近期,中国科学院金属研究所师昌绪先进材料创新中心前沿材料研究部杨柯研究员带领的团队在含铜抗菌不锈钢的食品保鲜功能方面取得了创新研究进展,对发展新型结构/功能一体化的食品接触金属材料起到了重要引领作用。相关研究成果分别以“New strategy to delay food spoilage: Application of new food contact material with antibacterial function(延缓食品腐败的新策略:具有抗菌功能的新型食品接触材料的应用)和“Novel Cu-bearing stainless steel: a promising food preservation material(新型含铜不锈钢:一种有前景的食品保存材料)为题发表在Journal of Materials Science & Technology上。
该工作得到了国家自然科学基金、中国科学院青年创新促进会等项目的资助。
原文链接:1 2
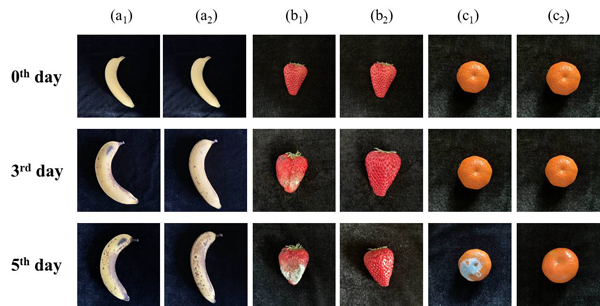
图1 随着时间延长,放置在304不锈钢和304-Cu不锈钢餐盘中的新鲜水果的外观变化,(a)香蕉;(b)草莓;(c)沙糖桔。下角标:1=304不锈钢;2=304-Cu不锈钢。
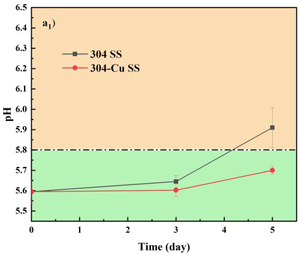
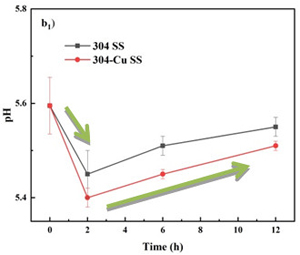
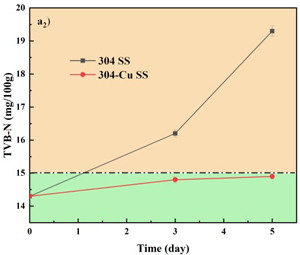
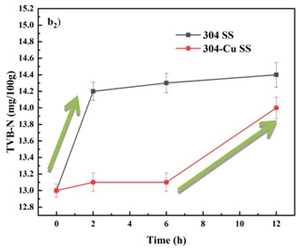
图2 在不同放置温度下,在304不锈钢和304-Cu不锈钢餐盘中的冷鲜肉的pH值和盐基氮(TVB-N)值变化情况,(a)4℃±1℃;(b)23℃±2℃。下角标:1=pH;2=TVB-N
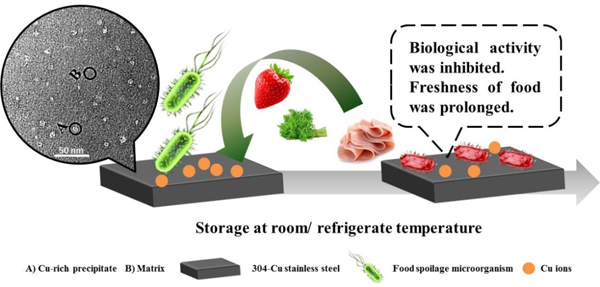
图3 含铜抗菌不锈钢延长食品保鲜时间的机制示意图
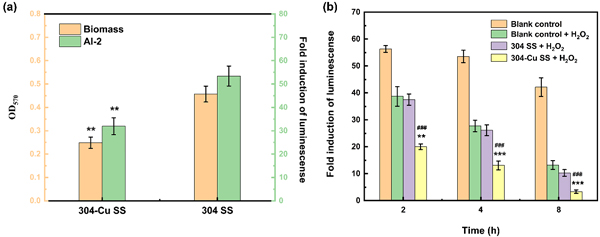
图4 (a)304不锈钢和304-Cu不锈钢与E.coli共培养10小时后,其表面生物膜形成量及对应的AI-2信号表达水平;(b)不同处理组对AI-2信号活性的影响。
