 )
) 1 福建师范大学心理学院, 福州 350117
2 华侨大学旅游学院, 福建 泉州 362021
收稿日期:2017-10-12出版日期:2018-09-15发布日期:2018-07-27基金资助:福建省自然科学基金计划项目(2018J01719)Effects of nicotine on implicit and explicit memory
LIN Jingyuan1,2, LIN Wuji1, MENG Yingfang1( )
) 1 School of Psychology, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
2 College of Tourism, Huaqiao University, Quanzhou 362021, China
Received:2017-10-12Online:2018-09-15Published:2018-07-27摘要/Abstract
摘要: 胆碱是一种与记忆密切相关的物质, 以往研究主要探讨不同胆碱类药物对外显记忆的影响, 内隐记忆受胆碱影响与外显记忆是否相同仍存在争议。实验1采用词汇判断与词汇再认任务, 比较内隐记忆与外显记忆在拟胆碱药物尼古丁的影响下, 记忆成绩是否发生变化。结果表明, 摄入尼古丁后, 内隐与外显记忆成绩都有一定程度的下降, 但内隐记忆受影响的程度更大。为进一步探讨尼古丁对两种记忆的影响, 实验2分别在编码前与提取前摄入尼古丁, 观察其对两种记忆不同阶段的影响, 并使用ERP技术观察其中受影响的成分。结果表明, 编码前摄入尼古丁使内隐记忆与外显记忆的概念加工都受到影响, 而对知觉加工没有影响。提取前摄入尼古丁则对两种记忆的概念加工与知觉加工都产生影响, 但是对内隐记忆的影响更大。上述结果表明, 拟胆碱物质尼古丁对记忆影响的情况与实验任务较为一致, 而与记忆种类关系较小。对两种记忆的影响不同可能主要源于两种记忆采用不同的实验任务导致, 两者的生理机制有一定程度的重叠。
图/表 8
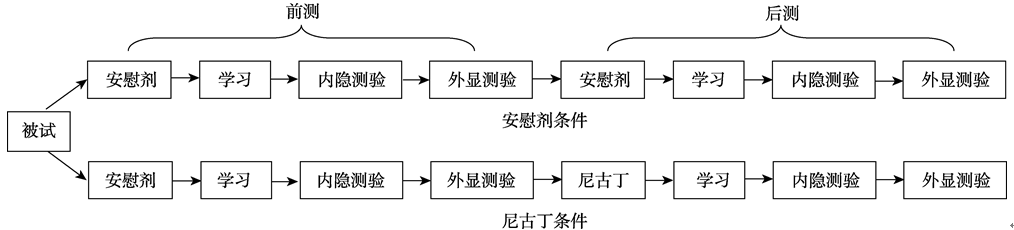
图1实验流程
 图1实验流程
图1实验流程表1外显记忆任务的正确率和反应时
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正确率 | 0.38(0.21) | 0.23(0.20) | 0.35(0.27) | 0.41(0.25) | 0.16(0.15) | 0.05(0.12) | 0.14(0.11) | 0.09(0.10) |
| 反应时(ms) | 857(149) | 861(147) | 932(206) | 896(201) | 950(238) | 899(275) | 1030(372) | 965(278) |
表1外显记忆任务的正确率和反应时
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正确率 | 0.38(0.21) | 0.23(0.20) | 0.35(0.27) | 0.41(0.25) | 0.16(0.15) | 0.05(0.12) | 0.14(0.11) | 0.09(0.10) |
| 反应时(ms) | 857(149) | 861(147) | 932(206) | 896(201) | 950(238) | 899(275) | 1030(372) | 965(278) |
表2内隐记忆任务的启动量
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 启动量 | 59(44) | 6(45) | 21(34) | 44(44) | 47(42) | 10(38) | 32(42) | 37(33) |
表2内隐记忆任务的启动量
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | 尼古丁 | 安慰剂 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 启动量 | 59(44) | 6(45) | 21(34) | 44(44) | 47(42) | 10(38) | 32(42) | 37(33) |
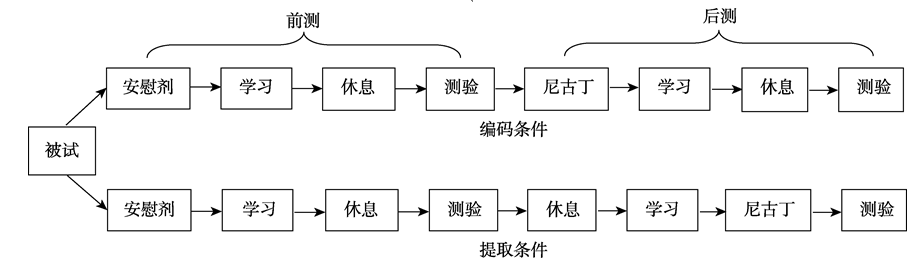
图2实验流程
 图2实验流程
图2实验流程表3外显记忆任务的正确率和反应时
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编码 | 提取 | 编码 | 提取 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正确率 | 0.33(0.24) | 0.26(0.18) | 0.33(0.18) | 0.28(0.18) | 0.10(0.11) | 0.09(0.09) | 0.11(0.10) | 0.06(0.09) |
| 反应时(ms) | 1015(345) | 814(115) | 925(211) | 860(149) | 1020(347) | 875(150) | 944(184) | 888(191) |
表3外显记忆任务的正确率和反应时
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编码 | 提取 | 编码 | 提取 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正确率 | 0.33(0.24) | 0.26(0.18) | 0.33(0.18) | 0.28(0.18) | 0.10(0.11) | 0.09(0.09) | 0.11(0.10) | 0.06(0.09) |
| 反应时(ms) | 1015(345) | 814(115) | 925(211) | 860(149) | 1020(347) | 875(150) | 944(184) | 888(191) |
表4内隐记忆任务的启动量
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编码 | 提取 | 编码 | 提取 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 启动量 | 26(19) | 18(31) | 24(20) | 1(23) | 21(27) | 28(26) | 19(21) | 3(22) |
表4内隐记忆任务的启动量
| 指标 | 深加工编码 | 浅加工编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编码 | 提取 | 编码 | 提取 | |||||
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 启动量 | 26(19) | 18(31) | 24(20) | 1(23) | 21(27) | 28(26) | 19(21) | 3(22) |
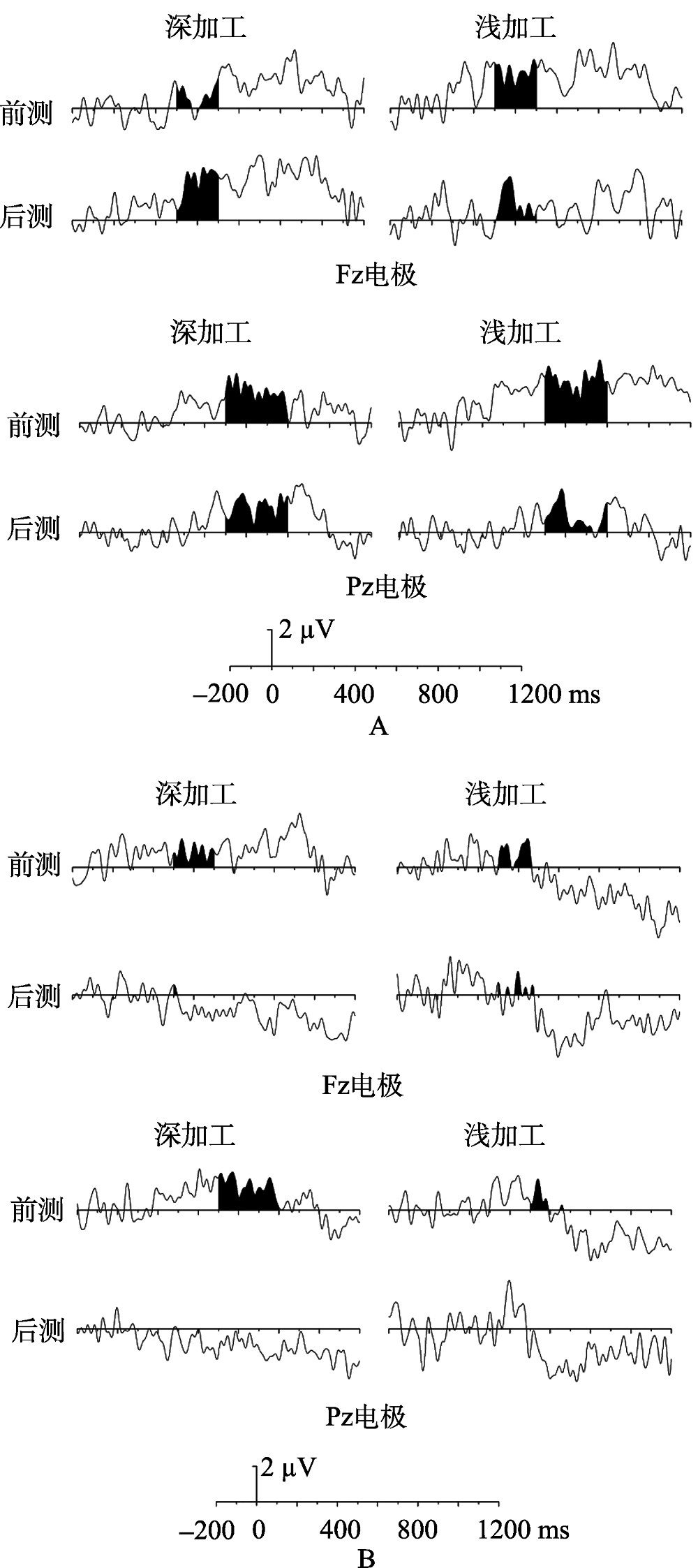
图3外显记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件
 图3外显记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件
图3外显记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件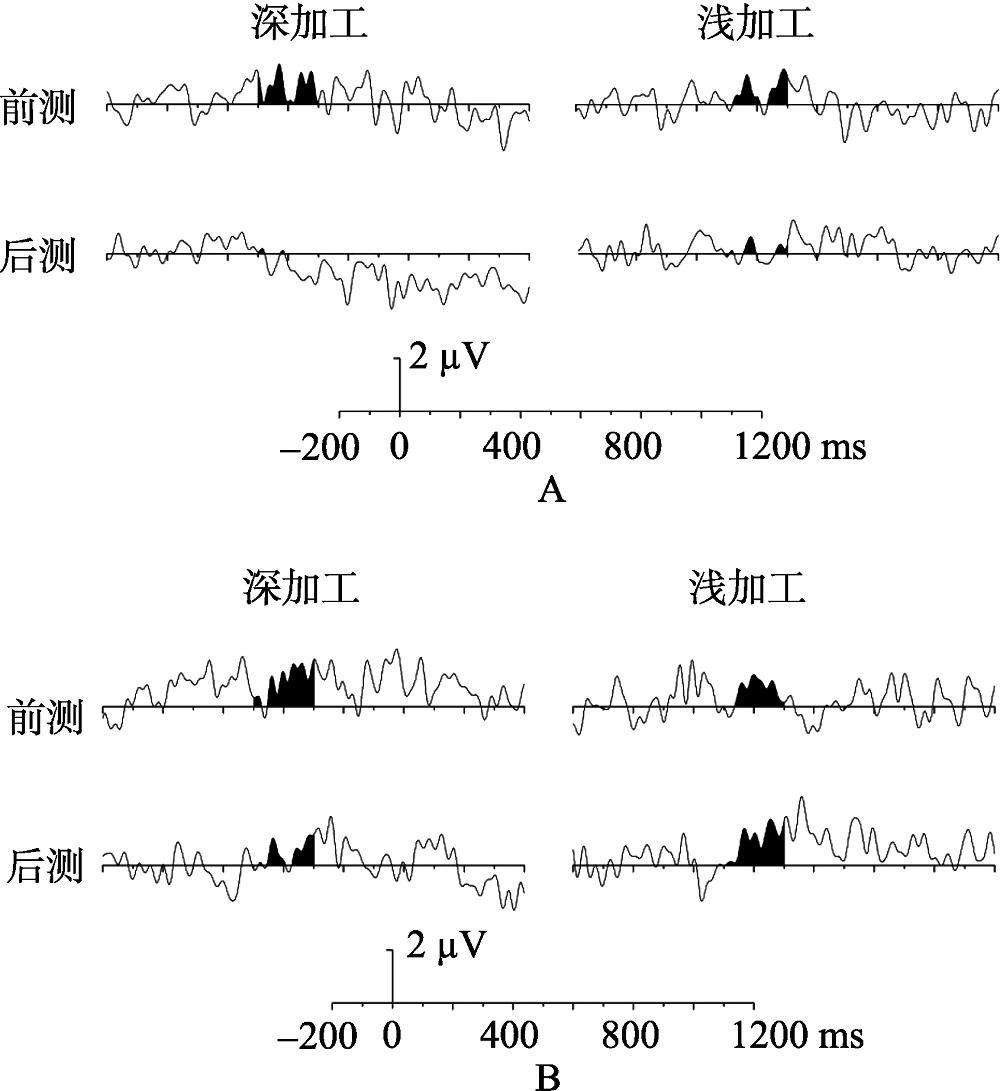
图4内隐记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件
 图4内隐记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件
图4内隐记忆的新旧词差异波, A为编码前摄入尼古丁条件, B为提取前摄入尼古丁条件参考文献 47
| 1 | Alipour A., Aerab-Sheybani K., & Akhondy N . ( 2012). Effects of handedness and depth of processing on the explicit and implicit memory. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 32, 29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.01.005URL |
| 2 | Bentley P., Driver J., & Dolan R. J . ( 2009). Modulation of fusiform cortex activity by cholinesterase inhibition predicts effects on subsequent memory. Brain, 132( 9), 2356-2371. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp176URL |
| 3 | Bentley P., Driver J., & Dolan R. J . ( 2011). Cholinergic modulation of cognition: Insights from human pharmacological functional neuroimaging. Progress in Neurobiology, 94( 4), 360-388. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.06.002URL |
| 4 | Bentley P., Vuilleumier P., Thiel C. M., Driver J., & Dolan R. J . ( 2003). Cholinergic enhancement modulates neural correlates of selective attention and emotional processing. NeuroImage, 20( 1), 58-70. doi: 10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00302-1URL |
| 5 | Brooks B. M., Gardiner J. M., Kaminska Z., & Beavis Z . ( 2001). Implicit versus explicit retrieval of surnames of famous people: Dissociative effects of levels of processing and age. Journal of Memory & Language, 44( 1), 118-130. |
| 6 | Buccafusco J. J., Letchworth S. R., Bencherif M., & Lippiello P. M . ( 2005). Long-lasting cognitive improvement with nicotinic receptor agonists: Mechanisms of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic discordance. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 26, 352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2005.05.007URL |
| 7 | Cabeza, R., & Moscovitch, M. ( 2013). Memorysystems, processing modes, and components: Functional neuroimaging evidence. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8( 1), 49-55. doi: 10.1177/1745691612469033URL |
| 8 | Danion J. M., Zimmermann M. A., Willard-Schroeder D., Grangé D., Welsch M., Imbs J. L., & Singer L . ( 1990). Effects of scopolamine, trimipramine and diazepam on explicit memory and repetition priming in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology, 102( 3), 422-424. doi: 10.1007/BF02244116URL |
| 9 | Dumas J. A., McDonald B. C., Saykin A. J., McAllister T. W., Hynes M. L., West J. D., & Newhouse P. A . ( 2010). Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal activity during episodic memory encoding in postmenopausal women: A pilot study. Menopause, 17( 4), 852-859. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3181e04db9URL |
| 10 | FitzGerald D. B., Crucian G. P., Mielke J. B., Shenal B. V., Burks D., Womack K. B., … Heilman K. M . ( 2008). Effects of donepezil on verbal memory after semantic processing in healthy older adults. Cognitive & Behavioral Neurology, 21( 2), 57-64. |
| 11 | Gais , S., & Born, J. ( 2004). Low acetylcholine during slow- wave sleep is critical for declarative memory consolidation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101( 7), 2140-2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0305404101URLpmid: 14766981 |
| 12 | Gazzaniga, M. S . ( 1998). Brain and conscious experience. Advances in Neurology, 77, 181-192;discussion 192-193. |
| 13 | Guo C. Y., Gao C. J., & Li B. B . ( 2013). FN400 effect: Conceptual processing in explicit memory test. Advances in Psychological Science, 21( 9), 1521-1530. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.01521URL |
| 14 | [ 郭春彦, 高传吉, 李兵兵 . ( 2013). Fn400效应: 外显记忆测量中的概念启动加工. 心理科学进展, 21( 9), 1521-1530.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.01521URL |
| 15 | Huang, J. J . ( 2008). The study on the addiction of smoking behavior in urban residents (Unpublished master’s thesis). Zhejiang University. |
| 16 | [ 黄晶晶 . ( 2008). 城市居民吸烟行为的成瘾性研究 (硕士学位论文). 浙江大学.] |
| 17 | Knopman, D. ( 1991). Unaware learning versus preserved learning in pharmacologic amnesia: Similarities and differences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 17( 5), 1017-1029. |
| 18 | Korsnes, M. S., & Magnussen, S. J . ( 2014). Fmri evidence for dissociation between priming and conscious recognition. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience, 13( 3), 509-517. doi: 10.1142/S0219635214500149URLpmid: 25164357 |
| 19 | Kukolja J., Thiel C. M., & Fink G. R . ( 2009). Cholinergic stimulation enhances neural activity associated with encoding but reduces neural activity associated with retrieval in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 29( 25), 8119-8128. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0203-09.2009URL |
| 20 | Levin E. D., McClernon F. J., & Rezvani A. H . ( 2006). Nicotinic effects on cognitive function: Behavioral characterization, pharmacological specification, and anatomic localization. Psychopharmacology, 184, 523-539. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0164-7URL |
| 21 | Lin W. J., Meng Y. F., & Lin J. Y . ( 2017). Effects of interference on retrieval process in implicit memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49( 7), 897-908. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00897URL |
| 22 | [ 林无忌, 孟迎芳, 林静远 . ( 2017). 提取干扰对内隐记忆的影响. 心理学报, 49( 7), 897-908.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00897URL |
| 23 | Lozito, J. P., & Mulligan, N. W . ( 2010). Exploring the role of attention during implicit memory retrieval. Journal of Memory & Language, 63( 3), 387-399. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2010.06.007URL |
| 24 | MacLeod, C. M . (2008). Implicit memory tests: Techniques for reducing conscious intrusion. In J. Dunlosky & R. A. Bjork (Eds.), Handbook of metamemory and memory (pp. 245-263). New York, NY, US: Psychology Press. |
| 25 | Meng, Y. F., & Guo, C. Y . ( 2007). The asymmetric effect of interference at encoding or retrieval on implicit and explicit memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39( 4), 579-588. |
| 26 | [ 孟迎芳, 郭春彦 . ( 2007). 编码与提取干扰对内隐和外显记忆的非对称性影响. 心理学报, 39( 4), 579-588.] |
| 27 | Meng, Y. F., & Guo, C. Y . ( 2009). The asymmetric relationship between encoding and retrieval in implicit and explicit memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41( 8), 694-705. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2009.00694URL |
| 28 | [ 孟迎芳, 郭春彦 . ( 2009). 内隐与外显记忆的编码与提取非对称性关系. 心理学报, 41( 8), 694-705.] |
| 29 | Meng, Y. F., & Yu, H. L . ( 2012). The dissocciation between encoding and retrieval in implicit and explicit memory. Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), ( 3), 50-55. |
| 30 | [ 孟迎芳, 于海莉 . ( 2012). 内隐记忆与外显记忆编码与提取加工的分离. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版), ( 3), 50-55.] |
| 31 | Narme P., Peretz I., Strub M. L., & Ergis A. M . ( 2016). Emotion effects on implicit and explicit musical memory in normal aging. Psychology and Aging, 31( 8), 902-913. doi: 10.1037/pag0000116URLpmid: 27599018 |
| 32 | Paller K. A., Voss J. L., & Boehm S. G . ( 2007). Validating neural correlates of familiarity. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11( 6), 243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.04.002URLpmid: 17475539 |
| 33 | Prull M. W., Lawless C., Marshall H. M., & Sherman A. T . ( 2016). Effects of divided attention at retrieval on conceptual implicit memory. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 5. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00005URLpmid: 26834678 |
| 34 | Roediger, H. L., III, & McDermott, K. B . ( 1993). Implicit memory in normal human subjects. In F. Boller & J. Grafman (Eds.), Handbook of neuropsychology (Vol.8, pp. 63-131). Amsterdam: Elsevier. |
| 35 | Rogers, J. L., & Kesner, R. P . ( 2003). Cholinergic modulation of the hippocampus during encoding and retrieval. Neurobiology of Learning & Memory, 80( 3), 332-342. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7427(03)00063-7URLpmid: 14521875 |
| 36 | Rosier A. M., Cornette L., Dupont P., Bormans G., Mortelmans L., & Orban G. A . ( 1999). Regional brain activity during shape recognition impaired by a scopolamine challenge to encoding. European Journal of Neuroscience, 11( 10), 3701-3714. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00784.xURLpmid: 10564377 |
| 37 | Rugg M. D., Mark R. E., Walla P., Schloerscheidt A. M., Birch C. S., & Allan K . ( 1998). Dissociation of the neural correlates of implicit and explicit memory. Nature, 392( 6676), 595-598. doi: 10.1038/33396URL |
| 38 | Schifano, F., & Curran, H. V . ( 1994). Pharmacological models of memory dysfunction? A comparison of the effects of scopolamine and lorazepam on word valence ratings, priming and recall. Psychopharmacology, 115( 3), 430-434. doi: 10.1007/BF02245086URL |
| 39 | Sheldon, S. A. M., & Moscovitch, M. ( 2010). Recollective performance advantages for implicit memory tasks. Memory, 18( 7), 681-697. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2010.499876URLpmid: 20721805 |
| 40 | Sutherland M. T., Ross T. J., Shakleya D. M., Huestis M. A., & Stein E. A . ( 2011). Chronic smoking, but not acute nicotine administration, modulates neural correlates of working memory. Psychopharmacology, 213( 1), 29-42. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2013-6URL |
| 41 | Tang, X. T . ( 2013). The effect of interferenceatretrieval on implicit memory (Unpublished master’s thesis). Fujian Nornal University. |
| 42 | [ 唐小庭 . ( 2013). 提取干扰对内隐记忆的影响 (硕士学位论文). 福建师范大学.] |
| 43 | Verneau M., van der Kamp J., Savelsbergh G. J. P., & de Looze, M. P. ( 2014). Age and time effects on implicit and explicit learning. Experimental Aging Research, 40( 4), 477-511. doi: 10.1080/0361073X.2014.926778URLpmid: 25054644 |
| 44 | Voss, J. L., & Paller, K. A . ( 2006). Fluent conceptual processing and explicit memory for faces are electrophysiologically distinct. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(3), 926-933. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3931-05.2006URLpmid: 16421312 |
| 45 | Warburton D. M., Skinner A., & Martin C. D . ( 2001). Improved incidental memory with nicotine after semantic processing, but not after phonological processing. Psychopharmacology, 153( 2), 258-263. doi: 10.1007/s002130000565URL |
| 46 | Zhao, L. ( 2010). ERPs experimental course. Nanjing, China: Southeast University Press. |
| 47 | [ 赵仑 . ( 2010). ERPs实验教程. 南京: 东南大学出版社.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 孟迎芳, 董月晴, 陈荃. 概念内隐记忆中的注意促进效应[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 469-480. |
| [2] | 黄发杰,孟迎芳,严颖. 提取干扰对不同类型内隐记忆的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(5): 572-583. |
| [3] | 林无忌, 孟迎芳, 林静远. 提取干扰对内隐记忆的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(7): 897-908. |
| [4] | 叶晓红;陈幼贞;孟迎芳. 回想、熟悉性与启动在编码过程的认知神经机制[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(9): 1101-1110. |
| [5] | 刘英杰;魏萍;丁锦红;郭春彦. 内隐重复效应影响外显工作记忆的年龄差异[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(3): 321-330. |
| [6] | 夏依婷;冷英;陈燕;王纪妹;程晓荣;卢家楣. 汉语颠倒词加工中重复知盲发生的水平[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(12): 1583-1595. |
| [7] | 孟迎芳. 内隐与外显记忆编码阶段脑机制的重叠与分离[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(1): 30-39. |
| [8] | 冷英,陈旭莲. 汉字多音字加工过程中的重复知盲效应[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(12): 1370-1379. |
| [9] | 王娟,张积家,谢书书,袁爱玲. 结合东巴文学习汉字对幼儿汉字字形记忆的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(05): 519-533. |
| [10] | 李月婷,李琦,郭春彦. 内隐和外显记忆测验中情绪词差异的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(07): 735-742. |
| [11] | Soledad Ballesteros and Julia Mayas. 保留的跨通道启动与老化:对于近期观点的总结[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(11): 1063-1074. |
| [12] | 孟迎芳, 郭春彦 . 内隐与外显记忆的编码与提取非对称性关系[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(08): 694-705. |
| [13] | 张倩秋,张积家. 加工水平对普通话与粤语记忆语言依赖效应的影响 [J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(05): 795-806. |
| [14] | 孟迎芳,郭春彦. 编码与提取干扰对内隐和外显记忆的非对称性影响[J]. 心理学报, 2007, 39(04): 579-588. |
| [15] | 孟迎芳,郭春彦. 内隐记忆和外显记忆的脑机制分离:面孔再认的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(01): 15-21. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4251
