陈亮,郝祎纯,李巧茹,丁景轩
(河北工业大学 土木与交通学院,天津 300401)
摘要:
为更加准确地进行交通量预测,针对传统的BP神经网络随机赋值、收敛速度慢等问题,提出了改进麻雀搜索算法(sparrow search algorithm,SSA)优化的BP神经网络预测模型。该模型结合SSA位置更新原理和鸡群优化算法中公鸡位置更新方法对麻雀搜索算法进行改进,在避免算法陷入局部最优和位置更新无效的同时有效地提高了算法的收敛速度。利用改进麻雀搜索算法对BP神经网络的权值和阈值进行寻优赋值,得到了改进SSA-BP神经网络预测模型。利用交通量数据,对LSTM神经网络、BP神经网络、SSA-BP神经网络和改进SSA-BP神经网络4种预测模型进行训练和测试,以MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE和EC 5个指标对预测结果进行对比分析。结果表明:BP神经网络优于LSTM神经网络,且麻雀搜索算法优化BP神经网络预测模型相较于BP神经网络预测模型MAE降低了0.28 veh/(3 min)、MAPE降低了1%、MSE降低了2.72 veh/(3 min)、RMSE降低了 0.04;改进麻雀搜索算法优化BP神经网络预测模型相较于BP神经网络预测模型MAE降低了1.31 veh/(3 min)、MAPE降低了4%、MSE降低了9.2 veh/(3 min)、RMSE降低了0.18,且拟合度更接近于1。改进SSA-BP预测模型的性能优于SSA-BP神经网络预测模型,且有效提高了BP神经网络的预测精度,拟合度达到0.98,该模型适用于交通量预测,能够为智能交通系统提供可靠的预测值。
关键词: 交通量预测 BP神经网络 改进麻雀搜索算法 权值 阈值
DOI:10.11918/202207077
分类号:U491.1
文献标识码:A
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(51908187)
Traffic volume forecast model based on BP neural network optimized by improved sparrow search algorithm
CHEN Liang,HAO Yichun,LI Qiaoru,DING Jingxuan
(School of Civil and Transportation, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300401, China)
Abstract:
ln order to make traffic prediction more accurately, aiming at the problems of random assignment and slow convergence of the traditional BP neural network, an improved sparrow search algorithm(SSA) is proposed to optimize the BP neural network prediction model. The model combines the SSA position update principle and the rooster position update method in the chicken optimization algorithm to improve the sparrow search algorithm, which avoids the algorithm from falling into the local optimum and the ineffectiveness of the position update, and at the same time effectively improves the convergence speed of the algorithm. The improved sparrow search algorithm is used to optimize the weights and thresholds of the BP neural network, and the improved SSA-BP neural network prediction model is obtained. The four prediction models, namely, LSTM neural network, BP neural network, SSA-BP neural network and improved SSA-BP neural network, were trained and tested with traffic data, and the prediction results were compared and analyzed in terms of MAE, MAPE, MSE, RMSE and EC. The results show that the BP neural network is better than the LSTM neural network, and the optimized BP neural network prediction model with sparrow search algorithm reduced MAE by 0.28 veh/(3 min), MAPE by 1%, MSE by 2.72 veh/(3 min), and RMSE by 0.04 compared with the BP neural network prediction model; the optimized BP neural network prediction model with improved sparrow search algorithm reduced MAE by 1.31 veh/(3 min), MAPE by 4%, MSE by 9.2 veh/(3 min), RMSE by 0.18, and the goodness-of-fit was closer to 1. The improved SSA-BP prediction model outperforms the SSA-BP neural network prediction model and effectively improves the prediction accuracy of the BP neural network with a goodness-of-fit of 0.98, which is suitable for traffic volume prediction and can provide reliable prediction values for intelligent transportation systems.
Key words: traffic volume forecast BP neural network improved sparrow search algorithm weight threshold
陈亮, 郝祎纯, 李巧茹, 丁景轩. 改进SSA优化的BP神经网络交通量预测模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2024, 56(7): 94-101. DOI: 10.11918/202207077.

CHEN Liang, HAO Yichun, LI Qiaoru, DING Jingxuan. Traffic volume forecast model based on BP neural network optimized by improved sparrow search algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2024, 56(7): 94-101. DOI: 10.11918/202207077.

基金项目 国家自然科学基金(51908187) 作者简介 陈亮(1978—),男,副教授 通信作者 李巧茹,qiaoruli129@hebut.edu.cn 文章历史 收稿日期: 2022-07-15
Abstract Full text Figures/Tables PDF
改进SSA优化的BP神经网络交通量预测模型
陈亮, 郝祎纯, 李巧茹

 , 丁景轩
, 丁景轩 河北工业大学 土木与交通学院,天津 300401
收稿日期: 2022-07-15; 录用日期: 2022-09-03; 网络首发日期: 2024-05-06
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金(51908187)
作者简介: 陈亮(1978—),男,副教授
通信作者: 李巧茹,qiaoruli129@hebut.edu.cn
摘要: 为更加准确地进行交通量预测,针对传统的BP神经网络随机赋值、收敛速度慢等问题,提出了改进麻雀搜索算法(sparrow search algorithm, SSA)优化的BP神经网络预测模型。该模型结合SSA位置更新原理和鸡群优化算法中公鸡位置更新方法对麻雀搜索算法进行改进,在避免算法陷入局部最优和位置更新无效的同时有效地提高了算法的收敛速度。利用改进麻雀搜索算法对BP神经网络的权值和阈值进行寻优赋值,得到了改进SSA-BP神经网络预测模型。利用交通量数据,对LSTM神经网络、BP神经网络、SSA-BP神经网络和改进SSA-BP神经网络4种预测模型进行训练和测试,以MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE和EC 5个指标对预测结果进行对比分析。结果表明: BP神经网络优于LSTM神经网络,且麻雀搜索算法优化BP神经网络预测模型相较于BP神经网络预测模型MAE降低了0.28 veh/(3 min)、MAPE降低了1%、MSE降低了2.72 veh/(3 min)、RMSE降低了0.04;改进麻雀搜索算法优化BP神经网络预测模型相较于BP神经网络预测模型MAE降低了1.31 veh/(3 min)、MAPE降低了4%、MSE降低了9.2 veh/(3 min)、RMSE降低了0.18,且拟合度更接近于1。改进SSA-BP预测模型的性能优于SSA-BP神经网络预测模型,且有效提高了BP神经网络的预测精度,拟合度达到0.98,该模型适用于交通量预测,能够为智能交通系统提供可靠的预测值。
关键词: 交通量预测 BP神经网络 改进麻雀搜索算法 权值 阈值
Traffic volume forecast model based on BP neural network optimized by improved sparrow search algorithm
CHEN Liang, HAO Yichun, LI Qiaoru

 , DING Jingxuan
, DING Jingxuan School of Civil and Transportation, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300401, China
Abstract: ln order to make traffic prediction more accurately, aiming at the problems of random assignment and slow convergence of the traditional BP neural network, an improved sparrow search algorithm(SSA) is proposed to optimize the BP neural network prediction model. The model combines the SSA position update principle and the rooster position update method in the chicken optimization algorithm to improve the sparrow search algorithm, which avoids the algorithm from falling into the local optimum and the ineffectiveness of the position update, and at the same time effectively improves the convergence speed of the algorithm. The improved sparrow search algorithm is used to optimize the weights and thresholds of the BP neural network, and the improved SSA-BP neural network prediction model is obtained. The four prediction models, namely, LSTM neural network, BP neural network, SSA-BP neural network and improved SSA-BP neural network, were trained and tested with traffic data, and the prediction results were compared and analyzed in terms of MAE, MAPE, MSE, RMSE and EC. The results show that the BP neural network is better than the LSTM neural network, and the optimized BP neural network prediction model with sparrow search algorithm reduced MAE by 0.28 veh/(3 min), MAPE by 1%, MSE by 2.72 veh/(3 min), and RMSE by 0.04 compared with the BP neural network prediction model; the optimized BP neural network prediction model with improved sparrow search algorithm reduced MAE by 1.31 veh/(3 min), MAPE by 4%, MSE by 9.2 veh/(3 min), RMSE by 0.18, and the goodness-of-fit was closer to 1. The improved SSA-BP prediction model outperforms the SSA-BP neural network prediction model and effectively improves the prediction accuracy of the BP neural network with a goodness-of-fit of 0.98, which is suitable for traffic volume prediction and can provide reliable prediction values for intelligent transportation systems.
Keywords: traffic volume forecast BP neural network improved sparrow search algorithm weight threshold
城市道路交通量是非线性动态数据,受时间、天气、道路条件等多方面因素影响。其广泛应用于道路规划,交通管控,事故分析,智能交通建设等多个方面。但仅依据现有交通量进行分析、应用,易造成与未来趋势匹配度的现象。所以,进行合理有效地交通量预测是解决道路规划管理不当,交通设施无法满足道路使用者需求等众多问题的关键。
随着机器学习的不断发展,国内外学者建立了BP神经网络交通量预测模型[1-2]。BP神经网络作为交通量预测主体,可以按照误差逆向传播,其各节点的个数可以根据数据进行调节,能够映射多种复杂的非线性关系,适用于对短时交通流进行预测。但BP神经网络存在精度不高,容易陷入局部最优且收敛速度较慢的问题。为进一步改善其性能,提出了一系列寻优算法优化的BP神经网络预测模型,通过灰狼优化算法[3-5]、蝙蝠算法[6]、粒子群算法[7-9]、人工峰群算法[10]、遗传算法[11-12]等对BP神经网络的权值和阈值进行赋值,增强网络寻优能力,加快收敛速,但算法的进化过程复杂,迭代速度较慢、且精度较低。
为更好利用BP神经网络进行交通量预测,保证BP神经网络充分发挥作用的同时,进一步加强模型寻优速度和预测精度。采用麻雀搜索算法(SSA)[13-14]优化BP神经网络,该算法流程简单,可以有效加快收敛速度、提高预测精度。但由于算法以跳跃方式进行寻优,导致结果可能陷入局部最优点,使预测精度较低,且在寻优时存在位置更新无效的风险,以至于无法完成寻优过程。为此,结合位置更新原理和鸡群优化算法对SSA进行改进,改进后的SSA-BP神经网络模型能有效避免算法出现局部最优和位置更新无效的问题,增强全局搜索能力,提高预测精度,加快收敛速度。最后通过3 min交通量数据对LSTM神经网络模型,BP神经网络模型、SSA-BP神经网络模型、改进SSA-BP神经网络模型进行训练和测试,并对测试结果进行对比。
1 改进麻雀搜索算法 1.1 BP神经网络BP神经网络是多层前馈网络,包含输入层、隐含层、输出层3层结构,层间采用权值和阈值连接,其结构如图 1所示。在预测时,网络随机初始化权值和阈值后利用内置激活函数得到预测值,通过真实值与预测值的误差反向传播对权值和阈值进行调整,直至满足要求后得到完整网络结构并进行预测。BP神经网络具有很强的捕捉能力[15],能够映射多种复杂的非线性关系[16],适用于交通量预测,但其权值通过沿局部改善的方向逐渐进行调整,使得局部搜索能力大于全局搜索能力,容易陷入局部最优,并且学习过程较长,收敛速度较慢,会导致预测精度下降,对数据使用造成影响,为此,可通过寻优算法对网络进行优化提高网络性能。
Fig. 1
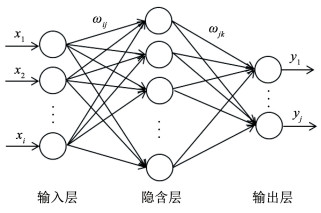 图 1 BP神经网络结构图 Fig. 1 Structure diagram of BP neural network
图 1 BP神经网络结构图 Fig. 1 Structure diagram of BP neural network 1.2 麻雀搜索算法麻雀搜索算法(SSA)[17]是于2020年提出的一种新型生物群优化算法, 有效解决了寻优能力差、收敛速度慢的问题,该思想源于麻雀群捕食与反捕食的过程。麻雀群在捕食以及反捕食的过程中将群体分为发现者, 加入者以及侦察者, 发现者负责确定食物所在位置并提供方向, 当发现者确定食物位置后, 加入者前往合适的位置获取食物, 在觅食过程中侦查者时刻警惕群体内部以及其他种群为获取能量发生的攻击行为, 当出现攻击行为时, 群体会做出反捕食行为。算法以适度值为判断依据,按照一定的规则进行迭代寻优。其具体规则如下。
1) 初始化种群位置,该种群共n只麻雀,每只麻雀的位置以
2) 取10%~20%适度值较高的个体作为发现者负责搜索食物,为了寻找更优质的食物,且满足群体觅食需求,发现者搜索范围应大于加入者的搜索范围,并在每次迭代寻优的过程中按照式(1)更新位置。
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}x_{i, j}^t \cdot \exp \left(\frac{-i}{\alpha \cdot t_{\max }}\right), R_2 <\mathrm{ST} \\x_{i, j}^t+Q \cdot \boldsymbol{L}, R_2 \geqslant \mathrm{ST}\end{array}\right.$ (1)
式中:xti, j为第t次迭代时第i只麻雀在第j维的位置;α为(0, 1]的随机数;tmax为最大迭代次数;Q为服从正态分布的随机数;L为一个1×d的矩阵,每个元素的值均为1;R2为预警值,R2∈[0, 1];ST为安全值,ST∈[0.5, 1]。
当R2 < ST时,则表示环境安全,未出现捕食者,此时可以扩大搜索范围;当R2>ST时,则表示有捕食者,需要前往其他安全的位置进行搜索。
3) 加入者依据食物质量、位置进行判断并获取能量,当加入者察觉发现者获得更加优质的食物时会前往争夺,争夺成功即可替代发现者的位置(在此过程中发现者与加入者的数量保持动态变化),否则按照式(2)更新加入者位置。
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}Q \cdot \exp \left(\frac{x_{\text {worst }}^t-x_{i, j}^t}{i^2}\right), i>\frac{2}{n} \\x_p^{t+1}+\left|x_{i, j}^t-x_p^{t+1}\right| \cdot \boldsymbol{A}^{+} \cdot L, \text { 其他 }\end{array}\right.$ (2)
式中:xtworst为第t次迭代时的全局最差位置;xpt为第t次迭代时发现者目前占据的最优位置;A 为一个1×d的矩阵,且每个元素随机赋值1或-1;A+为A的摩尔-彭若斯广义逆。
当i>2/n时,则表示第i只麻雀适度值较低,在争夺食物时缺乏竞争力导致未获得食物,处于饥饿状态,为更好满足种群需求,种群应飞往其他地方觅食。
4) 在种群中随机选取10%~20%个体作为侦察者,侦察者察觉危险情况发出信号后种群搜索新的位置进行觅食,并按照式(3)更新侦察者的位置。
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}x_{\text {best }}^t+\beta \cdot\left|x_{i, j}^t-x_{\text {best }}^t\right|, f \neq f_g \\x_{i, j}^t+K \cdot \frac{\left|x_{i, j}^t-x_{\text {worst }}^t\right|}{\left(f-f_{\mathrm{w}}\right)+\varepsilon}, f=f_{\mathrm{g}}\end{array}\right.$ (3)
式中:xtbest为第t次迭代时的全局最优位置;β为步长及方向控制参数,是服从标准正态分布的随机数;K为随机数,K∈[-1, 1];fg为全局最优位置的适度值;fw为全局最差位置的适度值;ε为最小的常数。
当f>fg时,表示个体位于种群边缘,容易受到攻击;当f=fg时, 表示个体处于种群之中,但也存在危险靠近的可能,需向其他个体靠近。
5) 种群通过不断的位置更新,寻找最优位置和适度值。该算法流程简单,收敛速度快,搜索能力强。
1.3 算法改进麻雀搜索算法虽然具有收敛速度较快,寻优能力强等突出特点,与BP神经网络结合可以加快收敛速度,提高预测精度,但算法采用跳跃方式向最优位置靠近,依旧存在陷入局部最优的风险。为此从原算法位置更新原理出发,并结合鸡群优化算法[18-20]对算法位置更新方式进行改进,使得改进算法与BP神经网络结合后具有更快的收敛速度,更强的全局搜索能力,能充分提高预测精度。
原算法中发现者位置更新公式形如
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}x_{i, j}^t \cdot(1+Q \cdot \boldsymbol{L}), R_2 <\mathrm{ST} \\x_{i, j}^t+Q \cdot \boldsymbol{L}, R_2 \geqslant \mathrm{ST}\end{array}\right.$ (4)
加入者位置更新式(2)中,当i≤2/n(其他)时,采用跳跃的方式进行寻优,利用该方式进行寻优时容易跳过最优值得到次优值或跳入局部最优点。在鸡群优化算法中公鸡位置更新时采用randn(0, 1)形式对更新位置进行随机移动选取,具体更新方式为式(5),利用其随机移动方式可以有效避免加入者因跳跃方式而陷入局部最优点的问题。为此结合鸡群优化算法中公鸡位置更新方式对加入者位置更新公式进行改进,并通过平均值方式避免随机选取位置造成的偏差,增加搜索密度,改进后的加入者位置更新公式为式(6)。
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=x_{i, j}^t \cdot(1+\operatorname{randn}(0, 1))$ (5)
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}Q \cdot \exp \left(\frac{x_{\text {worst }}^t-x_{i, j}^t}{i^2}\right), i>\frac{2}{n} \\x_p^{t+1}+\frac{1}{d} \sum\limits_{n=1}^d\left[\operatorname{randn}(0, 1) \cdot\left(x_{i, j}^t-x_p^{t+1}\right)\right]\end{array}\right.$ (6)
侦察者的位置更新公式中,在f=fg时存在分母为零的可能,为此增加其绝对值形式,并去除非必要的分子绝对值,得到新的侦查者位置更新公式(7)。
$x_{i, j}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}x_{\text {best }}^t+\beta \cdot\left|x_{i, j}^t-x_{\text {best }}^t\right|, f \neq f_{\mathrm{g}} \\x_{i, j}^t+K \cdot \frac{\left(x_{i, j}^t-x_{\text {worst }}^t\right)}{\left|f-f_{\mathrm{w}}\right|+\varepsilon}, f=f_{\mathrm{g}}\end{array}\right.$ (7)
1.4 改进性能测试为验证改进算法性能,本文采用CEC2021-Schwefel函数对原算法和改进算法进行测试。该函数为高度非线性、多峰函数,存在一个全局最优点和多个局部最优点,适用于对算法的全局搜索能力和收敛速度进行检验,其函数如式(8)所示,在三维空间的图像如图 2所示。函数搜索范围为[-500, 500],全局最优解fbest≈-837.99。
Fig. 2
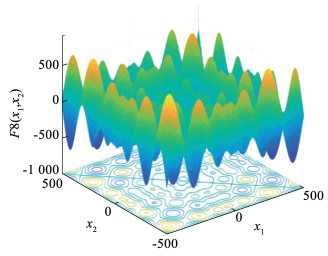 图 2 函数三维图 Fig. 2 The function of three dimensional figure
图 2 函数三维图 Fig. 2 The function of three dimensional figure 采用相同参数对原算法与改进算法进行仿真,算法的最优解位置及寻优过程如图 3所示。函数三维空间图像中每一个峰值均为一个局部最优解。两种算法的最优解位置为红色圆标处,其中原算法的最优位置为[420.97, -302.52],最优解为-719.53;改进算法的最优位置为[420.97, 420.97],最优解为-837.97,改进算法寻优所得值更优,且十分接近真实最优解。在寻优过程中,原算法经历30次迭代达到最优值,改进算法迭代11次得到最优值且只需6次迭代则可以得到原算法最优值位置。结果表明, 改进算法有效避免陷入局部最优并提高了收敛速度,在解决复杂、非线性、没有先验信息的并行问题时表现出了优越性能。
Fig. 3
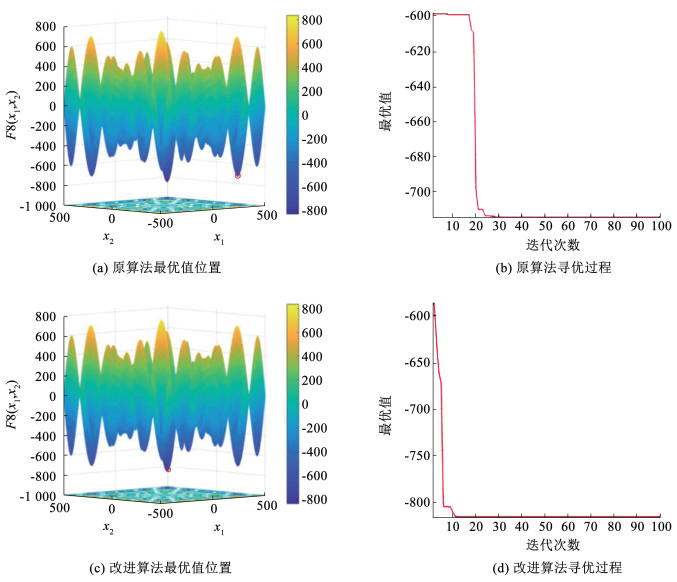 图 3 算法性能测试 Fig. 3 Algorithm performance test
图 3 算法性能测试 Fig. 3 Algorithm performance test 2 优化模型利用改进麻雀搜索算法对BP神经网络的权值和阈值进行优化,提高BP神经网络的预测水平,其优化模型流程如图 4所示,具体优化步骤如下。
Fig. 4
 图 4 优化流程图 Fig. 4 Optimization flow chart
图 4 优化流程图 Fig. 4 Optimization flow chart 步骤1?建立4个输入节点、4个隐含节点和1个输出节点的BP神经网络结构,并设定学习率、迭代次数等参数。
步骤2? 建立训练数据集及测试数据集,并对数据按照式(9)进行归一化处理。
$y=\frac{y-y_{\min }}{y_{\max }-y_{\min }}$ (9)
步骤3? 在参数范围内随机选定种群进化次数、种群规模、发现者比例等参数。
步骤4? 对归一化的数据集进行训练和测试,获取BP神经网络初始权值和阈值作为初始麻雀种群。
步骤5? 计算种群中个体的适度值并排序,确定全局最优、最差适度值及其所在位置。
步骤6? 对麻雀种群进行分类,并利用改进麻雀搜索算法对发现者、加入者、侦察者的位置进行更新。
步骤7? 重新计算适度值,当满足精度要求或达到进化次数后停止迭代,否则返回步骤5继续迭代。
步骤8? 利用最优麻雀种群对BP神经网络的权值和阈值赋值。
步骤9? 调用BP神经网络网络进行训练和预测,得到初始预测值。
步骤10? 调整种群进化次数、种群规模、发现者比例的参数值,比较不同参数值时网络的预测值。
步骤11? 选取预测值最优时的参数值为网络设定参数值,并得到最终预测值。其中种群迭代次数为20,发现者数量为20%、ST为0.8[14]。
3 交通量预测及对比分析 3.1 交通量预测改进SSA-BP神经网络预测模型适用于任何路段的交通量预测。在预测时应选取符合实际交通状况且正常交通状态下的样本,并需去除缺失和漂移的数据。因节假日与工作日的交通状况存在差异,所以在选取数据时采用同为工作日或同为节假日数据进行预测,获取的样本中每日数据对预测结果所产生的影响相同。
现通过明尼苏达大学德卢斯交通实验室平台公布的城市道路交通量数据获取2021年10月19日— 23日和26日—30日的全天交通量数据并以3 min为一周期进行处理。采用19日—23日数据为训练集,其中19日—22日为输入,23日为输出;26日—30日为测试集,其中26日—29日为输入,30日为真实值。利用MATLAB2018b通过捕捉每日输入交通量间的非线性关系对LSTM模型、BP模型、SSA-BP模型以及改进SSA-BP模型进行预测步长为4,步数为1的训练和测试,其中设置参数见表 1。
表 1
LSTM神经网络 4 4 1 0.01 100 0.000 001
BP神经网络模型 4 4 1 0.01 100 0.000 001
SSA-BP模型 4 4 1 0.01 100 0.000 001 20 5 -5 0.2
改进SSA-BP模型 4 4 1 0.01 100 0.000 001 20 5 -5 0.2
表 1 预测模型参数设置 Tab. 1 Prediction model parameter setting
在预测时LSTM模型、BP模型、SSA-BP模型、改进SSA-BP模型收敛所需时间分别为13、4、2、1 s,其中改进SSA-BP模型收敛速度最快,有效提高了BP模型的性能。4种模型的预测值与真实值对比、误差如图 5所示。由图 5可知,LSTM模型预测误差大部分集中在5~10 veh/(3 min),误差很大,BP模型预测误差部分高于5 veh/(3 min)、最大达到14 veh/(3 min);利用SSA对BP模型改进后大部分误差不超过4 veh/(3 min),但仍有个别的样本误差大于8 veh/(3 min),SSA-BP模型的预测精度高于BP模型,但不够理想。利用改进SSA算法对BP模型改进后误差均不超过4 veh/(3 min),相较于SSA-BP模型误差进一步减小,相较于BP模型精度提升更加明显,其预测精度可以更加满足数据使用要求。
Fig. 5
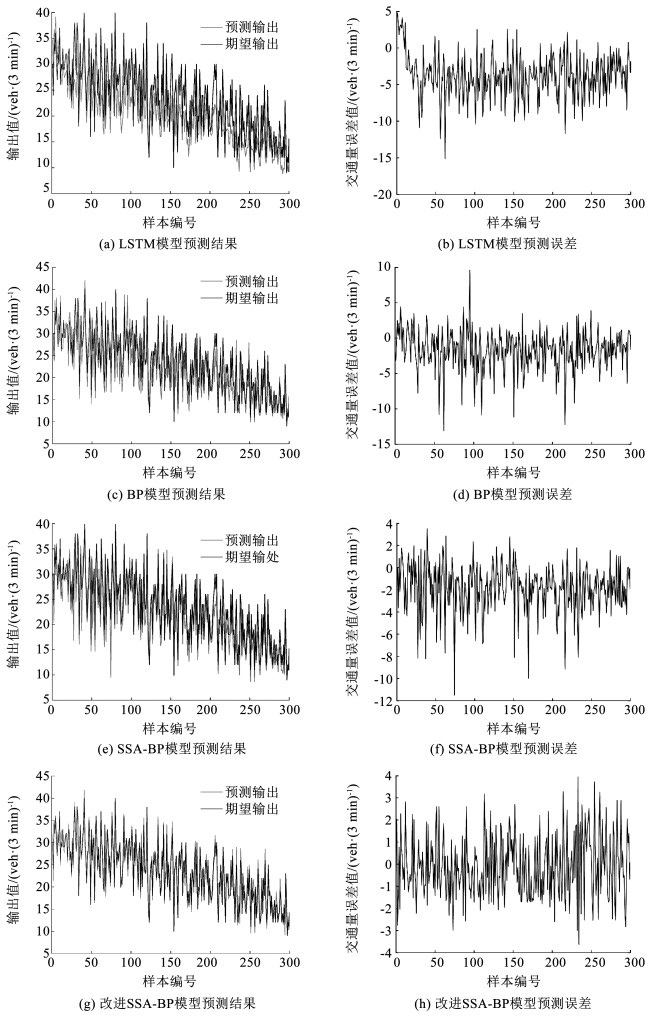 图 5 模型预测结果 Fig. 5 Model prediction results
图 5 模型预测结果 Fig. 5 Model prediction results 3.2 对比分析采用平均绝对误差(MAE),平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE),均方误差(MSE),均方根误差(RMSE)及拟合度(EC)5个指标对预测结果进行分析:
$\begin{gathered}\text { MAE }=\frac{1}{n} \sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left|x_i-\dot{x}_i\right| \\\text { MAPE }=\frac{1}{n} \sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left|\frac{x_i-\hat{x}_i}{x_i}\right| \times 100 \% \end{gathered}$
$\begin{gathered}& \text { MSE }=\frac{1}{n} \sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left(x_i-\hat{x}_i\right)^2 \\& \text { RMSE }=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left(x_i-\hat{x}_i\right)^2} \\& \text { EC }=1-\frac{\sqrt{\sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left(x_i-\hat{x}_i\right)^2}}{\sqrt{\sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left(x_i\right)^2}+\sqrt{\sum\limits_{i=1}^n\left(\hat{x}_i\right)^2}}\end{gathered}$
式中xi、
由表 2所示指标结果可知,BP模型相较于LSTM模型MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE分别降低了1.62 veh/(3 min)、6%、12.4 veh/(3 min)、0.15,拟合度提高了0.05,所以BP模型更适于交通量预测。SSA-BP模型与BP模型相比MAE降低了0.28 veh/(3 min)、MAPE降低了1%、RMSE降低了0.04、MSE仅降低2.72 veh/(3 min),误差改善较小。改进SSA-BP模型与BP模型相比MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE分别降低了1.31 veh/(3 min)、4%、9.2 veh/(3 min)、0.18,且拟合度更接近1。综合来看,改进SSA-BP模型预测精度更高,其性能优于SSA-BP模型,可以有效改善BP模型性能,且预测时产生的误差对交通量预测的影响较小,适用于交通量预测。
表 2
LSTM神经网络 4.13 17 23.70 0.48 0.89
BP神经网络 2.51 11 11.30 0.33 0.94
SSA-BP神经网络 2.23 10 8.58 0.29 0.95
改进SSA-BP神经网络 1.20 7 2.10 0.15 0.98
表 2 模型预测误差 Tab. 2 Model prediction error
4 结论本文利用改进麻雀搜索算法优化BP神经网络得到改进SSA-BP神经网络预测模型。对LSTM、BP、SSA-BP和改进SSA-BP模型进行训练和测试,并对预测性能指标进行对比分析,得到以下结论:
1) 通过结合鸡群优化算法将原算法跳跃寻优改为移动寻优,增大寻优密度、避免陷入局部最优;改进发现者指数形式,加快了收敛速度;改进侦察者分母形式,避免位置更新无效,得到改进麻雀搜索算法。
2) 采用CEC2021-Schwefel函数对原算法和改进后算法进行测试,证实改进算法性能优于原算法性能。
3) 通过改进麻雀搜索算法对BP神经网络的权值和阈值进行赋值,得到改进SSA-BP神经网络预测模型。对LSTM、BP、SSA-BP、改进SSA-BP 4种神经网络预测模型进行测试,结果表明BP模型性能优于LSTM模型,改进SSA-BP模型相较于BP模型收敛速度提高了3 s,MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE分别降低了1.31 veh/(3 min)、4%、9.2 veh/(3 min)、0.18,EC提高了0.04。改进SSA-BP模型预测精度更高、收敛速度更快,具有更优的性能,是较好的交通量预测模型,能够为智能交通系统提供可靠的数据支撑。
参考文献
[1] ZHANG Qianqian, LIU Shifeng. Urban traffic flow prediction model based on BP artificial neural network in Beijing area[J]. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 2018, 21(4): 849. DOI:10.1080/09720529.2018.1479167
[2] 杨凤满. 基于人工神经网络的交通流预测方法综述[J]. 公路交通科技, 2020, 37(增刊1): 130.
YANG Fengman. Overview of traffic flow prediction methods based on artificial neural network[J]. Highway Traffic Science and Technology, 2020, 37(Sup.1): 130.
[3] 张艺铭, 陈明明, 石磊, 等. 基于IGWO-BP算法的轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2021, 39(3): 85.
ZHANG Yiming, CHEN Mingming, SHI Lei, et al. Short-term passenger flow forecast of rail transit based on IGWO-BP algorithm[J]. Traffic Information and Safety, 2021, 39(3): 85.
[4] 张兴辉, 樊秀梅. 反向学习的灰狼算法优化及其在交通流预测中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(5): 879.
ZHANG Xinghui, FAN Xiumei. Optimization of backward learning gray wolf algorithm and its application in traffic flow prediction[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(5): 879.
[5] 张文胜, 郝孜奇, 朱冀军, 等. 基于改进灰狼算法优化BP神经网络的短时交通流预测模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(2): 196.
ZHANG Wensheng, HAO Ziqi, ZHU Jijun, et al. Optimization of short-term traffic flow prediction model based on BP neural network based on improved gray wolf algorithm[J]. Transportation Systems Engineering and Information, 2020, 20(2): 196. DOI:10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2020.02.029
[6] 曹洁, 沈钧珥, 张红, 等. 优化的BP神经网络短时交通流预测方法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2020, 39(5): 58.
CAO Jie, SHE Juner, ZHANG Hong, et al. Optimized BP neural network short-term traffic flow forecasting method[J]. Sensors and Microsystems, 2020, 39(5): 58. DOI:10.13873/J.1000-9787(2020)05-0058-03
[7] MA Qiufang. Design of BP neural network urban short-term traffic flow prediction software based on improved particle swarm optimization[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019, 2073(1): 020085. DOI:10.1063/1.5090739
[8] 余良碧, 郑伟, 赵志璞, 等. 基于VMD分解的PSO-BP神经网络短时交通流预测[J]. 交通世界, 2021(33): 1.
YU Liangbi, ZHENG Wei, ZHAO Zhipu, et al. PSO BP neural network for short-term traffic flow prediction based on VMD decomposition[J]. Traffic World, 2021(33): 1.
[9] 李松, 刘力军, 翟曼. 改进粒子群算法优化BP神经网络的短时交通流预测[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2012, 32(9): 2045.
LI Song, LIU Lijun, ZHAI Man. Improved particle swarm optimization for short-time traffic flow prediction based on BP neural network[J]. Systems Engineering Theory & Practice, 2012, 32(9): 2045. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2012.09.024
[10] 李文越, 周思源, 庞京城. 基于人工蜂群算法优化BP神经网络的交通流预测[J]. 山东交通学院学报, 2017, 25(1): 34.
LI Wenyue, ZHOU Siyuan, PANG Jingcheng. Traffic flow prediction based on BP neural network optimized by artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Shandong Jiaotong University, 2017, 25(1): 34.
[11] 卢建中, 程浩. 改进GA优化BP神经网络的短时交通流预测[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(1): 127.
LU Jianzhong, CHENG Hao. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on improved GA-optimized BP neural network[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 38(1): 127.
[12] ZHUN Chunmei, YAN Changpeng, XU Xiaoli, et al. Research on the application of the prediction of the expressway traffic flow based on the neural network with denetic algorithm[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 1165(189/193): 4400.
[13] 黄龙杨, 夏正洪, 贾鑫磊. 基于SSA-BP的离港航班滑出时间预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(16): 6607.
HUANG Longyang, XIA Zhenghong, JIA Xinlei. Prediction of departure flight sliding time based on SSA-BP[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(16): 6607. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.16.029
[14] XUE Jiankai, SHEN Bo. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: sparrow search algorithm[J]. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2020, 8(1): 22.
[15] 代亮, 梅洋, 钱超, 等. 基于深度学习的短时交通量预测研究综述[J]. 计算机学, 2019, 46(3): 39.
DAI Liang, MEI Yang, QIAN Chao, et al. Review of short-term traffic volume forecasting based on deep learning[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(3): 39.
[16] 张海亮. 基于改进GA-BP的模糊神经网络在高速公路交通量预测中的研究[J]. 公路, 2021, 66(9): 292.
ZHANG Hailiang. The research of fuzzy neural network based on improved GA-BP in expressway traffic forecast[J]. Highway, 2021, 66(9): 292.
[17] 张伟康, 刘升, 任春慧. 混合策略改进的麻雀搜索算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(24): 74.
ZHANG Weikang, LIU Sheng, REN Chunhui. Sparrow search algorithm improved by mixed strategy[J]. Computer Engineering and Application, 2021, 57(24): 74.
[18] 张莹杰, 张树群. 改进约束鸡群算法在神经网络的应用[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2018, 40(12): 2252.
ZHANG Yingjie, ZHANG Shuqun. Application of improved constrained chicken swarm algorithm in neural network[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2018, 40(12): 2252.
[19] SANCHARI D, GAO Xiazhi, KARI T, et al. Recent studies on chicken swarm optimization algorithm: a review (2014—2018)[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review: International Science and Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(2): 1737.
[20] CI Yusheng, WU Hailong, SUN Yichen, et al. A prediction model with wavelet neural network optimized by the chicken swarm optimization for on-ramps metering of the urban expressway[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 26(3): 356.
