摘要/Abstract
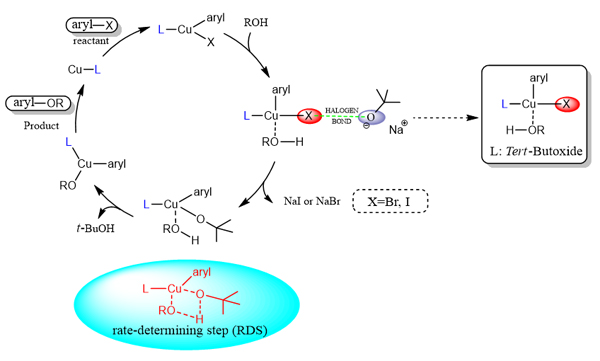
本工作提出了Cu催化的2-(2-碘苯基)-1-乙醇分子内Ullmann C―O偶联反应机理, 并用密度泛函理论(density functional theory, DTF)计算验证. 催化循环从原位生成的亚铜配合物开始, 亚铜配合物经氧化加成生成Cu(III)配合物; Cu(III)配合物和反应物醇配位形成四配位Cu(III)配合物; 然后四配位Cu(III)配合物被O-卤键活化, 活化后进行配体交换; 最后经还原消除释放烷基芳基醚并再生催化剂. 量化计算显示叔丁醇离子不仅是一种碱而且还扮演催化剂物种的角色. 然后, 计算各步反应能垒表明配体交换是整个反应的决速步骤. 计算结果与实验结果吻合较好, 证明了计算机理的合理性.
关键词: 密度泛函理论, 铜催化, Ullmann C―O偶联, 叔丁醇离子
The mechanism of Cu catalyzed intramolecular Ullmann C―O coupling reaction of 2-(2-iodophenyl)ethan-1-ol was proposed and verified by density functional theory (DFT). All of the structures have been fully optimized using N,N-dimethylformamide as solvent by the Gaussian16 package with the B3LYP functional. In the process of optimization, the standard 6-31G (d) basis set was used for C, O, N and H atoms, while Stuttgart basis set (SDD) was used for Cu and I atoms. Grimme D3 method was used for dispersion correction of all calculations. The frequency calculation is carried out at the same theoretical level to determine whether the calculated geometry is minimum (zero imaginary frequency) or transition states (one imaginary frequency). The extra single-point calculations, including solvation and dispersion corrections, on the optimized geometries were employed to obtain improved Gibbs energy values with B3LYP/def2-tzvp in the continuum solvation model based on density (SMD). The intrinsic reaction coordinates (IRC) of all transition states were calculated to confirm that the structure connects the reactant and the product. The calculation shows that catalytic cycle starts from the in-situ formation of cuprous complex, and cuprous complex undergo oxidative addition to give Cu(III) complexes. The Cu(III) complex is coordinated with alcohol to form a four-coordinated Cu(III) complex. Then the substrate is activated by O-halogen bond, and the intermediates underwent ligand exchange to form another Cu(III) complexes, which transmits the desired alkyl aryl ethers and regenerates the catalyst cycle. Quantitative calculation shows that the reaction mechanism can be divided into four steps: (1) oxidative addition, (2) coordination effect, (3) ligand exchange, (4) reductive elimination. First, it was found that tert-butoxide was not only a base, but also a catalyst species. Secondly, it is pointed out that ligand exchange is the rate-determining step of the whole reaction. Before the ligand exchange, it is activated by a slowly approaching tert-butoxide to form a halogen bond (XB). The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental data, which proves the rationality of the calculation mechanism and helps to explain the Ullmann reaction mechanism.
Key words: density functional theory, Cu catalyzed, Ullmann C―O coupling, tert-butoxide
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
