摘要/Abstract
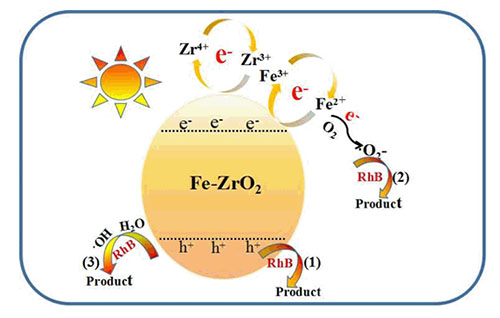
金属有机骨架(UiO-66)具有大的比表面积和强的吸附能力,且金属锆离子高度有序地排列在框架中.先采用UiO-66的结构特点使其吸附Fe3+,再通过煅烧前驱体Fe3+/UiO-66的方法成功制备出Fe掺杂的ZrO2纳米光催化剂Fe-ZrO2.通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、N2吸附-脱附、红外光谱(FT-IR)和紫外-可见光吸收光谱(UV-vis DRS)等方法对催化剂的形貌和结构进行表征,利用荧光(PL)和电化学阻抗对催化剂的电化学性能进行分析.最后,研究了催化剂对罗丹明B溶液的可见光降解作用,结果表明通过煅烧Fe3+/UiO-66前驱体的方法制备的Fe-ZrO2催化剂,在可见光照射下对罗丹明B的降解率为83%,循环三次后降解率依然能够达到78%,稳定性好.
关键词: UiO-66, Fe-ZrO2, 可见光催化, RhB, 光降解
A new porous crystalline materials Zr-containing organic framework of UiO-66 has a large specific surface area, strong adsorption capacity, and the highly ordered arrangement of metal ions in its crystal structure. In this study, because UiO-66 has a good structural features, Fe-doped nano-ZrO2 photocatalyst of Fe-ZrO2 were successfully prepared by the adsorption of Fe3+ onto UiO-66, and calcination of the precursor of Fe3+/UiO-66, subsequently. The morphology and structure of the catalyst were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS). The electrochemical performance of the catalyst was analyzed by fluorescence (PL) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Finally, the photodegradation of rhodamine B solution by the catalysis of Fe-ZrO2 was studied. The results showed that the degradation rate of rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irritation was 83% in 120 min with the catalyst of Fe-ZrO2 from the calcination of the precursor Fe3+/UiO-66. The catalyst has a promising stability. The degradation rate to RhB could still reach 78% after three cycles.
Key words: UiO-66, Fe-ZrO2, visible-light photocatalysis, RhB, photodegradation
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
