1 武汉大学经济与管理学院
2 武汉大学组织营销研究中心, 武汉 430072
收稿日期:2017-04-06出版日期:2019-01-25发布日期:2018-11-26通讯作者:崔楠基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71472141);* 国家自然科学基金项目(71472142);* 国家自然科学基金项目(71772141);* 国家自然科学基金项目资助(71872140)Enjoy the present or wait for the future? Effects of individuals’ view of time on intertemporal choice
XU Lan1,2, CHEN Quan1, CUI Nan1,2,*, LU Kaili11 Economics and Management School, Wuhan University
2 Research Center for Organizational Marketing of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
Received:2017-04-06Online:2019-01-25Published:2018-11-26Contact:CUI Nan 摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究通过三组实验考察了线性和循环两种时间观对跨期决策的影响。实验1表明与循环时间观的人相比, 线性时间观的人在跨期决策时更倾向于选择近期选项(假设1)。实验2进一步验证假设1, 并且验证了时间感知的中介作用(假设2)。实验3考察了时间标记(有标记 VS. 无标记)对主效应的调节作用(假设3)。实验结果发现, 在无标记情境下, 线性时间观的人们会比循环时间观的人们更偏好近期选项; 而在有标记情境下, 这种效应会被减弱。本研究揭示了时间观可以作为个体跨期决策偏好的一种影响因素, 并丰富了主观时间感知角度的跨期决策研究。
图/表 3

图1循环时间观操控
 图1循环时间观操控
图1循环时间观操控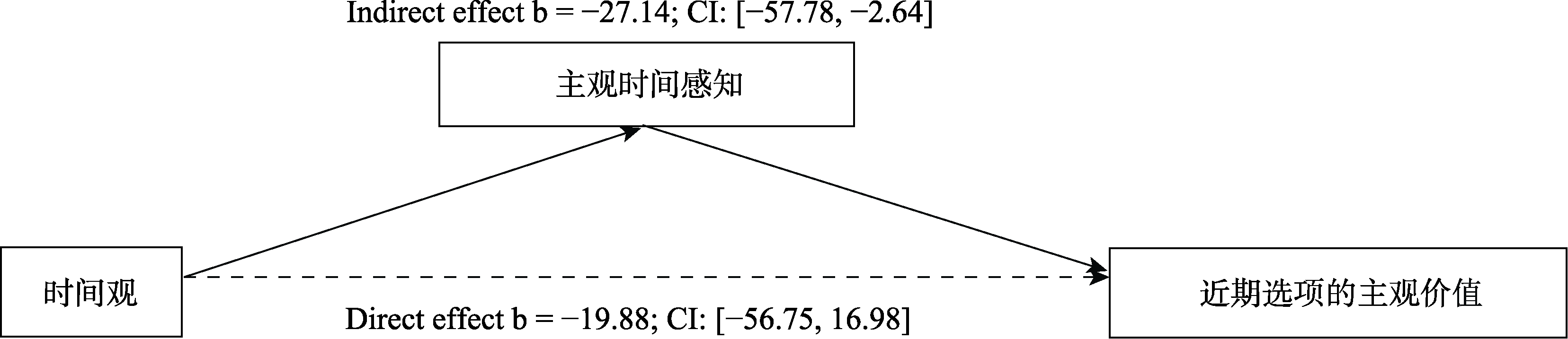
图2实验2中主观时间感知的中介作用
 图2实验2中主观时间感知的中介作用
图2实验2中主观时间感知的中介作用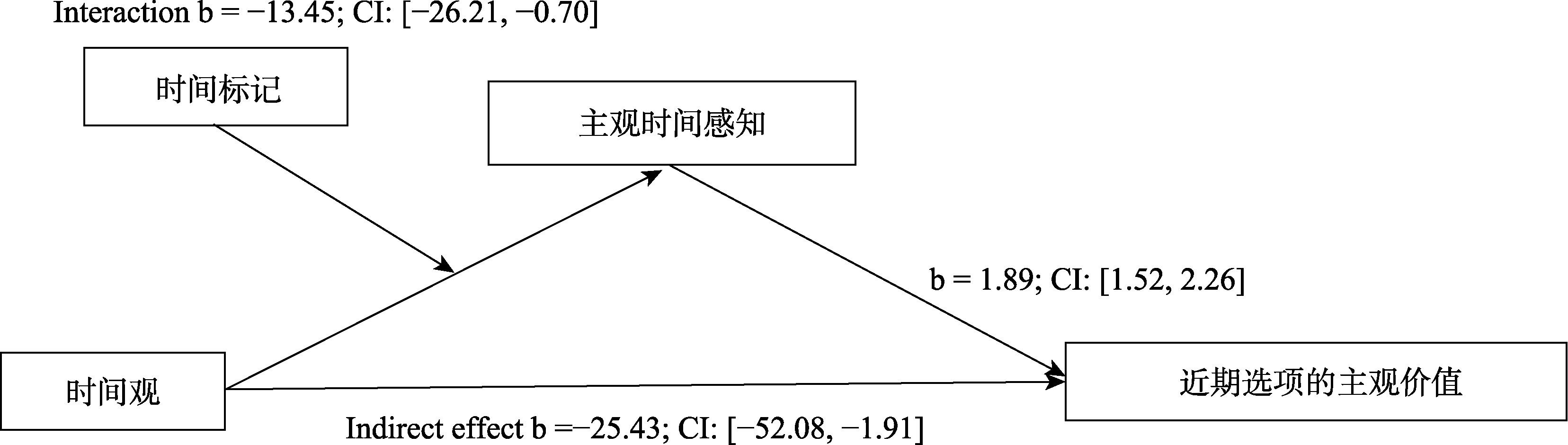
图3实验3中调节的中介效应
 图3实验3中调节的中介效应
图3实验3中调节的中介效应参考文献 43
| [1] | Baltes P.B . ( 1987). Theoretical propositions of life-span developmental psychology: On the dynamics between growth and decline. Developmental Psychology, 23( 5), 611-626. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.23.5.611URL |
| [2] | Barkley R. A., Edwards G., Laneri M., Fletcher K., & Metevia L . ( 2001). Executive functioning, temporal discounting, and sense of time in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional defiant disorder (ODD). Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 29( 6), 541-556. doi: 10.1023/A:1012233310098URL |
| [3] | Block R.A . ( 1978). Remembered duration: Effects of event and sequence complexity. Memory & Cognition, 6( 3), 320-326. doi: 10.3758/BF03197462URL |
| [4] | Block R.A., & Zakay D. , ( 1997). Prospective and retrospective duration judgments: A meta-analytic review. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 4( 2), 184-197. doi: 10.3758/BF03209393URLpmid: 21331825 |
| [5] | Brown S.W . ( 1995). Time, change, and motion: The effects of stimulus movement on temporal perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 57( 1), 105-116. doi: 10.3758/BF03211853URLpmid: 7885802 |
| [6] | Caillois R.& McKeon N. ,( 1963). Circular time, rectilinear time. Diogenes, 11( 42), 1-13. |
| [7] | Fraisse P. ( 1984). Perception and estimation of time. Annual Review of Psychology, 35, 1-37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.35.020184.000245URL |
| [8] | Frederick S., Loewenstein G., & O'Donoghue T . ( 2002). Time discounting and time preference: A critical review. Journal of Economic Literature, 40( 2), 351-401. doi: 10.1257/002205102320161311URL |
| [9] | Gibbons H., Brandler S., & Rammsayer T. H . ( 2003). Dissociating aspects of temporal and frequency processing: A functional ERP study in humans. Cortex, 39( 4-5), 947-965. doi: 10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70872-4URLpmid: 14584561 |
| [10] | Graham R.J . ( 1981). The role of perception of time in consumer research. Journal of Consumer Research, 7( 4), 335-342. doi: 10.1086/208823URL |
| [11] | Hayes A. F. ( 2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation,and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: Guilford Press. |
| [12] | Huang X.T., Xu G.G . ( 1997). Test the change/ segmentation model (I). Acta Psychologica Sinica, 29( 3), 326-334. |
| [ 黄希庭, 徐光国 . ( 1997). 对变化/分割模型的检验(1). 心理学报 , 29( 3), 326-334. ] | |
| [13] | Jiang C-M., Liu H-Z., Cai X-H., & Li S . ( 2016). A process test of priority models of intertemporal choice. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48( 1), 59-72. |
| [ 江程铭, 刘洪志, 蔡晓红, 李纾 . ( 2016). 跨期选择单维占优模型的过程检验. 心理学报, 48( 1), 59-72.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00059URL | |
| [14] | Kassam K. S., Gilbert D. T., Boston A., & Wilson T. D . ( 2008). Future anhedonia and time discounting. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 44( 6), 1533-1537. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2008.07.008URL |
| [15] | Kim B.K., & Zauberman G. , ( 2009). Perception of anticipatory time in temporal discounting. Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, and Economics, 2( 2), 91-101. doi: 10.1037/a0017686URL |
| [16] | Kim B.K., & Zauberman G. , ( 2013). Can Victoria's Secret change the future? A subjective time perception account of sexual-cue effects on impatience. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 142( 2), 328-335. doi: 10.1037/a0028954URLpmid: 22686639 |
| [17] | Kim B. K., Zauberman G., & Bettman J. R . ( 2012). Space, time, and intertemporal preferences. Journal of Consumer Research, 39( 4), 867-880. doi: 10.1086/666464URL |
| [18] | Li A. M., Sun H. L., Xiong G.X., Wang X.T., & Li B . ( 2016). The effect and cognitive mechanism of “time poverty” on intertemporal choice and proactive behavior. Advances in Psychological Science, 24( 6), 874-884. |
| [ 李爱梅, 孙海龙, 熊冠星, 王笑天, 李斌 . ( 2016). “时间贫穷”对跨期决策和前瞻行为的影响及其认知机制. 心理科学进展, 24( 6), 874-884.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00874URL | |
| [19] | Liang Z-Y.&Liu H., ( 2011). Exploring the nature of intertemporal choice. Advances in Psychological Science, 19( 7), 959-866. |
| [ 梁竹苑, 刘欢 . ( 2011). 跨期选择的性质探索. 心理科学进展, 19( 7), 959-966.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2011.00959URL | |
| [20] | Lightfoot C., & Lyra M. C. D.P . ( 2000). Culture, self and time: Prospects for the new millennium. Culture & Psychology, 6( 2), 99-104. |
| [21] | Liu Y.&Sun Y., ( 2016). Time unpacking effect and its impact on intertemporal decision making. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48( 4), 362-370. |
| [ 刘扬, 孙彦 . ( 2016). 时间分解效应及其对跨期决策的影响. 心理学报, 48( 4), 362-370.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00362URL | |
| [22] | Loewenstein G., & Thaler R.H . ( 1989). Anomalies: Intertemporal choice. The Journal of Economic Perspectives, 3( 4), 181-193. |
| [23] | Lynch Jr J. G., Marmorstein H., & Weigold M. F . ( 1988). Choices from sets including remembered brands: Use of recalled attributes and prior overall evaluations. Journal of Consumer Research, 15( 2), 169-184. doi: 10.1086/jcr.1988.15.issue-2URL |
| [24] | May F. ( 2017). The effect of future event markers on intertemporal choice is moderated by the reliance on emotions versus reason to make decisions. Journal of Consumer Research, 44( 2), 313-331. doi: 10.1093/jcr/ucw081URL |
| [25] | McCormack T. ( 2014). Three types of temporal perspective: Characterizing developmental changes in temporal thought. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1326( 1), 82-89. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12504URLpmid: 25312781 |
| [26] | Moser C., Stauffacher M., Krütli P., & Scholz R. W . ( 2012). The influence of linear and cyclical temporal representations on risk perception of nuclear waste: An experimental study. Journal of Risk Research, 15( 5), 459-476. doi: 10.1080/13669877.2011.636836URL |
| [27] | Overton W.F . ( 1994). The arrow of time and the cycle of time: Concepts of change, cognition, and embodiment. Psychological Inquiry, 5( 3), 215-237. doi: 10.1207/s15327965pli0503_9URL |
| [28] | Poynter W.D., & Homa D. , ( 1983). Duration judgment and the experience of change. Perception & Psychophysics, 33( 6), 548-560. doi: 10.3758/BF03202936URLpmid: 6622190 |
| [29] | Rachlin H., & Jones B.A . ( 2008). Social discounting and delay discounting. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 21( 1), 29-43. doi: 10.1002/bdm.567URL |
| [30] | Read D., Frederick S., & Scholten M . ( 2013). DRIFT: An analysis of outcome framing in intertemporal choice. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 39( 2), 573-588. doi: 10.1037/a0029177URLpmid: 22866891 |
| [31] | Reynolds B.& Schiffbauer R. , ( 2004). Measuring state changes in human delay discounting: An experiential discounting task. Behavioural Processes, 67( 3), 343-356. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2004.06.003URLpmid: 15518985 |
| [32] | Ruscher J.B . ( 2012). Describing grief under cyclical versus linear conceptions of time. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 31( 3), 321-330. doi: 10.1177/0261927X12446600URL |
| [33] | Samuelson P.A . ( 1937). A note on measurement of utility. Review of Economic Studies, 4( 2), 155-161. doi: 10.2307/2967661URL |
| [34] | Sheth B.R., & Shimojo S. ,( 2000). In space, the past can be recast but not the present. Perception, 29( 11), 1279-1290. doi: 10.1068/p3114URLpmid: 11219985 |
| [35] | Siddiqui R. A., May F., & Monga A . ( 2014). Reversals of task duration estimates: Thinking how rather than why shrinks duration estimates for simple tasks, but elongates estimates for complex tasks. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 50( 1), 184-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2013.10.002URL |
| [36] | Suo T., Zhang F., Zhao G. X., & Li H . ( 2014). The influence of time perception difference on intertemporal choice. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46( 2), 165-173. |
| [ 索涛, 张锋, 赵国祥, 李红 . ( 2014). 时间感知差异对跨期选择倾向的影响作用. 心理学报, 46( 2), 165-173.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00165URL | |
| [37] | Swinyard W.R . ( 1993). The effects of mood, involvement, and quality of store experience on shopping intentions. Journal of Consumer Research, 20( 2), 271-280. doi: 10.1086/jcr.1993.20.issue-2URL |
| [38] | Takahashi T. . ( 2006). Time-estimation error following Weber- Fechner law may explain subadditive time-discounting. Medical Hypotheses, 67( 6), 1372-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.05.056URLpmid: 16872753 |
| [39] | Tam L.& Dholakia U. , ( 2013). Saving in cycles: How to get people to save more money. Psychological Science, 25( 2), 531-537. doi: 10.1177/0956797613512129URLpmid: 24357616 |
| [40] | Wittmann M., Leland D. S., Churan J., & Paulus M. P . ( 2007). Impaired time perception and motor timing in stimulant-dependent subjects. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 90( 2-3), 183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.03.005URLpmid: 1997301 |
| [41] | Yamada Y. ( 2004). The generative life cycle model: Integration of Japanese folk images and generativity. In E. de St. Aubin, D. P. McAdams & T.-C. Kim (Eds.), The generative society: Caring for future generations(pp. 97-112). Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association. |
| [42] | Yamada Y.& Kato Y. ,( 2006). Images of circular time and spiral repetition: The generative life cycle model. Culture & Psychology, 12( 2), 143-160. |
| [43] | Zauberman G., Kim B. K., Malkoc S. A., & Bettman J. R . ( 2009). Discounting time and time discounting: Subjective time perception and intertemporal preferences. Journal of Marketing Research, 46( 4), 543-556. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.46.4.543URL |
相关文章 11
| [1] | 宋锡妍, 程亚华, 谢周秀甜, 龚楠焰, 刘雷. 愤怒情绪对延迟折扣的影响:确定感和控制感的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 456-468. |
| [2] | 王盼盼, 何嘉梅. 情景预见对跨期决策的影响机制[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(1): 38-54. |
| [3] | 周蕾,李爱梅,张磊,李纾,梁竹苑. 风险决策和跨期决策的过程比较:以确定效应和即刻效应为例[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(3): 337-352. |
| [4] | 王鹏,王晓田,高娟,黎夏岚,徐静. 适应性时间管理:死亡意识对时间知觉和跨期决策的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(12): 1341-1350. |
| [5] | 李爱梅, 王海侠, 孙海龙, 熊冠星, 杨韶丽. “长计远虑”的助推效应:怀孕与环境跨期决策 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(8): 858-867. |
| [6] | 刘扬;孙彦. 时间分解效应及其对跨期决策的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(4): 362-370. |
| [7] | 刘洪志;江程铭;饶俪琳;李纾. “时间折扣”还是“单维占优”? ——跨期决策的心理机制[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(4): 522-532. |
| [8] | 李爱梅;彭元;熊冠星. 孕妇更长计远虑?——怀孕对女性跨期决策偏好的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(11): 1360-1370. |
| [9] | 索涛;张锋;赵国祥;李红. 时间感知差异对跨期选择倾向的影响作用[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(2): 165-173. |
| [10] | 何嘉梅,黄希庭,尹可丽,罗扬眉. 时间贴现的分段性[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(04): 474-484. |
| [11] | 黄飞,李育辉,张建新. 年级还是年龄?两种不同的效应来源 ——以青少年人格横断比较为例 [J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(12): 1287-1296. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4363
