3.中国市政工程设计院华北设计研究总院有限公司西安分公司,西安 710016
1.School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an 710055, China
2.Key Laboratory of Northwest Water Resource, Environment and Ecology, Ministry of Education, Xi'an 710055, China
3.Xi'an Branch of North China Municipal Engineering Design & Research Institute Co. Ltd., Xi'an 710016, China
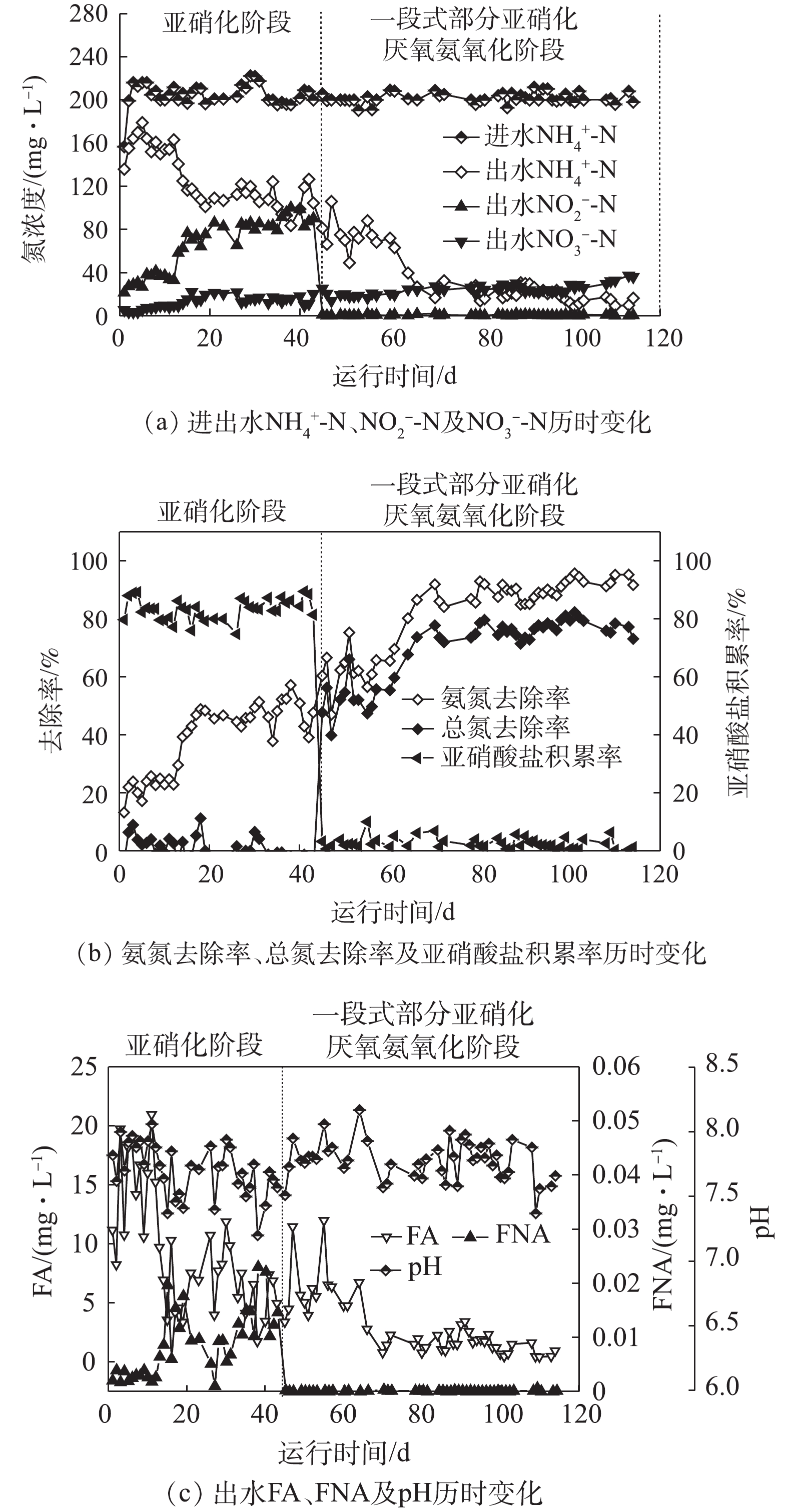
采用序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor, SBR)研究了一段式部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺处理中低浓度氨氮废水的运行稳定性。结果表明,在温度为35 ℃、进水氨氮浓度为200 mg·L
,平均去除率为75.84%,成功实现了一段式部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化的稳定运行。污泥中氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria, AOB)和厌氧氨氧化菌(anaerobic ammonia oxidation, Anammox)活性(以
,NOB被成功抑制,AOB与Anammox菌之间形成良好的协同作用,保证了稳定的脱氮效果。FISH结果表明,污泥中的优势菌为AOB和Anammox菌,从微生物角度佐证了一段式部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化反应器维持较好脱氮效果的长期运行稳定性。一段式部分亚硝化厌氧氨氧化工艺的稳定运行可为厌氧氨氧化技术处理中低浓度氨氮废水提供参考。
The stability of single-stage partial nitritation-anammox process was studied using a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) treating medium and low-strength ammonia wastewater. Results showed that TN removal loading and average TN removal efficiency could reach 0.24 kg·(m
and 75.84% in the single-stage partial nitritation-anammox reactor, respectively, at 35 ℃, the influent ammonia concentrations of 200 mg·L
. The stable running of the reactor was achieved with high performance of nitrogen removal. The activities of ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria (Anammox) stably maintained at about 877.24 mg·(g·d)
-N), respectively. At the same time, the activity of nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) decreased from 60.84 mg·(g·d)
-N), thus NOB was successfully inhibited. AOB and Anammox bacteria could build a better collaborative relationship that ensured the stable nitrogen removal effect. The FISH results indicated that AOB and Anammox bacteria were dominant bacteria, which proved the long stability of efficient nitrogen removal for the single stage partial nitritation-anammox process from the viewpoint of microbiology. The stable operation of the single stage partial nitritation-anammox process provides reference for medium and low-strength concentration ammonia wastewater treatment by anaerobic ammonia oxidation technology.
.
Performance of reactor
Variations of DO, pH, nitrogen and FA concentrations during a typical cycle
Variations of sludge concentration in the reactor
反应器中AOB、NOB及Anammox活性变化
Variations in activities of AOB, NOB and Anammox in the reactor
反应器中AOB、NOB及Anammox FISH图
FISH pictures of AOB, NOB and Anammox bacteria in reactor
| [1] | 郑平, 徐向阳, 胡宝兰. 新型生物脱氮技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| [2] | KUENEN J G. Anammox bacteria: from discovery to application[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(4): 320-326. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1857 |
| [3] | KARTAL B, KUENEN J G, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M. Sewage treatment with anammox Science[J]. Science, 2010, 328: 702-703. doi: 10.1126/science.1185941 |
| [4] | ALI M, OSHIKI M, OKABE S. Simple, rapid and effective preservation and reactivation of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacterium Candidatus Brocadia sinic[J]. Water Research, 2014, 57: 215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.036 |
| [5] | YANG W, HE S L, HAN M, et al. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure in the start-up and substrate inhibition stages of an anammox reactor[J]. Journal of Bioscience & Bioengineering, 2018, 126(1): 88-95. |
| [6] | MIAO Y Y, PENG Y Z, ZHANG L, et al. Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: Effect of influent C/N ratios[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 664-672. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.072 |
| [7] | MIAO L, WANG K, WANG S, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using real-time controlled three-stage sequence batch reactor (SBR) system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 159: 258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.058 |
| [8] | MOLINUEVO B, GARCIA M C, KARAKASHEV D, et al. Anammox for ammonia removal from pig manure effluents: Effect of organic matter content on process performance[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(7): 2171-2175. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.10.038 |
| [9] | LACKNER S, GILBERT E M, VLAEMINCK S E, et al. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences: An application survey[J]. Water Research, 2014, 55: 292-303. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.02.032 |
| [10] | HU Y H, ZHAO X H, ZHAO Y Z. Achieving high-rate autotrophic nitrogen removal via Canon process in a modified single bed tidal flow constructed wetland[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 237: 329-335. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.033 |
| [11] | ZHANG Z J, CHEN S H, WU P. Start-up of the canon process from activated sludge under salt stress in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR)[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(16): 6309-6314. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.040 |
| [12] | 王嗣禹, 刘灵婕, 王芬, 等. 溶解氧对悬浮与附着生长系统短程硝化反应的影响机制[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12): 5430-5437. |
| [13] | YUE X, YU G, LIU Z, et al. Fast start-up of the CANON process with a SABF and the effects of pH and temperature on nitrogen removal and microbial activity[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 254: 157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.019 |
| [14] | POOT V, HOEKSTRA M, GELEIJNSE M A A, et al. Effects of the residual ammonium concentration on NOB repression during partial nitritation with granular sludge[J]. Water Research, 2016, 106: 518-530. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.028 |
| [15] | CUI H, ZHANG L, ZHANG Q, et al. Stable partial nitrification of domestic sewage achieved through activated sludge on exposure to nitrite[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 278: 435-439. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.004 |
| [16] | 范建华, 张朝升, 方茜, 等. 通过控制泥龄实现亚硝酸盐型同步硝化反硝化[J]. 中国给水排水, 2007, 23(3): 102-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2007.03.027 |
| [17] | LIU G Q, WANG J M. Long-term low DO enriches and shifts nitrifier community in activated sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47: 5109-5117. |
| [18] | MIAO Y Y, ZHANG L, YANG Y D, et al. Start-up single partial nitrification-anammox process treating low-strength sewage and its restoration from nitrate accumulation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 218: 771-779. |
| [19] | GRAAF V D A A, DE BRUIJN P D, ROBERTSON L A, et al. Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Microbiology, 1996, 142(8): 2187-2196. doi: 10.1099/13500872-142-8-2187 |
| [20] | HE S L, CHEN Y, QIN M, et al. Effects of temperature on anammox performance and community structure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 260: 186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.090 |
| [21] | SUN S H, SONG Y, YANG X J, et al. Strategies for improving nitrogen removal under high sludge loading rate in an anammox membrane bioreactor operated at 25 °C[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 183: 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2018.03.011 |
| [22] | 国家环境保护局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. |
| [23] | ANTHONISEN A C, LOEHR R C, PRAKASAM T B S, et al. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid[J]. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 1976, 48(5): 835-852. |
| [24] | AMANN R I, KRUMHOLZ L, STAHL D A. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1990, 172(2): 762-770. doi: 10.1128/JB.172.2.762-770.1990 |
| [25] | AMANN R I, BINDER B J, OLSON R J, et al. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1990, 56(6): 1919-1925. |
| [26] | DAIMS H, BRUHL A, AMANN R, et al. The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all bacteria: Development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 1999, 22(3): 434-444. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(99)80053-8 |
| [27] | MOBARRY B K, WAGNER M, URBAN V, et al. Phylogenetic probes for analyzing abundance and spatial organization of nitrifying bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(6): 2156-2162. doi: 10.1128/AEM.62.6.2156-2162.1996 |
| [28] | WAGNER M, RATH G, AMANN R I, et al. In situ identification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 1995, 18(2): 251-264. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80396-6 |
| [29] | JURETSCHKO S, TIMMERMANN G, SCHMID M, et al. Combined molecular and conventional analyses of nitrifying bacterium diversity in activated sludge: Nitrosococcus mobilis and Nitrospira-like bacteria as dominant populations[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 1998, 64(8): 3042-3051. |
| [30] | ADAMCAYK J, HESSELSOE M, IVERSEN N, et al. The isotope array a new tool that employs substrate-mediated labeling of rRNA for determination of microbial community structure and function[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(11): 6875-6887. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.11.6875-6887.2003 |
| [31] | DAIMS H, NIELSEN J L, NIELSEN P H, et al. In situ characterization of Nitrospira-like nitrite-oxidizing bacteria active in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(11): 5273-5284. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.11.5273-5284.2001 |
| [32] | KARTAL B, RATTRAY J, NIFTRIK L A V, et al. Candidatus “Anammoxoglobus propionicus” a new propionate oxidizing species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria[J]. Systematic & Applied Microbiology, 2007, 30(1): 39-49. |
| [33] | SCHRAMM A, DE BEER D, VAN DEN HEUVEL J C, et al. Microscale distribution of populations and activities of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. Along a macroscale gradient in a nitrifying bioreactor: Quantification by in situ hybridization and the use of microsensors[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(8): 3690-3696. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.8.3690-3696.1999 |
| [34] | SCHRAMM A, DE BEER D, GIESEKE A, et al. Microenvironments and distribution of nitrifying bacteria in a membrane-bound biofilm[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 2(6): 680-686. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00150.x |
| [35] | VADIVELU V M, YUAN Z G, FUX C, et al. The inhibitory effects of free nitrous acid on the energy generation and growth processes of an enriched nitrobacter culture[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(14): 4442-4448. |
| [36] | 韩志勇, 殷文翔, 刘新德. MBR-CANON工艺快速启动实验研究[J]. 工业催化, 2017, 25(5): 67-80. |
| [37] | 李军, 杜佳, 郑照明, 等. 间歇曝气实现厌氧氨氧化快速启动的研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(11): 200-26. |
| [38] | MIAO Y Y, ZHANG L, LI B K, et al. Enhancing ammonium oxidizing bacteria activity was key to single stage partial nitrification-anammox system treating low-strength sewage under intermittent aeration condition[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 231: 36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.01.045 |





 下载:
下载: 



 点击查看大图
点击查看大图