王振东,黄尚宇,李佳琪,黄海川,高远
(武汉理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,武汉430070)
摘要:
由于节能环保以及轻量化的要求,Cu/Al异种金属复合管件被广泛应用于各工业领域,为此探索一种Cu/Al管件间高效可靠的连接技术具有较大应用价值和研究意义。为了探究Cu/Al管半固态钎焊连接机理并优化相关工艺参数,基于新提出的磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊方法制备了Cu/Al异种金属管件钎焊接头,利用LS-DYNA分析了半固态钎料不同表观粘度参数下外管内壁的受力情况,采用材料力学拉伸试验机,能谱仪和电子探针显微分析仪研究了半固态Zn-Al系钎料固相率及组分对焊接接头质量的影响。结果表明:外管内壁所受压力幅值随着表观粘度的增大而减小,剪切应力随着表观粘度的增大而增大;半固态钎料固相率为0.8时钎料与母材间没有良好冶金结合,固相率为0.4时会导致钎料填充不足的缺陷。在二次放电电压7 kV,半固态Zn-Al钎料固相率为0.6的条件下,磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊工艺能够实现Cu/Al管的无钎剂有效连接;与Zn-3Al和Zn-22Al相比,Zn-15Al钎料制得的接头综合性能更好,是较为合适的Cu/Al管磁脉冲辅助半固态钎焊用Zn-Al钎料。
关键词: 钎焊 半固态 Cu/Al管 Zn-Al钎料 电磁成形
DOI:10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20190061
分类号:TG454
文献标识码:A
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51475345).
Preliminary study on the influence of solder solid phase rate and composition of Zn-Al filler metal on the quality of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering of Cu/Al tubes
WANG Zhendong, HUANG Shangyu, LI Jiaqi, HUANG Haichuan, GAO Yuan
(School of Material Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China )
Abstract:
Due to the requirements of energy saving, environmental protection and light weight, Cu/Al tubes are widely used in various industrial fields. Therefore, it is of great application value and research significance to explore a highly efficient and reliable joining technology between Cu/Al tubes. In order to explore the joint mechanism of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering of Cu/Al tubes and optimize the process parameters, Cu/Al dissimilar metal tubes joints was prepared by means of the new method of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering, the stress of the inner wall of the outer tube under different apparent viscosity parameters of semi-solid Zn-Al solder was analyzed based on LS-DYNA.The influence of solid state ratio and composition of semi-solid Zn-Al system solder on the quality of welded joint was studied by means of material mechanics tensile tester, energy dispersive spectrometer and electron probe microanalyzer. The results show that the pressure amplitude of the inner wall of the outer tube decreases with the increase of apparent viscosity, and the shear stress rises with the increase of apparent viscosity. When the solid phase ratio of the semi-solid brazing filler metal is 0.8, there is no good metallurgical bond between the brazing filler metal and the base metal, and the solid phase ratio of 0.4 causes defects in insufficient filler filling of the brazing filler metal. Under the condition of secondary discharge voltage of 7 kV and semisolid Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.6, the magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering process can realize the effective connection of Cu/Al pipe without flux; compared with Zn-3Al and Zn-22Al, the joint made of Zn-15Al solder has better comprehensive performance and is a more suitable Zn-Al solder for Cu/Al magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering.
Key words: brazing semi-solid Cu/Al tubes Zn-Al solder electromagnetic forming
王振东, 黄尚宇, 李佳琪, 黄海川, 高远. Zn-Al钎料固相率及组分对Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊接头质量的影响初探[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2020, 28(4): 1-7. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20190061.

WANG Zhendong, HUANG Shangyu, LI Jiaqi, HUANG Haichuan, GAO Yuan. Preliminary study on the influence of solder solid phase rate and composition of Zn-Al filler metal on the quality of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering of Cu/Al tubes[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2020, 28(4): 1-7. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20190061.

基金项目 国家自然科学基金资助项目(51475345) 通信作者 黄尚宇,E-mail:huangshy@whut.edu.cn 作者简介 王振东(1993—),男,硕士研究生;
黄尚宇(1963—),男,教授,博士生导师 文章历史 收稿日期: 2019-03-21 网络出版日期: 2019-10-11
Contents Abstract Full text Figures/Tables PDF
Zn-Al钎料固相率及组分对Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊接头质量的影响初探
王振东, 黄尚宇

 , 李佳琪, 黄海川, 高远
, 李佳琪, 黄海川, 高远 武汉理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,武汉 430070
收稿日期: 2019-03-21; 网络出版日期: 2019-10-11
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(51475345)
作者简介: 王振东(1993—),男,硕士研究生;
黄尚宇(1963—),男,教授,博士生导师.
通信作者: 黄尚宇,E-mail:huangshy@whut.edu.cn.
摘要: 由于节能环保以及轻量化的要求,Cu/Al异种金属复合管件被广泛应用于各工业领域,为此探索一种Cu/Al管件间高效可靠的连接技术具有较大应用价值和研究意义。为了探究Cu/Al管半固态钎焊连接机理并优化相关工艺参数,基于新提出的磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊方法制备了Cu/Al异种金属管件钎焊接头,利用LS-DYNA分析了半固态钎料不同表观粘度参数下外管内壁的受力情况,采用材料力学拉伸试验机,能谱仪和电子探针显微分析仪研究了半固态Zn-Al系钎料固相率及组分对焊接接头质量的影响。结果表明:外管内壁所受压力幅值随着表观粘度的增大而减小,剪切应力随着表观粘度的增大而增大;半固态钎料固相率为0.8时钎料与母材间没有良好冶金结合,固相率为0.4时会导致钎料填充不足的缺陷。在二次放电电压7 kV,半固态Zn-Al钎料固相率为0.6的条件下,磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊工艺能够实现Cu/Al管的无钎剂有效连接;与Zn-3Al和Zn-22Al相比,Zn-15Al钎料制得的接头综合性能更好,是较为合适的Cu/Al管磁脉冲辅助半固态钎焊用Zn-Al钎料。
关键词: 钎焊 半固态 Cu/Al管 Zn-Al钎料 电磁成形
Preliminary study on the influence of solder solid phase rate and composition of Zn-Al filler metal on the quality of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering of Cu/Al tubes
WANG Zhendong, HUANG Shangyu

 , LI Jiaqi, HUANG Haichuan, GAO Yuan
, LI Jiaqi, HUANG Haichuan, GAO Yuan School of Material Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
Abstract: Due to the requirements of energy saving, environmental protection and light weight, Cu/Al tubes are widely used in various industrial fields. Therefore, it is of great application value and research significance to explore a highly efficient and reliable joining technology between Cu/Al tubes. In order to explore the joint mechanism of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering of Cu/Al tubes and optimize the process parameters, Cu/Al dissimilar metal tubes joints was prepared by means of the new method of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering, the stress of the inner wall of the outer tube under different apparent viscosity parameters of semi-solid Zn-Al solder was analyzed based on LS-DYNA.The influence of solid state ratio and composition of semi-solid Zn-Al system solder on the quality of welded joint was studied by means of material mechanics tensile tester, energy dispersive spectrometer and electron probe microanalyzer. The results show that the pressure amplitude of the inner wall of the outer tube decreases with the increase of apparent viscosity, and the shear stress rises with the increase of apparent viscosity. When the solid phase ratio of the semi-solid brazing filler metal is 0.8, there is no good metallurgical bond between the brazing filler metal and the base metal, and the solid phase ratio of 0.4 causes defects in insufficient filler filling of the brazing filler metal. Under the condition of secondary discharge voltage of 7 kV and semisolid Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.6, the magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering process can realize the effective connection of Cu/Al pipe without flux; compared with Zn-3Al and Zn-22Al, the joint made of Zn-15Al solder has better comprehensive performance and is a more suitable Zn-Al solder for Cu/Al magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering.
Keywords: brazing semi-solid Cu/Al tubes Zn-Al solder electromagnetic forming
Cu合金和Al合金均具有良好的导电性、导热性和耐蚀性,广泛用于制冷、电子行业的冷凝器、散热器等核心部件的生产制备[1]。与Cu相比,Al价格便宜,密度较小,在实际工业生产中,Cu/Al管复合结构因其成本低、轻量化等优点得到广泛应用。为了保证良好的连接性能,通常采用焊接方法进行Cu/Al管的连接。由于Cu、Al间热物理性能差异较大,利用普通熔焊难以获得综合性能良好的焊接接头[2]。搅拌摩擦焊是一种适合异种金属连接的焊接方法,但并不适用于管件间的接头制备[3]。电阻焊可获得质量较好的Cu/Al管接头,且生产效率高,但其生产成本高,对设备运行平稳性要求也非常严格[4]。
钎焊在异种材料连接中应用较广,具有效率高、成本低、生产适应性强等诸多优点,是常见的Cu/Al异种金属连接方法[5]。但利用传统钎焊方法进行Cu/Al管焊接时存在钎料布置困难、钎剂具有一定腐蚀性以及施焊过程中钎料氧化等问题[6]。
为解决上述问题,本文充分利用电磁成形、半固态成形和钎焊的复合优势,提出了磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊新工艺[7],通过磁脉冲力驱动管件高速挤压薄壁筒状半固态钎料,借助其固相颗粒对管壁的径向冲击和轴向剪切去除母材表面氧化膜,无钎剂实现管件钎料的整体成形与扩散连接,高效抑制层状脆性金属间化合物的生长,提升接头综合性能。Zn-Al系列钎料广泛应用于Cu/Al钎焊[3],其成分直接决定了钎料的半固态温度窗口及不同温度下的固相率,而固相率直接影响半固态钎料的剪切流变行为和氧化膜去除效果,进而影响界面连接质量、钎缝组织结构及接头强度等。为此,本文采用不同固相率以及3种主流组分的半固态Zn-Al钎料进行试验,探讨其对Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊接头综合性能的影响。
1 试验1.1 试验材料试验选用外径21 mm,壁厚为1 mm的1060-Al为外管;外径17 mm,壁厚为2 mm的T2-Cu为内管。钎料采用浙江新锐焊接科技有限公司生产的Zn-3Al、Zn-15Al和Zn-22Al,厚度均为0.4 mm,宽度5 mm。上述试验材料化学成分如表 1所示。
表1(Table 1)
T2-Cu - 0.003 7 Bal 0.004 2 0.051 - - - 0.0038 0.003 9 0.003 2
1060-Al Bal. 0.250 0 0.150 0.700 0 - 0.400 0.80 0.15 - - -
Zn-3Al 3.210 Bal. 0.419 0.032 0 - 0.067 0.02 - - - 0.004 0
Zn-15Al 14.95 Bal. 0.521 0.012 0 - 0.031 0.01 - - - 0.002 0
Zn-22Al 22.13 Bal. 0.433 0.021 0 - 0.022 0.02 - - - 0.003 0
表 1 Cu、Al管以及Zn-Al系钎料化学成分(质量分数/%)Table 1 Chemical composition of Cu, Al and Zn-Al solder (wt.%)
1.2 试验原理试验采用自行开发的磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊系统,其工作原理如图 1所示。首先通过充电回路对高压电容器进行充电,直至达到设定电压。而后电磁成形机放电,使Al外管在磁脉冲力的作用下发生变形,Al管-钎料-Cu一体管成形。然后感应加热机对内管进行加热,通过热传导使钎料升温至合适的半固态温度,再次放电,利用磁脉冲力间接作用使半固态钎料发生剧烈的径向压缩与轴向剪切变形。在此过程中,半固态钎料的固相颗粒会对母材表面产生撞击和刮擦复合作用,去除母材表面的氧化膜[8],帮助液相钎料润湿母材并进行扩散,实现大气环境下无钎剂钎焊。
图 Figure1(Fig.Figure1)
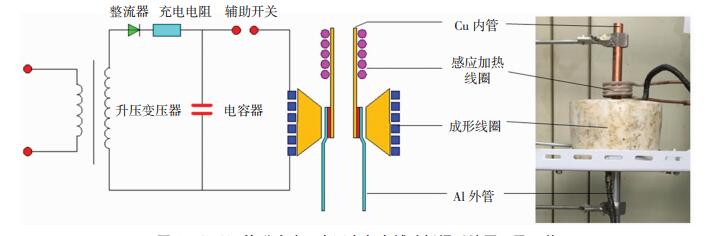 图 1 Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊系统原理及工装Fig.1 Principle and tooling of Cu/Al tubes magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering system
图 1 Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊系统原理及工装Fig.1 Principle and tooling of Cu/Al tubes magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering system1.3 试验方法将钎料和Cu、Al管待焊部位表面用砂纸打磨后放入丙酮溶液进行超声波清洗。Al管-钎料-Cu管装配好后进行第1次放电成形使其成为一体,从而解决钎料布置问题并使钎料片与母材充分接触。再次充电后,接通感应加热机对内管进行加热,待钎料达到设定的半固态温度时断电并进行第2次放电成形,冷却后即得到冶金结合的Cu/Al管接头。第一、二次放电电压分别为8和7 kV,电容550 μF。
试验所用集磁器外径84 mm,内径23 mm,高60 mm。电磁成形线圈外径98 mm,内径86 mm,截面尺寸为6 mm×5 mm,匝间距3 mm,共11匝。感应加热线圈外径35 mm,内径25 mm,匝数为4匝,感应加热电流为20 A。
利用STA449F3同步热分析仪对3种Zn-Al钎料进行差式扫描量热法(DSC)测试和分析,获得各自的固、液相线以及钎料固相率随温度变化关系曲线[9-10]。选取Zn-15Al在不同固相率下进行Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊试验,分析钎料固相率对接头焊接质量的影响。分别选用Zn-3Al,Zn-15Al和Zn-22Al在同一固相率下进行Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊试验,探究Zn-Al钎料组分对接头焊接质量的影响。
利用SHT4106微机控制电液伺服万能试验机对接头进行拉伸测试,接头的显微组织和物相组成通过Nikon Eclipse LV100 POL透反射偏光显微镜和附加INCA X-Act能谱仪的JXA-8230电子探针显微分析仪进行观察和分析。
2 磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊二次放电成形有限元建模采用LS-DYNA软件进行电磁场、结构场和流场的耦合模拟分析,流体表观粘度通过RTW-10型熔体物性测试仪测得,并利用JOLY等人[11]提出的半固态合金表观粘度模型进行拟合,得到Zn-15Al的表观粘度模型为:ηa=0.54e5.99fs,其中η为表观粘度,fs为固相率。
电磁成形线圈和集磁器定义为刚体模型,1060Al管和Cu管定义为Johnson-Cook本构模型,其形式为
$\sigma = \left( {A + B{{\overline \varepsilon }^{{p^n}}}} \right)(1 + C\ln {\dot \varepsilon ^*})\left( {1 - {T^{{*^m}}}} \right).$
式中:
材料Johnson-Cook本构参数及电磁性能参数如表 2所示,磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊有限元模型如图 2所示。
表2(Table 2)
T2-Cu 250 292 0.31 0.025 1.09 1.75 1
1060-Al 120 200 0.30 0.010 1.00 2.83 1
表 2 Cu、Al管Johnson-Cook本构参数及电磁性能参数Table 2 Johnson-Cook constitutive parameters and electromagnetic performance parameters of Cu, Al
图 Figure2(Fig.Figure2)
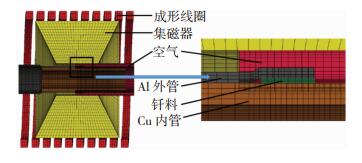 图 2 磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊有限元模型Fig.2 Finite element model of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering
图 2 磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊有限元模型Fig.2 Finite element model of magnetic pulse-semisolid hybrid assisted soldering3 结果与讨论3.1 钎料固、液相线及固相率与温度关系根据DSC测试结果,3种Zn-Al钎料的固、液相线如表 3所示。
在合金熔化过程中,当加热速率一定时,系统所吸收的熔化热与合金熔化量成正比。根据Speil公式[10],
表3(Table 3)
Zn-3Al 380.8 408.7
Zn-15Al 380.5 455.1
Zn-22Al 421.2 495.3
表 3 3种钎料固、液相线Table 3 3 Solidus(TS) and liquidus(TL) temperatures of Zn-Al solder
$H = K \times A.$ (1)
式中:H为相变吸收的熔化热;A为相应DSC曲线峰的面积;K为常数。
则在某一温度下合金的固相率为
${f_{\rm{s}}} = 1 - \frac{{\Delta {H_T}}}{{\Delta H}}.$ (2)
式中:fs为样品中固相的含量,即固相率;△HT为样品从开始熔化至温度T所吸收的熔化热;△H为样品完全熔化所吸收的熔化热。
由式(1)、(2)可得
${f_{\rm{s}}} = 1 - \frac{{{A_T}}}{A}.$ (3)
式中:AT为相应DSC曲线上峰从起点到T温度的面积;A为相应DSC曲线上峰的总面积。
根据以上方法计算得到的3种钎料固相率与温度的关系如图 3所示。
图 Figure3(Fig.Figure3)
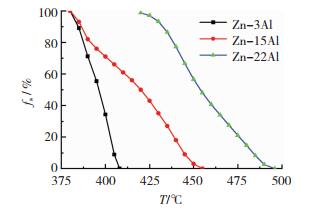 图 3 3种钎料固相率与温度关系曲线Fig.3 Relationship between solid fraction and temperature of Zn-Al solder
图 3 3种钎料固相率与温度关系曲线Fig.3 Relationship between solid fraction and temperature of Zn-Al solder3.2 二次放电成形模拟分析根据半固态Zn-15Al表观粘度模型进行多物理场耦合仿真,在Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊过程中半固态钎料的流动行为见图 4。
图 Figure4(Fig.Figure4)
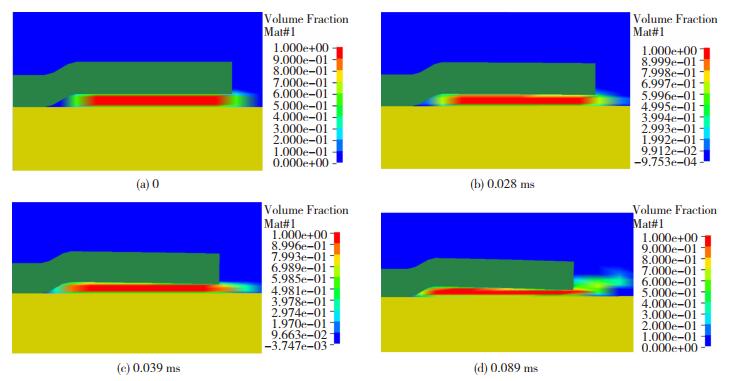 图 4 不同钎焊时间的半固态钎料流动行为Fig.4 Flow behavior of semisolid Zn-Al solder in different brazing time
图 4 不同钎焊时间的半固态钎料流动行为Fig.4 Flow behavior of semisolid Zn-Al solder in different brazing time由于外管端口处为自由端,约束力最小,因此,此处最先缩径变形并带动其他部分运动,如图 4(b)所示,迫使半固态钎料发生径向压缩和轴向剪切流动。内侧钎料在外管作用下向扩口段深处快速流动,填满外管颈部与内管之间的空隙(图 4(c)),而外侧钎料则被快速挤出管端(图 4(d)),在此过程中半固态钎料撞击和刮擦Al管内表面,从而对母材进行去膜和润湿扩散。
在Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊工艺中,Al母材表面氧化膜的去除与钎料和Al界面处的压力和剪切应力有较大关系,图 5为不同表观粘度下外管内壁处所受压力幅值和剪切应力的变化情况。由图 5可知:外管内壁所受到的压力幅值随着半固态钎料表观粘度的增大而减小,最后趋近于40 MPa;外管内壁所受的剪切应力随着半固态钎料表观粘度的增大而增大,最后趋近于6 MPa。根据Shi等人[8]的研究结果,这种压力和剪切应力的复合作用具有很好的去膜效果。
图 Figure5(Fig.Figure5)
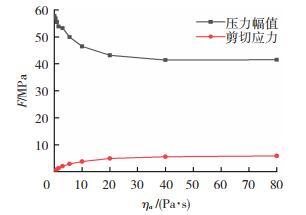 图 5 不同表观粘度下外管内壁所受压力幅值和剪切应力变化曲线Fig.5 Curves of pressure amplitude and shear stress on the inner wall of outer tube under different apparent viscosities
图 5 不同表观粘度下外管内壁所受压力幅值和剪切应力变化曲线Fig.5 Curves of pressure amplitude and shear stress on the inner wall of outer tube under different apparent viscosities另外,可以发现当表观粘度大于40 Pa ·s时压力幅值和剪切应力基本不变,根据Zn-15Al表观粘度模型ηa=0.54 e5.99fs可计算此时的固相率为0.72。要保证良好的钎焊质量,在母材界面处需要足够的液相钎料对母材进行润湿和扩散,因此,固相率不能过高;母材氧化膜的破碎主要由半固态钎料中固相颗粒的撞击和刮擦作用决定,固相率也不能过低,因此,后续在此基础上分别在固相率为0.4、0.6和0.8条件下进行试验,考察半固态钎料固相率对Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊质量的影响。
3.3 钎料固相率对焊接质量的影响图 6为固相率0.4(426 ℃)时Cu/Zn-15Al/Al接头图片,可以看到钎料被挤出较多,焊缝区存在明显钎料填充不足现象。原因在于半固态钎料的固相率过低,表观粘度过小,导致钎料在受到外管挤压时很大部分流出接头区,造成焊缝区钎料填充不足。从上述试验现象可以看出,钎料固相率过低时,会导致钎料填充不足,严重影响接头焊接质量,因此,固相率为0.4时不能得到可靠的Cu/Al管接头。
图 Figure6(Fig.Figure6)
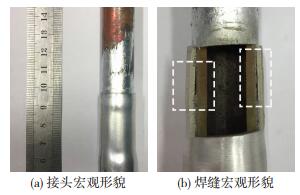 图 6 固相率为0.4时接头照片Fig.6 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.4:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) appearance of welding seam
图 6 固相率为0.4时接头照片Fig.6 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.4:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) appearance of welding seam由图 7(a)可知,当固相率为0.8(391 ℃)时,钎料基本无挤出,说明钎料填缝良好。但从焊缝区的微观界面结构来看,见图 7(b),钎料和两母材界面处存在明显的缝隙,说明钎料并未与母材形成有效的冶金连接。
图 Figure7(Fig.Figure7)
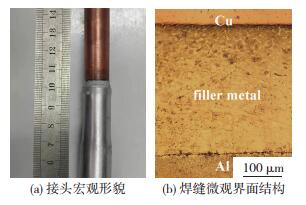 图 7 固相率为0.8时接头照片Fig.7 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.8:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) microstructure of welding seam
图 7 固相率为0.8时接头照片Fig.7 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.8:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) microstructure of welding seam由于此时固相率过高,半固态钎料基本上没有流动性[12],在受到挤压时,半固态钎料中的固相颗粒几乎成为一个整体,对母材界面没有足够的刮擦作用,因此, 无法充分去除母材表面的氧化膜。另一方面,过少的液相中有很大一部分被固相包围,Al管界面处缺乏充足的液相润湿母材并与母材进行相互扩散,致使钎料和母材之间没有产生冶金结合,因此,固相率为0.8时也无法得到良好冶金结合的Cu/Al接头。
图 8所示为固相率0.6(410 ℃)时Cu/Zn-15Al/Al接头图片。由图 8(a)可以看到,有少量钎料被挤出,说明半固态钎料有较好的流动性。对焊缝区显微组织进行观察可以发现,钎料和母材之间形成了良好的冶金结合,焊缝区域组织分布均匀,没有明显的孔洞等缺陷,表明半固态钎料固相率为0.6时能够获得焊接质量良好的Cu/Al接头。
图 Figure8(Fig.Figure8)
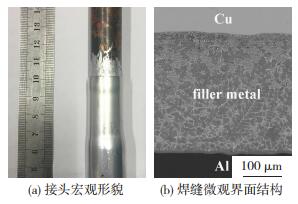 图 8 固相率为0.6时接头照片Fig.8 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.6:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) microstructure of welding seam
图 8 固相率为0.6时接头照片Fig.8 Joint with Zn-Al solder solids phase ratio of 0.6:(a) appearance of Cu/Al joint; (b) microstructure of welding seam3.4 钎料组分对焊接质量的影响对Zn-3Al,Zn-15Al和Zn-22Al在固相率为0.6(温度分别为384、410、448 ℃)时制得的Cu/Al接头进行力学拉伸测试。图 9的测试结果显示,3种接头均断裂于Al母材,说明以上3种钎料制得的钎焊接头质量良好。
图 Figure9(Fig.Figure9)
 图 9 Cu/Al钎焊接头拉伸测试结果Fig.9 Tensile test result of Cu/Al joints
图 9 Cu/Al钎焊接头拉伸测试结果Fig.9 Tensile test result of Cu/Al joints图 10为Cu/Zn-3Al/Al,Cu/Zn-15Al/Al和Cu/Zn-22Al/Al接头焊缝显微组织图片。由图 10可知,焊缝中钎料填充饱满,组织分布均匀,Al母材和钎料发生了明显的扩散生长,在Cu侧形成了较薄的扩散层,表明3种钎料均与母材形成了良好的冶金结合。
图 Figure10(Fig.Figure10)
 图 10 Cu/Al接头焊缝显微组织Fig.10 Microstructure of Cu/Al joints
图 10 Cu/Al接头焊缝显微组织Fig.10 Microstructure of Cu/Al joints根据相关研究[13-15],钎焊温度接近Cu-Al共晶温度(548 ℃)时,采用Zn-Al钎料钎焊的Cu/Al接头在Cu侧易形成以层状CuAl2为主的脆性金属间化合物层,在受到外力作用时接头常在此处断裂而失效,因此,本文对3种Cu/Al接头Cu侧界面进行了显微结构分析,结果见图 11。从图 11(a)可知,Zn-3Al/Cu界面区由两层结构组成,与Cu基体相邻的是一层浅色组织1,与钎料相邻的是一层锯齿状组织2,EDS分析结果(表 4)表明,浅色组织为扩散层,而锯齿状组织为Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7。扩散层通过Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7与钎料组织相连,Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7具有“犬牙交错”般的“咬合”结构,根据Ji等人[16]的研究,这种结构能将界面区与钎料基体紧紧“钉扎”在一起阻止裂纹在界面区附近扩展,从而提高接头的力学性能。图 11(b)为Zn-15Al/Cu界面区显微组织,可以看到,其与Zn-3Al/Cu界面区显微组织相似,同样由浅色扩散层3和锯齿状Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7的4组成。相比之下,Zn-15Al/Cu界面区的Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7外形更加规则,这是因为钎焊温度较高,Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7生长更加充分均匀。在Cu/Zn-22Al/Al接头中(图 11(c)),Cu界面区组织也由扩散层5和Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7的6组成。因为随着钎料中Al含量的增加,钎焊温度会相应升高,高温停留时间也会变长,因此,与Zn-3Al和Zn-15Al相比,Zn-22Al/Cu界面区的Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7相明显变粗,并向钎料中生长,另一方面,临近界面处出现更多粗大的α-Al,并与Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7相连。这种结构容易使其界面区产生应力集中,成为裂纹萌生的来源,进而降低接头的力学性能[16]。
图 Figure11(Fig.Figure11)
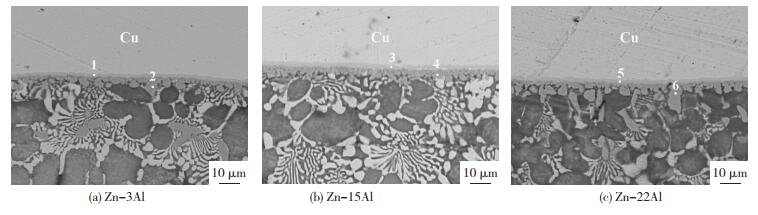 图 11 接头Cu侧界面显微组织Fig.11 Microstructure of the interfacial zones near Cu substrate of Cu/Al
图 11 接头Cu侧界面显微组织Fig.11 Microstructure of the interfacial zones near Cu substrate of Cu/Al表4(Table 4)
metal PositionAtomic fraction / % Possible phase
Al Cu Zn
Zn-3Al1 32.24 49.98 17.78 Diffusion layer
2 54.80 36.14 9.06 Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7
Zn-15Al3 35.14 46.49 18.37 Diffusion layer
4 57.93 32.28 9.79 Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7
Zn-22Al5 30.67 47.30 22.03 Diffusion layer
6 52.54 38.42 9.04 Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7
表 4 图 11中标记区域的EDS分析结果Table 4 EDS results of regions marked in Fig. 11 Fill
由以上分析结果可知,3种Zn-Al钎料在固相率为0.6时均能制得焊接质量良好的Cu/Al钎焊接头,Cu侧界面区均由扩散层和Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7相组成,未出现脆性的CuAl2组织,拥有良好的界面结构。但Zn-3Al固-液半固态温度窗口较窄,仅为22 ℃左右,因此,很难准确控制其固相率。Zn-22Al固-液半固态温度窗口较大,达到74 ℃,但因其固相率为0.6时对应的温度较高,导致接头Cu侧扩散层相连的Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7及α-Al具有较为粗大的外形,降低了接头的力学性能。而Zn-15Al固-液半固态温度窗口合适,容易准确控制其固相率,且在接头近Cu侧界面区的组织和界面结构均有利于提升接头的强度,因此,Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊选用Zn-15Al钎料较为合适。
4 结论1) 在磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊工艺中,半固态Zn-Al钎料固相率过高会导致钎料与母材不能良好冶金结合,而固相率过低又会使钎料填充不足。固相率为0.6时较为合适,能够获得焊接质量良好的钎焊接头,接头拉伸强度超过Al母材强度。
2) Cu/Zn-3Al/Al、Cu/Zn-15Al/Al和Cu/Zn-22Al/Al近Cu侧界面区均由扩散层和Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7组成,相比之下,Zn-15Al固-液半固态温度区间更加合适,接头近Cu侧的界面区显微结构更好,是较为合适的Cu/Al管磁脉冲-半固态复合辅助钎焊用Zn-Al钎料。
参考文献
[1] LEI Y, HUANG S, LIU W, et al. Dissimilar Cu/Al tube joint by EMF-assisted brazing[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 95(9-12): 4039-4047. DOI:10.1007/s00170-017-1535-z
[2] COLMENEROA N, OROZCO M S, MACíASE J, et al. Optimization of friction stir spot welding process parameters for Al-Cu dissimilar joints using the energy of the vibration signals[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 100(9-12): 2795-2802. DOI:10.1007/s00170-018-2779-y
[3] 肖勇.超声波辅助Cu/Al液相钎焊接头冶金连接机制及性能研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014.
[4] 安振之, 张希川, 刘中仁, 等. 微机控制型插入式铜-铝管对焊机的研制[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 1998, 20(S1): 74-76, 80.
AN Zhenzhi, ZHANG Xichuan, LIU Zhongren, et al. Computer control automatic butt resistance welding equipment for Cu-Al pipes[J]. Journal of Shenyang Polytechnic University, 1998, 20(S1): 74-76, 80.
[5] BERLANGA-LABARI C, ALBíSTUR-GO?I A, BALERDI-AZPILICUETA P, et al. Study and selection of the most appropriate filler materials for an Al/Cu brazing joint in cooling circuits[J]. Advanced Manufacturing Processes, 2011, 26(2): 236-241.
[6] 王梓宇, 黄尚宇, 雷雨, 等. 铝-铜异种金属管磁脉冲辅助钎焊研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2018, 25(2): 147-153.
WANG Ziyu, HUANG Shangyu, LEI Yu, et al. Research on magnetic pulse assisted brazing of Al-Cu dissimilar metal tube[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2018, 25(2): 147-153.
[7] 黄尚宇, 黄海川, 雷雨, 等.一种半固态无钎剂辅助的异种金属钎焊装置及方法: 2018111327246[P]. 2018-09-27.
[8] SHI Lei, YAN Jiuchun, HAN Yanfei, et al. Behaviors of oxide layer at interface between semi-solid filler metal and aluminum matrix composites during vibration[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2011, 27(8): 746-752.
[9] 刘正林.铝铜钎焊用Zn-Al钎料及其焊接工艺的研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2009.
[10] 余忠土, 张恒华, 邵光杰, 等. 半固态铝合金中固相分数差热扫描法的研究[J]. 物理测试, 2002(1): 22-25.
YU Zhongtu, ZHANG Henghua, SHAO Guangjie, et al. Study of Solid Content in Aluminum Alloys Reheated to Semisolid State by DSC[J]. Physics Examination and Testing, 2002(1): 22-25.
[11] JOLY P A, MEHRABIAN R. The rheology of a partially solid alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1976, 11(8): 1393-418. DOI:10.1007/BF00540873
[12] 石磊, 闫久春, 韩焱飞, 等. 一种具有球晶组织的半固态Zn-Al合金钎料[J]. 材料工程, 2010(10): 65-68.
SHI Lei, YAN Jiuchun, HAN Yufei, et al. Development of a Semi-solid Zn-Al Alloy Filler Metal with Globular Grains[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010(10): 65-68.
[13] BRAUNOVIC M, ALEKSANDROV N. Intermetallic compounds at aluminum-to-copper and copper-to-tin electrical interfaces[C]//proceedings of the 38th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts. 1992: 25-34.
[14] NIU Zhiwei, YE Zheng, HUANG Jihua, et al. Interfacial structure and properties of Cu/Al joints brazed with Zn-Al filler metals[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 138: 78-88. DOI:10.1016/j.matchar.2018.01.054
[15] JI Feng, XUE Songbai. Growth behaviors of intermetallic compound layers in Cu/Al joints brazed with Zn-22Al and Zn-22Al-0.05Ce filler metals[J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 51: 907-915.
[16] JI Feng, XUE Songbai, LOU Jiyuan, et al. Microstructure and properties of Cu/Al joints brazed with Zn-Al filler metals[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(2): 281-287. DOI:10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61172-2
