摘要/Abstract
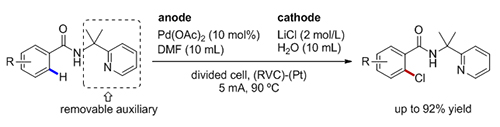
芳香族卤代物是非常重要的合成砌块, 卤化反应是有机合成中最基本也是最重要的反应之一. 本工作利用2-(吡啶基)异丙基胺(PIP胺)作为双齿导向基团, 以LiCl作为卤素来源, 通过电化学阳极氧化的策略成功实现了钯催化的芳烃邻位C(sp 2)—H键的氯代反应. 此反应条件官能团耐受性强, 底物适用范围广, 同时能兼容噻吩等杂芳环类底物, 为合成(杂)芳基氯代物提供了一种简洁高效的方法. 该反应可以安全的放大到克级制备, 显示了潜在的工业应用前景. 通过连续的邻位碳氢键溴代和氯代反应还能得到高度复杂的2,5,6-三取代的苯甲酰胺类化合物.
关键词: 有机电合成, 过渡金属催化, 碳氢键活化, 阳极氧化, 氯代反应
Aryl halides are key building blocks in organic synthesis for the construction of valuable natural products, medicinal and agricultural chemicals via transition metal-catalyzed coupling or substitution reactions. Halogenation is one of the most fundamental and important reactions in organic synthesis. Electrochemical transition-metal-catalyzed C—H functionalization has emerged as a powerful tool for molecular synthesis with the prospect of avoiding the use of costly and toxic oxidants or reductants, thereby reducing the footprint of undesirable, toxic byproducts. The palladium-catalyzed electrochemical C—H chlorination of benzamide derivatives directed by PIP amine directing group under divided cells has been demonstrated, in which readily available inorganic halides salts serve as halogen sources. The reaction features a broad substrate scope, high functional group tolerance, and compatibility of thiophene substrates. This reaction could be conducted on a gram scale, which is important for future application. Additionally, the sequential bromination and chlorination of C(sp 2)—H bond constructs highly functionalized aromatic carboxylic acid derivatives. The typical procedure is as follows: The electrolysis was carried out in an H-type divided cell (anion-exchange membrane), with a RVC anode (10 mm×10 mm×12 mm) and a platinum cathode (10 mm×10 mm×0.2 mm). The anodic chamber was charged with Pd(OAc)2 (5.6 mg, 0.025 mmol, 10 mol%) and benzamide derivative (0.25 mmol, 1.0 equiv.) and dissolved in DMF (10 mL). LiCl (847.8 mg, 20.0 mmol) was added in the cathodic chamber and dissolved in water (10 mL). Then the reaction mixture was electrolyzed under a constant current of 5 mA at 90 ℃ until the complete consumption of the starting material as monitored by TLC or 1H NMR. After the reaction, EtOAc (50 mL) was added to dilute the mixture and then washed with water (20 mL×3) and then with brine (20 mL). The organic fraction was dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel flash chromatography to give the chlorination product.
Key words: organic electrosynthesis, transition metal catalysis, C—H activation, anodic oxidation, chlorination
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
