摘要/Abstract
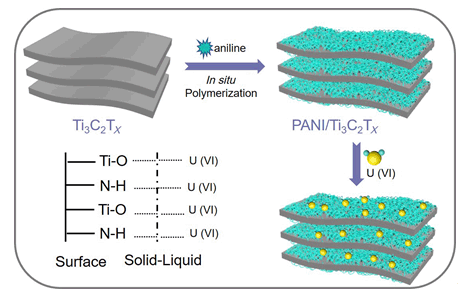
采用原位聚合法合成新型PANI/Ti3C2Tx有机无机复合纳米材料,并应用于对U(VI)的吸附去除研究.实验结果表明:整个吸附过程受溶液pH和离子强度影响较大,在pH=5.0,室温条件下PANI/Ti3C2Tx对U(VI)表现出较高的吸附容量(102.8 mg/g),这一数值远远高于原始Ti3C2Tx对U(VI)的饱和吸附量(36.6 mg/g).此外,结合傅立叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectrometry,FTIR)和X射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS)的分析结果表明PANI/Ti3C2Tx中含氧官能团和氨基基团与U(VI)发生络合作用,从而大大提高了其吸附性能.基于此研究,PANI/Ti3C2Tx可作为具有前景的复合材料应用于含U(VI)废水的净化中.
关键词: PANI/Ti3C2Tx, 铀U(VI), 吸附, 作用机制
Remediation of nuclear wastewater containing U(VI) is very important to human health and environmental ecosystems. Recently, numerous kinds of adsorbents such as clay minerals, carbon-based material and layered double hydroxides etc. have been extensively investigated for effective containing U(VI) wastewater treatment. A representative class of two-dimensional material, "Mxene" has received multidisciplinary interests due to their widespread application in the fields of batteries, supercapacitors and wastewater treatment. Unfortunately, the adsorption capacity of pristine Mxene is frequently limited due to the low quantity of surface functional groups. It was obviously that synthesizing functionalized Mxene materials with plenty functional groups is of great importance for wastewater remediation. In this manuscript, polyaniline modified Mxene composites (PANI/Ti3C2Tx) were successfully synthesized by a in situ polymerization method and were characterized by a series of methods including SEM, FT-IR, XRD and XPS techniques. The adsorption behavior of U(VI) on PANI/Ti3C2Tx was systematically explored by batch experiment. The experiment results showed that the removal process was obviously affected by the ion strength, indicating the formation of outer-sphere surface complexes. Meanwhile, the thermodynamic results manifested that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic reaction. Based on Langmuir model fit, the maximum adsorption capacity of U(VI) on polyaniline modified Mxene composites was calculated to be 102.8 mg/g at pH=5.0 and 298 K, which was superior than that of U(VI) on pristine Ti3C2Tx (36.6 mg/g). In addition, spectroscopy characterizations including Fourier transform infrared spectrometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were applied to study the underlying interaction mechanism, which was mainly attributed to the strong surface complexion between surface functional groups (oxygen-containing groups and amino groups) and U(VI). This work herein pointed out that PANI/Ti3C2Tx materials were promising adsorbent for the efficient removal of U(VI) in the environmental pollution remediation.
Key words: PANI/Ti3C2Tx, U(VI), adsorption, interaction mechanism
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
