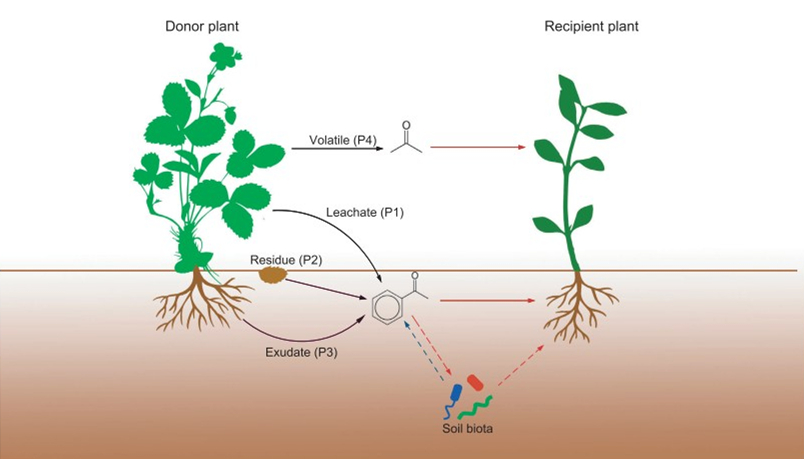
Figure 1 The different release pathways and effects of allelochemicals. The allelopathy plant (left) can release allelochemicals through four pathways (black arrows): leaching by rain (P1), decomposition of plant residues (P2), exudation from roots (P3) and volatilisation (P4). The allelochemicals can affect the test plant directly (red arrows) or indirectly through their effect on soil biota (dashed red arrows). Soil biota can also affect allelochemicals, such as through conversion or degradation of allelochemicals.
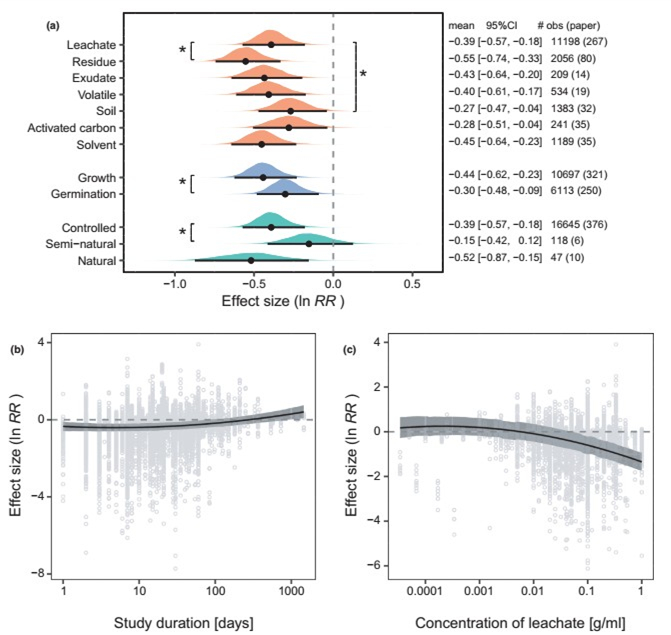
Figure 2 Effects of different aspects of study design on allelopathy. (a) Effects of the type of method (orange), the type of performance measure (blue) and the experimental environment (green) on allelopathy. (b) Effect of study duration on allelopathy. (c) Effect of the concentration of leachates on allelopathy. In (a) for each category (parameter), the posterior distribution is plotted with the mean and 95% credible interval. The text on the right displays the mean, 95% credible interval (CI), and the number of observations (obs) and papers. An asterisk indicates a significant difference between the level of interest and the reference level. In (b) and (c), curves of the estimated effects are shown with their 95% credible intervals. Negative values of the effect size (ln RR) indicate that allelopathy inhibits plant performance.
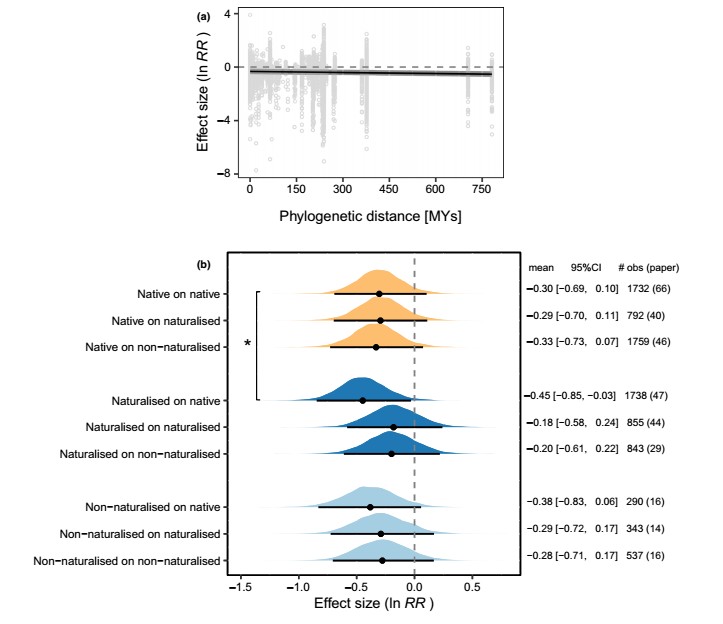
Figure 3 Effects of evolutionary history on allelopathy. (a) Effect of phylogenetic distance between allelopathy and test species on allelopathy. The curve of the estimated effect is shown with its 95% credible interval. (b) Effects of origin of allelopathy and test species on allelopathy when tested with the leachate method. Effects of native, non-naturalised alien and naturalised alien allelopathy species are shown in dark blue, light blue and orange. For each category (parameter), the posterior distribution is plotted with the mean and 95% credible interval. The text on the right displays the mean, 95% credible interval (CI), and the number of observations (obs) and papers. Negative values of the effect size (ln RR) indicate that allelopathy inhibits plant performance. An asterisk indicates significant difference between reference level (native on native) and the other.
该研究成果于近期发表在国际生态学Top期刊Ecology Letters上。本研究第一作者为张致杰博士,通讯作者为刘艳杰研究员。相关论文信息:Zhang Z, Liu Y*, Yuan L, Weber E, van Kleunen M (2020) Effect of allelopathy on plant performance: a meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, doi: 10.1111/ele.13627.
