摘要/Abstract
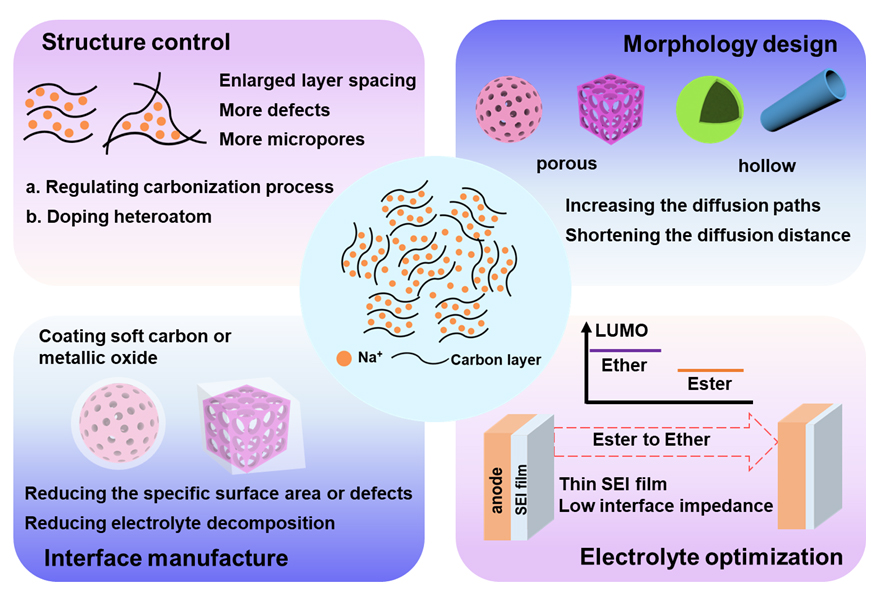
钠离子电池因具有成本低、安全性高等优势, 被认为是一种非常适合应用于大规模储能领域的电化学储能技术. 合适的负极材料是促进钠离子电池实现商业化的关键之一. 硬碳材料由于具有丰富的碳源、低成本、无毒环保, 且储钠电位低而被认为是最可能被实用化的钠离子电池负极材料. 然而硬碳负极的实际应用中也面临着首周库伦效率低、长循环稳定性不足以及倍率性能较差等问题, 近年来众多研究者致力于硬碳负极的性能优化研究, 本Review从结构调控、形貌设计、界面构造、电解液优化四方面总结了近年来钠离子电池硬碳负极的性能优化策略研究进展, 分析了每种优化策略的优点和不足, 并进一步讨论了钠离子电池硬碳负极实用化进程中面临的瓶颈问题和挑战.
关键词: 钠离子电池, 负极, 硬碳, 性能优化, 实用化
Sodium ion batteries (SIBs) have been regarded as a very suitable electrochemical energy storage technology for large-scale energy storage due to its low cost and high safety. Suitable anode material is one of the keys to boosting the commercialization process of SIBs. Significantly, hard carbon (HC) anode is considered as the most practical anode material for SIBs due to its rich natural sources, low cost, non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and low sodium storage voltage. However, hard carbon anode also faces the problems of low initial Columbic efficiency, insufficient long cycle stability and poor rate performance, which restrict its practical application in SIBs. In recent years, extensive investigations have been done to improve the performance of hard carbon anode, herein, this review discusses the recent progress of performance optimization strategies of hard carbon anode from four aspects, including structure control, morphology design, interface manufacture, and electrolyte optimization and conducts an analysis of the merits and demerits of each optimization method. Moreover, this review also discusses the bottlenecks and challenges in the process of practical application of hard carbon anode for sodium ion batteries.
Key words: sodium ion battery, anode, hard carbon, performance optimization, practical application
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
