 )
) 1 南京工业大学学生事务部, 南京 210000
2 苏州大学教育学院, 苏州 215000
收稿日期:2017-06-02出版日期:2018-09-15发布日期:2018-07-27基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31271084);江苏高校哲学社会科学研究项目(2017SJBFDY366);江苏省高校辅导员工作研究会专项(16FYHYB030)Is implicit knowledge abstract? Evidence from implicit sequence learning transfer
DAI Hui1, ZHU Chuanlin2, LIU Dianzhi2( )
) 1 Student Affairs Office, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 210000, China
2 School of Education, Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, China
Received:2017-06-02Online:2018-09-15Published:2018-07-27摘要/Abstract
摘要: 内隐知识是否具有抽象和概括性, 已有研究有着不同的争议, 而迁移是检验习得知识是否具有抽象性的有效手段。探索RSI从0 ms至1000 ms中5种条件下内隐序列学习的迁移差异, 并试图证实随着RSI的变化, 迁移发生从无到有的变化, 以迁移来证明内隐知识的抽象性。结果发现:随着RSI的增加, 迁移出现了从无到有的质变, 证明了内隐知识可具有抽象性; 内隐序列学习效应和转移组段的新异刺激效应共同促进了迁移的产生, 纯粹的内隐序列学习是产生迁移的必要非充分条件, 转移组段(新异刺激)则加速促进了内隐知识的学习; 本实验条件下产生的不可知但可迁移的内隐知识具有边缘意识特点。
图/表 7
表1不同RSI实验被试分布情况
| 组别 | 0 ms | 250 ms | 500 ms | 750 ms | 1000 ms | 共计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 | 26 | 22 | 26 | 24 | 26 | 124 |
| 控制组 | 25 | 24 | 26 | 75 |
表1不同RSI实验被试分布情况
| 组别 | 0 ms | 250 ms | 500 ms | 750 ms | 1000 ms | 共计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 | 26 | 22 | 26 | 24 | 26 | 124 |
| 控制组 | 25 | 24 | 26 | 75 |
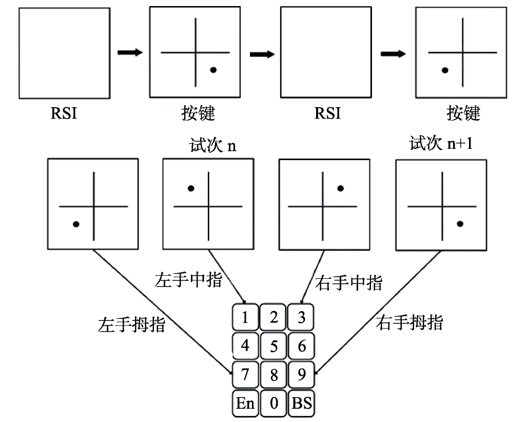
图1学习阶段刺激位置及按键
 图1学习阶段刺激位置及按键
图1学习阶段刺激位置及按键
图2RSI = 0 ms、250 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图
 图2RSI = 0 ms、250 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图
图2RSI = 0 ms、250 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图
图3RSI = 500 ms、750 ms、1000 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图
 图3RSI = 500 ms、750 ms、1000 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图
图3RSI = 500 ms、750 ms、1000 ms各组段反应时变化曲线图表2RSI = 500 ms、750 ms、1000 ms控制组数据
| RSI | Block contrast | t | df | p | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSI = 500 ms | B5-B4 | 0.91 | 24 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| B5-B6 | 1.94 | 24 | 0.66 | 0.36 | |
| RSI = 750 ms | B5-B4 | 0.20 | 23 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| B5-B6 | 1.67 | 23 | 0.11 | 0.32 | |
| RSI = 1000 ms | B5-B4 | 0.09 | 25 | 0.93 | 0.02 |
| B5-B6 | 1.12 | 25 | 0.27 | 0.22 |
表2RSI = 500 ms、750 ms、1000 ms控制组数据
| RSI | Block contrast | t | df | p | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSI = 500 ms | B5-B4 | 0.91 | 24 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| B5-B6 | 1.94 | 24 | 0.66 | 0.36 | |
| RSI = 750 ms | B5-B4 | 0.20 | 23 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| B5-B6 | 1.67 | 23 | 0.11 | 0.32 | |
| RSI = 1000 ms | B5-B4 | 0.09 | 25 | 0.93 | 0.02 |
| B5-B6 | 1.12 | 25 | 0.27 | 0.22 |
表3不同RSI内隐学习量和迁移量的数据比较[M (SD)]
| 学习量和迁移量 | RSI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ms | 250 ms | 500 ms | 750 ms | 1000 ms | |
| 纯粹学习量(RT8-RT7) | 21.95 (5.12) | 19.90 (5.05) | 11.37 (3.94) | 11.74 (2.11) | 14.60 (3.83) |
| 受新异刺激影响的学习量(RT8-RT9) | 37.93 (5.71) | 14.36 (5.11) | 16.57 (3.03) | 16.02 (2.74) | 16.43 (3.70) |
| 纯粹迁移量(RT15-RT14) | 5.63 (8.91) | 12.42 (6.29) | 13.23 (4.40) | 10.01 (4.81) | 12.83 (2.45) |
| 受新异刺激影响的迁移量(RT15-RT16) | 5.29 (3.01) | 16.63 (5.81) | 16.52 (5.31) | 19.35 (4.35) | 19.84 (3.72) |
表3不同RSI内隐学习量和迁移量的数据比较[M (SD)]
| 学习量和迁移量 | RSI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ms | 250 ms | 500 ms | 750 ms | 1000 ms | |
| 纯粹学习量(RT8-RT7) | 21.95 (5.12) | 19.90 (5.05) | 11.37 (3.94) | 11.74 (2.11) | 14.60 (3.83) |
| 受新异刺激影响的学习量(RT8-RT9) | 37.93 (5.71) | 14.36 (5.11) | 16.57 (3.03) | 16.02 (2.74) | 16.43 (3.70) |
| 纯粹迁移量(RT15-RT14) | 5.63 (8.91) | 12.42 (6.29) | 13.23 (4.40) | 10.01 (4.81) | 12.83 (2.45) |
| 受新异刺激影响的迁移量(RT15-RT16) | 5.29 (3.01) | 16.63 (5.81) | 16.52 (5.31) | 19.35 (4.35) | 19.84 (3.72) |

图4不同RSI学习量、迁移量条形图
 图4不同RSI学习量、迁移量条形图
图4不同RSI学习量、迁移量条形图参考文献 40
| 1 | Abrahamse, E, L., & Verwey, W, B. ( 2008). Context dependent learning in the serial RT task. Psychological Research, 72( 4), 397-404. doi: 10.1007/s00426-007-0123-5URLpmid: 2367391 |
| 2 | Chen H., Yang Z. L., Han Y. C., & Zeng Y. J . ( 2009). A review of researches on the consciousness of implicit learning. Psychological Science, 32(4), 891-893. doi: 10.1360/972009-782 |
| 3 | [ 陈寒, 杨治良, 韩玉昌, 曾玉君 . ( 2009). 内隐学习的意识性研究述评. 心理科学, 32( 4), 891-893.] |
| 4 | D'Angelo, M C., Milliken B., Jiménez L., & Lupiá?ez J . ( 2013). Implementing flexibility in automaticity: Evidence from context-specific implicit sequence learning. Consciousness and Cognition, 22( 1), 64-81. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2012.11.002URL |
| 5 | Destrebecqz, A., & Cleeremans, A. ( 2001). Can sequence learning be implicit? New evidence with the process dissociation procedure. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 8( 2), 343-350. |
| 6 | Dienes Z., Kuhn G., Guo X., & Jones, C.( 2011). Communicating structure, affect, and movement. In P. Rebuschat, M. Rohmeier, J. A. Hawkins, & I. Cross(Eds.), Language and music as cognitive systems (pp. 156-169). Oxford University Press. |
| 7 | Dienes, Z., & Longuet-Higgins, C. ( 2004). Can musical transformations be implicitly learned? Cognitive Science, 28( 4), 531-558. doi: 10.1207/s15516709cog2804_2URL |
| 8 | French R. M., & Cleeremans, A.,( 2002) .Implicit learning and consciousness: An empirical, philosophical, and computational consensus in the making (pp160-170) Psychology Press An empirical, philosophical, and computational consensus in the making (pp.160-170). Psychology Press. |
| 9 | Frensch, P. A., & Miner, C. S . ( 1994). Effects of presentation rate and individual differences in short-term memory capacity on an indirect measure of serial learning. Memory & Cognition, 22( 1), 95-110. |
| 10 | Fu Q., Bin G., Dienes Z., Fu X., & Gao X . ( 2013). Learning without consciously knowing: Evidence from event-related potentials in sequence learning. Consciousness and Cognition, 22( 1), 22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2012.10.008URL |
| 11 | Fu Q., Dienes Z., & Fu X . ( 2010). Can unconscious knowledge allow control in sequence learning? Consciousness and Cognition, 19( 1), 462-474. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2009.10.001URLpmid: 19910211 |
| 12 | Guo, X. Y., & Yang, Z. L . ( 2002). The research history of implicit learning. Psychological Development and Education, 18( 3), 85-90. |
| 13 | [ 郭秀艳, 杨治良 . ( 2002). 内隐学习的研究历程. 心理发展与教育, 18( 3), 85-90.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4918.2002.03.016URL |
| 14 | Huang J., Dai H., Ye J., Zhu C., Li Y., & Liu D . ( 2017). Impact of response stimulus interval on transfer of non-local dependent rules in implicit learning: An ERP investigation. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 2107. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02107URL |
| 15 | Huang J. P., Zhang J. X., & Liu D Z . ( 2015). The inlfuence of transfer chuck number and position on implicit sequence learning. Journal of Psychological Science, 38( 6), 1326-1333. |
| 16 | [ 黄建平, 张剑心, 刘电芝 . ( 2015). 内隐序列学习中转移组块的数量和位置效应. 心理科学, 38( 6), 1326-1333.] |
| 17 | James, W. ( 2010). The principles of psychology, Vol I. In Dover books on philosophy & psychology. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. doi: 10.1037/10538-000URL |
| 18 | Jiménez L., Vaquero J. M., & Lupiá?ez J . ( 2006). Qualitative differences between implicit and explicit sequence learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory and Cognition, 32( 3), 475-490. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.32.3.475URLpmid: 16719660 |
| 19 | Knowlton, B. J., & Squire, L. R . ( 1996). Artificial grammar learning depends on implicit acquisition of both abstract and exemplar-specific information. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn, 22( 1), 169-181. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.22.1.169URL |
| 20 | Kuhn, G., & Dienes, Z. ( 2005). Implicit learning of nonlocal musical rules: Implicitly learning more than chunks. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn., 31( 6), 1417-1432. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.31.6.1417URLpmid: 16393055 |
| 21 | Kuhn, G., & Dienes, Z. ( 2006). Differences in the types of musical regularity learnt in incidental- and intentional- learning conditions. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 59( 10), 1725-1744. doi: 10.1080/17470210500438361URL |
| 22 | Mathews R. C., Buss R. R., Stanley W. B., Blanchardfields F., Cho J. Ryeul., & Druhan B . ( 1989). Role of implicit and explicit processes in learning from examples: A synergistic effect. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory and Cognition, 15( 6), 1083-1100. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.15.6.1083URL |
| 23 | Norman, E. ( 2010). “The Unconscious” in current psychology. European Psychologist, 15( 3), 193-201. doi: 10.1027/1016-9040/a000017URL |
| 24 | Norman E., Price M. C., & Duff S. C . ( 2006). Fringe consciousness in sequence learning: The influence of individual differences. Consciousness and Cognition, 15( 4), 723-760. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2005.06.003URLpmid: 16154763 |
| 25 | Norman E., Price M. C., Duff S. C., & Mentzoni R. A . ( 2007). Gradations of awareness in a modified sequence learning task. Consciousness and Cognition, 16( 4), 809-837. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2007.02.004URLpmid: 17433717 |
| 26 | Reber, A. S . ( 1976). Implicit learning of artifical grammars. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 6( 6), 855-863. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5371(67)80149-XURL |
| 27 | Pothos, E. M . (2007). Theories of artificial grammar learning. Psychological Bulletin, 133( 2), 227-244. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.2.227URLpmid: 17338598 |
| 28 | Price, M. C . ( 2002). Measuring the fringes of experience. Psyche, 7( 7), 8-16. |
| 29 | Rünger, D. ( 2012). How sequence learning creates explicit knowledge: The role of response-stimulus interval. Psychological Research, 76( 5), 579-590. doi: 10.1007/s00426-011-0367-yURLpmid: 21786123 |
| 30 | Rünger, D., &Frensch, P. A . ( 2008). How incidental sequence learning creates reportable knowledge: The role of unexpected events. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 34( 5), 1011-1026. doi: 10.1037/a0012942URLpmid: 18763888 |
| 31 | Rünger, D., &Frensch, P. A . ( 2010). Defining consciousness in the context of incidental sequence learning: Theoretical considerations and empirical implications. Psychological Research PRPF, 74( 2), 121-137. doi: 10.1007/s00426-008-0225-8URL |
| 32 | Sanchez D. J., Yarnik E. N., & Reber P. J . ( 2015). Quantifying transfer after perceptual-motor sequence learning: How inflexible is implicit learning? Psychological Research, 79( 2), 327-343. doi: 10.1007/s00426-014-0561-9URL |
| 33 | Schwarb, H., & Schumacher, E. H . ( 2010). Implicit sequence learning is represented by stimulus—response rules. Memory & Cognition, 38( 6), 677-688. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.6.677URLpmid: 20852232 |
| 34 | Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. ( 2014). Implicit transfer of reversed temporal structure in visuomotor sequence learning. Cognitive Science, 38( 3), 565-579. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12098URLpmid: 24215394 |
| 35 | Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. ( 2015). Effects of learning duration on implicit transfer. Experimental Brain Research, 233( 10), 2767-2776. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4348-zURLpmid: 26070899 |
| 36 | Weiermann, B. Cock, J., & Meier, B. ( 2010). What matters in implicit task sequence learning: Perceptual stimulus features, task sets, or correlated streams of information?. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory and Cognition, 36( 6), 1492-1509. doi: 10.1037/a0021038URL |
| 37 | Zhang, R. L., Liu, D. Z . ( 2014). The development of graded consciousness in artificial grammar learning. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46( 11), 1649-1660. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01649URL |
| 38 | [ 张润来, 刘电芝 . ( 2014). 人工语法学习中意识加工的渐进发展. 心理学报, 46( 11), 1649-1660.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01649URL |
| 39 | Zhang J. X., Wu Y., Chen X. Y., & Liu D. Z . ( 2014). Probabilistic implict sequence learning differences between individuals with high vs. low openness /feeling. Acta Psychologica Sinica,46( 12), 1793-1804. |
| 40 | [ 张剑心, 武燕, 陈心韵, 刘电芝 . ( 2014). 高低情感开放性者概率内隐序列学习进程差异. 心理学报, 46( 12), 1793-1804.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01793URL |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 曹娜,孟海江,王艳秋,邱方晖,谭晓缨,吴殷,张剑. 左侧背外侧前额叶在程序性运动学习中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(5): 597-608. |
| [2] | 姚尧,陈晓湘. 音乐训练对4~5岁幼儿普通话声调范畴感知能力的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 456-468. |
| [3] | 宋晓蕾, 李洋洋, 杨倩, 游旭群. 反应手的不同状态对联合任务中观察学习的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(9): 975-984. |
| [4] | 柳武妹, 雷亮, 李志远, 苏云, 黄晓治. 触摸, 还是不触摸?先前触摸促进新产品接受[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(7): 782-792. |
| [5] | 李美佳,庄丹琪,彭华茂. 基于问题解决式的类比推理的老化:表面相似性和结构相似性的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(11): 1282-1291. |
| [6] | 潘东旎,王道湍,李雪冰. 基于手机APP的双维n-back训练的认知与情绪效益[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(10): 1105-1119. |
| [7] | 朱祖德, 段懿行, 王穗苹. 个体差异对工作记忆训练迁移效果的调节[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(8): 1022-1030. |
| [8] | 杨海波;刘电芝. 片段再认任务在内隐序列学习研究中的有效性检验[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(3): 230-237. |
| [9] | 李爱梅;李斌;许华;李伏岭;张耀辉;梁竹苑. 心理账户的认知标签与情绪标签对消费决策行为的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(7): 976-986. |
| [10] | 张剑心;武燕;陈心韵;刘电芝. 高低情感开放性者概率内隐序列学习进程差异[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(12): 1793-1804 . |
| [11] | 王力,陈安涛. 习得性空间联结的迁移依赖于语义工作记忆[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(5): 605-613. |
| [12] | 陈小丽,曲折,王优,丁玉珑. 光栅朝向分辨学习中存在关于45°对角线对称的镜像迁[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(09): 969-974. |
| [13] | 张奇,赵弘. 算术应用题二重变异样例学习的迁移效果[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(04): 409-417. |
| [14] | 付秋芳, 刘永芳, 傅小兰. 知识类别和特点对内隐序列学习的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2004, 36(05): 525-533. |
| [15] | 丁锦红,袁汝兵,郭春彦,田学红. 中小学生内隐序列学习的机制[J]. 心理学报, 2004, 36(04): 476-481. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4253
