 ± 0.22 | 0.51 ± 0.27 | 0.55 ± 0.22 | 0.48 ± 0.25 |

图4不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的细节再认正确率
 图4不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的细节再认正确率
图4不同情绪类型下记住片段和忘记片段的细节再认正确率表3不同情绪条件下记住和忘记片段的要义和细节回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 要义回忆 | 0.29 ± 0.10 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.16 ± 0.08 |
| 细节回忆 | 0.10 ± 0.11 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.05 ± 0.06 |
表3不同情绪条件下记住和忘记片段的要义和细节回忆正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 要义回忆 | 0.29 ± 0.10 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.16 ± 0.08 |
| 细节回忆 | 0.10 ± 0.11 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.05 ± 0.06 |
表4不同情绪条件下记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 细节再认 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.62 ± 0.26 | 0.77 ± 0.12 | 0.70 ± 0.19 |
| 仅有要义再认 | 0.56 ± 0.20 | 0.46 ± 0.24 | 0.56 ± 0.25 | 0.43 ± 0.25 |
表4不同情绪条件下记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率(M ± SD)
| 记忆类型 | 中性视频 | 负性视频 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | 记住片段 | 忘记片段 | |
| 细节再认 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.62 ± 0.26 | 0.77 ± 0.12 | 0.70 ± 0.19 |
| 仅有要义再认 | 0.56 ± 0.20 | 0.46 ± 0.24 | 0.56 ± 0.25 | 0.43 ± 0.25 |
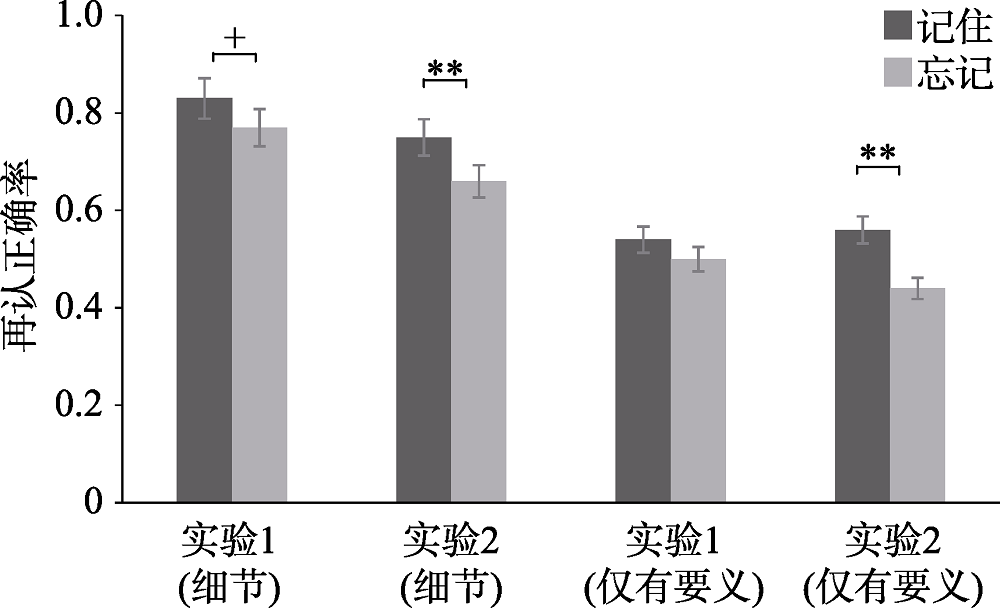
图5实验1和2中记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率
 图5实验1和2中记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率
图5实验1和2中记住和忘记片段的细节和仅有要义再认正确率参考文献 46
| [1] | Adolphs R., Denburg N. L., &Tranel D . ( 2001). The amygdala's role in long-term declarative memory for gist and detail. Behavioral Neuroscience, 115( 5), 983-992. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.115.5.983URLpmid: 11584931 |
| [2] | Adolphs R., Tranel D., &Buchanan T. W . ( 2005). Amygdala damage impairs emotional memory for gist but not details of complex stimuli. Nature Neuroscience, 8( 4), 512-518. doi: 10.1038/nn1413URLpmid: 15735643 |
| [3] | Bai X. J., Wang Y. Y., &Yang H. B . ( 2012). The impact of mood-congruence on intentional forgetting. Journal of Psychological Science, 35( 1), 9-15. |
| [ 白学军, 王媛媛, 杨海波 . ( 2012). 情绪一致性对有意遗忘的影响. 心理科学, 35( 1), 9-15.] | |
| [4] | Bailey ,K., &Chapman P. , ( 2012). When can we choose to forget? An ERP study into item-method directed forgetting of emotional words. Brain and Cognition, 78( 2), 133-147. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2011.11.004URLpmid: 22240487 |
| [5] | Bancroft T. D., Hockley W. E., &Farquhar R . ( 2013). The longer we have to forget the more we remember: The ironic effect of postcue duration in item-based directed forgetting. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 39( 3), 691-699. doi: 10.1037/a0029523URLpmid: 22845067 |
| [6] | Barnier A. J., Conway M. A., Mayoh L., Speyer J., Avizmil O., &Harris C. B . ( 2007). Directed forgetting of recently recalled autobiographical memories. Journal of Experimental Psychology General, 136( 2), 301-322. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.136.2.301URLpmid: 17500653 |
| [7] | Basden , B.H., &Basden D.R . ( 1996). Directed forgetting: Further comparisons of the item and list methods. Memory, 4( 6), 633-653. doi: 10.1080/741941000URLpmid: 8934458 |
| [8] | Basden B. H., Basden D. R., &Gargano G. J . ( 1993). Directed forgetting in implicit and explicit memory tests: A comparison of methods. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 19( 3), 603-616. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.19.3.603URL |
| [9] | Bjork ,R.A . ( 1970). Positive forgetting: The noninterference of items intentionally forgotten. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 9( 3), 255-268. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5371(70)80059-7URL |
| [10] | Bjork ,R.A . ( 1972). Theoretical implications of directed forgetting. In A. W. Melton, & E. Martin (Eds.), Coding processes in human memory( pp. 217-235). Washington, DC: Winston. |
| [11] | Bjork ,R.A . ( 1989). Retrieval inhibition as an adaptive mechanism in human memory. In H. L. Rosdiger & F. I. M. Craik (Eds.), Varieties of Memory & Consciousness: Essays in Honor of Enddel Tulving ( pp.309-330). Hillside, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [12] | Bjork ,R.A., &Woodward A.E . ( 1973). Directed forgetting of individual words in free recall. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 99( 1), 22-27. doi: 10.1037/h0034757URL |
| [13] | Burke A., Heuer F., &Reisberg D . ( 1992). Remembering emotional events. Memory & Cognition, 20( 3), 277-290. |
| [14] | Cohens J . ( 1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Technometrics, 31( 4), 499-500. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-179060-8.50012-8URL |
| [15] | Conway M. A., Harries K., Noyes J., Racsma′ny M., &Frankish C. R . ( 2000). The disruption and dissolution of directed forgetting: Inhibitory control of memory. Journal of Memory and Language, 43( 3), 409-430. doi: 10.1006/jmla.2000.2706URL |
| [16] | Cui ,L.X., &Huang M.R . ( 2007). Effects of rumination and distraction on negative emotion and autobiographical memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39( 1), 78-87. |
| [ 崔丽弦, 黄敏儿 . ( 2007). 沉思和分心对负情绪和自传体记忆的影响. 心理学报, 39( 1), 78-87.] | |
| [17] | Fawcett J. M., Taylor T. L., &Lynn N . ( 2014). Event-method directed forgetting: Forgetting a video segment is more effortful than remembering it. Acta Psychologica, 144( 2), 332-343. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2013.07.005URLpmid: 23933003 |
| [18] | Fawcett J. M., Taylor T. L., &Nadel L . ( 2013). Intentional forgetting diminishes memory for continuous events. Memory, 21( 6), 675-694. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2012.748078URLpmid: 23301998 |
| [19] | Ge C., Tian Z., Zhang Z. N., &Sun B . ( 2015). The research of negative and neutral words on directed forgetting effects. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 13( 4), 461-465. |
| [ 葛操, 田峥, 张振宁, 孙彬 . ( 2015). 负性词语与中性词语的定向遗忘效应. 心理与行为研究, 13( 4), 461-465.] | |
| [20] | Geiselman ,R.E., &Bagheri B. ( 1985). Repetition effects in directed forgetting: Evidence for retrieval inhibition. Memory & Cognition, 13( 1), 57-62. doi: 10.3758/BF03198444URLpmid: 4010515 |
| [21] | Golding J. M., Long D. L., &Macleod C. M . ( 1994). You can°t always forget what you want: Directed forgetting of related words. Journal of Memory & Language, 33( 4), 493-510. doi: 10.1006/jmla.1994.1023URL |
| [22] | Hauswald A., Schulz H., Iordanov T., &Kissler J . ( 2011). ERP dynamics underlying successful directed forgetting of neutral but not negative pictures. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 6( 4), 450-459. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsq061URLpmid: 20601423 |
| [23] | Hupbach A . ( 2017). Long-term effects of directed forgetting. Memory, 26( 3), 321-329. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2017.1358748URLpmid: 28766463 |
| [24] | Jia ,H.Y., &Liang S.R . ( 2010). Emotion affects word- directed forgetting. Psychological Science, 33( 2), 416-418. |
| [ 贾宏燕, 梁拴荣 . ( 2010). 情绪对单字法定向遗忘的影响. 心理科学, 33( 2), 416-418.] | |
| [25] | Jia Z., Mao W. B., &Dong L. Y . ( 2014). Effect of events and self-relevance on directed forgetting of negative emotional memory. Psychological Science, 37( 4), 840-844. |
| [ 贾喆, 毛伟宾, 东利云 . ( 2014). 内容与自我关联性对负性情绪记忆定向遗忘的影响. 心理科学, 37( 4), 840-844.] | |
| [26] | Joslyn ,S.L., &Oakes M.A . ( 2005). Directed forgetting of autobiographical events. Memory & Cognition, 33( 4), 577-587. |
| [27] | Kensinger ,E.A . ( 2009). Remembering the details: Effects of emotion. Emotion Review, 1( 2), 99-113. doi: 10.1177/1754073908100432URL |
| [28] | Kensinger E. A., Garoff-Eaton R. J., &Schacter D. L . ( 2006). Memory for specific visual details can be enhanced by negative arousing content. Journal of Memory & Language, 54( 1), 99-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2005.05.005URL |
| [29] | Kensinger E. A., Garoff-Eaton R. J., &Schacter D. L . ( 2007). Effects of emotion on memory specificity: Memory trade- offs elicited by negative visually arousing stimuli. Journal of Memory and Language, 56( 4), 575-591. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2006.05.004URL |
| [30] | Kern R. P., Libkuman T. M., Otani H., &Holmes K . ( 2005). Emotional stimuli, divided attention, and memory . Emotion, 5( 4), 408-417. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.5.4.408URLpmid: 16366745 |
| [31] | Lehman M., &Malmberg K.J . ( 2009). A global theory of remembering and forgetting from multiple lists. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 35( 4), 970-988. doi: 10.1037/a0015728URLpmid: 19586264 |
| [32] | Nowicka A., Marchewka A., Jednoróg K., Tacikowski P., &Brechmann A . ( 2011). Forgetting of emotional information is hard: An fMRI study of directed forgetting. Cerebral Cortex, 21( 3), 539-549. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq117URLpmid: 20584747 |
| [33] | Ohman A., Flykt A., &Esteves F . ( 2001). Emotion drives attention: Detecting the snake in the grass. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 130( 3), 466-478. |
| [34] | Payne B.K., &Corrigan E .( 2007). Emotional constraints on intentional forgetting. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 43( 5), 780-786. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2006.07.005URL |
| [35] | Quinlan, C. K., & Taylor, T. L . ( 2014). “I never forget a face, but in your case I’ll be glad to make an exception”: Intentional forgetting of emotional faces. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology, 68( 3), 212-221. doi: 10.1037/cep0000024URL |
| [36] | Robinson A. K., Plaut D. C., &Behrmann M . ( 2017). Word and face processing engage overlapping distributed networks: Evidence from RSVP and EEG investigations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146( 7), 943-961. doi: 10.1037/xge0000302URLpmid: 28368200 |
| [37] | Sahakyan L., &Goodmon L.B . ( 2007). The influence of directional associations on directed forgetting and interference. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 33( 6), 1035-1049. |
| [38] | Sahakyan L., Delaney P. F., Foster N. L., &Abushanab B . ( 2013). Chapter four-list-method directed forgetting in cognitive and clinical research: A theoretical and methodological review. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 59, 131-189. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407187-2.00004-6URL |
| [39] | Snodgrass J.G., &Corwin J . ( 1988). Perceptual identification thresholds for 150 fragmented pictures from the snodgrass and vanderwart picture set. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 67( 1), 3-36. doi: 10.2466/pms.1988.67.1.3URLpmid: 3211683 |
| [40] | Tolin D. F., Hamlin C., &Foa E. B . ( 2002). Directed forgetting in obsessivecompulsive disorder: Replication and extension. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 40( 7), 793-803. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(01)00062-6URLpmid: 12074373 |
| [41] | Wessel I., &Merckelbach H . ( 2006). Forgetting “murder” is not harder than forgetting “circle”: List wise-directed forgetting of emotional words. Cognition and Emotion, 20 ( 1), 129-137. doi: 10.1080/02699930500260195URL |
| [42] | Woodward A.E., &Bjork R.A . ( 1971). Forgetting and remembering in free recall: Intentional and unintentional. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 89( 1), 109-116. doi: 10.1037/h0031188URL |
| [43] | Yang W. J., Yang J. H., Xiao X., &Zhang Q. L . ( 2012). Directed forgetting of negative memories and its mechanisms. Psychological Science, 35( 1), 50-55. |
| [ 杨文静, 杨金华, 肖宵, 张庆林 . ( 2012). 负性情绪材料的定向遗忘及心理机制. 心理科学, 35( 1), 50-55.] | |
| [44] | Yang W. J., Zhang Q. L., Wu Z. L., &Jia L . ( 2010). Intentional forgetting of emotional memory. Advances in Psychological Science, 18( 6), 871-877. |
| [ 杨文静, 张庆林, 伍泽莲, 贾磊 . ( 2010). 情绪性记忆的主动遗忘. 心理科学进展, 18( 6), 871-877.] | |
| [45] | Yonelinas A.P., &Jacoby L.L . ( 1995). The relation between remembering and knowing as bases for recognition: Effects of size congruency. Journal of Memory & Language, 34( 5), 622-643. doi: 10.1006/jmla.1995.1028URL |
| [46] | Zacks R. T., Radvansky G., &Hasher L . ( 1996). Studies of directed forgetting in older adults. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 22( 1), 143-156. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.22.1.143URLpmid: 8648283 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 程瑞, 卢克龙, 郝宁. 愤怒情绪对恶意创造力的影响及调节策略[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 847-860. |
| [2] | 宋琪, 陈扬. 需求和接受的授权型领导匹配对下属工作结果的影响:情绪耗竭的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 890-903. |
| [3] | 熊承清, 许佳颖, 马丹阳, 刘永芳. 囚徒困境博弈中对手面部表情对合作行为的影响及其作用机制[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 919-932. |
| [4] | 袁加锦, 张祎程, 陈圣栋, 罗利, 茹怡珊. 中国情绪调节词语库的初步编制与试用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 445-455. |
| [5] | 宋锡妍, 程亚华, 谢周秀甜, 龚楠焰, 刘雷. 愤怒情绪对延迟折扣的影响:确定感和控制感的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 456-468. |
| [6] | 莫李澄, 郭田友, 张岳瑶, 徐锋, 张丹丹. 激活右腹外侧前额叶提高抑郁症患者对社会疼痛的情绪调节能力:一项TMS研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 494-504. |
| [7] | 杨伟文, 李超平. 资质过剩感对个体绩效的作用效果及机制:基于情绪-认知加工系统与文化情境的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 527-554. |
| [8] | 侯娟, 朱英格, 方晓义. 手机成瘾与抑郁:社交焦虑和负性情绪信息注意偏向的多重中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(4): 362-373. |
| [9] | 刘宇平, 李姗珊, 何赟, 王豆豆, 杨波. 消除威胁或无能狂怒?自恋对暴力犯攻击的影响机制[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(3): 244-258. |
| [10] | 雷震, 毕蓉, 莫李澄, 于文汶, 张丹丹. 外显和内隐情绪韵律加工的脑机制:近红外成像研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 15-25. |
| [11] | 黄月胜, 张豹, 范兴华, 黄杰. 无关工作记忆表征的负性情绪信息能否捕获视觉注意?一项眼动研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 26-37. |
| [12] | 苗晓燕, 孙欣, 匡仪, 汪祚军. 共患难, 更同盟:共同经历相同负性情绪事件促进合作行为[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 81-94. |
| [13] | 华艳, 李明霞, 王巧婷, 冯彩霞, 张晶. 左侧眶额皮层在自动情绪调节下注意选择中的作用:来自经颅直流电刺激的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1048-1056. |
| [14] | 李树文, 罗瑾琏. 领导-下属情绪评价能力一致与员工建言:内部人身份感知与性别相似性的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1121-1131. |
| [15] | 张琪, 邓娜丽, 姜秀敏, 李卫君. 自我相关性影响情绪词汇加工的时间进程[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(8): 946-957. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4400
